CT影像学对血管性痴呆患者的诊断价值
范存庚


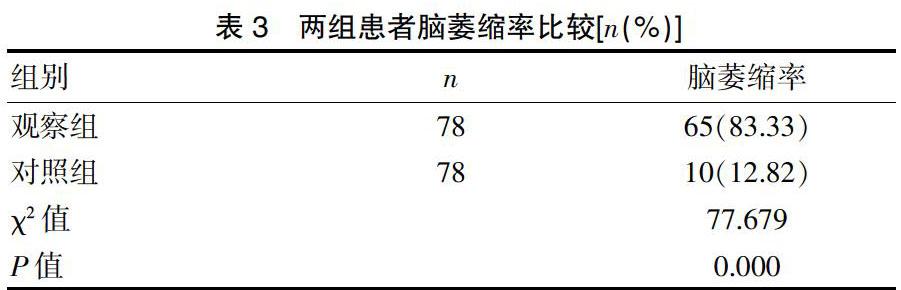
[摘要] 目的 探討CT影像学对血管性痴呆患者的诊断价值。 方法 选取本院2018年1月~2019年10月期间接诊的78例经CT影像学检查确诊为血管性痴呆的患者作为观察组,选取同期的78例非痴呆性脑卒中患者作为对照组,同样接受CT影像学检查,使用简易智力状态检查量表(MMSE)和日常生活能力评定量表(ADL)对比两组患者认知功能和生活自理能力,对比两组患者CT影像学检查表现及两组患者的脑萎缩率。 结果 观察组患者的MMSE评分和ADL评分分别为(21.65±1.45)分和(40.25±5.36)分,对照组患者的MMSE评分和ADL评分分别为(27.20±1.66)分和(60.78±3.26)分,观察组评分明显低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);两组患者的CT影像学表现结果表明,观察组患者的脑梗死面积比对照组大,部分患者在脑出血后出现梗死,病变的位置以皮质和皮质下为主,双侧和左侧为主要倾向;观察组患者的脑萎缩率达到83.33%,明显高于对照组的12.82%,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。 结论 CT影像学检查可以清晰且准确的反映出血管性痴呆患者的病灶位置和脑萎缩情况等,临床诊断价值较高,是一种高效、可靠的血管性痴呆检查方法,值得推广并应用。
[关键词] CT影像学;血管性痴呆;脑萎缩;脑卒中
[中图分类号] R749.1 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2020)16-0118-03
Diagnostic value of CT imaging in patients with vascular dementia
FAN Cungeng
Department of Medical Imaging, Ganzhou People's Hospital in Jiangxi Province, Ganzhou 341000, China
[Abstract] Objective To explore the diagnostic value of CT imaging in patients with vascular dementia. Methods 78 patients diagnosed with vascular dementia by CT imaging in our hospital from January 2018 to October 2019 were selected as the observation group. 78 non-dementia stroke patients during the same period were selected as the control group, and they also underwent CT imaging examination. The cognitive function and life self-care ability between the two groups were compared by using the Simple Mental State Examination Scale(MMSE) and the Daily Living Ability Assessment Scale(ADL). And the CT imaging examination performance and the brain atrophy rate between the two groups were compared. Results The MMSE score and ADL score of the observation group were(21.65±1.45) and(40.25±5.36) points respectively, while the MMSE score and ADL score of the control group were(27.20±1.66) and(60.78±3.26) points. The score of the observation group was significantly lower than that of the control group, with statistically significant difference(P<0.05). CT imaging results of the two groups showed that the cerebral infarction area of the observation group was larger than that of the control group, and some patients had infarction after cerebral hemorrhage. The location of the lesion was mainly cortex and subcortex, and the main tendency was bilateral and left. The brain atrophy rate of the observation group reaches 83.33%, which was significantly higher than that of the control group(12.82%), and the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05). Conclusion CT imaging can clearly and accurately reflect the location of lesions and brain atrophy in patients with vascular dementia, with relatively high clinical diagnosis value. It is an efficient and reliable vascular dementia examination method, which is worthy of promotion and application.
本次研究结果表明,观察组患者的MMSE评分、ADL评分明显低于对照组,表明观察组患者均表现出明显的痴呆症状。观察组患者的病灶位置多数在皮质、皮质下,具有比较明显的左侧和双侧倾向,并且梗死的面积比较大,与对照组患者具有比较大的差异,观察组患者脑萎缩率为83.33%,对照组脑萎缩率为12.82%,两组数据对比差异明显,具有统计学意义(P<0.05)。由此可见,CT影像学在诊断血管性痴呆上,具有比较高的诊断价值,具有良好的应用效果,应该得到更为广泛的推广与临床应用。
综上所述,CT影像学检查可以清晰且准确的反映出血管性痴呆患者的病灶位置和脑萎缩情况等,相关检查和诊断的准确率比较高,并且检查费用相对较低,经济适用,临床诊断价值比较高,是一种高效、可靠的血管性痴呆检查方法,值得推广并应用。
[参考文献]
[1] 钟必武,王宗明,王静.探讨CT影像学对于血管性痴呆的诊断价值[J].中国实用医药,2019,14(34):95-96.
[2] 刘玉涛,许予明,高远,等.阿尔茨海默病、血管性痴呆及额颞叶变性患者的脑MRI及CT平扫影像学特征分析[J].中国CT和MRI杂志,2018,(5):25.
[3] 吴佳慧,刘剑刚,李浩,等.阿尔茨海默病和血管性痴呆的病理机制及相关临床研究比较[J].浙江医学,2019,(11):121-122.
[4] 丁晓燕,咸海亮.头颅核磁共振在诊断脑血管性痴呆中的临床价值[J].影像研究与医学应用,2018,(14):101.
[5] 田金洲,解恒革,秦斌,等.适用于中国人群的血管性痴呆筛查和诊断框架[J].中华内科杂志,2019,58(1):10.
[6] 李维.探讨头颅血管磁共振在脑血管性痴呆患者中临床诊断价值[J].影像研究与医学应用,2018,(5):15-16.
[7] 陈赟,何志聪,范燕明,等.简明精神状态量表联合蒙特利尔认知评估量表在血管性痴呆认知功能障碍中的初步应用[J].中国医学创新,2019,16(4):83-87.
[8] 阮世旺.血管性痴呆危险因素及影像学特征[J].中国实用神经疾病杂志,2017,(7):30.
[9] 相振宇,蔡强,李军东,等.颈内动脉颅内段钙化与腔隙性脑梗死影像学相关性研究[J].中国药物与临床,2017, 17(11):1631-1633.
[10] 罗燕.血管性痴呆的诊断和治疗进展[J].国际神经病学神经外科学杂志,2017,(5):147.
[11] 顾雨铖,徐运.脑小血管病与血管性认知损害:关注神经影像学[J].国际脑血管病杂志,2017,25(3):244-250.
[12] 王玲,田荣华.磁共振成像与颅脑CT在老年多发性脑梗死诊断中的对比研究[J].中外医学研究,2019,17(1):71-72.
[13] 吴佳慧,刘剑刚,李浩,等.阿尔茨海默病和血管性痴呆的病理機制及相关临床研究比较[J].浙江医学,2019(11):20-21.
[14] QL Zhang,P Lu,JW Zhang.Association of serum lipoprotein -associated phospholipase A2 with vascular dementia after ischemic stroke[J].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi,2018, 98(15):1171-1175.
[15] 王道仁.CT与磁共振成像对多发性脑梗死诊断价值对比研究[J].中国药物与临床,2019,(11):1803-1804.
(收稿日期:2020-01-09)

