Growth retrieval of stressed bacterial cells:logic and contradictions
Rashed Noor,Syed Abdullah Ibn Asaduzzaman
1Department of Life Sciences,School of Environment and Life Sciences,Independent University,Bangladesh.
Study of bacterial stress response against an array of stress signals like heat shock and oxidative stress has been well accomplished so far.Several stress factors cause microorganisms to go under the viable but nonculturable state.However,the growth resuscitation of bacterial cells from such viable but nonculturable state is still obscure.Current review briefly focused on the growth revival of the viable but nonculturable cells and placed the possible model of growth resuscitation.The significance of such type of study on the viable but nonculturable cells principally relies upon clinical sectors whereby some pathogens are found to be latent for many days and thereby imparting the false negative results as well as in the food industries whereby the viable but nonculturable cells may cause massive damage in the public health upon their resuscitation.
Key words:Bacterial,VBNC cells,Stress response,Stress signals,Growth revival
Background
Homeostasis in bacterial metabolic pathways as well as regulation of the house keeping genes encoding the essential proteins greatly depends on the harmonized inter- and intra-signal transduction pathways assisted by a variety of sigma factors which work in association with RNA polymerase to transcribe the corresponding genes [1].Such a process can be ensured by the sufficient uptake of nutrients for the synthesis of the macromolecules by the bacterial cells as well as depend on the existing abiotic factors like temperature,redox potential,pH,water activity,several chemicals,etc.[2].Agitations in any of these components cause the bacterial cells to undergo stressed conditions leading to a heterogeneous community of a given bacterial cell population; i.e.,(1) some cells still remain living and culturable with the capacity to form colony forming units,colony forming units (CFUs) on agar; (2) a large proportion of cells become viable but nonculturable(VBNC) losing the capacity to form colonies on agar plates; and (3) some cells become ruptured with the concomitant exclusion of DNA and other cytoplasmic materials,and eventually those cells die [2-6].
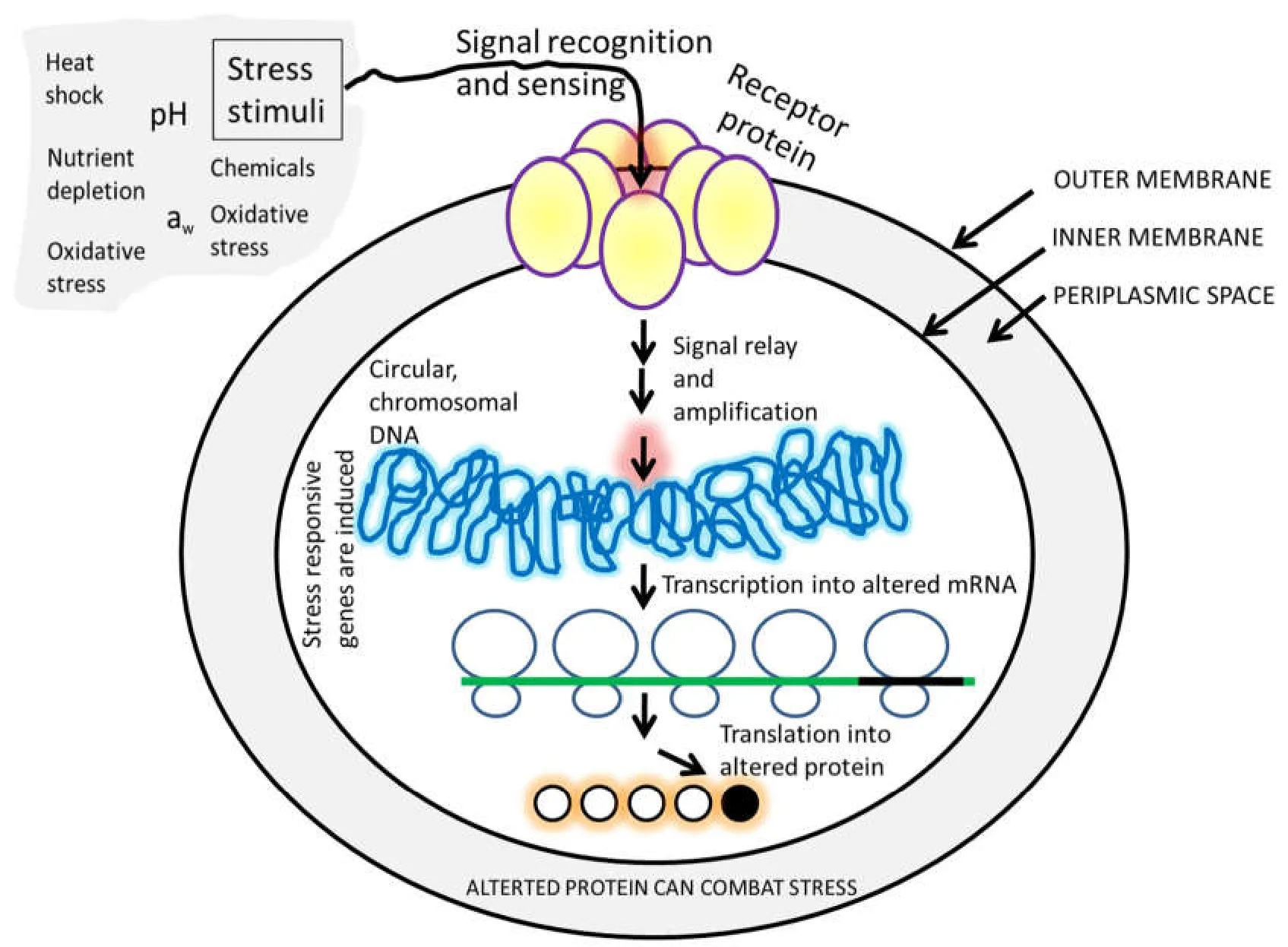
Figure1 Simplistic model of stress signal transduction within bacterial cells.The cell membrane receptors recognize and sense the stress signals which is in turn transduced into the cytoplasm in order to trigger the stress responsive genes.
