The value of real-time three-dimensional echocardiography in evaluating left ventricular function for different degrees of heart failure
Qin Wang, Jin-Ping Wang
Department of Ultrasound Medicine, The First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui University of Chinese Medicine, Hefei 230031, Anhui
Keywords:RT-3DE Heart failure Heart function classification The correlation
ABSTRACT Objective: To explore the value and feasibility of real-time three-dimensional echocardiography(RT-3DE) in evaluating left ventricular function in patients with different degrees of heart failure. Methods: The 60 heart failure patients in the case group were divided into three subgroups according to the New York Heart Association (NYHA) classification: 12 cases of cardiac function grade II, 35 cases of cardiac function grade III, 13 cases of cardiac function grade IV, and the other 30 cases of healthy subjects as control group. Compare the left ventricular end-diastolic volume(LVEDV), left ventricular end-systolic volume(LVESV), left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), and left ventricular 16, 12, and 6 segments reaching the minimum systolic volume time standard deviation standardized value (Tmsv SD%), left ventricular 16, 12 and 6 segments reaching the minimum systolic volume time standardized values of the maximum difference(Tmsv DIF%),analysis of the correlation between the above left ventricular function-related parameters and cardiac function grading. Results: (1)There were statistically significant differences in LVEDV and LVESV between each group(p<0.001).There was no statistically significant difference in LVEF between the cardiac function grade II group and the control group,and between the grade IV group and the grade III group(p=0.094 and 0.246). (2) compared with the control group,all parameters related to RT-3DE evaluation of left ventricular synchronization were prolonged in the case group, and the difference was statistically significant(p<0.001). The differences of Tmsv 16-SD% and Tmsv 16-DIF% in each subgroup of the case group were statistically significant(p<0.001). (3)LVEF was negatively correlated with NYHA classification of cardiac function(rs=-0.779, p<0.001), and LVEDV, LVESV, Tmsv 16-SD%, Tmsv 12-SD%, Tmsv 6-SD%, Tmsv 16-DIF%, Tmsv 12-DIF%, Tmsv 6-DIF% were positively correlated with NYHA function classification,showing strong correlation(rs=0.710, 0.785, 0.885, 0.675, 0.605, 0.885, 0.695, 0.622, p<0.001), among them, Tmsv 16-SD% and Tmsv 16-Dif% have the highest correlation. Conclusion: RT-3DE can comprehensively evaluate the impairment of cardiac function. The measured parameters of left ventricular function are strongly correlated with cardiac function classification, which has impo-rtant application value for clinical judgment of the severity of heartfailure.
1. Introduction
Heart failure (HF) is the end-stage of abnormal cardiac structure and/or function caused by various cardiovascular diseases[1]. Is attracting increasing attention due to its high incidence rate,readmission rate and high mortality. Zhang y et al.[2] research shows that the mortality rate of hospitalized heart failure patients is 4.1%, and the primary cause of death is left heart failure.Therefore,rapid and accurate assessment of the degree of heart function damage is the key to the treatment and prognosis of heart failure[3]. Real-time three-dimensional echocardiography (RT-3DE), as a new ultrasonic diagnosis technology,can comprehensively evaluate left ventricular function,with good accuracy and repeatability[4,5]. Previous studies[6,7] focused on RT-3DE to evaluate left ventricular systolic function in patients with heart failure, but there were few reports about the correlation between RT-3DE parameters and the severity of heart failure. In this paper, RT-3DE was used to evaluate the left ventricular systolic function and synchrony in 60 patients with different degrees of heart failure and 30 healthy subjects. The parameters were obtained and compared. The correlation between RT-3DE and the severity of HF was further analyzed to explore the application value and feasibility of RT-3DE in evaluating left ventricular function in different degrees of heart failure.
2. Data and Methods
2.1 Research Object
From April 2018 to March 2020, 60 patients with chronic heart failure were selected as the case group, including 41 males and 19 females, aged 33-94 years, The mean age was 69.27 ± 12.75 years old. According to NYHA cardiac function classification, the patients were divided into three subgroups:cardiac function class II Group (12 cases), cardiac function class III group (35 cases) and cardiac function class IV group (13 cases). The patients with cardiac resynchronization, pacemaker implantation and unclear RT-3DE images were excluded. Meanwhile,30 healthy volunteers in the same period were selected as the control group,including 17 males and 13 females, aged from 36 to 85 years, with an average age of 63.03 ± 13.22 years.There was no significant difference in general condition (gender, age, height, weight, body surface area) of each group. All subjects underwent real-time three-dimensional echocardiography after admission.
