风险规避偏好下农副产品自然风险管理策略的选择:外部采购还是农业保险?
陈 静,魏 航,陈敬贤
风险规避偏好下农副产品自然风险管理策略的选择:外部采购还是农业保险?
陈 静1,魏 航2,陈敬贤3
(1.山东工商学院 工商管理学院,山东 烟台 264005;2.上海财经大学 商学院,上海 200433;3.南通大学 商学院,江苏 南通 226019)
在农副产品加工行业,自己种植原材料有利于企业控制产品质量、获取低成本优势。然而,随着全球气候的变暖,恶劣天气等自然风险事件频发,这无疑加剧了农副产品制造商面对的自然风险。实践中,制造商可通过外部采购策略或农业保险策略降低自然风险带来的损失。然而,这两种策略各有利弊,对于风险规避制造商而言究竟哪种策略更为有效需进行深入探析。为此,本文以单周期风险规避农副产品制造商的计划产量决策模型为基础,研究企业自然风险管理策略的选择问题。通过比较研究,找出两种策略的实施条件,并给出农副产品制造商应对自然风险的占优策略。研究结果表明:(1)当制造商风险规避程度较低时,利用外部采购策略避险是无效的。这时,如果农业保险的安全因子足够低,农业保险策略可完全补偿缺货成本,并帮助制造商降低计划产量节约种植成本,进而提高CVaR值、改善运营状态;(2)当制造商风险规避程度较高时,外部采购策略可完全消除自然风险造成的产量波动并帮助企业进入该产品市场,而农业保险则是通过补偿自然风险引发的缺货成本帮助企业进入该产品市场。哪种策略更有效取决于外部采购价格和安全因子的大小关系;(3)随着原材料单位种植成本、不利事件发生概率、最终产品单位收益及单位缺货成本的上升,外部采购策略占优区域逐渐扩大而农业保险策略的占优区域逐渐减少。
农副产品自然风险管理;农业保险策略;外部采购策略;CVaR风险测度;计划产量决策
0 引言
Kazaz[1]曾指出,在农副产品加工行业,农副产品制造商自己种植原材料一方面有利于控制产品质量,另一方面有利于控制生产成本、规避市场风险。然而,随着全球气候的变暖,灾害性天气的增多,“自种原材料”的这种生产方式无疑加剧了农副产品制造商面对的自然风险。一旦发生自然风险事件(如干旱、水灾、火灾等),原材料可能大量减产,这将给企业带来巨额经济损失,甚至引发财务危机。2013年8月雹暴侵袭法国中部地区,恶劣天气造成波尔多等多个葡萄酒产区的葡萄园受到不同程度的破坏,经济损失高达1亿5千600万欧元。由于无法交付合同,许多红酒制造商面临系统性财务危机①资料来源:http://finance.ifeng.com/a/20130904/10599039_0.shtml。
自然风险事件造成的经济损失主要体现在:一,前期投入的种植成本无法收回;二,由于无法交付合同而引发高昂的缺货成本。实践中,农副产品制造商可利用控制型风险管理策略或融资型风险管理策略缓解自然风险。其中,控制型风险管理策略(如外部采购策略)通过降低或消除产量的波动,达到避险的目的。而融资型风险管理策略(如农业保险策略)可从财务角度缓解或消除企业利润的下方波动[2][3],进而实现风险的规避。2013年,海南橡胶集团在经历强台风“海燕”侵袭,集团所属25家基地分公司的橡胶树严重受损,报废损失株数达137万株,当年干胶损失约6500吨。幸运的是,集团此前购买了相关农业保险,受灾后及时获得保险公司1.5412亿元的橡胶树综合保险赔款,有效地解决了企业的燃眉之急②资料来源:http://finance.sina.com.cn/roll/20140404/160218716440.shtml。
尽管两种策略均可用于应对自然风险,然而,考虑到企业有限的资源及策略实施成本,农副产品制造商究竟选择哪种策略管理自然风险更有效成为农副产品制造商在运营管理实践中需要考虑的重要问题。此外,随着自然与经济环境复杂度的加剧,企业目标已不仅仅是风险中性情况下的期望利润最大化或期望成本最小化,而是要在损失最小化的前提下实现企业的运营目标。也就是说,企业所持有的差异化风险态度对企业决策的影响作用日益凸显[4]。特别是,具有风险规避态度的企业在生产经营中更加关注如何保持利润的稳定性,他们在实践中更愿意牺牲一部分期望利润来避免利润的下方波动[5]。可见,风险规避程度是影响农副产品制造商自然风险管理策略选择的一个重要因素。因此,如何根据自身的风险规避程度选择并制定最优的自然风险管理策略,也是管理实践与管理理论研究需要关注的重要问题之一。
