Efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese medicine kidney-nourishing formula for Alzheimer's disease in comparison with donepezil:a systematic review and meta-analysis
Fei-Zhou Li,Yi-Ni Zhang,Tong Zhang,Ling Liu,Ping Wang
1Clinical College of Chinese Medicine,Hubei University of Chinese Medicine,Wuhan,China.2Encephalopathy Department,Hubei Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Wuhan,China.3Institute of Gerontology,Hubei University of Chinese Medicine,Wuhan,China.
Abstract
Objective: Finding an effective therapy against Alzheimer’s disease(AD)has been associate increasingly pressing issue and traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) is widespread in the prevention and treatment of AD in China.The aim of this study was to judge the efficaciousness and safety of TCM kidney-nourishing (the changes of pathological state of kidney deficiency by means of TCM treatment and so on) formula (TKNF) for AD in comparison with donepezil. Methods: The retrieval period of seven databases was from the establishment of each database to April 2019.Two authors independently identified randomized controlled trials(RCTs),fetched data and assessed bias risk.Comprehensive analysis process was conducted with review manager for eligible and appropriate RCTs. Results:A complete of 981 AD patients from 13 studies were enclosed.Meta-analysis of RCTs showed that there was no significant difference in the improvement of Alzheimer's disease assessment scale-cognitive subscale score between 2 groups in short term,but the effect of long-term treatment may exceed donepezil;there was a significant difference in the improvement of activities of daily living score between 2 groups;there was a significant difference in TCM curative efficacy between 2 groups with long-term treatment.There was no significant difference in the incidence of adverse events between 2 groups.The quality of the evidence was high or moderate. Conclusion: Compared with donepezil,TKNF was an effective drug for AD patients and the clinical application of TKNF was safe.TKNF's long-term benefits need more evidence to verify.
Key words:Alzheimer's disease,Traditional Chinese medicine,Kidney-nourishing formula,Donepezil,Systematic review,Meta-analysis
Background
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is seen as a degenerative brain disease with a slow and gradual decline in cognitive function and disposing capacity.The number of individuals living with dementedness worldwide nowadays is calculable at 50 million,2/3 of which are AD,and this figure is predicted to reach 152 million by 2050.Since global health costs for dementia patients are estimated to reach$1 trillion in 2018 and are expected to be doubled by 2030,which implies AD has been identified as one of the world's health priorities,the growing burden of malady can challenge the current health care system and national economy[1,2].At the same time,AD has constituted a serious threat to human health.The average life span of typical AD patients after diagnosis is just over 101 months or about 8.5 years [3].In England and Wales,AD has even become the number one killer of health [1].Moreover,within the coming back years,the low-income and middle-income countries are predicted to be the main force in increasing the prevalence of dementia [4],which deserves the eye of researchers.
Since 1998,clinical trials of 100 drugs have been conducted,but solely 4 were approved for the treatment of AD,and these medications can only improve some of the symptoms [1].Therapy that can alter the potential pathology of AD has not yet been discovered [5].Donepezil,a cholinesterase inhibitor,is currently recommended as a drug to delay the progression of cognitive impairment in AD.Nevertheless,its side effects cannot be ignored [6].Therefore,it is urgent to seek new drugs for the treatment of AD.
AD is generally diagnosed as Chidai in traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) [7].The description of dementia-related symptoms can be found in historical book entitled Zuo Zhuan (The Spring and Autumn Annals) (722 B.C.E.-468 B.C.E.) in the Pre-Qin Dynasty,and the name of Chidai was first proposed by Sun Simiao in Huatuo Shenyi Mizhuan(Biography of Hua Tuo's Medicine)(618 B.C.E.-907 C.E.),a Chinese medicine classical book published in the Tang Dynasty.For a long time,TCM has been known for its wide variety of herbs and long-standing clinical practice,who accumulated abundant clinical experience in the struggle against AD.The Chinese medicine classical book entitled Huangdi Neijing (The Yellow Emperor's Internal Classic)(221 B.C.E.-220 C.E.)provides a theoretical basis for establishing a link between kidney and dementia.Therefore,nourishing kidney has become an important treatment for dementia by TCM clinicians nowadays.Compounds extracted from herbal medicines have been proven to be effective in alleviating dementia and have the advantages of low toxicity and multi-target [8].Western medicine for AD is limited by single-targeted therapy,which may not be suitable for the treatment of AD.So TCM compound has great potential in preventing and treating AD by multi-link,multi-target,and multi-channel integration effect[9].
Considering that consensus on diagnosis and treatment of AD in TCM recommends the kidney-nourishing (the change of pathological state of kidney deficiency by means of TCM treatment and so on)therapy as the basic principle for the treatment of AD [7],we organized this systematic review with meta-analysis,to assess the clinical efficacy and safety of traditional Chinese medicine kidney-nourishing formula (TKNF) in AD patients,compared with donepezil.
Methods
This systematic review and meta-analysis adhered to the preferred reporting items in systematic reviews and meta-analyses statement [10].This study has been registered on Prospero platform with an assigned number CRD42019132880.
Database and search strategies
Two reviewers (Fei-Zhou Li and Yi-Ni Zhang)independently searched the subsequent electronic databases from their inception to April 2019:Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials,Excerpta Medica Database,PubMed,China Biological Medicine Database,China National Knowledge Infrastructure,Wanfang Database,Chinese Scientific Journals Database.The following search terms were employed in combination:(Alzheimer's disease OR senile dementia) AND(traditional Chinese medicine OR kidney-nourishing)AND (donepezil OR cholinesterase inhibitor OR aricept) AND (randomized controlled trial OR controlled clinical trial OR randomized clinical trial).The retrieval strategy for PubMed can be found(Supplementary Table1).Only Chinese and English documents were included.Besides,the authors also hand-searched the reference lists to look for relevant literature.
Inclusion criteria and exclusion criteria
Types of participants
All included participants were definitively diagnosed with AD according to the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders [11],or Recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer's Association Work Groups on Diagnostic Guidelines for Alzheimer's Disease [12],or Chinese Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Alzheimer's Disease or Other Dementia[13],or National Institute of Neurological and Communicative Diseases and Stroke/Alzheimer's Disease and Related Disorders Association Alzheimer's Criteria [14].Studies involving vascular dementia,frontotemporal degeneration,Lewy body dementia and other types of dementia were excluded.
Types of intervention
The intervention of the experimental groups was TKNF,regardless of the dosage,the form and the course of treatment.The control groups were interpreted with donepezil.Studies comparing TKNF with acupuncture,moxibustion,massage,and other TCM treatments were excluded.
Types of outcome measures
Alzheimer's disease assessment scale-cognitive subscale (ADAS-Cog) [15] and activities of daily living (ADL) scale were the main outcomes we chose.TCM curative efficacy and adverse events were taken as the secondary outcome indicators.Standards for TCM curative efficacy refer to guiding principle of clinical research on new drugs of TCM[16].
Types of studies
The authors included randomized controlled trials(RCTs) involving TKNF compared with donepezil in the treatment of AD.As for differences like age,gender,race,the region of the research,and the blind method were not considered in this study.Animal experiments,case reports,and observational studies were excluded.Neither the literature without available outcome to analyze nor the republished literature was included in the study.
Study selection and data collection
Two researchers (Fei-Zhou Li and Yi-Ni Zhang)independently completed the document retrieval in step with the search strategy strictly.Firstly,according to the title and abstract,the literature searched were preliminarily screened.After that,literature that meets the requirements were found for further full-text screening.In these processes,the reasons for eliminating documents were documented.Any differences between the 2 were decided by a discussion with the third author(Ping Wang).Then,2 researchers (Fei-Zhou Li and Yi-Ni Zhang) severally extracted information including the name of the first author,year of publish,title,diagnostic criteria,sample size,mean age,disease duration,intervention,dose,course of treatment,outcome measurements,and follow-up time.
Assessment of risk of bias in individual studies
Risk bias of each study was evaluated with the tool provided by the Cochrane Collaboration [17].The judgment of bias risk included seven aspects:random sequence generation,allocation concealment,blinding of participants and personnel,blinding of outcome assessment,incomplete outcome data,selective reporting,and other bias.Two researchers(Fei-Zhou Li and Yi-Ni Zhang) conducted quality evaluations separately,and any divergences were settled through discussions with the third reviewer(Ping Wang).The score ranged from 0 to 7.