2.2 Instruments and Methods
Philips IE Elite Color ultrasonic diagnostic instrument, equipped with three-dimensional probe x5-1 (frequency 1-5Mhz) and QLAB software. Instruct the examinee to take the left side lying position and connect the ECG lead, synchronous mode, the quasistandard of the face-cut chamber and the four pointed heart can obtain the data parameter equal frequency frame pitch, the figure electrocardiography can enable the full volume three-dimensional mode,instruct the patient to hold his breath at the end of breath, and collect four continuous and stable heart rate and cardiac cycle dynamic maps (the above operations are all completed by senior doctors); The QLAB workstation was used to import images, and the sampling points were placed at the end of diastolic and systolic phase of left ventricle respectively at the four chamber and two chamber apical heart images of the two sides of the mitral annulus and the apex of the heart to automatically sketch the left ventricular endocardium. Some images need to be manually adjusted to obtain the left ventricular end diastolic volume, LVEDV, left ventricular end systolic volume (LVESV),left ventricular ejection fraction,(LVEF) and obtain the time volume curve,and obtain the parameters related to the asessment of left ventricular synchrony: the standardized value of the minimum volume time difference (Tmsv-SD%) and the standardized value of the maximum difference value (Tmsv-DIF%).
2.3 Statistical Methods
SPSS 22.0 statistical software was used to analyze the data,which was expressed by composition ratio,and the difference between groups was tested by ×2 test. The measurement data were first tested for normality and homogeneity of variance in each group, consistent with normal distribution or near normal distribution, expressed as x±s, with homogeneous variance, using single factor (AVOVA) analysis of variance, using Bonferroni method for multiple comparison,with uneven variance,using weleh or brown test as the final result, using tamhane's T2 method for multiple comparison, p< 0.05, it was considered that there was statistical difference; if the distribution was skewed, using The mean effective number (Q1, Q3) indicated that the difference was statistically significant by Kruskal wallish test and Bonferroni correction method. Spearman correlation analysis was used to analyze the correlation between the variables with ordered classification, and RS was used to show the correlation coefficient,with p< 0.05 as the difference.
3. Results
3.1 RT-3DE evaluation of left ventricular systolic function
There were statistically significant differences in LVEDV and LVESV between each group(p<0.001). There was no statistically significant difference in LVEF between the cardiac function grade II group and the control group,and between the grade IV group and the grade III group(p=0.094 and 0.246)(Table 1).
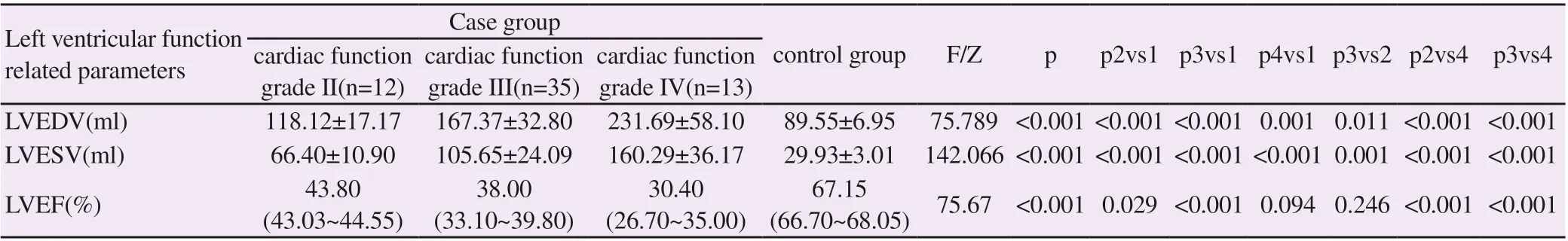
Table 1 RT-3DE analysis of parameters related to the assessment of left ventricular conventional systolic function
3.2 RT-3DE evaluation of left ventricular synchrony
Compared with the controlgroup,all parameters related to RT-3DE evaluation of left entricularsynchronization were prolonged in the case group, and the differencewas statistically significant(p<0.001). The differences of Tmsv 16-SD% and Tmsv 16-DIF% in each subgroup of the case group were statistically significant(p<0.001)(Table 2).
The curve of time volume change of healthy people in the control group is inverted parabola, and each curve runs orderly and regularly. The rising and falling range of the curve is relatively deep, and the peak time is the same (Fig. 1); the curve of patients with heart failure in the case group runs disorderly, which may cross and / or reverse, and the peak time is not the same (Fig. 2).
