超声弹性成像评价瘤内注射臭氧化盐水治疗兔VX-2瘤的效果
王凌霄 罗荣 蒋海波 宋禹杉 金修才 杨朝爱 杨继金
[摘要] 目的 運用超声弹性成像技术定量评价不同次数瘤内注射臭氧化盐水治疗兔VX-2瘤的效果。 方法 新西兰荷瘤大白兔48只,采用标签法随机分为4组。其中G0组12只注射1次低温生理盐水,实验组36只在超声引导下分别给予肿瘤体积2倍臭氧化生理盐水,并根据注射次数分为G1组(1次)、G2组(2次,1次/d)、G3组(3次,1次/d),每组各12只。分别于术前,术后4、8 d测量肿瘤的长径(a)、短径(b)和弹性值(B/A),根据公式V=1/2ab2计算各组肿瘤体积(V),并比较肿瘤生长率。 结果 G1、G3组术后4 d肿瘤生长率低于G0组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);G1、G2、G3组术后8 d肿瘤生长率低于G0组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。术后4 d,四组肿瘤组织弹性值比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);其中,G1、G2、G3组兔VX-2瘤组织弹性值低于G0组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。术后8 d,四组肿瘤组织弹性值比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);其中,G1、G2、G3组兔VX-2瘤组织弹性值低于G0组,且G2、G3组低于G1组,G3组低于G2组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。 结论 二维超声联合弹性成像技术,可以更客观、全面地评价不同次数瘤内注射相同浓度臭氧化盐水对兔VX-2瘤的治疗效果,且以多次治疗后肿瘤组织弹性值下降最明显。
[关键词] 臭氧;臭氧化水;超声弹性成像;VX-2瘤
[中图分类号] R735.7 [文献标识码] A [文章编号] 1673-7210(2020)07(c)-0008-04
Effect of intraocular injection of ozonated saline on rabbit VX-2 tumor by evaluation of ultrasound elastography
WANG Lingxiao1 LUO Rong2 JIANG Haibo1 SONG Yushan1 JIN Xiucai1 YANG Chao′ai2 YANG Jijin2
1.Department of Ultrasound, Changhai Hospital, the Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200433, China; 2.Department of Intervention, Changhai Hospital, the Second Military Medical University, Shanghai 200433, China
[Abstract] Objective To evaluate the effect of different times of intraocular injection of ozonized saline on VX-2 tumor in rabbits by ultrasound elastography. Methods A total of 48 New Zealand tumor-bearing white rabbits were randomly divided into four groups by labeling. Among them, 12 rabbits were in the G0 group (injected with low-temperature normal saline, once), while 36 rabbits of the experimental group were given twice the volume of ozonized normal saline under ultrasound guidance, and according to the number of injections, they were divided into G1 (one time), G2 (two times, once a day), G3 group (three times, once a day), with 12 rabbits in each group. The long diameter (a), short diameter (b) and elasticity value (B/A) of the tumor were measured before operation, four and eight days after surgery. The tumor volume (V) was calculated by the formula V=1/2ab2 and tumor growth rate were compared. Results The tumor growth rate of the G1, G3 group four days after surgery were lower than that of the G0 group, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05); the tumor growth rate of G1, G2 and G3 groups were lower than that of the G0 group eight days after surgery, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Four days after surgery, the elasticity value of the tumor tissues in the four groups were statistically significant (P < 0.05); among them, the elasticity value of the VX-2 tumor tissues in the G1, G2 and G3 groups were lower than that in the G0 group, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Eight days after surgery, the elasticity value of the tumor tissues in the four groups were statistically significant (P < 0.05); among them, the elasticity value of the VX-2 tumor tissues in the G1, G2 and G3 groups were lower than that in the G0 group, while the G2 and G3 groups were lower than that in the G1 group, and G3 group was lower than G2 group, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). Conclusion Two-dimensional ultrasound combined with elastography can more objectively and comprehensively evaluate the therapeutic effect of different times of intraocular injection of the same concentration of ozonated saline on rabbit VX-2 tumors, and the most obvious decrease in tumor tissue elasticity value after multiple treatments.