Such stress signals are sensed by the increase in the outer membrane porin precursors in the periplasmic space of the model bacteriumEscherichia coliwhich has been mostly studied,and afterward the signals are transduced and amplified through numerous signal carrier proteins into the cytoplasm inducing the upregulation of the stress responsive genes [1].An ingenious model illustrating such signal transduction in course of bacterial stress management has been outlined in Figure1.The stress signals; i.e.,heat shock,cold shock,alteration in pH,redox potential and water activity (aw),the reactive oxygen species (ROS,imparting the oxidative stresses),etc.are recognized and sensed by the cell membrane receptors (i.e.,by the PDZ domain of the YQF motif in case ofE.coli); and the signal is then transduced into the cytoplasm which in turn triggers the stimulation of the gene or a set of gene(s) required for the production of the necessary stress responsive proteins and chaperons like DnaK-J,GroE-L,etc.[1,7].This is to be pondered that if the stress signals are not appropriately traded with the bacterial cells,sooner or later a major fraction of the cells tend to die or go under the VBNC state [8,9].Present reviews focused on the general stress signal relay into the bacterial cells required to combat the resultant stress.The activation of the stress responsive genes together with the corresponding proteins have been pointed.The interesting aspect of this review was to discuss about the possible transformation of the VBNC cells into the culturable form.The allied mechanisms have been discussed.Study of VBNC cells is significant in terms of understanding the biological aging due to (1) the gradual decline in stress resistance mechanism,and (2)the gathering of aggregated proteins due to the accumulation of ROS with a concomitant loss of cytoplasmic superoxide dismutase activity (SodA,SodB); which are collectively known as the growth arrest [5].The visibility of such state can be accomplished by checking the expression type of universal stress responsive sigma factor,σE,the heat shock sigma factor σHor σE[1-3].However,till the concept of VBNC formation and the ROS theory,leading to this bacterial CFU loss on the agar plates remain obscure.Current study has thus been designed to infer the possible resuscitation of the VBNC cells which may be in complementarity to point out to causes of VBNC formation.Such findings could be helpful in clinical microbiology as well where lots of false negative results for bacterial culture tests are not unlikely; and which stands as a major challenging issue in the disease diagnosis.Indeed,VBNC bacteria have long been known as a key concern in the assessment of mass public-health risk since certain Gram-negative bacteria,including the widely known bacteriumEscherichiacoli,and alsoVibriocholerae,V.vulnificuswas previously shown to get entry into their VBNC state thus remaining unidentified in the clinical samples; and the serious pathological outcome could be nourished when they resuscitated into their vegetative forms,causing active infections within their corresponding hosts [9].Moreover,the knowledge on the VBNC cell resuscitation would be useful to maintain the food safety in a large scale.