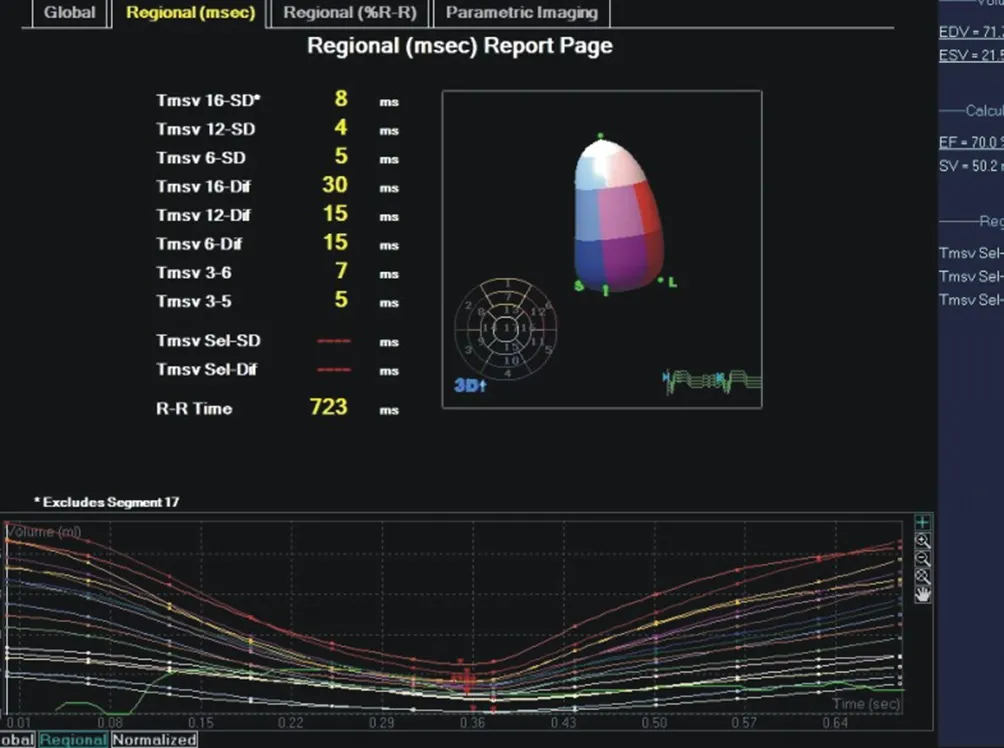
Fig.1 Time volume curve of control group
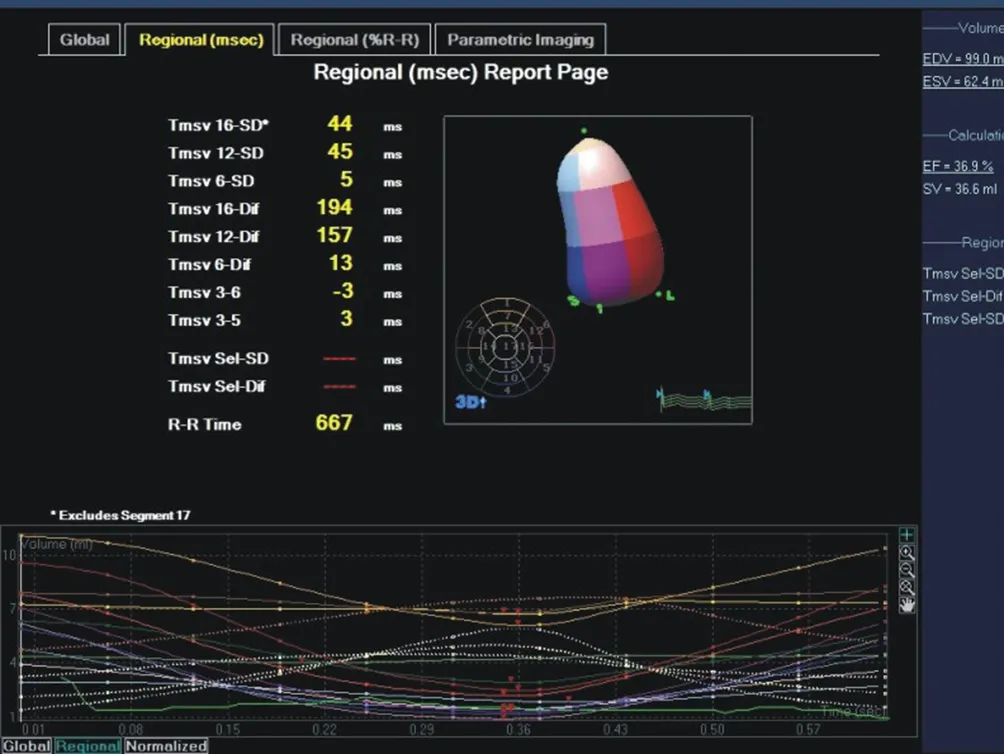
Fig. 2 Time volume curve of case group
3.3 RT-3DE comprehensive evaluation of left ventricular function related parameters and NYHA classification correlation analysis
According to the results of this study,LVEF was negatively correlated with NYHA classification of cardiac function(rs=-0.779,p<0.001), and LVEDV, LVESV, Tmsv 16-SD%, Tmsv 12-SD%, Tmsv 6-SD%, Tmsv 16-DIF%, Tmsv 12-DIF%, Tmsv 6-DIF% were positively correlated with NYHA function classification, showing strong correlation(rs=0.710, 0.785, 0.885, 0.675, 0.605,0.885,0.695,0.622,p<0.001),among them,Tmsv 16-SD% and Tmsv 16-Dif% have the highest correlation(Table 2).
