硫酸镁预防剖宫产术产妇寒战的meta分析
尚勇 李帆 胡振飞 邹田田
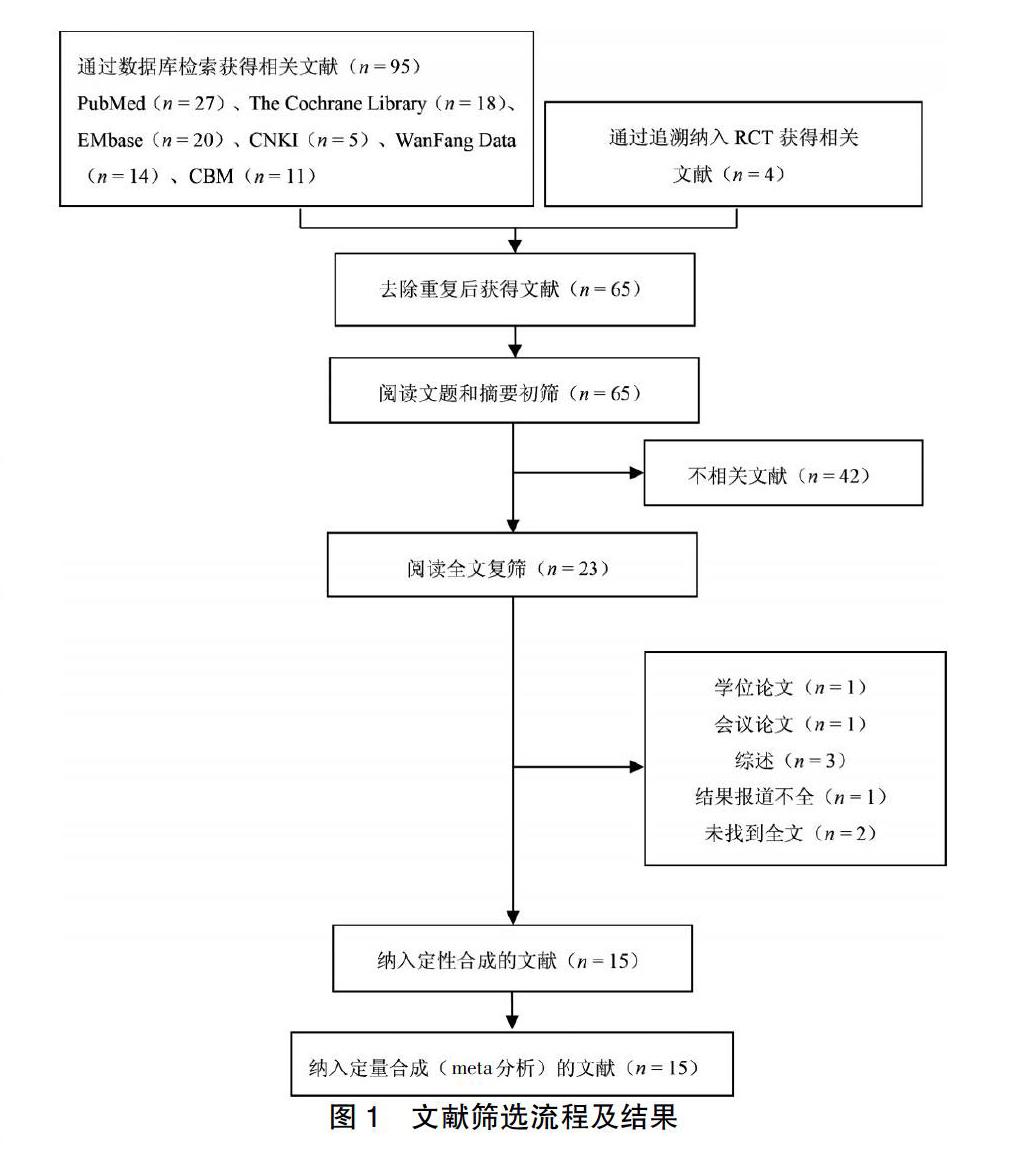

[摘要] 目的 評估硫酸镁预防剖宫产术产妇寒战的临床应用效果。 方法 计算机检索PubMed、The Cochrane Library(2019年第8期)、EMbase、万方数据知识服务平台(WanFang Data)、中国知网(CNKI)、中国生物医学文献数据库(CBM),查找有关硫酸镁对实施剖宫产术的产妇寒战影响的随机对照试验(RCT),检索时限为建库—2019年8月。根据所纳入RCT参考文献的相关文献进行追溯。采用RevMan 5.3软件进行meta分析,GRADE证据质量评价评估meta分析结果的证据等级。 结果 最终纳入15篇文献,1043例患者,使用硫酸镁患者532例。meta分析结果显示:试验组产妇寒战发生率低于对照组(RR = 0.48,95%CI:0.37~0.63,P < 0.000 01)。静脉注射亚组产妇寒战发生率低于对照组(RR = 0.46,95%CI:0.33~0.66,P < 0.0001);蛛网膜下腔注射亚组产妇寒战发生率与对照组比较,差异无统计学意义(P = 0.12);硬膜外注射亚组产妇寒战发生率低于对照组(RR = 0.38,95%CI:0.21~0.67,P = 0.0009)。蛛网膜下腔麻醉亚组产妇寒战发生率低于对照组(RR = 0.53,95%CI:0.36~0.78,P = 0.001);腰硬联合麻醉亚组产妇寒战发生率低于对照组(RR = 0.45,95%CI:0.29~0.68,P = 0.0002)。不同给药方式亚组meta分析结果质量等级均为“Moderate”。 结论 静脉注射、硬膜外注射硫酸镁能够预防行剖宫产术产妇寒战的发生,但蛛网膜下腔注射硫酸镁预防行剖宫产术产妇寒战的效果尚待评估。
[关键词] 硫酸镁;剖宫产术;寒战;meta分析
[中图分类号] R714.3 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2020)07(c)-0103-06
Meta-analysis of Magnesium Sulfate to prevent shivering during cesarean section
SHANG Yong LI Fan HU Zhenfei ZOU Tiantian
Department of Anesthesiology, the First Affiliated Hospital of Xinjiang Medical University, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, Urumqi 830054, China
[Abstract] Objective To evaluate the effect of Magnesium Sulfate to prevent shivering during cesarean section. Methods Databases including PubMed, The Cochrane Library (Issue 8, 2019), EMbase, Wanfang Data Knowledge Service Platform (WanFang Data), China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI), China Biology Medicine disc (CBM) were searched for computer to collect the randomized controlled trails (RCT) about the effect of Magnesium Sulfate