Involvement of chaperons and sigma factors in coordination to the stress signals
The signal transduction and the genetic network required for opposing the stress has been extensively analyzed so far among which the stress dealing chaperons and the heat shock proteins in coordination with the sigma factors (σS,σE,σHand σE) have been outlined as the leading stress responsive candidates [1-3,10-15].As stated earlier,a number of chaperons have been reported including GroEL,DnaK,the ATP-dependent proteases of Lon,HslUV,Clp,FtsH(HflB),and the periplasmic protease DegP has been well reported which get engaged in (i) protein folding and refolding,(ii) protein quality control and the degradation of the protein aggregate due to carbonylation,and the (iii) removal of damaged proteins,which altogether are required to respond against stress [1,16].Interestingly,the heat shock proteins are usually activated at 42-48 °C in case ofE.coli,where the cells have been noticed to be solely non-culturable [1].Besides,an array of research on the bacterial signal transduction of different stress stimuli has been conducted in case ofEscherichia coli,Bacillusspp.,Salmonellaspp.,Pseumonasaeruginosa,P.fluorescence,P.putida,and others [7,12,13,17-24].The associated network(s) engaged in such stress signal transduction have been evidently reported by different groups [1].
VBNC cells
As a tactic for protecting bacterial cells under various stress circumstances,the formation of VBNC state has been widely detected in the bacterial population [9,25-28].In contrast to the culturable cells,the cytosols of the VBNC cells is not as molecularly crowded as the required gene expression is minimal here due to nutrient deselection or other stresses [27].VBNC cells,difficult in distinguishing from the dead or dying cells,are widely known to impart a substantial threat to human health,and these cells can remain non-growing for long time,and hence escaping their detection through the traditional microbiological procedures [9,25].Specifically,the VBNC cells have been reported to survive the antibiotic challenge,ethanol,acid and etc.surprisingly followed by their regrowth [24,29].The ability of producing the virulence factors in the VBNC state has been evident in several bacteria likeEscherichia coli,L.pneumophila,Vibrio cholerae,etc.which in turn confer the viability of the VBNC state bacteria [9,30,31].
Hypothesis
During the stress signal transduction,the first impact of the stress both in situ or in vitro can be noticed as the bacterial cells enter into the VBNC state due to the accumulation of ROS like the superoxide anion (O2-),hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and hydroxyl radical (HO.)[1,3,4,23].Compared to the culturable cells,the VBNC cells lack the expression of the required gene or the expression can be very low as the cells are at dormant stage.However,as a protection mechanism under physiological stress,formation of VBNC cells has been widely known which is also clinically significant as they escape the microbiological detection procedure [9,19,20,26].Besides,they can resist against antibiotic challenge and other chemicals with an amazing capacity of regrowth even with the potential of producing virulence factors as observed inEscherichiacoli,L.pneumophila,Vibrio cholerae,etc.[9,24,27,29,31].Our recent results on the work on the possible transformation of VBNC bacteria into their vegetative forms showed that the growth resuscitation ofBacillus cereuscould be achieved even at high temperature(60°C) stress when theBacillusculture was augmented with the supplementation of the extracellular extracts fromPseudomonas aeruginosa[39].It can be stipulated that a fraction of the VBNC cells ofB.cereuscould utilize those extracts as well could utilize the substrates imparted in the medium fraction as a result of σE-dependent cell lysis when heat shock was implemented [1-3].