[Key words] Ozone; Ozonated water; Ultrasound elastography; VX-2 tumors
医用臭氧于20世纪初开始应用于医学,现已广泛应用于腰椎间盘突出症[1]、组织缺血再灌注等疾病的治疗[2]。19世纪80年代,臭氧治疗肿瘤的实验研究及作为临床恶性肿瘤治疗的辅助手段的报道逐渐出现[3-7]。有学者认为[8-9],单独使用臭氧治疗恶性肿瘤可使肿瘤部分灭活,与化疗的效果相同。前期动物實验研究中,多采用CT或高频超声测量肿瘤大小,通过计算肿瘤生长率比较治疗效果。然而,瘤内注射臭氧对肿瘤治疗作用的早期,主要是对肿瘤细胞和血管的直接破坏,引起组织坏死和变性,在肿瘤体积发生变化前,组织弹性或许已发生变化。应力超声弹性成像技术[10]正是通过测定组织应变,并计算感兴趣区域与周围组织应变比值,从而判断该区域的组织硬度,可以较好地定量评价感兴趣区域的组织硬度。兔VX-2瘤内注射臭氧治疗后,瘤组织的弹性变化鲜见报道。本研究旨在运用超声弹性成像技术定量评价不同次数瘤内注射臭氧化盐水治疗兔VX-2瘤的效果。
1 对象与方法
1.1 实验动物
经海军军医大学动物实验伦理委员会审批通过。入组新西兰大白兔48只,实验动物生产许可证号:SCXK(沪)2015-0005,体重2.0~2.5 kg,由海军医学研究提供,瘤株由中山医院医学动物试验中心馈赠。将VX-2瘤块自瘤兔左后腿内侧肌肉内取出,生理盐水冲洗干净后,切取周边的活性组织,将其剪成1 mm×1 mm×1 mm碎块放置在生理盐水中备用,随后将1粒瘤组织植入大白兔后腿内侧肌肉,待肿瘤长径长至1.0~1.5 cm时开始实验。
1.2 实验分组及处理
将符合实验条件的48只瘤兔采用标鉴法随机分为4组,每组12只。其中G0组为对照组(注射低温生理盐水1次),G1、G2、G3组为实验组。G1组注射臭氧化生理盐水1次、G2组注射臭氧化生理盐水2次(1次/d)、G3组注射臭氧化生理盐水3次(1次/d)。
1.3 实验方法
所有瘤兔采用上海化学试剂供应站分装厂提供的3%的硫酸戊巴比妥钠(0.8~1.0 mL/kg,湖北鸿运隆精细化有限公司,生产批号:57-33-0)耳缘静脉麻醉后采用高频超声测量肿瘤最大切面的长径(a)、短径(b),根据公式V=1/2ab2计算肿瘤体积。随后,在高频超声引导下瘤内注射2倍肿瘤体积的低温生理盐水或臭氧化生理盐水(臭氧用德国赫尔曼公司生产的Medozone型臭氧发生器制备),臭氧化生理盐水为20 μg/mL臭氧气体通入低温生理盐水中制作而成,时间为20 min,在制作及实验过程中均采用冰袋维持低温环境。
采用日立公司HI VISION Preirus彩色多普勒超声诊断仪,L15-4线阵探头,频率4~15 MHz,充分暴露兔荷瘤部位,所有操作均由同1名检查者完成,分别获取术前,术后4、8 d肿瘤组织最大切面,冻结图像后分别测量长径(a)和短径(b)3次,取平均值。切换至弹性成像模式,将肿瘤组织和兔正常肌肉组织放置感兴趣区域内,并轻微加压探头至提示压力适中,分别勾画肿瘤治疗区组织和兔正常肌肉组织,获取组织B/A值,测量3次,取平均值。