现有研究中,与本文相关的理论研究可分为两大类:第一类,利用控制型风险管理策略应对产品产出不确定风险。如利用采购策略、库存控制策略、计划产量制定或供应链协调机制管理农副产品产出不确定风险。Kazaz和Webster[6]研究了产出不确定风险下农产品制造商(如果汁制造商)如何制定果树种植计划及最终产品销售价格的问题。Grosfeld-Nir和Gerchak[7]对定制系统下考虑随机产出与需求的多批量生产决策的研究文献进行了综述。赵霞和吴方卫[8]研究了收益共享合同及单位价格补贴的风险共担机制对农产品供应商、制造商以及整个供应链绩效的影响。冯颖等[9]研究了随机产出与需求下TPL介入下的农产品供应链协调问题。张文杰和骆建文[10]研究了随机产出随机需求下的基于数量承诺的供应链期权契约问题。Giri等[11]研究了随机产出和需求下三级供应链的协调问题。Hu等[12]考虑当允许部分产品延期订货时,制造商与零售商如何利用期权合约进行计划产量及产品订货量的制定。Li等[13]研究了随机需求和产出下季节性产品的期权采购合约形式的选择及优化问题。第二类,利用融资型风险管理策略缓解产品产出不确定风险,如商业保险。这些研究主要以定性描述、案例研究或实证方法从市场结构、政府补贴、法律制度等角度对商业保险的权责划分、补偿机制设计及推行进行政策性分析。黄琦等[14]基于中国31个省(市)2007-2014年面板数据,测量了农业保险市场竞争度HHI,并以空间计量方法研究农业保险市场结构对农业保险区域收敛发展的影响。王国军等[15]采用国内10家产险公司2007-2014年共8年的177份地区承保汇总数据,运用二项回归模型和条件相关模型对我国农业保险中是否存在信息不对称问题进行了实证分析。少数文献从定量角度研究商业保险在应对供给或产出不确定风险时的作用。Dong等[16]比较研究了库存、防范措施及商业保险在两阶段生产链下如何应对生产中断风险。
通过归纳总结可以看到,以往运营领域关于农副产品自然风险管理的研究,大多侧重于利用控制型风险管理策略(如计划产量制定、外部采购或库存控制)应对因自然风险导致的产出波动。这些研究多以风险中性假设为前提。少有文献考虑融资型风险管理策略,特别是农业保险在企业实践运营中的应用问题。为此,本文将风险偏好视为农副产品制造商进行自然风险管理的一个重要动因,以风险规避企业为研究对象,对农副产品制造商自然风险管理策略的选择问题展开定量研究。本文以单周期风险规避农副产品制造商的计划产量决策模型为基础,比较研究外部采购策略与农业保险策略在农副产品自然风险管理中的运作机理,以期找出外部采购的适用条件和最优采购方案、农业保险的适用条件和最优投保方案,分析企业风险规避程度对自然风险管理策略选择的影响,并为农副产品制造商进行自然风险管理策略的选择提供理论依据及策略建议。
1 基本问题
1.1 问题描述
外部采购作为一种控制型风险管理策略,可保障农副产品制造商获取必需的原材料,从而规避产量的波动。农业保险作为一种融资型风险管理策略,可降低农副产品制造商在自然风险事件发生后的经济损失,进而缓解企业利润的下方波动。尽管两种策略都可用于应对自然风险,然而,需要指出的是,外部采购原材料的成本较高,而购买农业保险需要预先支付一定保费。如果投保期内未发生自然风险事件,这笔保费将成为沉没成本。这时,农副产品制造商必须对两种策略的成本与收益进行权衡,才能确保实施外部采购策略或农业保险策略是有效的。因此,帮助企业找出外部采购策略或农业保险策略的适用条件成为本文研究的一个首要目的。此外,外部采购策略或农业保险策略以不同方式缓解自然风险,那么,哪种策略更有效,成为本文研究的另一核心问题。本文研究的具体问题包括:(1)在什么条件下农副产品制造商可利用外部采购策略管理自然风险?在外部采购策略下,农副产品制造商的最优计划产量及外部采购量应如何制定?(2)在什么条件下农副产品制造商可利用农业保险策略管理自然风险?在农业保险策略下,农副产品制造商的最优计划产量及保险策略应如何制定?(3)在什么条件下,外部采购策略占优于农业保险策略?在什么条件下,农业保险策略占优于外部采购策略?