on shivering for cesarean section. The retrieval time limit from repository to August 2019. The literature was tracked based on the references included in the RCT. Meta-analysis was conducted using RevMan 5.3 software, GRADE of evidence quality was used to evaluate the evidence level of meta-analysis results. Results Finally, 15 references were included, including 1043 patients and 532 patients with Magnesium Sulfate. The results of meta-analysis showed that: the incidence of shivering in experimental group was lower than that in control group (RR = 0.48, 95%CI:0.37-0.63, P < 0.000 01). The incidence of shivering in intravenous subgroup was lower than that in control group (RR = 0.46, 95%CI:0.33-0.66, P < 0.0001); the incidence of shivering in subarachnoid injection subgroup had no statistically significant difference compared with control group (P = 0.12); the incidence of shivering in epidural injection subgroup was lower than that in control group (RR = 0.38, 95%CI:0.21-0.67, P = 0.0009). The incidence of shivering in subarachnoid anesthesia subgroup was lower than that in control group (RR = 0.53, 95%CI: 0.36-0.78, P = 0.001); the incidence of shivering in combined lumbar and epidural anesthesia subgroup was lower than that in control group (RR = 0.45, 95%CI: 0.29-0.68, P = 0.0002). Meta-analysis results for different administration subgroups were all evaluated as “Moderate”. Conclusion Intravenous injection and epidural injection of Magnesium Sulfate can prevent shivering in cesarean section, but the effect of subarachnoid injection of Magnesium Sulfate to prevent the occurrence of shivering in cesarean section remains to be evaluated.
