Target prediction and mechanism of Shiyangning in treatment of perianal eczema
Lan-Ye He, Xiao-Qiang Jia✉, Jia-Jun Li, Jing Xu, Rui Xie, Kai-Ming Li, Liang Su
1. Xiyuan Hospital, Chinese Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100091, China
2. Guang’anmen Hospital, Chinese Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100053, China
3. Institute for Chinese Materia Medica, Chinese Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing, 100070, China 4. Wangjing Hospital, Chinese Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences, Beijing 100102, China
Keywords:Shiyangning Perianal eczema Target Pathway Network pharmacology
ABSTRACT Objective: To explore the possible targets and signaling pathways of Chinese herbal compound "Shiyangning" in the treatment of perianal eczema(PE). Methods: The main active components and target proteins in Shiyangning were screened out by searching the Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform (TCMSP). PE Targets were retrieved and collected from Disease Databases such as Therapeutic Target Database (TTD). The protein-protein interaction (PPI) network was constructed and analyzed by STRING online database, and the network topology results were analyzed by Cytoscape 3.7.1 software. The common gene names of target proteins were checked in Uniprot database, and KEGG pathway function enrichment analysis was carried out through David database to study the possible signaling pathway of Shiyangning in the treatment of PE. Results: There were 238 core compounds, 152 targets and 233 PE disease targets. Six key targets (STAT3, IL6, TP53, EGFR, EGF and TNF) were obtained from the analysis of network topology. The results of pathway enrichment showed that PI3K-Akt signaling pathway and FoxO signaling pathway were the main pathways. Conclusion: Shiyangning treat PE mainly by regulating STAT3, IL-6 and other related inflammatory signaling pathways.
1. Introduction
Perianal Eczema is an inflammatory reaction that invades the epidermis and superficial dermis of the perianal region. It is characterized by pruritus, increased secretions, and recurrence [1]. The incidence is not limited by age and gender. The inflammation of perianal eczema is not only common in the perianal skin, but also involving perineum and external genitalia. Due to the extremely sensitivity of the perianal skin, the discomfort caused by perianal eczema can seriously affect the work and life of patients [2]. Clinically, western practitioners usually use medicine to treat perianal eczema, which can only alleviate symptoms and also has some adverse reactions. The evidence level for antihistamines and glucocorticoids used in the treatment of eczema is low [3], because of the particularity of perianal skin, the drugs in the guidelines for eczema are not suitable for its treatment. Perianal eczema belongs to the category of "dampness-heat" in traditional Chinese medicine. Shiyangning is based on the theory of " Pruritus begin because of the wind, so relieving pruritus must first remove the wind. " recorded in the Waikezhengzong(Orthodox Manual of Surgery), and combined with the main pathogenesis of "retention of wind, dampness, heat and disharmony between qi and blood". Previous studies have confirmed that Shiyangning could alleviate perianal itching and dampness, and could improve the shape of perianal skin lesions, reduce the area of perianal skin lesions, and reduce the recurrence rate of perianal eczema [4].Due to the uncertainty of the mechanism of the treatment of perianal eczema with Chinese medicine and the complexity of the components of Shiyangning, and there were few previous studies on the drug mechanism of perianal eczema, in this study, the possible active ingredients and their molecular mechanisms in Shiyangning will be predicted through research methods of network pharmacology [5]. By searching the reported targets of each Chinese medicine monomer in Shiyangning and perianal eczema disease, screening the intersection of the two and enriching analysis, then predict the mechanism of the Chinese medicine compound in the treatment of perianal eczema.
2. Methods
2.1 Materials
Effective components and target selection of Shiyangning Shiyangning is composed of 20g of Jingjie (Schizonepeta tenuifolia), 20g of Fangfeng (Saposhnikovia divaricata), 20g of Dafupi (Pericarpium arecae), 20g of Difuzi (Kochia scoparia fruit), 10g of Chantui (Cicada slough), 20g of Zicao (Radix Arnebiae) and 10g of Honghua (Carthamus tinctorious) . Through traditional Chinese medicine systems pharmacology database and analysis platform (TCMSP) [6], 7 traditional Chinese herbals, i.e. Jingjie (Schizonepeta tenuifolia), Fangfeng (Saposhnikovia divaricata), Dafupi (Pericarpium arecae), Difuzi (Kochia scoparia fruit), Chantui (Cicada slough), Zicao (Radix Arnebiae) and Honghua (Carthamus tinctorious) were used as herb name to search all the chemical components in the prescription of Shiyangning. Based on the absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME) [7], high-activity compounds in seven Chinese medicines were screened out. Due to the fact that Shiyangning is the topical drug, another key parameter of ADME, oral bioavailability (OB), was not used as the screening criteria, and only drug likeness (DL)≥0.18 [8]was used as the screening and extraction of active compounds. The DL is used to evaluate the similarity between compounds and known drugs. Query the standard protein name of the target through the Unitprot database [9], and use the TCMSP target to predict the target of the active ingredient.