1.2 策略描述及决策序列

图1 未采取任何策略时农副产品制造商的决策序列
Figure 1 Decision sequence of agricultural and sideline product manufacturers without any strategy
为了降低自然风险导致的原材料产出波动,农副产品制造商可采取外部采购策略或农业保险策略。
(1)外部采购策略
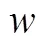
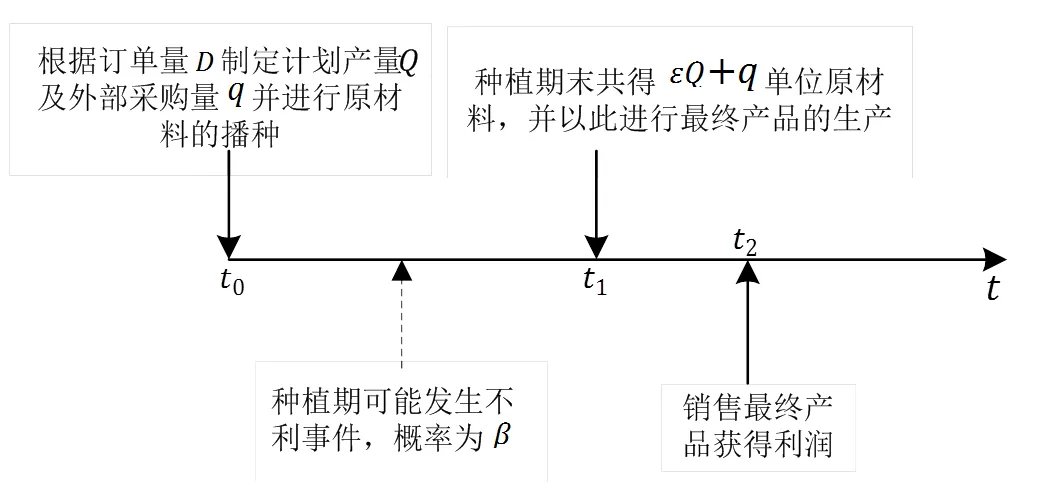
图2 外部采购策略下农副产品制造商的决策序列
Figure 2 Decision sequence of agricultural and sideline product manufacturers under external procurement strategy
(2)农业保险策略

图3 农业保险策略下农副产品制造商的决策序列
Figure 3 Decision sequence of agricultural and sideline product manufacturers under agricultural insurance strategy
1.3 风险测度方法
由于自然风险属于下方风险,且CVaR方法具有良好的数学性质[20],因此,本文以CVaR方法测度农副产品制造商的风险规避偏好。根据Rockafellar和Uryasev[21]的定义,制造商在未采取任何策略下的CVaR值可表述为:

1.4 模型假设
模型的其他基本假设如下:
2 无策略下的最优决策
2.1 决策目标
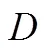
引理1无策略下制造商的CVaR值为:

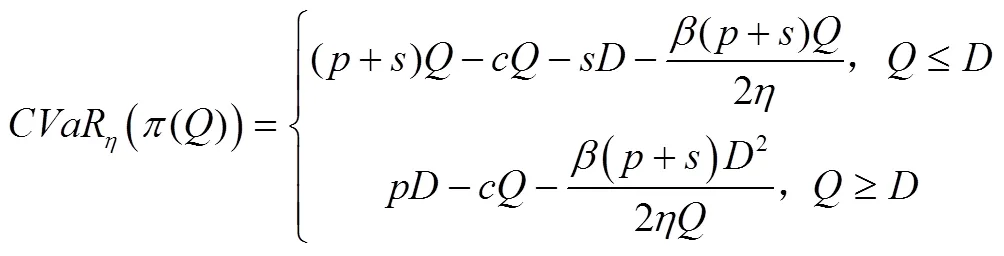
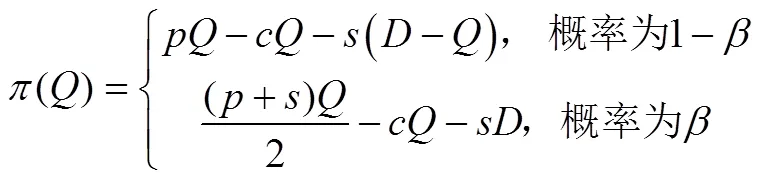
证毕!
