Comparison of the Effects of Pesticide Application on Biston suppressaria Larvae in Different Damage Stages
Hezai Lin,Shouping Cai,Xueyou He,Liqiong Zeng,Haitian Song,Qingquan Wu
1.Zhangpu County Forestry Bureau,Zhangpu 363200,China;2.Fujian Academy of Forestry Sciences,Key Laboratory of Timber Forest Breeding and Cultivation for Mountainous Areas in Southern China,State Forestry Administration,Fuzhou 350012,China;3.Pinghe Tianma State-owned Forest Farm,Pinghe,363000,China
Abstract [Objective]The paper was to determine the optimal control period of Biston suppressaria,the most serious defoliator in eucalyptus forests in southern Fujian Province.[Method]By spraying 2% abamectin+Bacilus thuringiensis powder in the forest,the first generation larvae of B.suppressaria was controlled in the early damage stage(May 2),middle damage stage(May 13)and late damage stage(May 30),respectively.[Result]When 500 g of pesticide was sprayed per 667 m2in the early damage stage of the first generation larvae,the population reduction rate was 97.5% at 5 d post spraying.When 500 g of pesticide was sprayed per 667 m2in the middle damage stage,the population reduction rate was 95.3% at 5 d post spraying.When 1 000 g of pesticide was sprayed per 667 m2in the late damage stage,the population reduction rate was 83.9%,conspicuously lower than those in the early and middle damage stage.If pesticides were sprayed in the early and middle damage stage,the second generation larvae would not cause harms,but the second generation larvae would cause slight harms if pesticides were sprayed in the late damage stage.[Conclusion]Control before the middle damage stage has significant effect on improving the control effect and reducing losses while reducing the usage of pesticides.
Keywords Biston suppresaria;Larvae;Chemical control;Control effect
Eucalyptus is an important timber tree species featured by barren tolerance,fast growth,high yield,short cycle,good economic benefit,etc.,and has been planted in a large area in Guangxi,Fujian,Guangdong and other regions in southern China[1].However,with the construction of large-area pure eucalyptus forests,the occurrence of pests has become more and more serious,especially inchworm defoliators of eucalyptus,which often break out in some areas in succession and could eat up the leaves of the entire eucalyptus forest in a short time,causing serious impact on the biomass and volume growth of eucalyptus[2-3].In Zhangpu County,Fujian Province,Biston suppressaria(Guenée)is the major insect pest of eucalyptus,and sometimes Biston panterinaria and Hypomecis punctinalis also occur together[2,4-5].Lin[4]studied the occurrence and life history of B.suppressaria in Zhangpu County,and found that B.suppressaria occurred three generations every year in Zhangpu;the larval stage of the first generation was from early May to early June,and the larval stage lasted about 35 d;the larval stage of the second generation was from early July to early August,and the larval stage of the third generation was from early September to late September.Generally,the larvae of the first generation occur severely,so the control of the first generation larvae is critical.Currently,there is a lag phenomenon in the control of B.suppressaria in production,that is,the measures are usually taken only after obvious damage symptoms are observed,and the early control is neglected,which leads to unsatisfactory control effect,and has already caused great losses even the control measures are adopted.Meantime,delayed control can easily lead to the situation of excessive application of pesticides and continuous occurrence of pests.Therefore,the differences of prevention and control effect in different stages were compared,in order to provide scientific basis for determining the optimal control stage.
1 Materials and Methods
1.1 General situation of experimental site The test was conducted in Dongfang Field,Tanyang Village,Changqiao Town,Zhangpu County,Fujian Province.The forest was pure eucalyptus forest,which was planted in 2015,with the forestation density of 1 500 trees/hm2,the tree height of 6-12 m,and the canopy density of 0.8.B.suppressaria basically occurred every year in the commonly occurred area.
1.2 Reagents The third generation product"Forest Green"produced by Wuhan Andersen Biotechnology Engineering Co.,Ltd.,with the ingredients of 2% abamectin+Bacilus thuringiensis powder,was sprayed in the forest by MD8026 knapsack power sprayer.
1.3 Forest control test Forest control test was carried out in May 2020,and power was sprayed in forest.The test forest was divided into three areas,with an interval of more than 50 m,and the control was carried out in three stages.The pri-mary control was carried out on May 2 in 09-030 group of Dongfang Field during lower instar larval stage (the 1stto 2ndinstar).The secondary control was carried out on May 13 in 09-050 group of Dongfang Field during middle instar larval stage(the 3rdto 4thinstar).The third control was carried out on May 30 in 09-080 group of Dongfang Field during elder larval stage(elder than the 5thinstar).At this time,the harm in the forest was more severe,and the leaf loss in the forest was greater.The specific information at different control periods are shown in Table 1.

Table 1 Information on the control of Biston suppresaria in different stages
1.4 Survey of control effects The population density in the forest was investigated by the method of sample branches,that is,sampling plants were selected in the shape of“Z” in the forest,and standard sample branches with a length of 50 cm were cut from the sample trees to count the number of insect populations on sample branches.Before the control,the population density of each experimental area was counted,and the situation of leaf loss was counted.The population density in the forest was investigated at 2 and 5 d post spraying,respectively.At least 30 sample branches were investigated each time.The population density of the second generation of B.suppressaria larvae and the status of leaf loss was investigated in each control experimental area in middle July,2020.The formula of population reduction rate was as follows.