Interestingly some other groups investigated on such VBNC formation as well as its resuscitation to the culturable forms especially in case ofE.coliin various conditions [33].In order to encounter the toxicity caused by the ROS,several species of bacteria have evolved the oxidative stress defense mechanism inclusive of the detoxifying enzyme systems like hydrogen peroxide reductase (converting the organic peroxide to alcohol and detoxifying hydrogen peroxide),catalase (detoxifying hydrogen peroxide into water and oxygen),and superoxide dismutase,converting superoxide to hydrogen peroxide and oxygen [1-4,23].Indeed,formation of the VBNC cells and their resuscitation has largely drawn the interest of the scientists for quite a long time.Such transformation has been successfully observed in case of several bacteria includingBacillusspp.,Escherichiacoli,Cryptococcus neoformans,Listeriamonocytogenes,etc.as a protective strategy in adverse conditions [13,18,32-34].An amazing observation was made whenL.plantarumstrain BM-LP14723 (causing beer spoilage)was found to enter into the VBNC state and then to recover from such state [35].Indeed the first observation on the resuscitation from the VBNC state into the culturable cells was made by using the bacteriumLactobacillus lindneriin the contemporary time by the same group [36].
Evaluation of the hypothesis
Apart from these evidences (as mentioned above),one of our recent researches on the resuscitation of VBNC cells showed the transformation of stressedE.coliVBNC cells into the culturable form upon supplementation of the extracellular fractions ofBacillusspp.[18].The other study exhibited the growth retrieval in case ofPseudomonas aeruginosaVBNC cells (due to heat shock) upon addition of the extracellular fractions of the stationary phase culture ofBacillusspecies [13].A similar result was noted by other group when alanine and asparagine were added to theBacillus subtilisspores transforming them into the vegetative cells.Along this line,a model has been proposed which intend to state the resuscitation of the VBNC cells upon organic (bacterial cell extracts) or inorganic supplements (Figure2).The consequence of stress has been extensively projected through the formation of both VBNC cells and the dead cells; i.e.,a heterogeneous population [5-8].A part of the VBNC cells and the dead cells have been suggested to undergo the early stationary phase specific σE-dependent lysis whose debris is actually thought to serve as nutrients for the remaining survivors; i.e.,the viable fraction in the culture in vitro [1-4,18].Therefore,the resuscitation of the VBNC cells in certain instances can be explicated by the alteration of the VBNC cells into the culturable ones cells.The study of expression of several stress responsive genes and chaperons would further endorse such hypothesis.
Empirical data
As stated earlier,the result of stress on the bacterial cells is mainly evident through the formation of the VBNC cells and the dead cells.Moreover,as mentioned in the previous reports,a large fraction of the VBNC cells and certainly the dead cells undergo σE-dependent lysis; and the resultant lysed debris may serve as nutrients for the remaining population for their survival with the consequent ability to form CFUs on agar [2-4,13,18].Therefore,in addition to the lysed debris of the bacterial population A (as shown in Figure2),the external supplementation with the extracellular fractions of the stationary phase bacterial culture B may further serve as the enhanced nutrient source for the VBNC fraction of the bacterial population A.Besides such organic nutrients (the extracellular fraction from bacterial culture),the supplementation with some inorganic metals like calcium or magnesium may also help the VBNC fraction to be culturable as suggested by our previous research [4].It is to be noted that though scarce,the investigation on the VBNC cell resuscitation has already been done by some groups.For example,the VBNC sate of the heat stressedE.colicells were found to retrieve upon supplementation with the extracellular fractions ofBacillusspp.[18]; and a similar pattern of growth revival ofP.aeruginosawas also noticed when the extracellular fractions ofBacillusspecies were added to theP.aeruginosaculture [13].Such an unforeseen observation regarding the VBNC cells is really interesting to think further on the resuscitation of the bacterial cells which have lost the CFU-forming ability on the agar under stressed conditions like heat- or cold shock,or the oxidative stresses,etc.