2.2 Collection of perianal eczema targets
In the OMIM database [10], TTD database [11], Drug Bank database [12], GeneCards database [13], use "perianal eczema", "perianal dermatitis", "anal eczema" as search terms to search for disease targets of perianal eczema.
2.3 Building protein-protein interactions (PPI)
The intersection of effective compound targets of 7 Chinese herbs in shiyangning and perianal eczema targets were uploaded to string 11.0[14]. In the software platform, the scoring condition of parameter setting was set to be > 0.70, the single function protein in the graph was removed to ensure that the final composition is high-confidence data, and finally output a visual graph of PPI for research and analysis, and count the target protein association frequency.
2.4 Network construction and analysis
According to the relationship among the components of traditional Chinese medicine, the components of single drug and the target, the active component target network was established. The PPI network was established by using the target of traditional Chinese medicine in the treatment of diseases, so as to obtain the relationship between the interaction between Shiyangning and the target of perianal eczema. The network composition was carried out by using the software of Cytoscape 3.7.1, and the PPI network was analyzed by means of degree, closeness and betweenness.
2.5 Enrichment analysis of KEGG pathway
The KEGG pathway enrichment analysis was performed on the standard protein names that have been screened by the Uniprot database in the DAVID database [], and the important KEGG pathways enriched were screened with P<0.01 to define the target of the traditional Chinese medicine compound of Shiyangning. The role of proteins in signal pathways to explain the mechanism and principle of Shiyangning in treating perianal eczema.
3. Results
3.1 Screening of active compounds in Shiyangning
After searching TCMSP with DL≥0.18 as the criteria, 48 compounds and 557 targets were found from Schizonepeta tenuifolia, 36 compounds and 502 targets were found from Saposhnikovia divaricate, 9 compounds and 124 targets were found from Pericarpium arecae, 9 compounds and 105 targets were found from Kochia scoparia fruit, 3 compounds and 18 targets were found from Cicada slough, 35 compounds and 340 targets were found from Radix Arnebiae, 98 compounds and 821 targets were found from Carthamus tinctorious, and a total of 2467 compound targets were obtained. After removing the duplicates, 162 targets remained, which were searched in UniProt database, and using "Homo sapiens" for elimination, and then the standard gene target of the active ingredient of traditional Chinese medicine (Gene symbol) was obtained. Among them, 10 of 162 targets did not have the "Homo sapiens" standard protein name, so there were 152 compound targets were left totally.
3.2 Collection of disease targets
Gene targets were obtained by searching the disease gene database with perianal eczema. Among them, OMIM, TTD, GeneCards, and DrugBank databases retrieved 93, 1, 147, and 0 targets, respectively. After deleting duplicate targets, 233 important targets were obtained.
3.3 Results of Protein interactions
Human gene expression is not a single expression, but a manifestation of interaction and cooperation to complete the function. Therefore, with the help of PPI, an interactive network of direct targets and indirect targets for treatment of herbal medicine was constructed, and the mechanism was deduced. The intersection of the component target protein of Shiyangning and the disease target protein of perianal eczema was made by Venn diagram, and 14 interaction targets were obtained (Fig.1). Target basic information was shown in Table 1. The PPI network diagram of Shiyangning target was constructed by STRING software, as shown in Fig. 2. With the confidence level (CI) > 0.70, the resulting PPI network contained 64 nodes, 386 edges, and the average degree was 12.1.
