肠道菌群失调对代谢综合征儿童免疫功能及血清炎症因子的影响
袁和秀

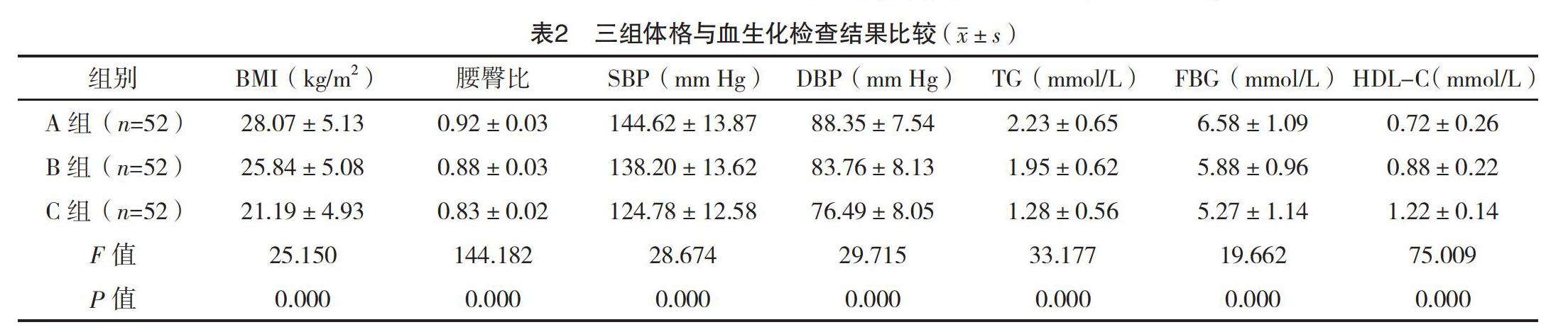

【摘要】 目的:探討肠道菌群失调对代谢综合征(MS)儿童免疫功能及血清炎症因子的影响。方法:选取2017年8月-2019年6月本院辖区内查体筛选出的128例MS患儿。经粪便涂片检查,肠道菌群失调的有76例,在出现肠道菌群失调的患儿中随机选择52例作为A组,其他未出现肠道菌群失调的52例代谢综合征患儿作为B组,随机选择查体正常的健康儿童52例作为C组。比较三组体格与血生化检查结果和免疫功能及血清炎症因子检测结果。结果:三组BMI、腰臀比、SBP、DBP、TG、FBG、HDL-C比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。三组IgA、IgM、IgG水平比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。C组IgA、IgM、IgG水平均低于A组和B组,B组IgM、IgG水平均低于A组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。三组TNF-α、IL-6、hs-CRP水平比较,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05);C组TNF-α、IL-6、hs-CRP水平均低于A组和B组,B组TNF-α、hs-CRP水平均低于A组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论:肠道菌群的改变与MS相关,一旦失调,会打破机体的免疫平衡,导致MS儿童免疫功能下降,血清炎症因子上升。
【关键词】 肠道菌群 代谢综合征 免疫功能 血清炎症因子
[Abstract] Objective: To investigate the effects of intestinal flora imbalance on immune function and serum inflammatory factors in children with metabolic syndrome (MS). Method: A total of 128 children with MS were selected from August 2017 to June 2019 within the jurisdiction of our hospital. According to stool smear, 76 cases had intestinal flora imbalance, among the children with intestinal flora imbalance, 52 cases were randomly selected as group A, 52 cases of MS without intestinal flora imbalance were selected as group B, and 52 cases of healthy children with normal physical examination were randomly selected as group C. The results of physical and blood biochemical examination, immune function and serum inflammation were compared among three groups. Result: The differences in BMI, waist-hip ratio, SBP, DBP, TG, FBG and HDL-C among three groups were statistically significant (P<0.05). Comparison of IgA, IgM and IgG levels among three groups, the differences were statistically significant (P<0.05). The IgA, IgM and IgG levels of group C were all lower than those of group A and B, and the IgM and IgG levels of group B were all lower than those of group A, there were statistically significant differences (P<0.05). The levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and hs-CRP in the three groups were significantly different (P<0.05). The levels of TNF-α, IL-6 and hs-CRP in group C were all lower than those in group A and B, and the levels of TNF-α and hs-CRP in group B were lower than those in group A, there were statistically significant differences (P<0.05). Conclusion: The change of intestinal flora is related to MS. Once the imbalance occurs, the immune balance of the body will be disturbed, leading to the decrease of immune function and the increase of serum inflammatory factors in children with MS.