Discussion
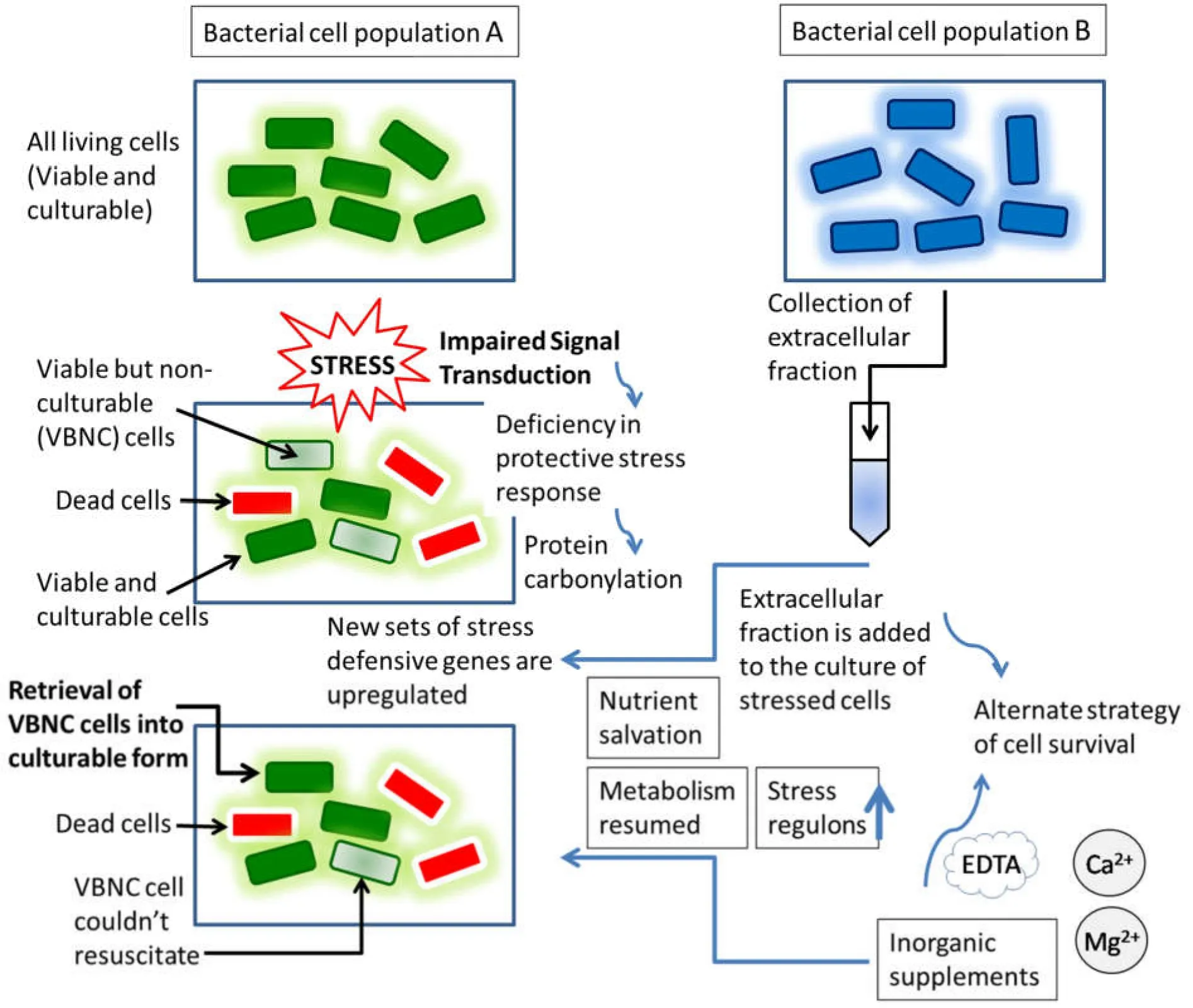
Figure2 Possible scheme of growth retrieval of stress sells of bacteria.The resuscitation of the bacterial population A can be explained by the transformation of the VBNC cells into the culturable cells as they are expected to utilize the extracellular fractions of the bacterial population B as nutrients.