Data synthesis and statistical analysis
The Review Manager 5.3 software was implemented in statistical analysis [18].The risk ratio (RR) and the mean difference (MD) were used as combined analysis statistics for dichotomous data and continuous data respectively.The confidence interval(CI)of each effect variable was expressed in 95%CI.Chi-square test and I2index were utilized to test statistical heterogeneity.When the heterogeneity was low (P-value >0.1 and I2<50%),a fixed effect model was used.IfP-value ≤ 0.10 in the heterogeneity test,subgroup analysis or a random effect model was performed.The descriptive analysis was conducted when heterogeneousness obviously existed among studies.In order to evaluate the possible publication bias,a funnel plot was applied.The Grading of Recommendations Assessment,Development and Evaluation (GRADE) [19]methodology was used to rate the qualities of proof.
Results
Studies search and screening results
Two thousand seven hundred and sixty-three studies were retrieved and no other documents were found by manual search.Among them,396 articles were considered duplicates.Two thousand two hundred and ninty-two articles were removed by title and abstract,including 1,051 animal experiments,246 reviews,178 summaries of clinical experience,355 non-RCTs,and 462 articles utilizing other treatments.For a further step,we screened the remaining 75 full texts for further identification,28 articles were removed with reasons:19 articles were not real RCTs,and 9 articles were not TKNF.Thus,the left 47 RCTs were evaluated to assess their bias risk.Finally,only 13[20-32]RCTs had a low risk of bias(more than 3 scores) and were ultimately enclosed within the meta-analysis(Figure1).
Quality assessment
The Cochrane bias risk score of the enclosed studies ranged from 4 to 7.Included studies were all RCTs,all of which referred to randomly group.Among them,11 studies described the distinctive methods of random sequences generation,such as computer random,table of random number,etc.And the other 2 [20,26] did not mention specific methods.Two studies [28,32] implemented the concealment allocation.One study [21] used a single-blind experimental scheme.Two [28,32] studies belonged to double-blind,double-simulated RCTs.One study[32] conducted a blinded evaluation of the outcome.No other bias was discovered in all enclosed studies.The bias summary and the bias for each study show as below(Figure2 and Figure3).
Study characteristics
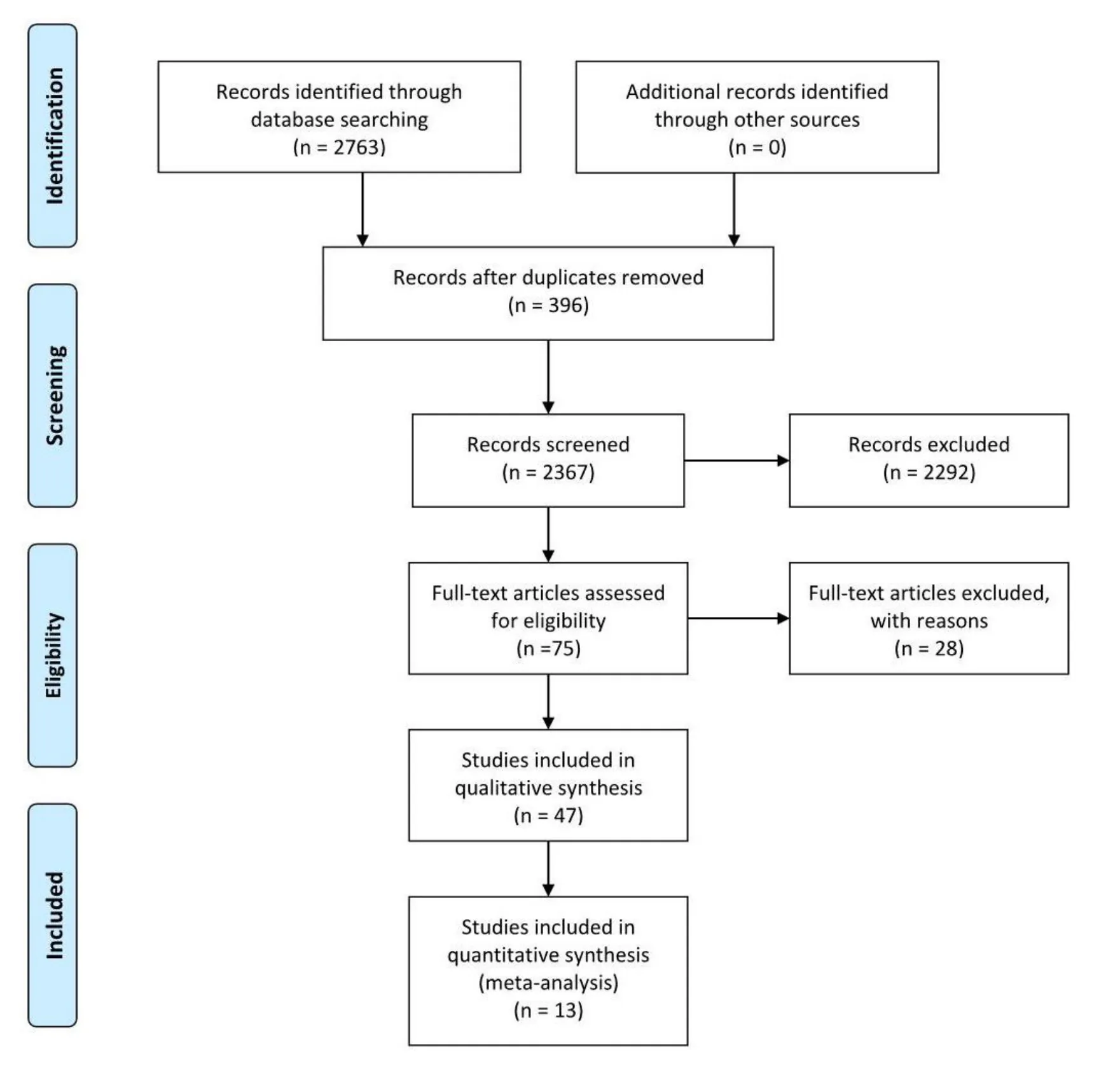
Table1 displays the characteristics extracted from the 13 articles included.Two studies [28,32] were published in English and the left were issued in Chinese journal.The 13 studies enclosed within the meta-analysis involved 981 patients with AD (499 within the experience group and 482 within the control group),whose sample size ranged from 30 to 144.All studies were carried out in China and mean aged 60.88 to 75.36 years.All studies referred to the disease duration before treatment,but 4 [20,21,29,32] of them didn’t give the average course of the disease.The period of therapy ranged from 40 days to 6 months.The experimental group was given TKNF,while the control group was given donepezil.In most studies,the dose of donepezil in the control group was 5 mg,but the dose of donepezil given in Li,H's study [27] was 10 mg.Follow-up time was illustrated solely in 1 study [28],which follow-up from 1 week to 48 week.The authors have listed the components of prescriptions used in each literature(Table2) and briefly analyzed the frequency of each component(Table3).
Clinical efficacy
ADAS-Cog in AD patients
Nine studies reported improvement of ADAS-Cog score after intervention,in which Yang [32] did not give exact values.Results of heterogeneity analysis based on the left eight studies were:P<0.001,I2=99%.Thus,a subgroup analysis was conducted in accordance with the course of treatment.Heterogeneity analysis of subgroup were:P= 0.14,I2=54%;P<0.001,I2=87%.There was still a large heterogeneity in the third subgroup.After removing Gang’s study[21]and Li,H’s study[27],which were thought of the possible sources of heterogeneousness due to short duration of treatment(40 days)and large dose of donepezil (10 mg),heterogeneity analysis of the left 6 studies were:P=0.14,I2=54%;P=0.14,I2=44%.Thus,we selected a fixed effect model.The results of the meta-analysis (MD = -0.91,95% CI:-2.94,1.12,P= 0.38) prompted that there was no significant difference between the experience groups and the control groups in the change of ADAS-Cog score in short-term (12 weeks).However,as the course of treatment extended to 24 weeks or more,there was a significant difference between 2 groups(MD = -1.92,95% CI:-3.00,-0.83,P= 0.005)(Figure4).