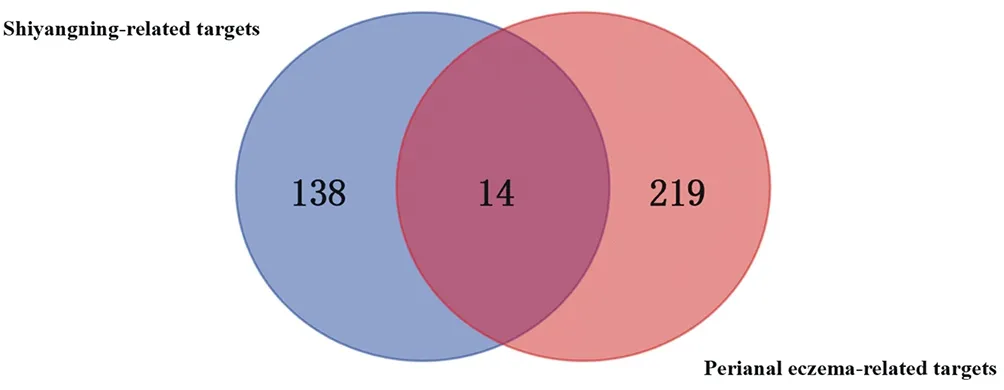
Fig.1 Shiyangning-related targets and perianal eczema -related targets
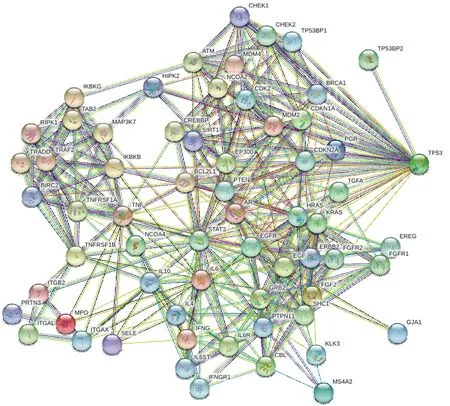
Fig.2 PPI network diagram of Shiyangning target
3.4 Results of network construction
Taking the median of twice the "node connection" as the threshold, the core nodes (hubs) of the TCM target-disease gene interaction network were selected [15].
At the same time, using the median of degree, closeness, and betweenness as the threshold, 6 genes (STAT3, IL6, TP53, EGFR, EGF, TNF) were selected as the target genes for Shiyangning in treating perianal eczema. STAT3 (Degree 31) was the most important candidate genes (Table. 2).
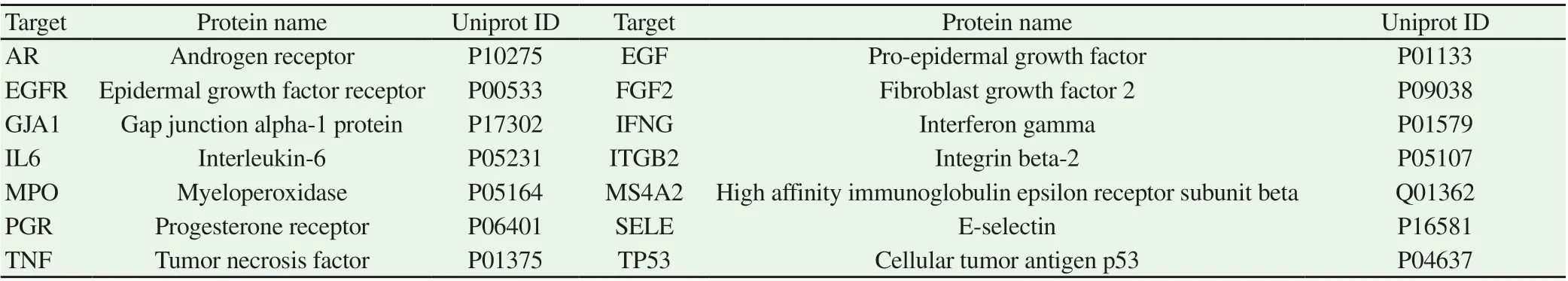
Table 1 Target information for Shiyangning in treating perianal eczema
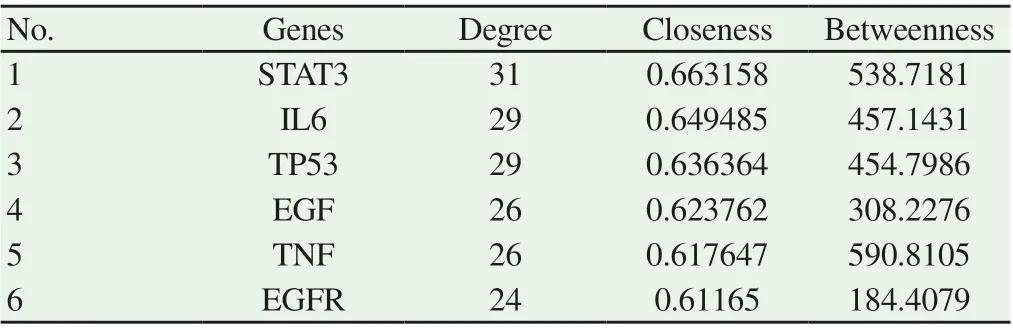
Table 2 Core genes for Shiyangning in treating perianal eczema
3.5 Analysis of KEGG pathway enrichment
In this study, the target protein genes of Shiyangning were enriched by KEGG pathway in the DAVID database, and 92 enrichment results were obtained. The Bonferroni method was used to correct P, and the top 10 enrichment pathways with significant effects were analyzed, as shown in Figure 3. The 10 most significant pathways of KEGG enrichment were prostate cancer, pathways in cancer, FoxO signaling pathway, Hepatitis B, Chronic myeloid leukemia, Viral carcinogenesis, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway, MicroRNAs in cancer, p53 signaling pathway, Glioma. Among them, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway and FoxO signaling pathway were enriched with the most genes, PI3K-Akt signaling pathway was enriched with 26 genes, and FoxO signaling pathway was enriched with 21 genes.
