小续命汤含药血清对氧糖剥夺模型大鼠星形胶质细胞的保护作用研究
向军 徐莉莉 杨峰 朱雯 蔡定芳
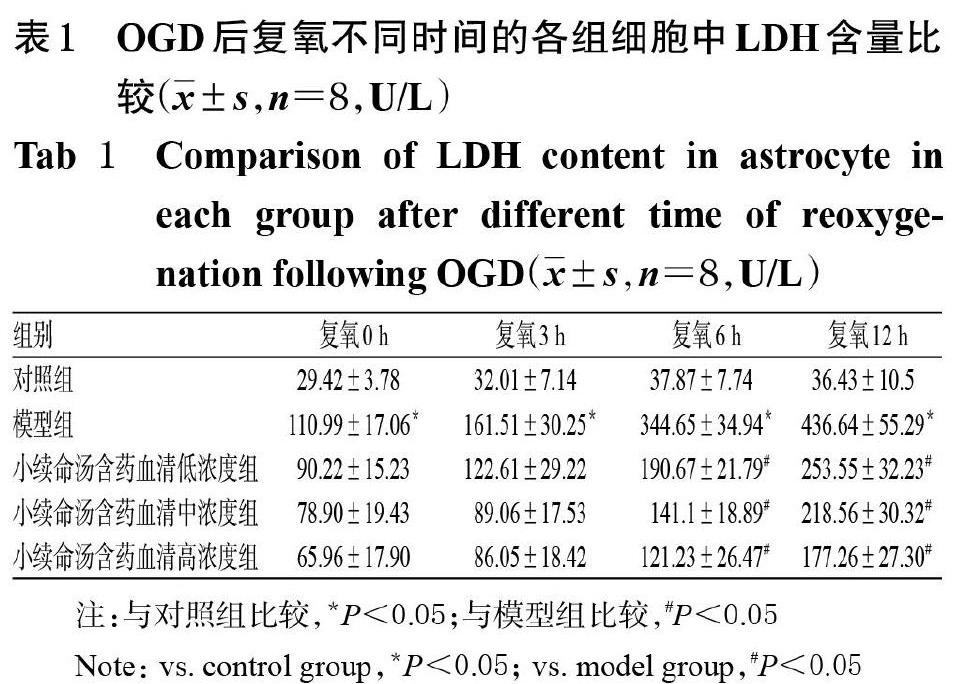
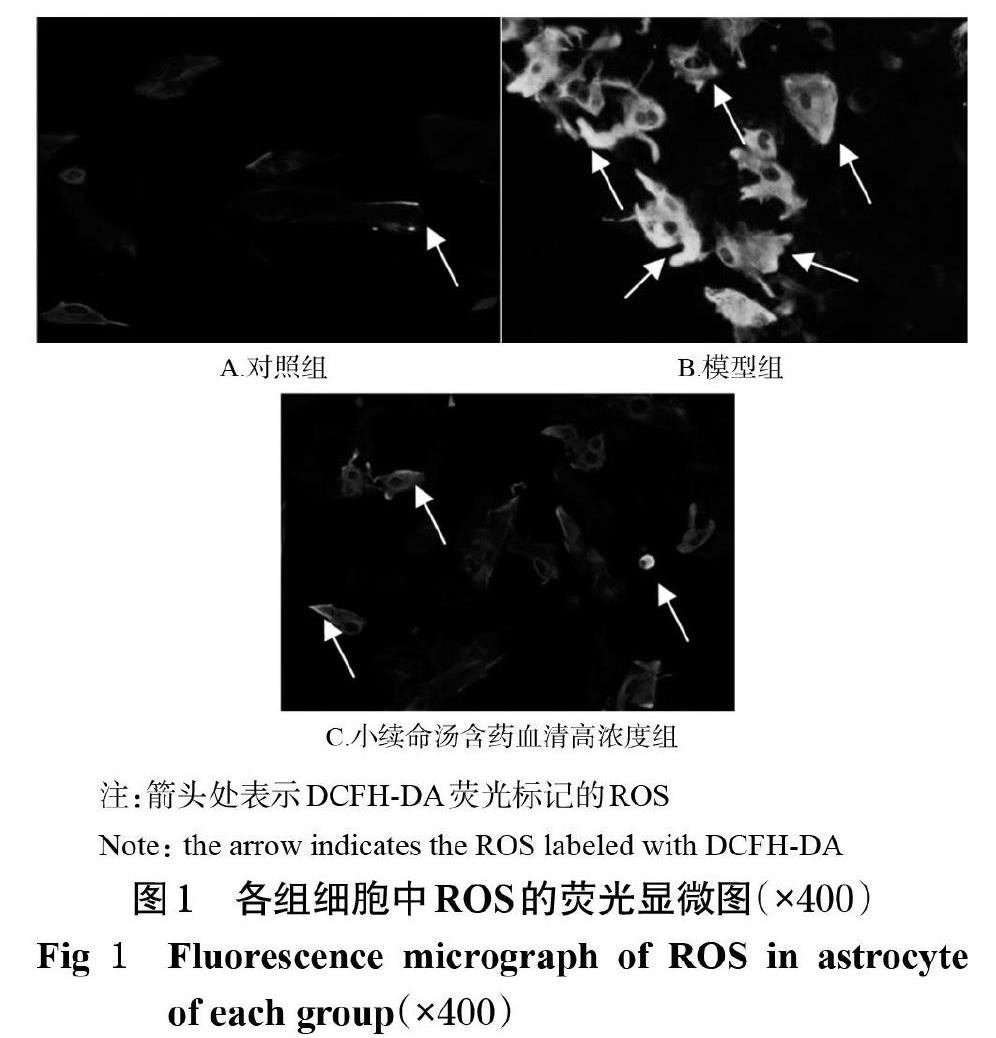
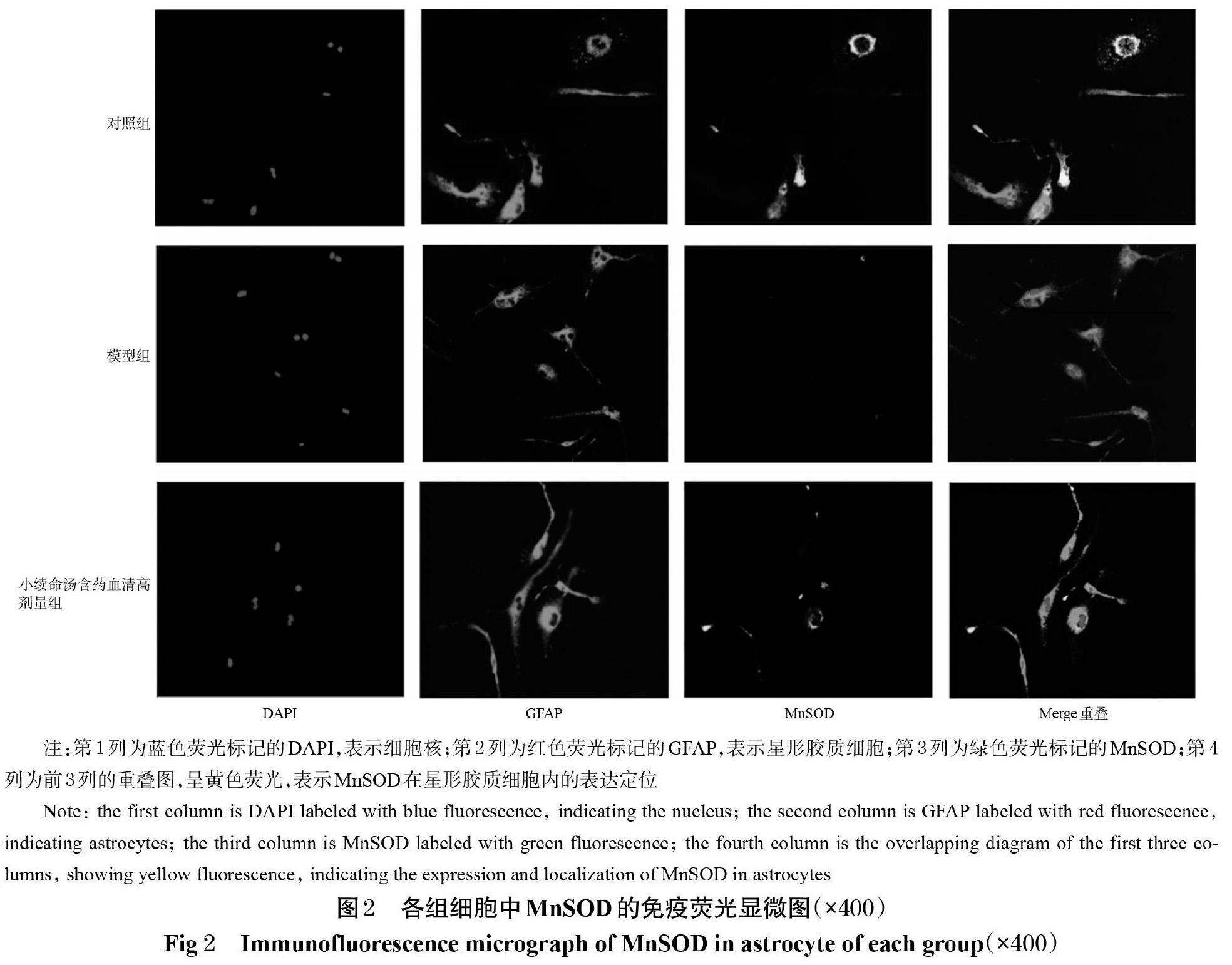
摘 要 目的:探討小续命汤含药血清对氧糖剥夺(OGD)模型大鼠星形胶质细胞的保护作用及其机制。方法:将体外培养的大鼠星形胶质细胞随机分为对照组、模型组和小续命汤含药血清低、中、高浓度组,其中对照组细胞不作任何处理,模型组和小续命汤含药血清低、中、高浓度组细胞经OGD 2.5 h后分别在0(即模型组不加药)、2.5%、5%、10%的小续命汤含药血清中复氧0、3、6、12 h,采用比色法检测细胞中乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)含量。取OGD后复氧12 h时的对照组、模型组和小续命汤含药血清高浓度组大鼠细胞,采用荧光探针法检测其活性氧(ROS)水平,采用免疫荧光双染法检测其锰超氧化物岐化酶(MnSOD)水平。结果:对照组细胞中LDH含量始终保持在较低水平;模型组细胞分别在OGD后复氧0~12 h时,其LDH含量从(110.99±17.06) U/L逐渐上升至(436.64±55.29) U/L,均显著高于对照组(P<0.05);与OGD后复氧相同时间点的模型组比较,小续命汤含药血清低、中、高浓度组细胞中LDH含量均不同程度地降低,并表现出时间和剂量依赖趋势,其中小续命汤含药血清各浓度组细胞在OGD后复氧6、12 h时其LDH含量均较模型组显著降低(P<0.05)。OGD后复氧12 h时,模型组细胞中ROS水平显著高于对照组,MnSOD水平显著低于对照组(P<0.05);小续命汤含药血清高浓度组细胞中ROS水平显著低于模型组,MnSOD水平显著高于模型组(P<0.05)。结论:小续命汤含药血清可能通过上调MnSOD的水平,清除过量的ROS,从而减轻OGD导致的大鼠星形胶质细胞损伤,发挥其保护作用。
关键词 小续命汤;含药血清;星形胶质细胞;氧糖剥夺;保护作用;机制