ADL in AD patients
Eleven studies reported improvement of ADL score after intervention.Based on the heterogeneity analysis results (P= 0.05,I2= 45%),a subgroup analysis was conducted in accordance with the course of treatment.The heterogeneity analysis results were:P=0.13,I2=44%;P=0.31,I2=16%.Thus,a fixed effect model was utilized.
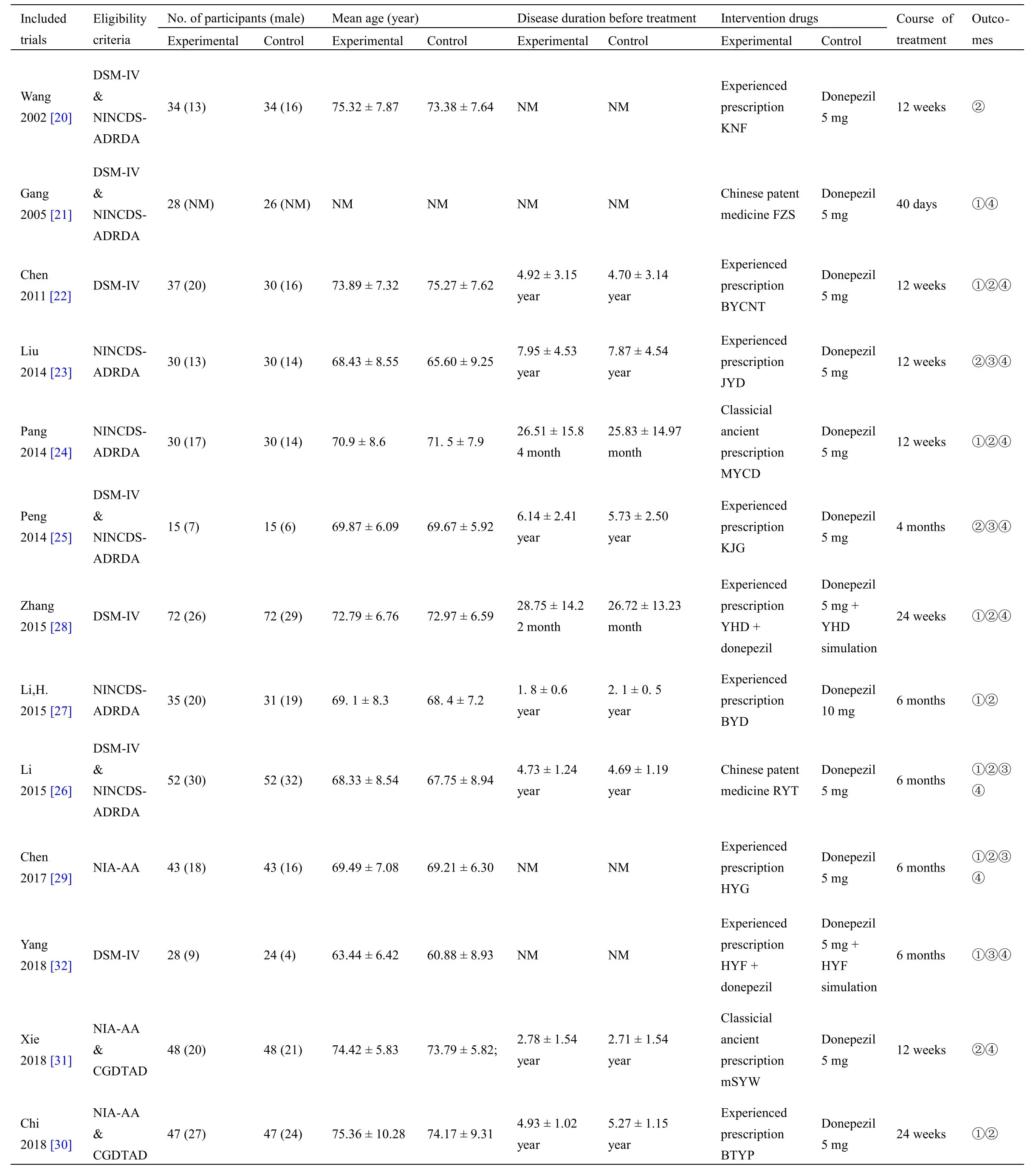
Table1 Characteristics of the included studies
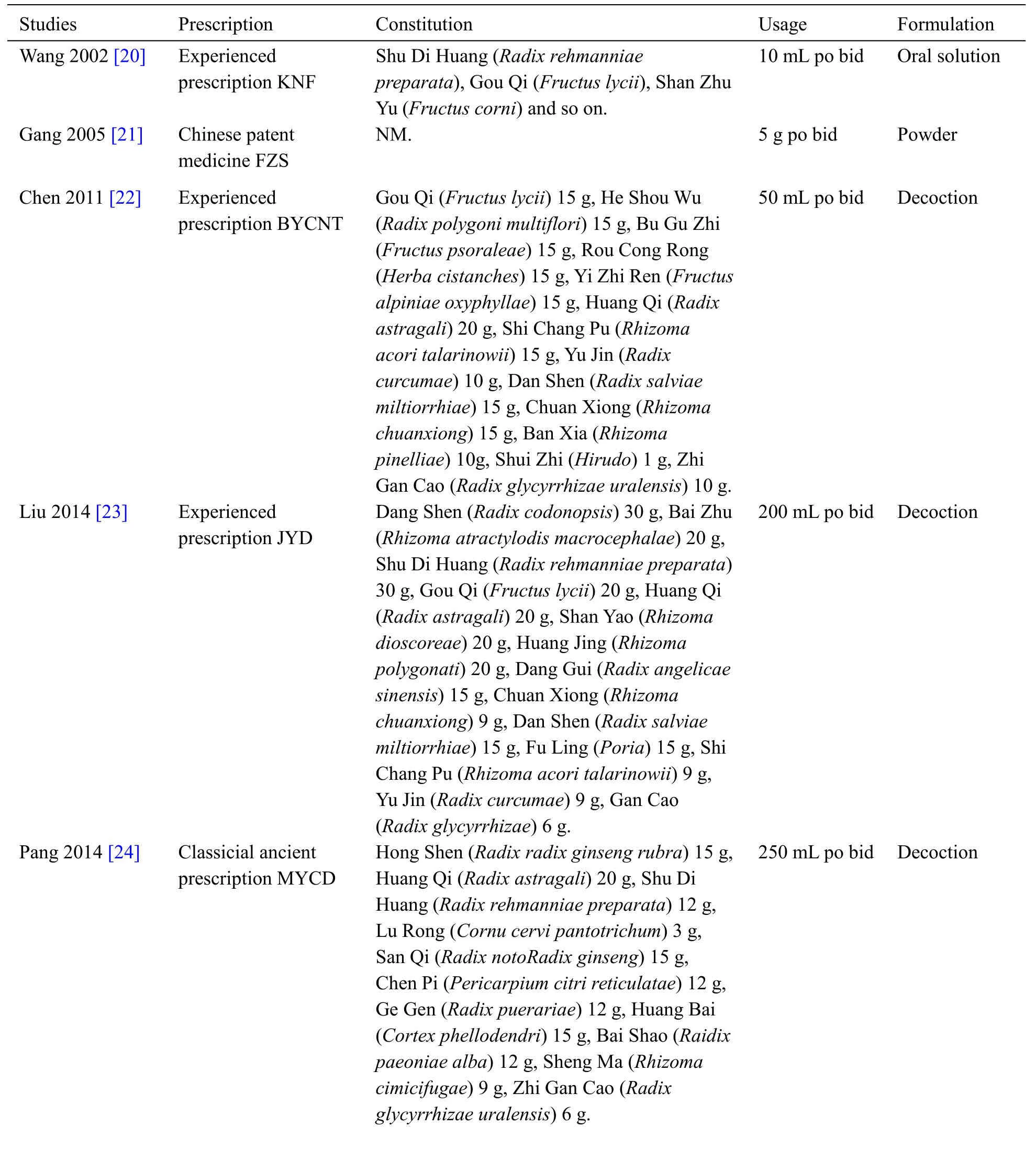
Table2 The ingredients of each prescription
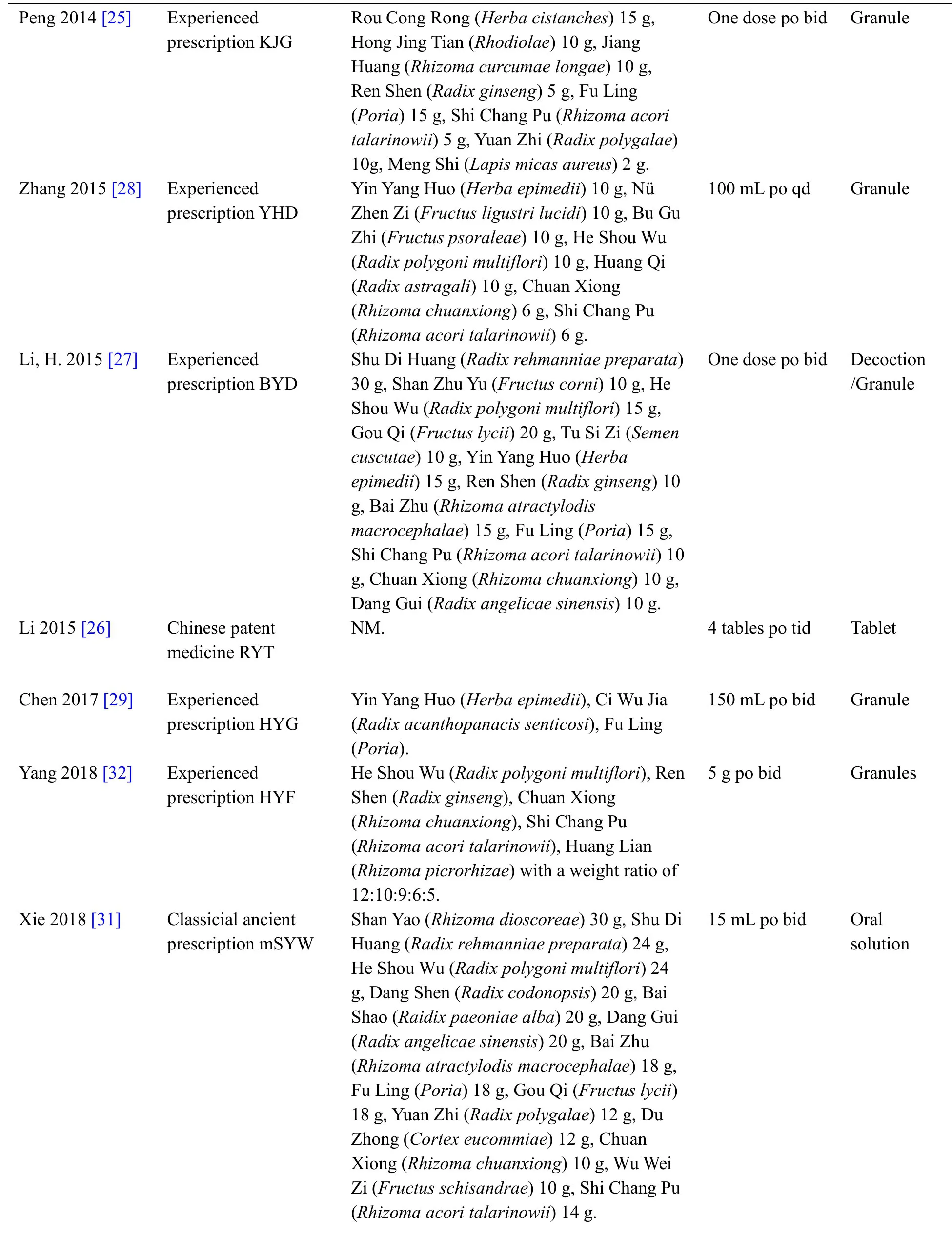
Table2 The ingredients of each prescription(Continued)