计算肿瘤体积(V)及计算肿瘤生长率(GR=术后肿瘤体积/术前肿瘤体积),其中V4/V0为术后4 d肿瘤生长率,V8/V0为术后8 d肿瘤生长率,V8/V4为术后8 d相对术后4 d肿瘤生长率。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS 21.0软件对所得数据进行统计分析。计量资料以均数±标准差(x±s)表示,采用单因素方差分析,进一步两两比较采用LSD-t检验。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
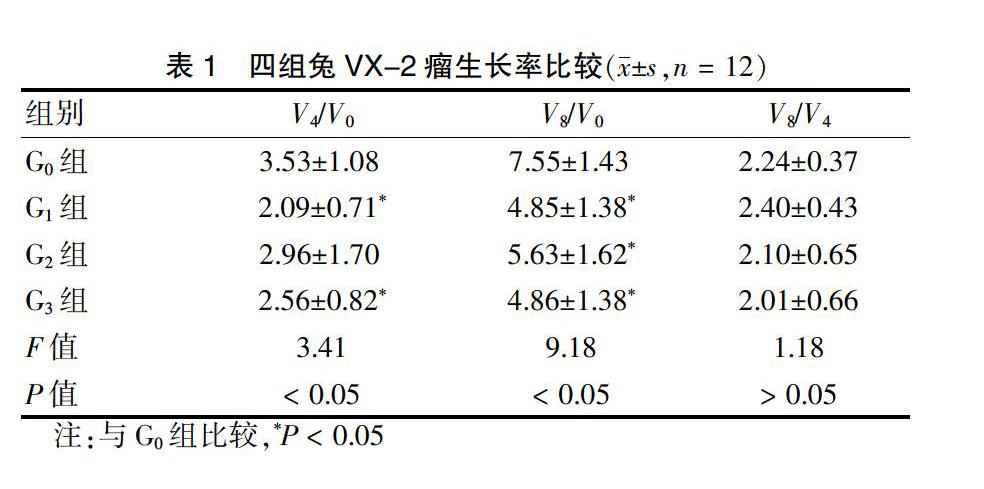
2.1 四组兔VX-2瘤生长率比较
G1、G3组V4/V0肿瘤生长率低于G0组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。G1、G2、G3组V8/V0肿瘤生长率低于G0组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。各组V8/V4肿瘤生长率比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。见表1。
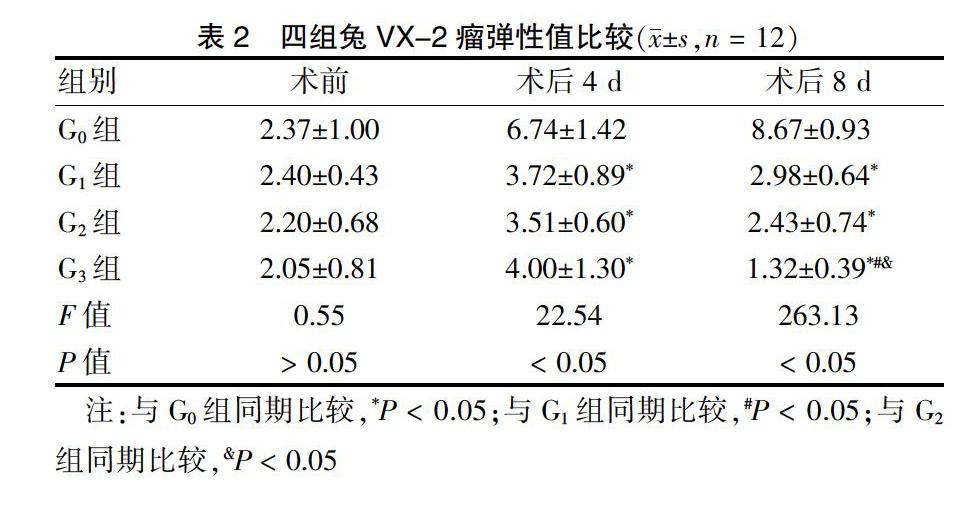
2.2 四组兔VX-2瘤弹性值比较
术前四组肿瘤组织弹性值比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。术后4 d,四组肿瘤组织弹性值比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);其中,G1、G2、G3组兔VX-2瘤组织弹性值低于G0组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表2、图2。术后8 d,四组肿瘤组织弹性值比较,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);其中,G1、G2、G3组兔VX-2瘤组织弹性值低于G0组,且G2、G3组低于G1组,G3组低于G2组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。见表2。
3 讨论
医用臭氧通过游离出1个原子氧,与肿瘤组织内有机分子反应,生成自由基,从而破坏细胞膜和细胞器微分子结构,对肿瘤组织起到直接和间接的杀灭作用[11-13]。魏强等[14]发现,不同浓度的臭氧治疗兔VX-2瘤均可不同程度抑制肿瘤生长,但差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。超声弹性成像技术虽在临床上应用广泛,而瘤内注射臭氧化盐水后瘤组织的弹性变化相关研究尚无报道。