ABSTRACT OBJECTIVE: To investigate the protective effects of drug-contained serum of Xiaoxuming decoction (XXM)on astrocyte of oxygen and glucose deprivation model rats, and to explore its mechanisms. METHODS: The astrocytes of rats were randomly divided into control group, model group and XXM low-dose, middle-dose, high-dose groups. The cells in the control group were not treated; after 2.5 h of OGD, model group and XXM low-dose, middle-dose, high-dose groups were reoxygenated for 0, 3, 6, 12 h in 0 (i.e. the model group was not added with drugs), 2.5%, 5%, 10% of XXM, respectively. The content of lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) was detected by colorimetry. The reactive oxygen species (ROS) level was detected by fluorescence probe method, and the expression of Manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD) was determined by immunofluorescence double staining method in control group,model group and XXM high-dose group after 12 h of reoxygenation following OGD. RESULTS: The content of LDH in the control group was always kept at a low level; LDH content in the model group gradually increased from (110.99±17.06) U/L to (436.64±55.29) U/L after 0-12 h of reoxygenation following OGD, which was significantly higher than that in the control group (P<0.05). Compared with model group at the same time point after reoxygenation following OGD, the contents of LDH in the cells of XXM low-dose, medium-dose and high-dose groups were decreased to different extents, and showed a time-and dose-dependent trend. The contents of LDH in XXM groups at 6 and 12 h after reoxygenation following OGD were significantly lower than that of the model group (P<0.05). At 12 h after reoxygenation following OGD, the levels of ROS in model group were significantly higher than control group, while the level of MnSOD was significantly lower than control group (P<0.05). The level of ROS in XXM high-dose group was significantly lower than model group, while the level of MnSOD was significantly higher than model group (P<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: XXM can protect astrocyte by up-regulating levels of MnSOD, scavenging excessive oxygen free radicals, to relieve the OGD induced astrocytic injury, with protective effect.