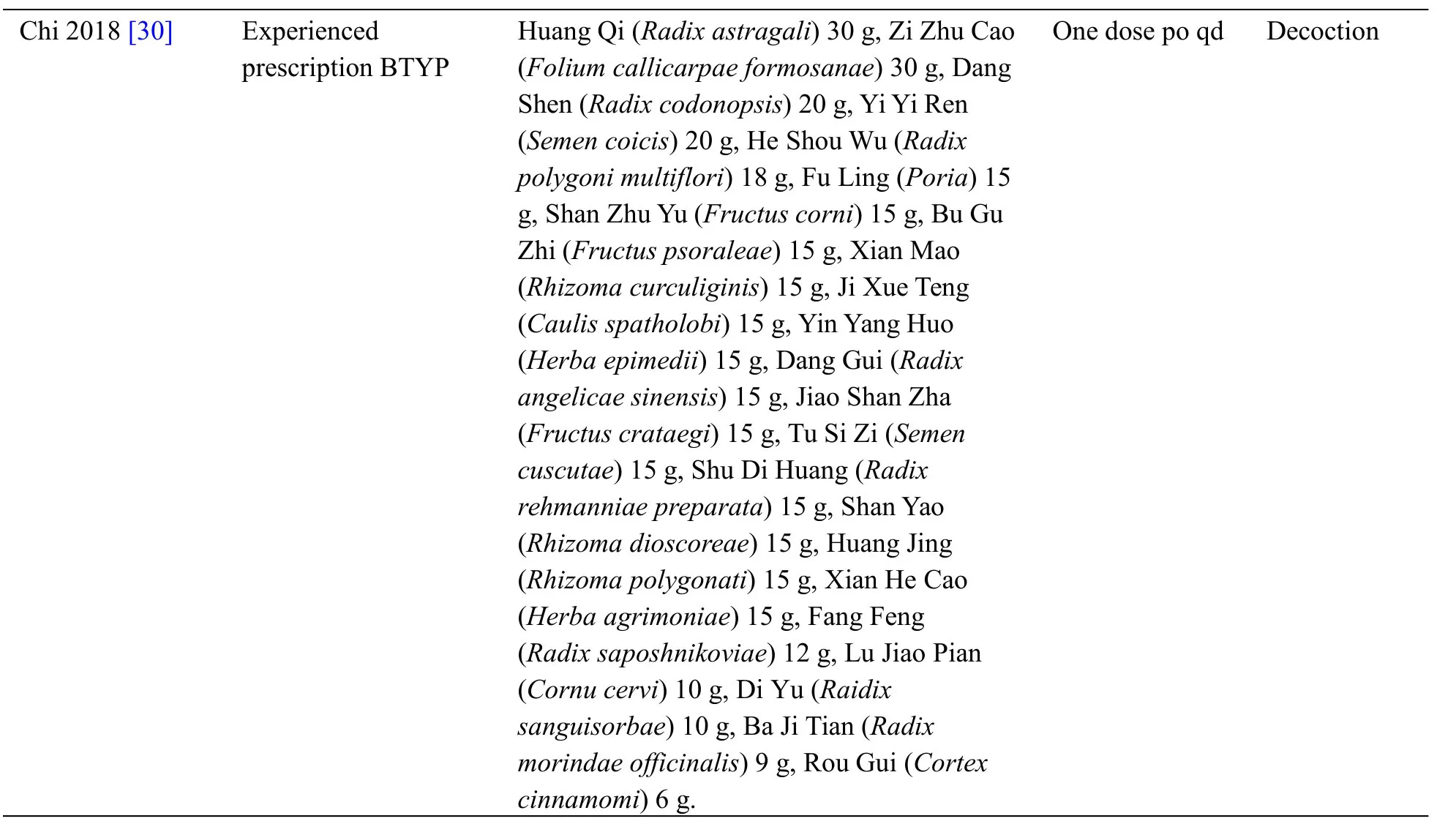
Table2 The ingredients of each prescription(Continued)
The results of the meta-analysis (MD = -1.67,95% CI:-2.81,-0.52,P= 0.004;MD =-6.79,95%CI:-12.16,-1.42,P= 0.01; MD = -3.24,95% CI:-4.25,-2.23,P<0.001) suggested that there was a significant difference between the experience groups and the control groups in the change of ADL score,regardless of the treatment course (Figure5).After eliminating Li,H’s study [27] due to large dose of donepezil,the result of meta-analysis (MD = -2.89,95% CI:-3.98,-1.80,P<0.001; heterogeneityP=0.60,I2= 0%) was in good agreement with those before(Figure6).