Since the mid-19thCentury till date,microbial discovery and its mysterious ways of work have perplexed great minds of science and one such great discoveries of the microbial world,is the art of VBNC states of microorganisms [37].As mentioned earlier,VBNC simply refers to a state in bacteria where the bacteria are alive but are not in a dividing state due to confinement of the bacterial cell to a very low metabolic activity in response to unfavorable environmental conditions including temperatures,nutrient depletion,oxidative radicals etc.[1-3,14-19].However,to understand where it all starts from,it is important to jog our memory through the section of homeostasis in bacterial metabolic pathways and regulation of the housekeeping genes that play a crucial part by encoding essential proteins that greatly depend on various signal transduction pathways assisted by a variety of sigma factors that work in close association with RNA polymerase to transcribe the corresponding genes [2,3,9,28].These processes can only be fulfilled if the appropriate uptake of nutrients for macromolecule synthesis is done under its normal abiotic parameters like temperature,redox potential,pH,water activity,several chemicals,etc.[2,3].Disruption of the normal factors may lead the microbial cell being stressed to face any of the following three fates:(I) some cells still remain living and culturable,(II) a large proportion of cells become viable but nonculturable,losing its capacity to form colonies on agar plates; and (III) some cells become ruptured with the concomitant exclusion of DNA and other cytoplasmic materials,and eventually those cells die [2,3].This may then give rise to a heterogeneous bacterial community [1-5].
These stress signals are sensed by the increase in the outer membrane porin precursors in the periplasmic space of the most studied model bacteriumEscherichia coli.These all may finally lead to the upregulation of stress responsive genes by the signal transduction and amplification through numerous signal carrier proteins into the cytoplasm as illustrated in Figure1.To mitigate the bacterial stress,the stimulation of these genes or a set of gene(s) are required for the production of necessary stress responsive proteins and chaperons like DnaK-J,GroE-L,etc.[1,2,14] Thus it is to ponder if the management of stress signals is not well handled,a large fraction of the cells in the bacterial community may become viable but non-culturable,[15,16] but can be reversed back through resuscitation factors [1-5,9,11].
Conclusion
A range of studies on the bacterial signal transduction network in order to combat the stress has been conducted so far.Based on that knowledge,current review proposed a simplistic model of such signal transduction showing the activation of stress specific genes with the resuscitation synthesis of altered protein(s) which is just an incremental knowledge to the present understanding of stress management pathway within the bacterial cells.However,the possible revival of the VBNC cells into the culturable cells has been implicated through the supplementation of the extracellular bacterial extracts or by the inorganic materials which really drew a novel insight into the existing knowledge on the possible resuscitation of the stressed cells into their culturable form.
- Life Research的其它文章
- Science in Chinese medicine
- Artificial intelligence and the future of medicine:a multidimensional analysis
- Amyloid beta peptides,tau protein acetylation and therapeutic strategies for treating Alzheimer’s disease:a review
- A cross-sectional study of the relationships between ethnicity and occupational classes with mental wellbeing in the UK
- Aqueous wood-ash extract of Parkia biglobosa causes reproductive toxicity in female mice
- Tear and serum electrolyte concentrations as a biomarker in primary glaucoma subjects