本研究显示,不同次数瘤内注射臭氧均可抑制肿瘤生长。短时间观察,单次注射治疗抑制肿瘤生长率的效果最明显。但不同次数比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05)。究其原因,可能与低剂量(单次)臭氧作为一种强氧化剂,既能直接破坏肿瘤组织和微血管,还参与激活体内免疫机制,诱导合成与释放干扰素、肿瘤细胞坏死因子、白细胞介素等细胞因子共同抗肿瘤有关[15-17]。然而,连续多次瘤内注射臭氧可以导致肿瘤膨胀,短时间内药物吸收较慢,外观上出现肿瘤抑制抵消现象,甚至继续增大。因此,单纯利用肿瘤生长率评价瘤内注射臭氧治疗兔VX-2瘤的效果缺乏严谨性。另外,臭氧对肿瘤组织直接和间接的破坏作用都会改变组织结构排列和活性,组织弹性变化可能较生长率能更客观、准确评价治疗效果[18]。
超声弹性成像[19-21]是在二维声像图基础上,根据不同组织弹性系数及压力后组织应变的不同,收集片段信号,进行彩色编码成像,计算病变组织与正常组织硬度上的差别。临床上,关于超声弹性成像技术对甲状腺结节、乳腺结节等疾病的良恶性鉴别诊断作用已得到广泛研究证实。韩世龙等[22]利用臭氧治疗兔VX-2瘤后病理分析,发现肿瘤消融区周边为乳糜样坏死组织,中间伴有组织液化、坏死,病理标本显示肿瘤细胞出现溶解、破裂等坏死表现。本研究发现,术后4 d实验组兔VX-2瘤弹性值较对照组明显下降,正是因为臭氧极不稳定,进入组织后能迅速与水分子结合生成反应性极高的过氧化氢、过氧化自由基;后者既能直接破坏细胞膜、线粒体膜,导致细胞核破裂、溶解,又能与生物膜上的不饱和脂肪酸发生过氧化作用,代谢产物引起连锁反应,进一步加重损伤致肿瘤组织液化坏死,从而肿瘤组织变软。然而,术后4 d实验组弹性值比较,差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),可能与观察时间较短,连续多次注射臭氧,药物未完全发挥作用有关,具体有待后续研究。术后8 d,G3组兔VX-2瘤弹性值继续降低,提示瘤内多次注射臭氧的治疗作用维持时间更长,效果更持久。
本研究尚存在一定局限性:①样本量较小,有待扩大样本量进一步研究;②观察时间较短,仍需延长观察时间继续研究臭氧的治疗效果。
综上所述,不同次数瘤内注射臭氧化盐水对兔VX-2瘤生长率的抑制作用差异无统计学意义(P > 0.05),但对肿瘤组织弹性值的影响明显,且以多次治疗肿瘤组织弹性值下降最明显。因此,二维超声联合弹性成像技术可以更好地评价瘤内多次注射臭氧治疗兔VX-2瘤的效果。
[参考文獻]
[1] Ezeldin M,Leonardi M,Princiotta C,et al. Percutaneous ozone nucleolysis for lumbar disc herniation [J]. Neuroradiology,2018,60(11):1231-1241.
[2] Smith NL,Wilson AL,Gandhi J,et al. Ozone therapy:an overview of pharmacodynamics,current research,and clinical utility [J]. Med Gas Res,2017,7(3):212-219.