In addition, although the enrichment results show that signal pathways such as prostate cancer, pathways in cancer, and MicroRNAs in cancer were related to tumors, the herbals in Shiyangning may have multiple targets and multiple pathways to treat tumors. Future research could be focus on the possible pharmacological effects of the Chinese medicine in Shiyangning compound on tumor prevention and treatment.
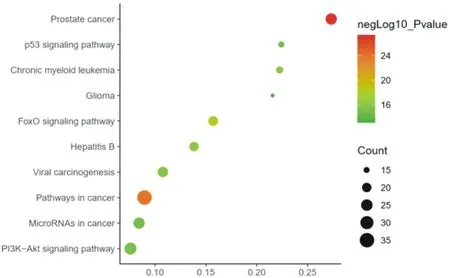
Fig.3 Key target genes KEGG pathway enrichment
4. Discussion
Shiyangning was based on the pathogenesis of perianal eczema, which is characterized by "retention of wind, dampness, heat and disharmony between qi and blood". Seven Chinese herbal medicines (Jingjie/Schizonepeta tenuifolia, Fangfeng/Saposhnikovia divaricata, Dafupi/Pericarpium arecae, Difuzi/Kochia scoparia fruit, Chantui /Cicada slough, Zicao/Radix Arnebiae and Honghua/Carthamus tinctorious) in the formula have the effect of expelling wind, activating blood and removing dampness, which have achieved good clinical effect.In this study, the topological analysis of the interaction network of effective compounds and targets in Shiyangning, the construction and analysis of PPI network and the enrichment of KEGG pathway function were carried out.According to PPI network diagram, the key proteins in the effective components of shiyangning were STAT3, IL6, TP53, EGFR, EGF, TNF, etc. Based on the results of KEGG, the main effects of Shiyangning were related to PI3K-Akt signaling pathway and FoxO signaling pathway.
It has been reported that up regulation of tumor growth factor (TNF) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) can mediate the activation of signal transmitter and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3) [16], STAT3 dephosphorylation could regulate interleukin-6 mediated signaling pathway [17], which led to cell growth and antiapoptosis. The inflammatory response was regulated by monitoring the differentiation of immature CD4 + T cells into T-helper (Th17) or regulatory T cells (Treg). The combination of EGF and receptors can transform extracellular cues into appropriate cellular responses [18], in addition, EFG and EGFR are enriched in PI3K Akt signaling pathway and FoxO signaling pathways.
Combined with the composition and disease mechanism of Shiyangning, the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway and FoxO signaling pathway may be the main regulatory pathways for traditional Chinese medicine to play a therapeutic role, while the STAT3 and IL-6-mediated signaling pathways play a key role.
In combination with the composition of Shiyangning formula and perianal eczema pathogenesis, PI3K Akt signal pathway and FOXO signal pathway may be the main regulatory pathway for the therapeutic effect of traditional Chinese medicine, while the STAT3 and IL-6-mediated signaling pathways play a key role.
Network pharmacology, as a media method for the study of traditional Chinese medicine, can be used to speculate the mechanism of action of traditional Chinese medicine compounds and monomers in vivo [19], but there are still unsatisfactory parts [20], such as the complete mechanism of pharmacology cannot be revealed, the possible mechanism of action of TCM only could be predicted through the existing database. Therefore, more experiments need to be combined to assist the verification.
To sum up, this study used network pharmacology to analyze the interaction between active herbal components, targets, and pathways of Shiyangning. It was found that Shiyangning and its active ingredients could play an effective role in the treatment of perianal eczema through multiple targets and pathways, which provided a certain reference for further research on the basis of pharmacodynamics of perianal eczema.
 Journal of Hainan Medical College2020年17期
Journal of Hainan Medical College2020年17期
- Journal of Hainan Medical College的其它文章
- Study of the AQP4 expression in traumatic brain edema and multimodal MRI imaging
- Analysis of two cases of patent ductus arteriosus ligation in preterm identical twins and literature review
- Role of 18F-FDG SPECT / CT imaging in the diagnosis and initial staging of lymphoma
- The value of real-time three-dimensional echocardiography in evaluating left ventricular function for different degrees of heart failure
- Association between polymorphism of MC4R rs489693 gene and disorder of glucose and lipid metabolism in schizophrenia patients treated with olanzapine
- Meta-analysis of traditional Chinese medicine and western medicine in treating retinal vein occlusion complicated by macular edema