蛛網膜下腔麻醉是剖宫产术常用的麻醉方式,具有起效快、麻醉效果确切等诸多优点。硫酸镁具有抑制子宫收缩、治疗胎儿宫内窘迫的作用。本研究中有6篇[9,11,13,15-17]经蛛网膜下腔注射硫酸镁,但亚组分析结果却显示,硫酸镁蛛网膜下腔注射亚组产妇寒战发生率与对照组比较,差异无统计学意义(P = 0.12),在预防剖宫产术寒战方面并未体现出明显优势。在3种给药方式中,静脉注射硫酸镁能够使药物快速发挥其药理作用。研究显示[8,17],蛛网膜下腔注射、硬膜外注射硫酸镁具有较高安全性。与蛛网膜下腔注射比较,硬膜外注射后,药物沿硬膜外间隙上下扩散,在此过程中部分药物经毛细血管吸收入血而发挥作用,但蛛网膜下腔注射给药并无上述过程[24]。因此,蛛网膜下腔注射与硬膜外注射的上述区别可能是导致蛛网膜下腔注射硫酸镁在预防寒战方面效果不佳的原因。
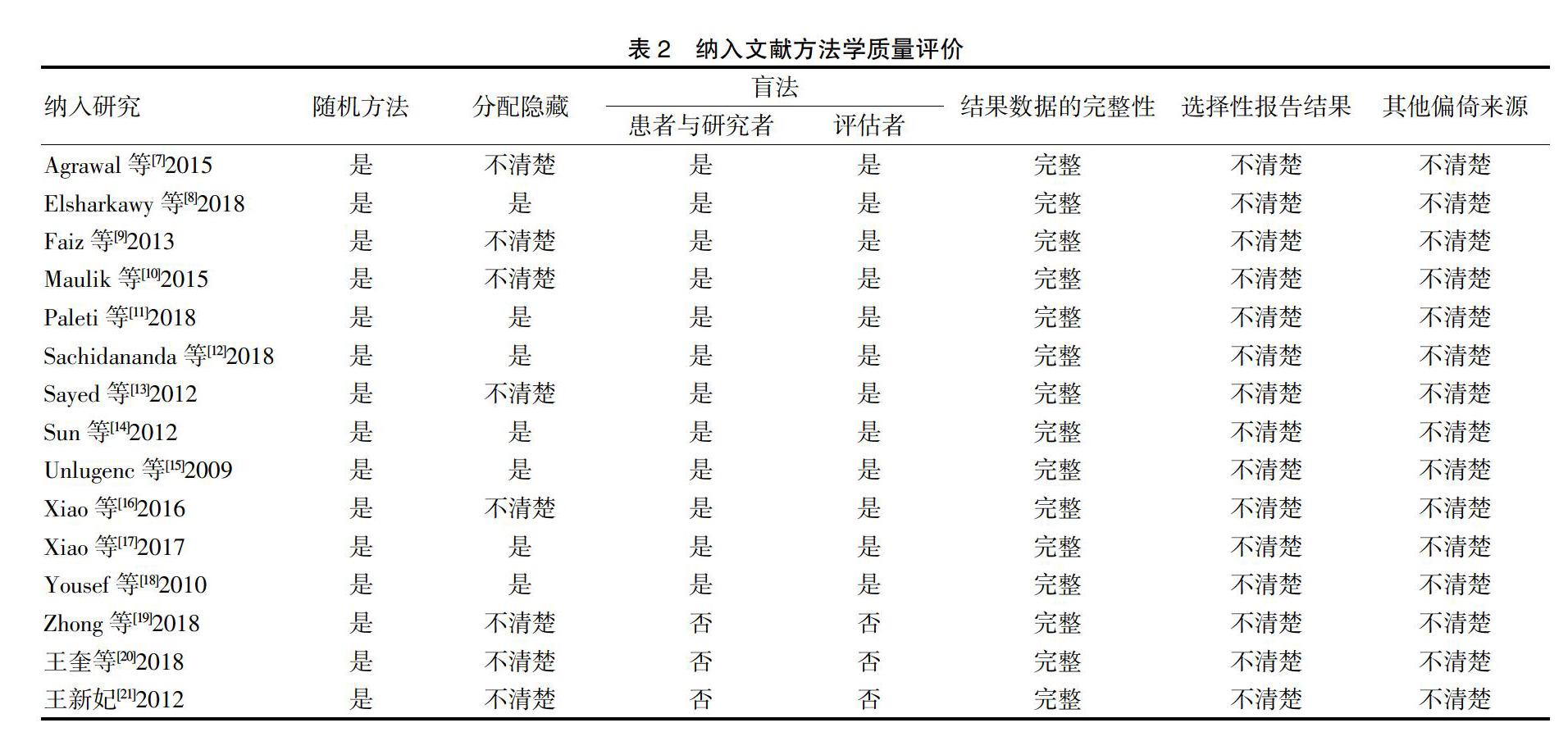
本研究共纳入15篇[7-21]RCT,其中7篇[8,11-12,14-15,17-18]采用分配隐藏,纳入研究整体质量尚可但仍存在局限性。首先,所纳入部分研究未报告研究对象年龄、各研究间硫酸镁用药剂量不同,可能影响本研究结果的可靠性;其次,15篇[7-21]RCT均为小样本量,所得结论仍需进一步加以明确;最后,硫酸镁不同给药方式的亚组meta分析结果质量等级均为“Moderate(中)”,故所得结论仍需更多高质量RCT加以验证。
综上所述,静脉注射、硬膜外注射硫酸镁能够预防行剖宫产术产妇寒战的发生,但蛛网膜下腔注射硫酸镁预防行剖宫产术产妇寒战的效果尚待评估。
[参考文献]
[1] Nasseri K,Ghadami N,Nouri B. Effects of intrathecal dexm-edetomidine on shivering after spinal anesthesia for cesarean section:a double-blind randomized clinical trial [J]. Drug Des Devel Ther,2017,11:1107-1113.
[2] Khezri MB,Mosallaei MA,Ebtehaj M,et al. Comparison of preemptive effect of intravenous ketorolac versus meperidine in patients undergoing cesarean section:A prospective,randomized,double-blind study [J]. Caspian J Intern Med,2018,9(2):151-157.