[3] Qing M,Yang CA,Jiang X,et al. Effectiveness of ozonated saline in the treatment of VX2 tumors in rabbits [J]. J Inter Med,2018(3):143-149.
[4] 郝珂楠,李新玲,何晓峰.臭氧治疗在临床医疗中的新进展[J].中华介入放射学电子杂志,2015,3(3):168-172.
[5] Sergio R,Schito L,Koritzinsky M,et al. Molecular targeting of hypoxia in radiotherapy [J]. Adv Drug Deliv Rev,2017,109:45-62.
[6] Bayer S,Kazancioglu HO,Acar AH,et al. Comparison of laser and ozone treatments on oral mucositis in an experi-mental model [J]. Lasers Med Sci,2017,32(3):673-677.
[7] 邱世香,赵茂林,胡文,等.臭氧治疗肿瘤的研究进展[J].西部医学,2019,31(12):1966-1968.
[8] Clavo B,Santana-Rodríguez N,Llontop P,et al. Ozone Therapy as Adjuvant for Cancer Treatment:Is Further Research Warranted? [J]. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med,2018:7931849.
[9] Hu B,Zheng J,Liu Q,et al. The effect and safety of ozone autohemotherapy combined with pharmacological therapy in postherpetic neuralgia [J]. J Pain Res,2018,11:1637-1643.
[10] Yagci B,Erdem Toslak I,Cekic B,et al. Differentiation between idiopathic granulomatous mastitis and malignant breast lesions using strain ratio on ultrasonic elastography [J]. Diagn Interv Imaging,2017,98(10):685-691.
[11] Megele R,Riemenschneider MJ,Dodoo-Schittko F,et al. Intra-tumoral treatment with oxygen-ozone in glioblastoma:A systematic literature search and results of a case series [J]. Oncol Lett,2018,16(5):5813-5822.
[12] Kuroda K,Yamashita M,Murahata Y,et al. Use of ozonated water as a new therapeutic approach to solve current concerns around antitumor treatment [J]. Exp Ther Med,2018,16(3):1597-1602.
[13] 魏强,方亮,杨继金,等.瘤内注射臭氧致兔VX2瘤组织超微结构改变的研究[J].介入放射学杂志,2013,22(10):830-833.
[14] 魏强,李慧,杨继金,等.瘤内注射臭氧治疗兔VX-2肿瘤的疗效研究[J].临床放射学杂志,2015,34(1):106-109.
[15] Miller DB,Snow SJ,Schladweiler MC,et al. Acute Ozone-Induced Pulmonary and Systemic Metabolic Effects Are Diminished in Adrenalectomized Rats [J]. Toxicol Sci,2016,150(2):312-322.
[16] Clay E,Patacchini R,Trevisani M,et al. Ozone-Induced Hypertussive Responses in Rabbits and Guinea Pigs [J]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther,2016,357(1):73-83.
[17] Wicher SA,Lawson KL,Jacoby DB,et al. Ozone-induced eosinophil recruitment to airways is altered by antigen sensitization and tumor necrosis factor-α blockade [J]. Physiol Rep,2017,5(24):e13538.
[18] Kuroda K,Azuma K,Mori T,et al. The Safety and Anti-Tumor Effects of Ozonated Water in Vivo [J]. Int J Mol Sci,2015,16(10):25108-25120.
[19] Hahn S,Lee YH,Lee SH,et al. Value of the Strain Ratio on Ultrasonic Elastography for Differentiation of Benign and Malignant Soft Tissue Tumors [J]. J Ultrasound Med,2017,36(1):121-127.
[20] 張小玲,何永津,邹剑曾,等.基于二维超声联合彩色多普勒血流成像及弹性成像的乳腺实性肿物诊断模型的建立及验证[J].现代医院,2019,19(10):1533-1536.
[21] 拉琼,杨锦茹.超声弹性成像应用于移植肾的研究进展[J].中国医药导报,2019,16(36):40-45.
[22] 韩世龙,朱晓黎,张猛,等.经皮注射医用臭氧治疗兔VX2移植瘤的实验研究[J].介入放射学杂志,2013,22(3):223-227.
(收稿日期:2019-12-30)