最终,农副产品制造商的决策目标可表述为:
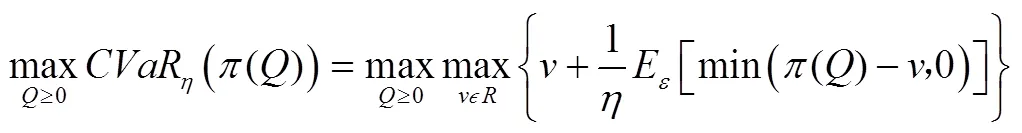
2.2 最优决策
定理1 无策略下农副产品制造商的最优决策为:
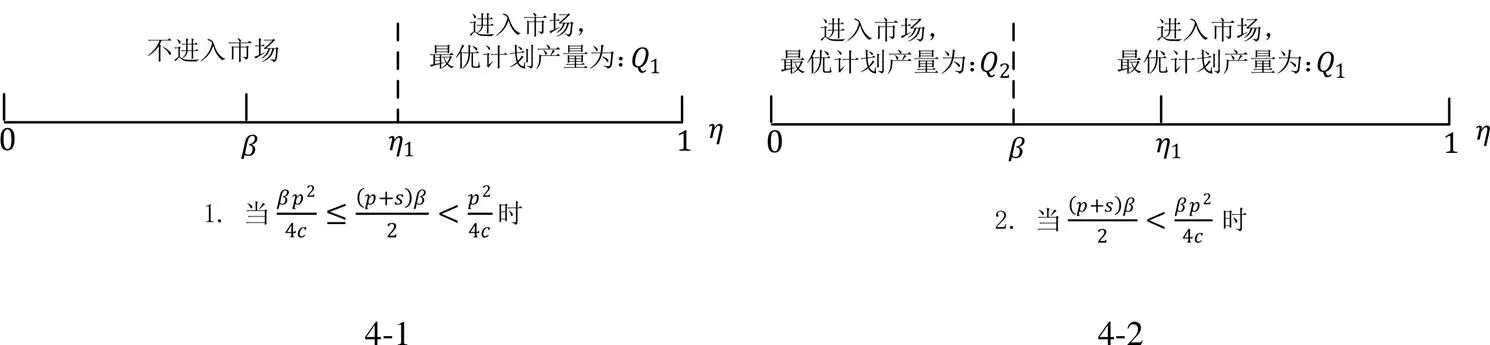
图4 无策略下农副产品制造商的最优决策
Figure 4 Optimal decision of agricultural and sideline product manufacturers without strategy
定理1的内容由图4给出。由图4可知,不采取任何策略管理自然风险时:
3 外部采购策略下的最优决策
3.1 决策目标
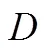
引理2外部采购策略下制造商的CVaR值为:

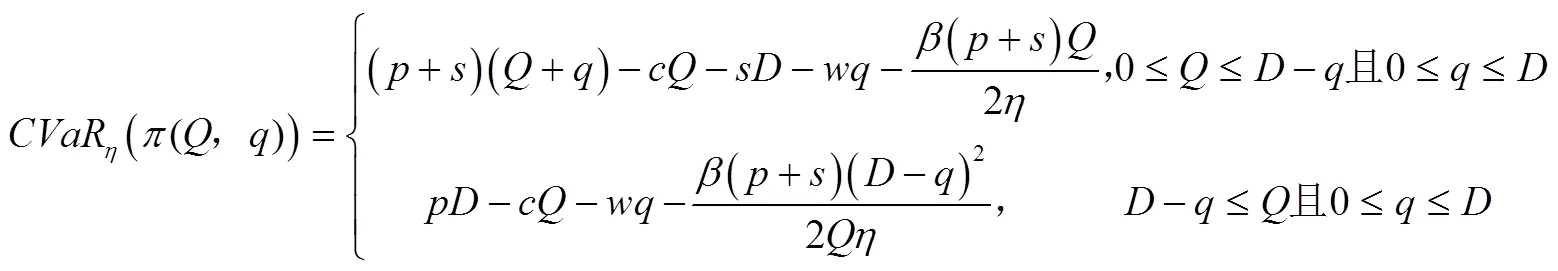
证明:证明过程与引理1类似,故略。
最终,农副产品制造商的决策目标可表述为:

3.2 最优决策
定理2 外部采购策略下农副产品制造商的最优决策为:

分类讨论不同取值区间下的局部最优解:
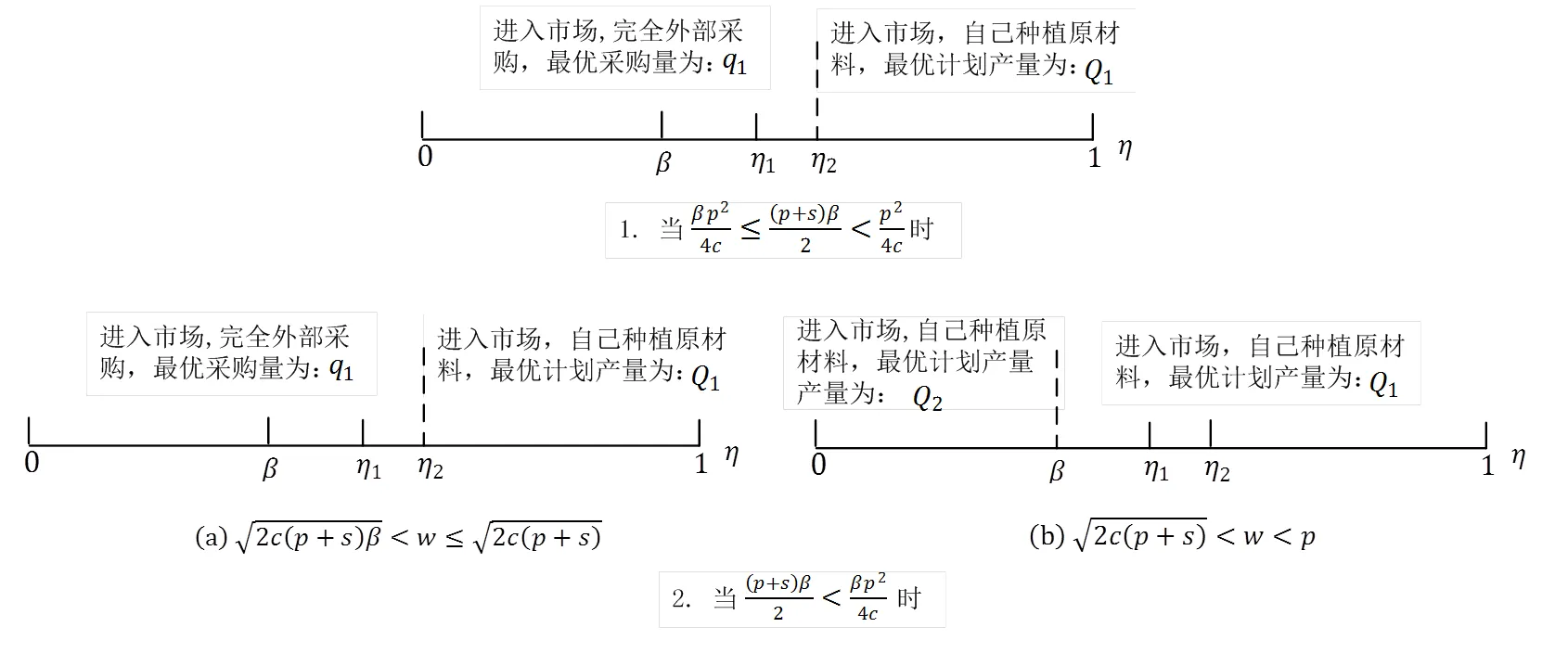
图5 外部采购策略下农副产品制造商的最优决策
Figure 5 Optimal decision of agricultural and sideline product manufacturers under external procurement strategy
定理2的内容由图5给出。由图5可知,若制造商利用外部采购策略管理自然风险:/p>