TCM curative efficacy
Five studies reported the improvement of TCM syndromes.Based on the heterogeneity test analysis(P=0.45,I2=0%),a fixed effect model was utilized.The result(RR=1.51,95%CI:1.28,1.78,P<0.001)suggested that there was a significant difference between the experience groups and the control groups.When subgroup analysis was applied,the result of meta-analysis (RR = 1.24,95% CI:0.94,1.63,P= 0.13; RR = 1.33,95% CI:0.82,2.16,P=0.24)showed that there was no significant difference between two groups in short term (12 weeks and 4 months).However,the effective rate beyond 24 weeks (RR=1.64,95%CI:1.32,2.04,P<0.001)of treatment with TKNF were better than donepezil(Figure7).
Adverse events
Adverse events were documented in 10 studies.Adverse events of TKNF were mainly manifested as nausea,diarrhea,constipation,dry mouth,etc.The main adverse events of donepezil included dizziness,nausea,loss of appetite,diarrhea,insomnia,etc.The adverse events in both groups were mild,and no serious life-threatening adverse events were found.Nine studies concluded that there was no significant difference between the 2 groups.One study [29]found that adverse events of TKNF had a lower incidence than donepezil.
Publication bias
Owing to the small number of studies,a publication bias test for ADAS-Cog and TCM curative efficacy couldnot be conducted.The shape of the funnel plot for ADL that was slightly asymmetrical indicated a potential publication bias(Figure8).
The quality of the evidence
On the basis of GRADE criteria,the quality of evidence was assessed as high or moderate.We summarized the results(Table4).
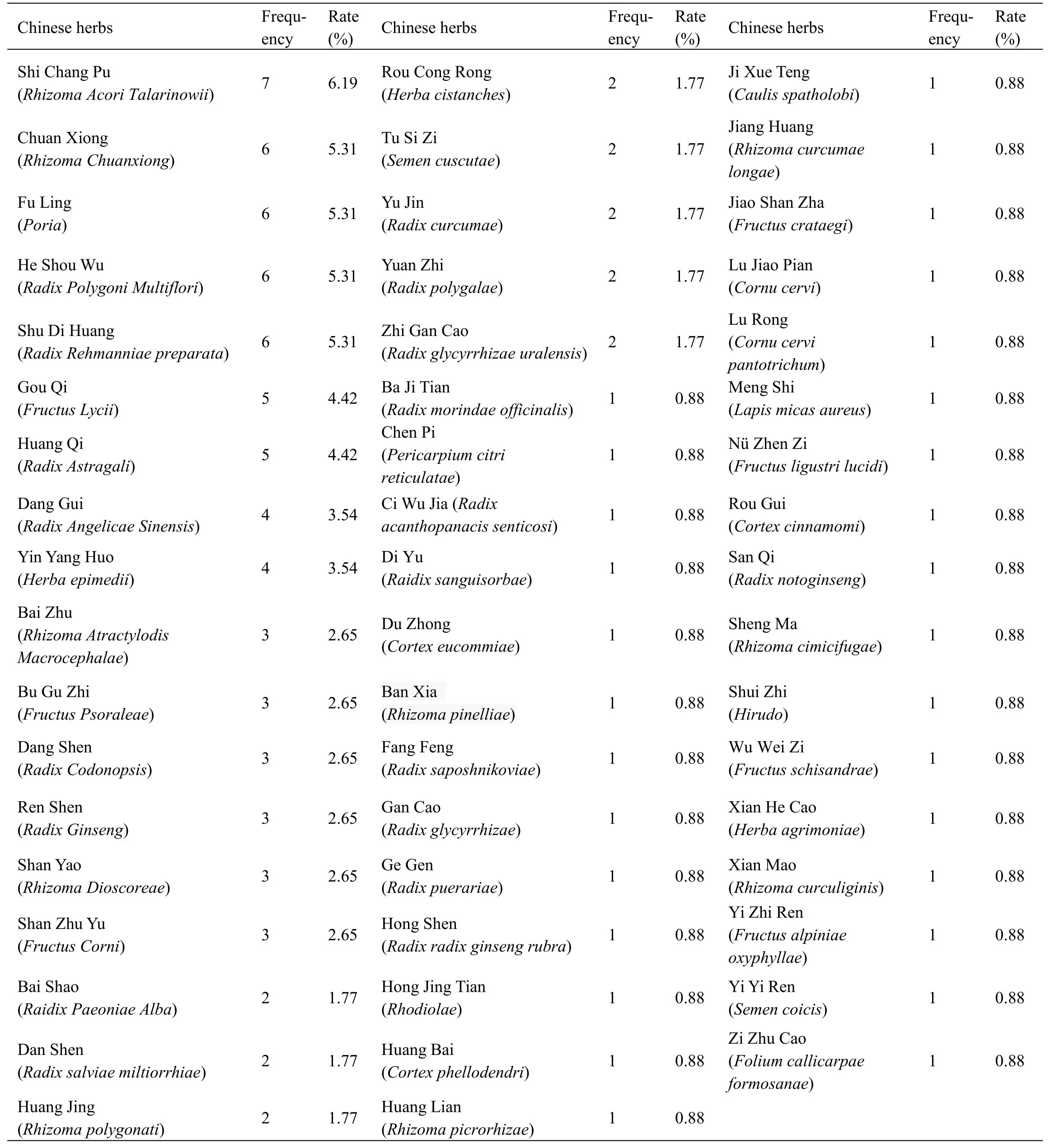
Table3 Frequencies of usage and distribution in traditional Chinese medicine
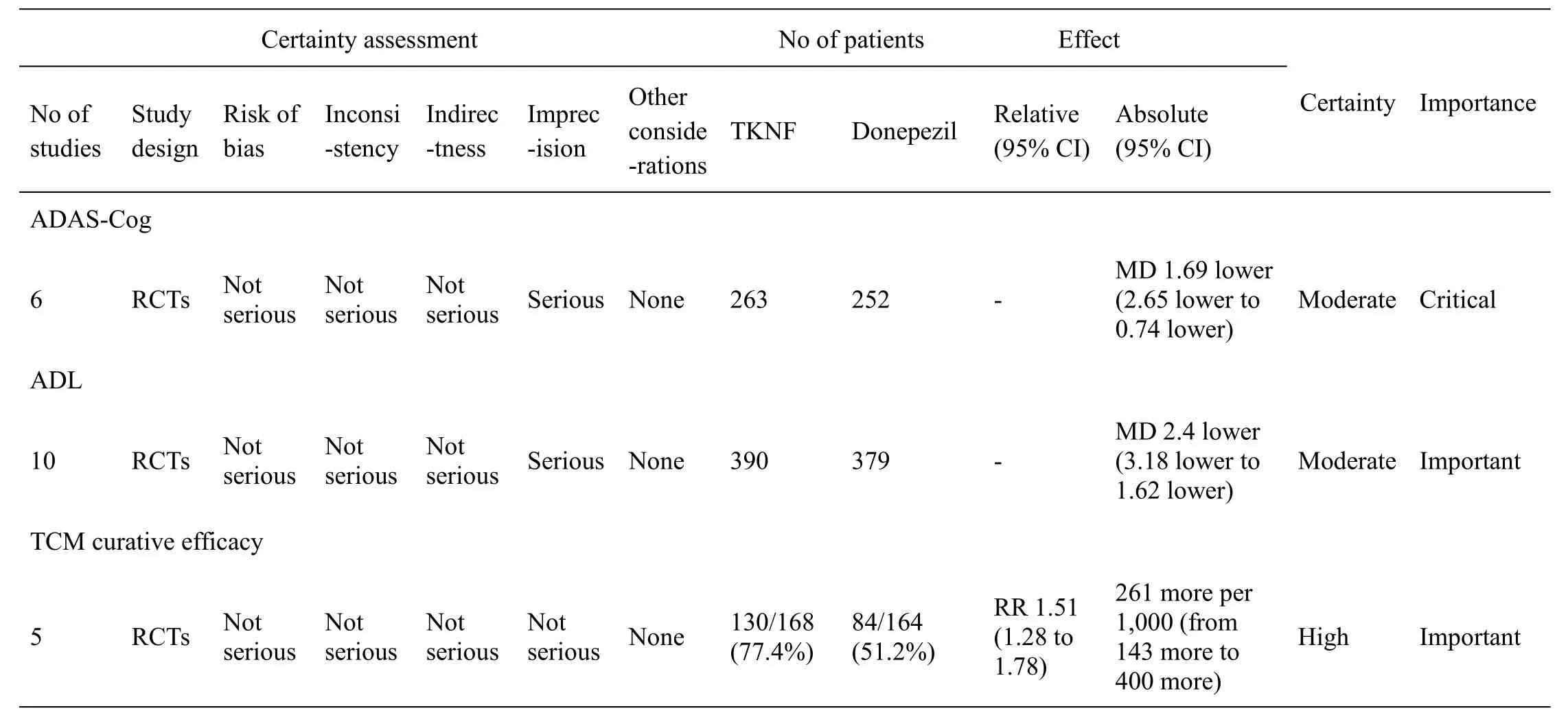
Table4 Quality of evidence by GRADE system
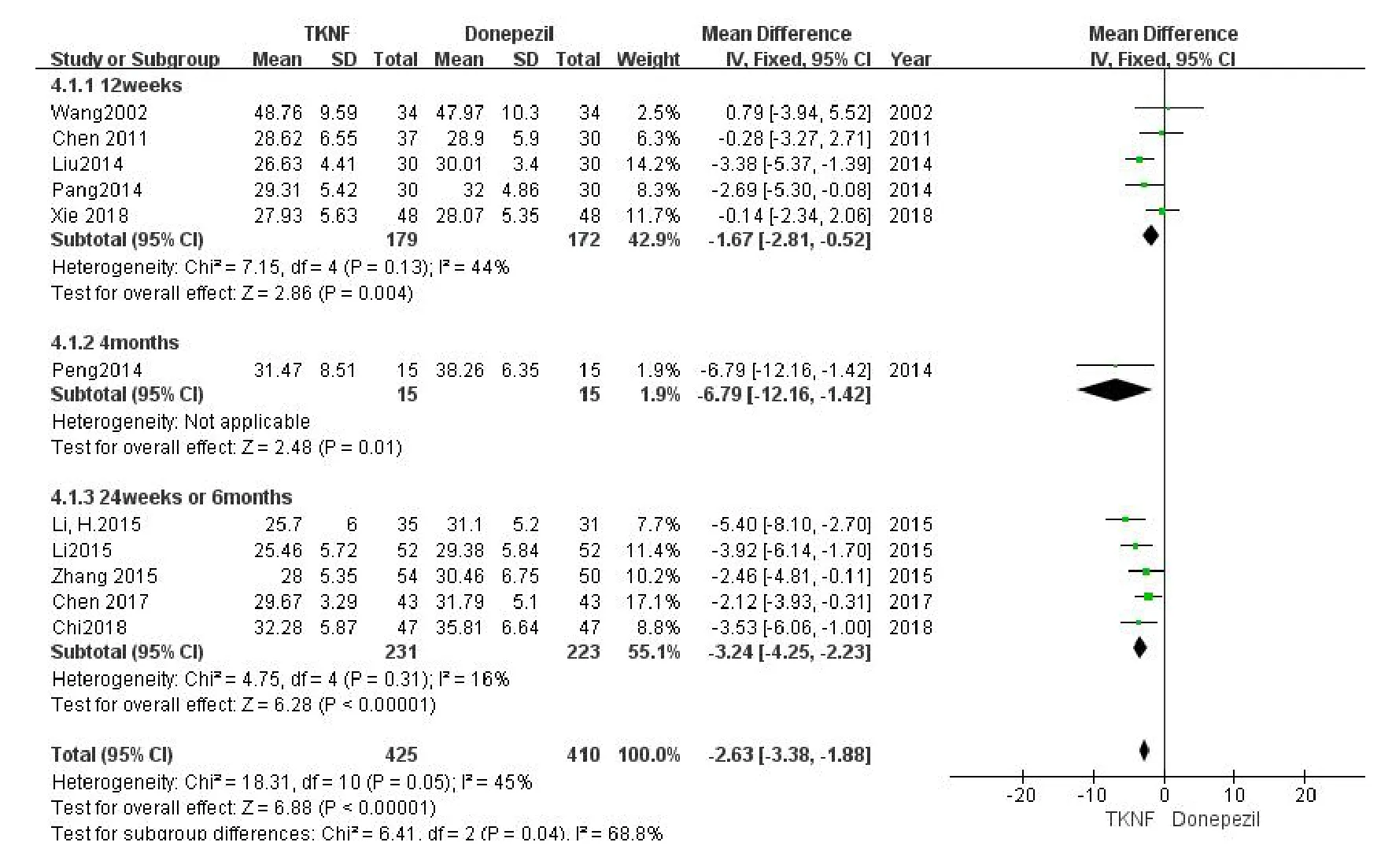
Figure5 The comparison of ADL between TCM kidney-nourishing formula and donepezil.CI,confidence interval;TKNF,traditional Chinese medicine kidney-nourishing formula;TCM,traditional Chinese medicine;ADL,activities of daily living.
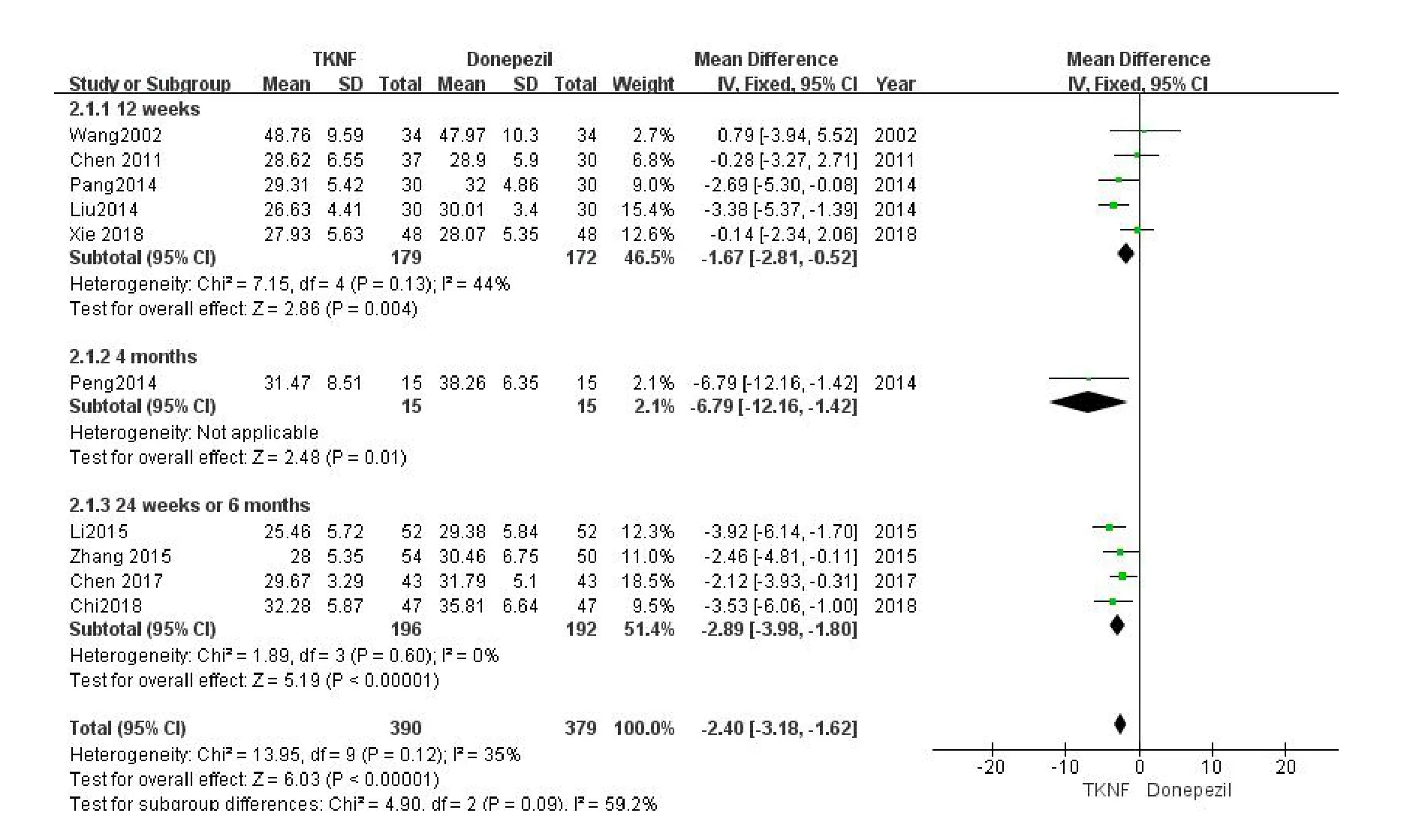
Figure6 The comparison of ADL between TCM kidney-nourishing formula and donepezil (without Li,H’s study).CI,confidence interval; TKNF,traditional Chinese medicine kidney-nourishing formula; TCM,traditional Chinese medicine;ADL,activities of daily living.