Population reduction rate=(Population quantity before control-Population quantity after control)/Population quantity before control×100
2 Results and Analysis
2.1 Control effects in different stages The control effects of pesticide application in different stages are shown in Table 2.In the early damage stage of larvae,500 g of pesticides were sprayed per 667 m2,and the population reduction rated were 76.7% and 97.5% at 2 and 5 d post spraying,respectively.The control effect was very significant.In the middle damage stage of larvae,500 g of pesticides were sprayed per 667 m2,and the population reduction rate was 68.7%,which was significantly lower than that in the early damage stage.The population reduction rate at 5 d post spraying was 95.3%,which had no significant difference with that on May 2.In the late damage stage of larvae,1 000 g of pesticides were sprayed per 667 m2,and the population reduction rates were 62.7% and 83.9% at 2 and 5 d post spraying,respectively,which were significantly lower than those sprayed in the early stage and the middle stage.
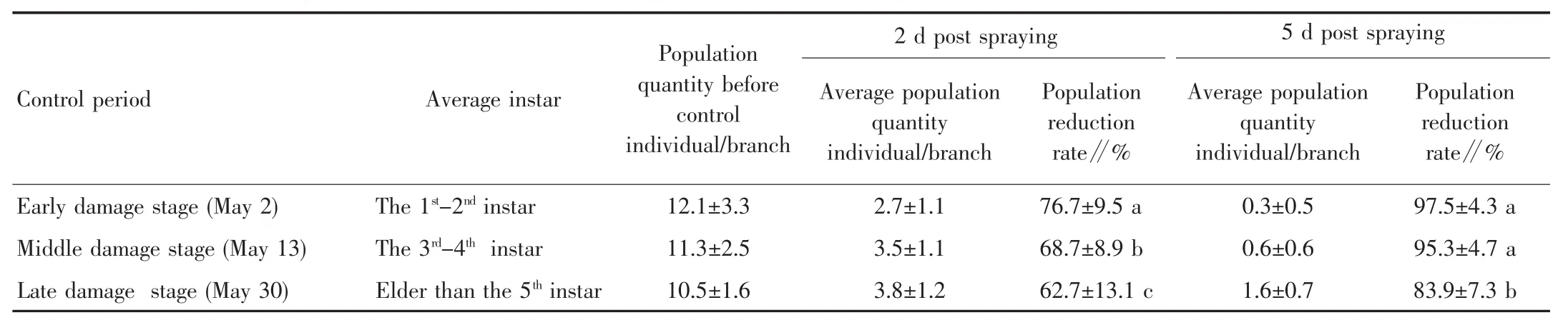
Table 2 Control effects of pesticide application on Biston suppresaria in different stages
2.2 Effects of pesticide application on the damage of B.suppresaria in different stages The effects of pesticide application on the damage of B.suppresaria in different stages are shown in Table 3.In the early damage stage,there was no obvious leaf loss due to the small instar of insect.After 500 g of pesticides were sprayed per 667 m2,the population density was reduced rapidly,and no leaf loss occurred in the late stage.In the middle damage stage,the larvae had caused slight leave loss before the control,but the population density was inhibited after the control,and the damage was not aggravated in the late stage.In the late damage stage,the larvae were elder than the 5thinstar,and the appetite of larvae increased sharply,causing serious leaf loss in the forest.Although 1 000 g of pesticides were sprayed per 667 m2,the population reduction rate was not as obvious as that in the early and middle damage stages,and the control effect was not ideal.There were still 2.6 larvae/branch on average in the late damage stage,and the second generation larvae still caused slight leaf loss in the forest.