[Key words] Intestinal flora Metabolic syndrome Immune function Serum inflammatory factor
研究显示,肠道菌群失调导致肠道细菌死亡后,脂多糖(LPS)作为细胞内毒素从溶解的菌体释放入肠道环境并进入血液循环,与其受体蛋白LPS结合蛋白相结合后引发宿主炎症级联反应,导致机体固有免疫被激活,通过一系列信号转导过程导致IL-6、TNF-α等炎症因子的大量表达[19-20]。因此,肠道菌群失调患者经常处于一种长期、慢性轻度炎症状态。本研究发现,C组TNF-α、IL-6、hs-CRP水平均低于A组和B组,B组TNF-α、hs-CRP水平均低于A组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。表明肠道菌群具有抗炎的作用,当肠道菌群失调时,人体会发生炎症反应,并影响着MS的发生,与上述研究结果一致。
综上所述,肠道菌群的改变与MS相关,一旦失调,会打破机体的免疫平衡,导致MS儿童免疫功能下降,血清炎症因子上升。通过平衡肠道菌群的结构,可以改善免疫功能,减少机体的炎症反应的发生,这为治疗MS儿童提供了新的依据。
参考文献
[1]邹步,唐莹,杨文玲,等.肠道菌群-FXR轴在代谢性疾病中的作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2019,35(9):1716-1720.
[2]谭新睿,张美真,李敏,等.肥胖儿童黑色棘皮病与脂肪因子和代谢综合征的关系[J].中国当代儿科杂志,2015,17(7):672-676.
[3]许文琦,王生,王艳,等.肠道菌群失调诱导肥胖发生发展的机制研究进展[J].世界临床药物,2018,39(6):417-421.
[4] Magge S N,Goodman E,Armstrong S C.The Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents: Shifting the Focus to Cardiometabolic Risk Factor Clustering[J].Pediatrics,2017,140(2):e20171603.
[5]林璋,祖先鹏,谢海胜,等.肠道菌群与人体疾病发病机制的研究进展[J].药学学报,2016,51(6):843-852.
[6]魏慧,赵金霞,刘湘源.肠道菌群在类风湿关节炎发病中的作用研究进展[J].中华医学杂志,2018,98(21):1723-1725.
[7] Pearl R L,Wadden T A,Hopkins C M,et al.Association between weight bias internalization and metabolic syndrome among treatment-seeking individuals with obesity: Weight Bias Internalization and Metabolic Syndrome[J].Obesity,2017,25(2):317-322.
[8]王鸿.肠道菌群與糖尿病、肥胖等代谢性疾病研究进展[J].西南医科大学学报,2018,41(3):280-283.
[9]黄强.腹泻型、便秘型及混合型肠易激综合征患者肠道菌群的差异性比较[J].国际医药卫生导报,2017,23(16):2577-2580.
[10]李晨,陈伟,王猛,等.肠道菌群失调与消化系疾病相关性研究进展[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2019,25(2):203-206.
[11]谢月萍,罗祖纯,戴霞.肠道菌群紊乱与糖尿病性便秘关系的研究进展[J].广西医科大学学报,2019,36(3):471-474.
[12]费嘉,罗军涛,章小英,等.短链脂肪酸在肠道菌群调节人体能量代谢中的作用[J].中华糖尿病杂志,2018,10(5):370-373.
[13]邓淑芳,于正,赖祯宏,等.肠道菌群在肥胖及相关代谢性疾病发生发展中的研究探讨[J].成都中医药大学学报,2014,37(4):102-106.
[14]薛晓强,白雪杉,林国乐,等.肠道菌群失调与中低位直肠癌术后吻合口漏相关性研究[J].中国实用外科杂志,2019,39(7):698-703.
[15]陈茜,薛勇,宋晓峰.糖尿病及糖尿病心血管并发症患者肠道菌群的特征[J].微生物学报,2019,59(9):1660-1673.
[16]郭攀,冯津萍,冯超,等.肠道菌群与相关疾病的研究进展[J].中华内科杂志,2019,58(6):476-480.
[17]邹大进.重视肠道菌群在肥胖与2型糖尿病发病中的作用[J].中国糖尿病杂志,2014,6(3):141-144.
[18]李航,方爱仙,潘淑兰,等.肠道菌群与高血压病主要危险因素的相关性及中药干预研究现状[J].中国微生态学杂志,2018,30(11):1343-1349.
[19]蒋伟伟,刘玉兰.肠道菌群与常见肝脏病[J].中华肝脏病杂志,2013,21(1):5-6.
[20]贾琼,段丽萍.肠道菌群在自身免疫病中作用的研究进展[J].中华内科杂志,2018,57(11):853-857.
(收稿日期:2020-02-10) (本文编辑:姬思雨)