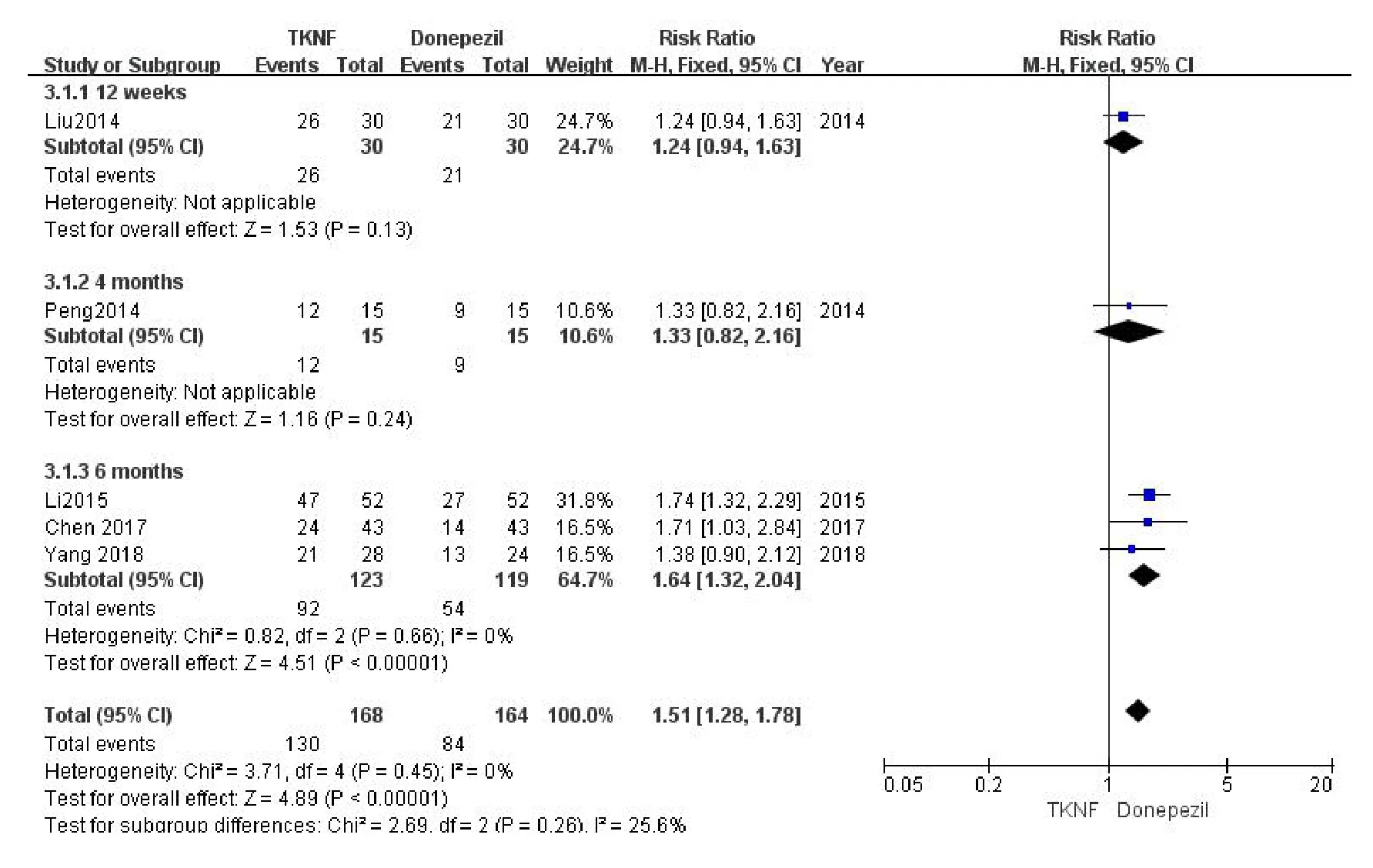
Figure7 The comparison of curative efficacy between TCM kidney-nourishing formula and donepezil.CI,confidence interval; TKNF,traditional Chinese medicine kidney-nourishing formula; TCM,traditional Chinese medicine.
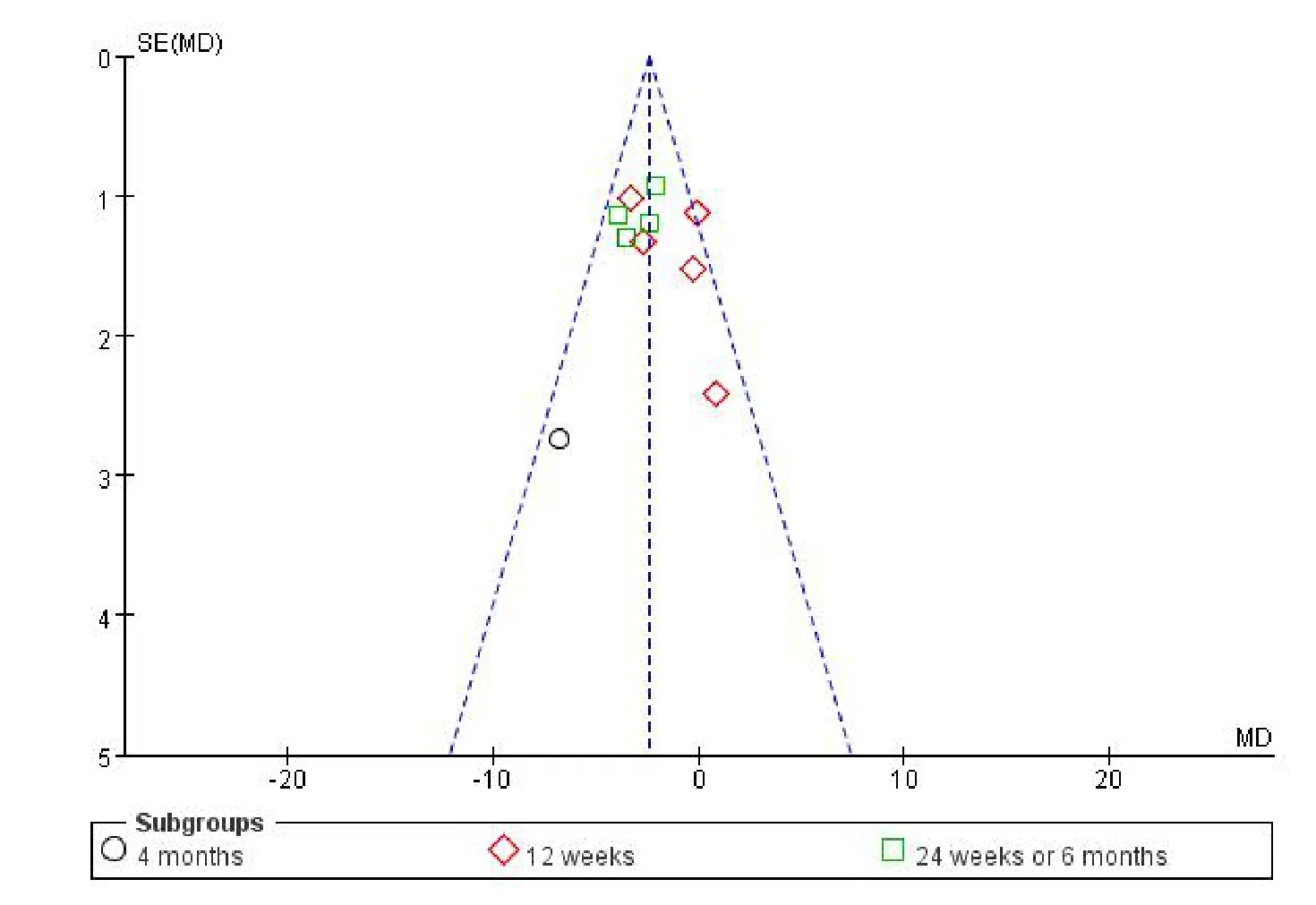
Figure8 Funnel plot based on ADL.ADL,activities of daily living;MD,mean difference.
