护理干预对酒依赖患者复饮预防的效果评价
张岩丽 朱春燕 石玉春
【摘 要】目的:本次实验针对酒依赖患者的护理治疗过程,分析护理干预模式对预防患者复饮的作用。方法:本次实验需分为两组研究对象,从2018年7月至2019年7月间在我院接受治疗的酒依赖患者中选取56例,将其随机均分。给对照组患者进行健康教育,观察组患者采取一对一教育模式,经过一段时间的护理后,对患者生活质量、患者配合度和患者复饮情况三项内容进行统计比较。结果:在护理效果上观察组患者数据均高于对照组,差异明显,P<0.05,有统计学意义。结论:在治疗过程中,如果对酒依赖患者采取护理干预模式,患者会更加积极地配合治疗,降低患者對酒精的依赖性,有效防止复饮,提高患者生活质量,值得推广。
【关键词】酒依赖患者;护理干预;预防;复饮
Evaluation of the effect of nursing intervention on prevention of alcohol dependence
Abstract:Objective This experiment aimed at the nursing treatment process of alcohol-dependent patients, and analyzed the effect of nursing intervention mode on preventing patients from drinking again. Methods: this experiment was divided into two groups. 56 patients with alcohol dependence who received treatment in our hospital between July 2018 and July 2019 were randomly divided into two groups. Patients in the control group were given health education, and patients in the observation group were given one-to-one education. After nursing for a period of time, statistical comparison was made on the three aspects of patients' quality of life, patients' cooperation degree and patients' rehydration status. Results: the data of the observation group were higher than that of the control group, the difference was significant, P < 0.05, with statistical significance. Conclusion: in the course of treatment, if the nursing intervention mode is adopted for alcohol-dependent patients, the patients will cooperate with the treatment more actively, reduce the patients' dependence on alcohol, effectively prevent refilling, and improve the patients' quality of life, which is worthy of promotion.
Key words: alcohol-dependent patients; Nursing intervention; Prevention; After drinking
【中图分类号】R473.5【文献标识码】B【文章编号】1005-0019(2020)13--01
酒依赖是患者在长期饮酒过程中造成酒精依赖的一种精神障碍现象,容易引发酒精中毒,为患者身体的损害和精神障碍类临床疾病的发生埋下隐患,从而对患者的身心健康造成极大的伤害[1]。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
本次实验从2018年7月至2019年7月间在我院接受治疗的酒依赖患者中,选取了56例作为研究对象,将这些研究对象随机均分为对照组和观察组,对比了患者的所有基本资料,发现数据的差异没有统计学意义(P>0.05)。
1.2 护理方法
给予观察组患者护理干预模式。具体措施如下。
1.2.1 一对一指导教育。护理人员针对患者的身体状况和心理压力进行分析,消除患者借酒消愁的依赖心理,讲解长期大量饮酒的危害和戒酒的必要性,给患者发放健康手册[2]。
1.2.2 利用电话和短信进行监督提醒。在患者出院后,为了有效防止患者复饮的情况发生,护理人员可在前五个月定期对患者情况进行查访,注意通话时间保持在二十分钟内,这个时间段既能让护理人员充分了解患者的近况,也不会因长时间的通话导致患者厌烦。
1.2.3 定期门诊随访和心理辅导。电话和短信监督虽然能起到一定作用,但患者自身还是占据主导地位,护理人员每隔两个月对患者进行定期门诊随访,了解患者的真实情况。
1.3 观察指标
对两组护理结果,包括患者生活质量、患者配合度和患者复饮情况三项内容进行统计比较。评分越高说明患者生活质量和配合度越高,患者复饮情况评分越低说明患者戒酒越成功。
1.4 统计学分析
本研究采用SPSS 20.0软件包对酒依赖患者的护理数据进行统计学分析,对护理结果的评分采用计量方式和t检验,差异显著性水平为P<0.05,有统计学意义。
2 结果
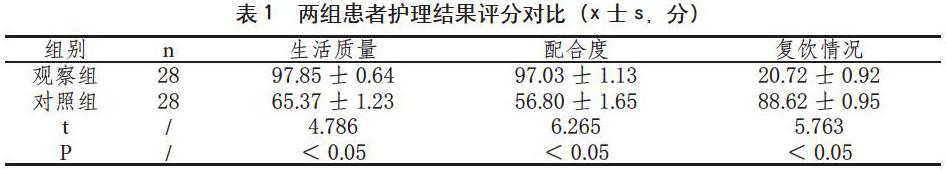
在护理结果上,观察组前两项评分都比对照组的评分高,观察组患者复饮情况评分比对照组低,因此观察组护理效果更好(P<0.05)。见下表1:
3 讨论
综上所述,在治疗过程中,如果对酒依赖患者采取护理干预模式,患者会更加积极地配合治疗[2-3],降低患者对酒精的依赖性,有效防止复饮,提高患者生活质量,值得推广。
参考文献
杜好瑞,李拴荣,穆俊林,等. 酒依赖患者戒断初期酒精渴求程度与睡眠障碍的关系[J]. 中华行为医学与脑科学杂志,2017,23(3):222-224.
庞良俊,尹良爽,朱春燕.男性酒依赖患者注意偏向与戒酒后复饮的相关分析[J].中华精神科杂志,2017,49(2):97-100.
陶然,朱建立,马梦颖,等.渐进式肌肉放松训练对酒依赖患者戒断期心理渴求和焦虑的作用[J].中国药物依赖性杂志,2017,25 (2):186-189.