4. Discussion
The results showed that RT-3DE could evaluate the left ventricular function,and its parameters had a strong correlation with the cardiac function grading, of which tmsv16 SD% and tmsv16 DIF% had the highest correlation, which had an important application value in clinical judgment of the severity of heart failure.
RT-3DE is a new technology that can evaluate the volume change of the whole and local segments of the heart in real time without simulating the geometry of the heart cavity,and simultaneously evaluate the left ventricular systolic synchrony [8,9], which has been widely used in clinical practice in recent years. With the development of science and technology, there are more and more reports about RT-3DE in assessing heart failure, most of the discussion discusses the value of evaluating left ventricular conventional systolic function and synchrony of heart failure [10,11], but there are few reports on the correlation between RT-3DE and heart failure grading.
Sasikumar Det al.[12]showed that RT-3DE was comparable to cardiac MRI in assessing ventricular volume.The results of this study showed that LVEDV and LVESV of each group had statistical differences (p<0.001),while LVEF increased with NYHA classification and gradually decreased, but there was no statistical difference between the control group and the level II group,the level III group and the level IV group, and there was statistical difference between the other groups.LVEF is a commonly used parameterin the traditional clinical evaluation of heart function, which can evaluate the heart function of patients with heart failure, but it can not distinguish the specific NYHA heart function grade, and the area under ROC curve is 0.408, p>0.05, when Huang Ying and other scholars reported that the reduced left ventricular blood score was used to evaluate moderate and severe HF, and it can not distinguish the level of distracted function.
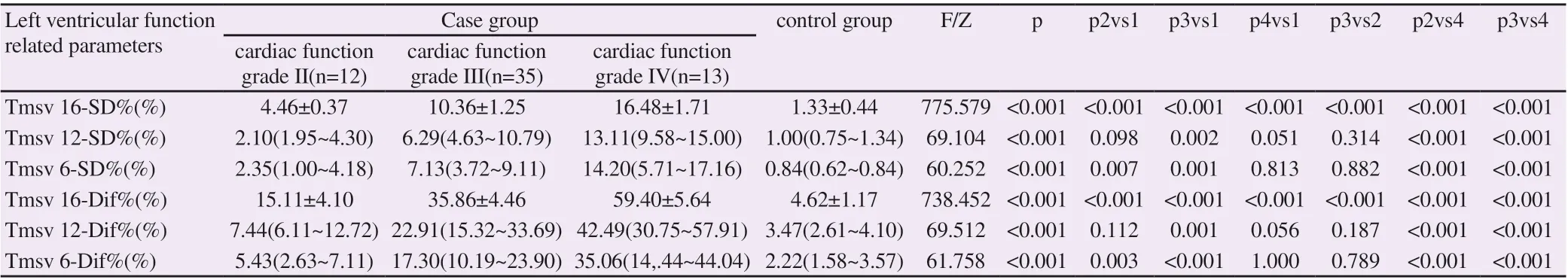
Table 2 Analysis of parameters related to RT-3DE assessment of left ventricular synchrony

Table 3 Correlation Analysis of parameters related to RT-3DE comprehensive assessment of left ventricular function and NYHA classification
In order to be able to pump blood through the heart to maintain the body's needs, in general, the ventricular wall will produce rhythmic contraction or relaxation; in heart failure, the heart, especially the left ventricle, will increase, resulting in the decrease of the movement of the ventricular wall, resulting in the asynchrony of the contraction and relaxation of the heart, resulting in the change of cardiac hemodynamics, affecting the systolic blood. De Marco E et al.[14] showed that RT-3DE can effectively identify left ventricular asynchrony, and the measurement repeatability is high, and the correlation between RT-3DE and tissue Doppler is good.Tmsv 16 SD%, Tmsv12 SD%, Tmsv 6 SD%, Tmsv 16-Dif%, Tmsv 12-Dif%and Tmsv 6-Dif% in the case group were significantly longer than those in the control group (p<0.001). RT-3DE has no angle dependence.It can accurately measure the local volume change of each segment of left ventricular wall, evaluate the hemodynamic change, evaluate the precise segment of left ventricular systolic delay and quantitatively evaluate the degree of myocardial asynchrony,so as to make a more comprehensive diagnosis of ventricular mechanical systolic asynchrony in HF patients.In order to minimize the effect of heart rate,RT-3DE was used in this study to evaluate the synchronization parameters, which were the standard deviation of systolic minimum volume time,the maximum difference value and the percentage after a R-R interval standardization. It was convenient for comparison between different patients,among which tmsv16 SD% and tmsv16 DIF% were statistically significant in all subgroups of the case group,indicating that these two groups of parameters could be used as evaluation.It is consistent with Ojala T et al[15] that the important indexes of different degrees of heart failure are estimated.