Discussion
Summary of main findings
The main findings of meta-analysis in this paper were as follows:(1) both TKNF and donepezil could improve cognitive impairment in AD patients in terms of ADAS-Cog score and the improvement of the 2 was similar in short term (12 weeks).However,when the duration of treatment was more than or equal to 24 weeks,the effect of TKNF was better than that of donepezil; (2) regardless of the duration of treatment,both TKNF and donepezil could improve the ability carrying out daily activities in AD patients in terms of ADL score; (3) when it came to TCM syndrome,both TKNF and donepezil could improve the TCM curative efficacy in AD patients.When the course of treatment was less than or equal to 12 weeks,the effect of the 2 was similar.However,as the course of treatment was extended to 24 weeks or 6 months,the benefits of TKNF was superior to donepezil; (4) TKNF was a relatively safe therapy for AD; (5) the quality of the evidence was moderate or high according to the GRADE.
Summary of major herbals
Among the formulations concerned in this study,a total of 53 Chinese herbal medicines were mentioned.Among them,Shi Chang Pu (Rhizoma acori talarinowii)was used most frequently,which totaling 7 times.After that,the drugs with frequency more than or equal to 4 times are Chuan Xiong (Rhizoma chuanxiong),Fu Ling (Poria),He Shou Wu (Radixpolygoni multiflori),Shu Di Huang(Radix rehmanniae preparata),Gou Qi (Fructus lycii),Huang Qi (Radix astragali),Dang Gui (Radix angelicae sinensis),Yin Yang Huo (Herba epimedii).Among them,Yin Yang Huo (Herba epimedii),Shu Di Huang (Radixrehmanniae preparata),He Shou Wu (Radix polygonimultiflori),and Gou Qi (Fructus lycii) are the most closely related to the tonifying kidney therapy of TCM.Yin Yang Huo (Herba epimedii) is closely associated with androgen hormones in TCM.The pharmacological effects of Yin Yang Huo (Herba epimedii)and its compounds on neuroplasticity-related brain functional recovery includes its effect on neurotrophic factors,neurogenesis,synaptic plasticity,and axon and myelin regeneration,which associate Yin Yang Huo (Herba epimedii) with brain functional recovery [33].Icariin is the main flavonoid in Yin Yang Huo (Herba epimedii),which has various pharmacological activities,and has a broad application prospect in the treatment and prevention of AD [34].Experiments based on rats model shows that Icariin can alter synthetic plasticity and function through the BDNF/TrkB/Akt pathway by increasing the expression of BDNF and the photosynthesis of its receptor TrkB as well as of Akt and CREB,which provided evidence that Icariin has a remarkable memory enhancing effect[35,36].
Gou Qi (Fructus lycii) and its extracts are believed to have the antiaging,neuroprotective,anti-AD,and antioxidant effects [37,38].The mechanism may be related to amyloid beta protein (Aβ).Gou Qi (Fructus lycii) extracts can significantly inhibit Aβ fibrillation,decompose the formed Aβ fibrils,decrease Aβ deposits and Aβ-induced neuro-cytotoxicity in the AD mice[39,40].
In addition,the combination of Shu Di Huang(Radix rehmanniae preparata)and Wu Wei Zi(Fructus schisandrae) can significantly increase the expression of SYP,PSD95,BDNF,TrkB and CREB protein related to learning and memory and the content of choline acetyltransferase in the brain,significantly reduce the content of acetylcholinesterase,significantly reduce the content of Aβ 1-40 and Aβ 1-42 in the hippocampus or serum,increase the expression of Akt protein,and reduce the content of GSK3β,tau,app and Aβ 1-42 protein expression in AD rats model [41].He Shou Wu (Radix polygoni multiflori) can significantly improve the learning and memory ability of AD rat model,which may be improved by increasing the content of miRNA-101 in hippocampus[42].
Limitations
Firstly,only Chinese and English studies were included.Other trials may have been done but not reported,possibly because of negative results.Since this review was restricted to published studies,publication bias was hard to avoid.Secondly,in the process of pooling data,the authors did not take into account the differences of inclusion criteria,dementia seriousness,intervention,dosage,duration of treatment and outcome measurement among studies,which may potentially bias our results.Thirdly,some detailed data were not reported in Yang’s study [32],which were also very crucial for our analysis.These insufficient data may limit the conclusion of our analysis.In addition,the number of subjects recruited in the trials was relatively small.Finally,these studies generally followed with interest the outcomes of intervention in a short period and most of the studies didn’t report the follow-up period.
Implication for research
On the one hand,these RCTs confirmed the relatively good safety of TKNF and its effectiveness in relieving symptoms in the short-term appliance.However,compared with long-term RCTs that are more likely to provide additional information,short-term trials are of limited value in assessing the actual clinical influence of TKNF on AD.Thus,future research should pay more attention to the long-term effect of TKNF and deserve a longer follow-up time.On the another,to detect clinically meaningful results,RCTs for TKNF need to be designed to assess both clinical presentation and brain lesions,rather than relying solely on MD in scores between groups,which we can refer to Li’s study [43].In addition,recent studies [44,45] of gut microbiota in AD patients have shown that their intestinal flora is different from that of subjects without dementia.Therefore,TCM scholars should also consider adding the detection of gut microbiota in relevant clinical trials.
Implication for clinical practice
Our results illustrated that TKNF seemed to ameliorate symptoms in AD patients as well as donepezil,but TKNF can be obtained more cheaply and easily,which means that it could be a kind of available alternation for donepezil,particularly in developing countries like China.Besides,based on previous research [46,47],which showed that conventional therapy has only nine months of cognitive improvement benefits,the long-term benefits of TKNF deserve researchers'attention.
Conclusion
To make a long story short,TKNF could be an alternative treatment for AD in clinical practice,especially for AD patients in developing countries like China.Additionally,long-term results seem gratifying.However,there is not enough evidence to support this conclusion,we should treat this conclusion with caution and further research still needed to be done to verify the long-term benefits of TKNF.
 Traditional Medicine Research2020年5期
Traditional Medicine Research2020年5期
- Traditional Medicine Research的其它文章
- The marriage of Chinese Imperial Medicine and China Academy of Chinese Medical Sciences:privilege and benefits for the people
- Study on an innovative natural drug for Alzheimer's disease reported as a sham
- The neuroprotective role of Panax notoginseng saponins in APP/PS1 transgenic mice through the modulation of cerebrovascular
- Ethnoveterinary medicines used against various livestock disorders in the flora of Shamozai Valley,Swat,KP Pakistan
- Molecular mechanism prediction analysis of compound Kushen injection in the treatment of COVID-19 based on network pharmacology and molecular docking
- South Asian medicinal plants and chronic kidney disease