[3] Nallam SR,Cherukuru K,Sateesh G. Efficacy of intravenous ondansetron for prevention of postspinal shivering during lower segment cesarean section:A double-blinded randomized trial [J]. Anesth Essays Res,2017,11(2):508-513.
[4] Lopez MB. Postanaesthetic shivering–from pathophysiology to prevention [J]. Rom J Anaesth Intensive Care,2018, 25(1):73-81.
[5] Jain A,Gray M,Slisz S,et al. Shivering Treatments for Targeted Temperature Management:A Review [J]. J Neurosci Nurs,2018,50(2):63-67.
[6] Higgins JPT,Green S(editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 [updated March 2011]. The Cochrane Collaboration. 2011. Available at:www.cochrane-handbook.org.
[7] Agrawal J,Singh K,Mittal R,et al. A randomized clinical study to evaluate the effect of intravenous magnesium sulphate for postoperative pain relief in patients undergoing lower segment caesarean section [J]. J Evolution Med Dent Sci,2015,72(4):12478-12484.
[8] Elsharkawy RA,Farahat TE,Abdelhafez MS. Analgesic effect of adding magnesium sulfate to epidural levobupivacaine in patients with pre-eclampsia undergoing elective cesarean section [J]. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol,2018, 34(3):328-334.