The key to the treatment of heart failure is to determine the degree of heart function damage. NYHA classification of cardiac function is a method to grade the patients according to the limitation of normal physical activity, which is widely used in clinical evaluation of the functional state of patients with heart disease[16]; This method is relatively simple, but has certain limitations,in the case of patients with similar heart failure, but with normal cardiac function, or in the case of patients who look healthy but actually have cardiac function decline There may be miscalculation; NYHA classification lacks quantitative evaluation and relies on doctors' subjective knowledge to make judgment; in addition, NYHA classification is also susceptible to non heart failure symptoms diagnosed as heart failure indicators. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to find quantitative parameters that may be related to NYHA classification.Hu Y et al.[17] studied the echocardiography and electrocardiography of 536 elderly patients with is chemic cardiomyopathy who had NYHA classification. The correlation analysis showed that the parameters measured by the two methods were significantly related to the cardiac function classification.The results showed that LVEF was negatively correlated with NYHA of cardiac function (rs=-0.779,p<0.001), and other parameters related to RT-3DE were strongly correlated with NYHA of cardiac function, and Tmsv 16-SD%, Tmsv 16-Dif%(rs=0.885, 0.885, p<0.001) had the highest correlation, suggesting that RT-3DE was closely related to the severity of heart failure Tmsv16 SD% and tmsv16 dif% are the most closely related to the classification of cardiac function.
With the continuous development of science and technology, RT-3DE has been further improved in terms of time,spatial resolution and Analysis Technology(such as high requirements for twodimensional image quality; when the cardiac cavity is significantly expanded, because the fan angle of the probe is relatively small, the chamber wall may appear outside the observation range,etc.), which is expected to become a routine method for assessing cardiac function and be applied in clinical practice. In addition, since this group is a small sample study, it is necessary to increase the sample size to further explore whether RT-3DE can determine the level of heart failure through some parameters.
In conclusion, RT-3DE as a new developing technology, can accurately measure the change of ventricular volume,evaluate the synchrony of myocardial contraction, and reflect the damage of heart function in patients with heart failure. The parameters related to left ventricular function assessed by RT-3DE have a strong correlation with the classification of heart function, which is of great application value in clinical judgment of the severity of heart failure and in the determination of heart failure grade Broad prospects.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2020年17期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2020年17期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Study of the AQP4 expression in traumatic brain edema and multimodal MRI imaging
- Analysis of two cases of patent ductus arteriosus ligation in preterm identical twins and literature review
- Role of 18F-FDG SPECT / CT imaging in the diagnosis and initial staging of lymphoma
- Association between polymorphism of MC4R rs489693 gene and disorder of glucose and lipid metabolism in schizophrenia patients treated with olanzapine
- Target prediction and mechanism of Shiyangning in treatment of perianal eczema
- Meta-analysis of traditional Chinese medicine and western medicine in treating retinal vein occlusion complicated by macular edema