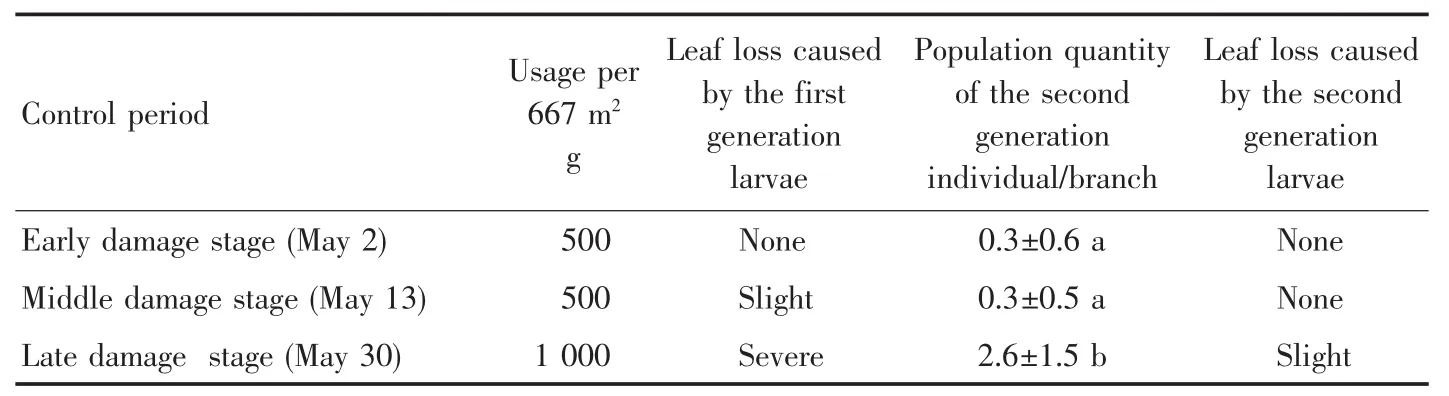
Table 3 Effects of pesticide application on the damage of Biston suppresaria in different stages
3 Conclusions and Discussion
B.suppresaria is a common and severe defoliator in eucalyptus at present,which has serious impact on the growth of eucalyptus.The feeding amount of B.suppresaria varies greatly among different stages(instar).Zhu[6]measured the instar and feeding amount of B.suppresaria,and found that the feeding amount of the 1stto 2ndinstar larvae accounted for only 0.52% of the total feeding amount,that of the 3rdto 4thinstar larvae accounted for 3.9%,and that of the 5thto 6thinstar larvae accounted for 95.68% of the total feeding amount.Wang et al.[7]also obtained similar results,and the feeding amount of the 5thto 6thinstar larvae accounted for 89.21% of the total feeding amount.Zheng[8]found that the feeding amount of the 5thto 6thinstar larvae accounted for 87.36% of the total feeding amount.Therefore,the feeding amount of B.suppresaria larvae increased sharply with the increase of larval instar,especially the 5thto 6thinstar larvae,which accounted for more than 85% of the total feeding amount of the larvae.Zou found[3]that eucalyptus was moderately and severely harmed by B.suppresaria,and the loss rates of timber volume per plant were 36%-44% and 66%-75%,respectively.It was observed in the forest that when eucalyptus stands showed obvious symptoms of being injured,the insects were usually above the 4thinstar,and it was during this period that the forest growers usually had the will to perform control measures,but the control had obviously lagged behind at this time,and the damage of pests had caused serious losses.
Through the control of B.suppresaria in different stages,it was found that the control effect of spraying 500 g of pesticides per 667 m2in the early and middle damage stages of B.suppresaria could reach more than 95% after 5 d.After the control,the eucalyptus stands were not damaged or slightly damaged,and the number of the second generation larvae was very low,without any harms.However,in the late damage stage of B.suppresaria,the pest had caused more severe damage,and the leaf loss of the forest was serious.Although 1 000 g of pesticides were sprayed per 667 m2to control the pest,the population reduction rate was only 83.9% after 5 d,and there were still mild damage of B.suppresaria in the second generation.This indicated that the earlier to control,the better the effect,the lighter the loss.Therefore,in the control of B.suppresaria,it is necessary to change the previous concept of control,abandon the psychology of"control after observing the harm",and effectively monitor the situation of eucalyptus forest and take timely control measures.Some studies suggested that when the population density exceeded 6 larvae per standard branch,it should be controlled in time[3].Our research results demonstrate that it is necessary to improve the awareness of early prevention and control,and early prevention and control can not only achieve good prevention and control effect,but also avoid or reduce the loss.If the control of B.suppresaria can be brought into the routine management of eucalyptus forest like fertilization and weeding,it will be more beneficial to reduce the harm caused by B.suppresaria.
Elder instar larvae often have less sensitivity to pesticides.Wang et al.[9]found that with the increase of instar,the sensitivity of Spodoptera exigua larvae to pesticides gradually decreased,and some drug-resistant related enzymes in larvae increased with the increase of instar.Liu et al.[10]also reached a similar conclusion when studying the sensitivity of S.exigua larvae to nuclear polyhedrosis virus.Therefore,in order to achieve better control effect,more pesticides are sprayed in practical application if the control period is delayed,which has greater impact on the environment and does not conform to the concept of pest management[11-12].Therefore,early pest control can not only achieve better control effect,but also reduce the usage of pesticides.Some biological agents,such as Beauveria bassiana and Metarhizium anisopliae,can be used to replace chemical pesticides,which not only control pests,but also reduce the impact on the environment,thus achieving the purpose of sustainable control.The research in this field still needs to be further studied.
- 植物病虫害研究(英文版)的其它文章
- Effects of Common Mineral Trace Elements on Immune Function of Livestock and Poultry
- Impacts of Different Weeding Methods on Weeds Control in Tobacco Fields in Anshun City
- Spectral and Photosynthetic Characteristics of Cotton under Chemical-controlled Topping Technology
- Synergistic Effect of Adjuvant Green Orange Peel Oil on Different Herbicides
- Effects of Guangxi Hepu Pearl Hydrolysate on Proliferation Activity and Apoptosis of Human Hepatic Stellate Cells
- Development of"Multi-Resistance Rice"by Pyramiding of Insect(Cry1C)and Blast Resistance(Pi1 and Pi2)Genes