[9] Faiz SH,Rahimzadeh P,Imani F,et al. Intrathecal injection of magnesium sulfate:shivering prevention during cesarean section:a randomized,double-blinded,controlled study [J]. Korean J Anesthesiol,2013,65(4):293-298.
[10] Maulik SG,Chaudhuri A,Mallick S,et al. Role of Magnesium Sulfate In Prolonging The Analgesic Effect of Spinal Bupivacaine For Cesarean Section In Severe Preeclamptics [J]. J Basic Clin Reprod Sci,2015,4(1):24-28.
[11] Paleti S,Prasad PK,Lakshmi BS. A randomized clinical trial of intrathecal magnesium sulfate versus midazolam with epidural administration of 0.75% ropivacaine for patients with preeclampsia scheduled for elective cesarean section [J]. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol,2018,34(1):23-28.
[12] Sachidananda R,Basavaraj K,Shaikh SI,et al. Comparison of Prophylactic Intravenous Magnesium Sulfate with Tramadol for Postspinal Shivering in Elective Cesarean Section:A Placebo Controlled Randomized Double-blind Pilot Study [J]. Anesth Essays Res,2018,12(1):130-134.
[13] Sayed JA,Fathy MA. Maternal and Neonatal Effects of Adding Two Different Doses of Intrathecal Magnesium Sulphate to Bupivacain Fentanyl Spinal Anesthesia in Mild Preeclamptic Patients Undergoing Caesarean Section [J]. J Am Sci,2012,8(6):435-441.
[14] Sun J,Wu X,Xu X,et al. A Comparison of Epidural Magnesium and/or Morphine With Bupivacaine for Postoperative Analgesia After Cesarean Section [J]. Int J Obstet Anesth,2012,21(4):310-316.
[15] Unlugenc H,Ozalevli M,Gunes M,et al. Comparison of intrathecal magnesium,fentanyl,or placebo combined with bupivacaine 0.5% for parturients undergoing elective cesarean delivery [J]. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand,2009, 53(3):346-353.
[16] Xiao F,Liu L,Zhang WP,et al. Effect of adding magnesium sulfate to intrathecal low-dose of bupivacaine for patients with severe pre-eclampsia undergoing cesarean delivery [J]. Int J Clin Exp Med,2016,9(10):19749-19756.
[17] Xiao F,Xu W,Feng Y,et al. Intrathecal magnesium sulfate does not reduce the ED50 of intrathecal hyperbaric bupivacaine for cesarean delivery in healthy parturients:a prospective,double blinded,randomized dose-response trial using the sequential allocation method [J]. BMC Anesthesiol,2017,17(1):8.
[18] Yousef AA,Amr YM. The effect of adding magnesium sulphate to epidural bupivacaine and fentanyl in elective caesarean section using combined spinal-epidural anaesthesia:a prospective double blind randomised study [J]. Int J Obstet Anesth,2010,19(4):401-404.
[19] Zhong HY,Zhang WP. Effect of intravenous magnesium sulfate on bupivacaine spinal anesthesia in preeclamptic patients [J]. Biomed Pharmacother,2018,108:1289-1293.
[20] 王奎,朱宇麟.硫酸鎂对剖宫产产妇行舒芬太尼复合布比卡因腰硬联合麻醉的效果及术后镇痛的影响[J].医学临床研究,2018,35(10):1984-1986.
[21] 王新妃.小剂量硫酸镁预防剖宫产术中寒战发生的临床观察[J].中国药师,2012,15(10):1467-1468.
[22] 张红,冯艺,潘芳,等.全身麻醉术后寒战相关危险因素的研究[J].临床麻醉学杂志,2010,26(3):203-205.
[23] Wu LX,Huang X,Sun L. The efficacy of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antagonists on improving the postoperative pain intensity and satisfaction after remifentanil-based anesthesia in adults:a meta-analysis [J]. J Clin Anesth,2015,27(4):311-324.
[24] Martin-Flores M. Epidural and Spinal Anesthesia [J]. Vet Clin North Am Small Anim Pract,2019,49(6):1095-1108.
(收稿日期:2019-12-06)