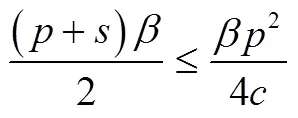

4 农业保险策略下的最优决策
4.1 决策目标
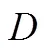
引理3农业保险策略下制造商的CVaR值为:


其中,
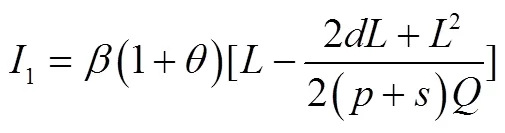

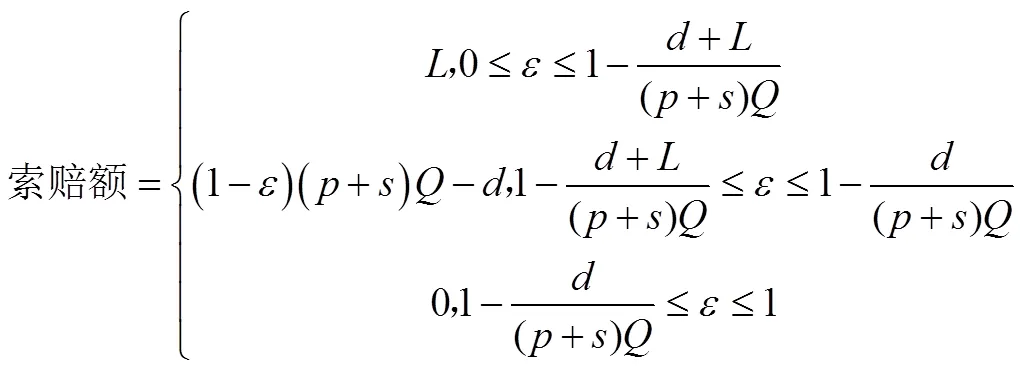
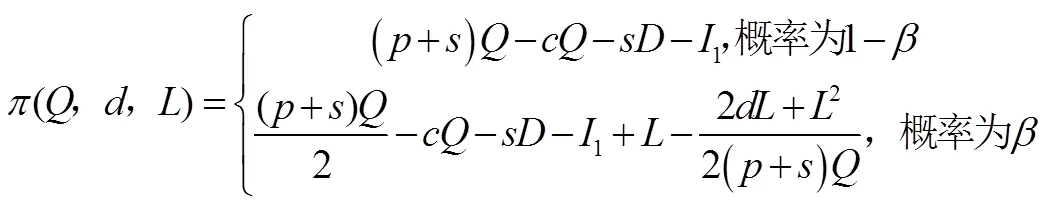
最终,农副产品制造商的决策目标可表述为:
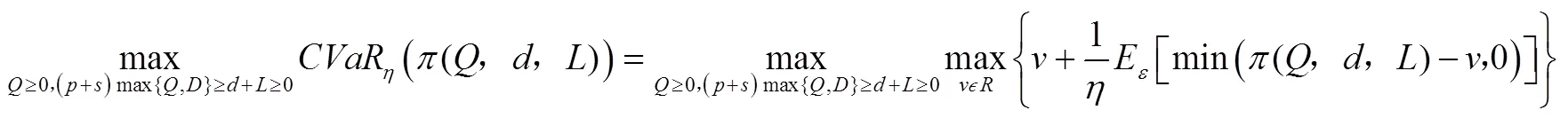
4.2 最优决策
定理3 农业保险策略下农副产品制造商的最优决策为:
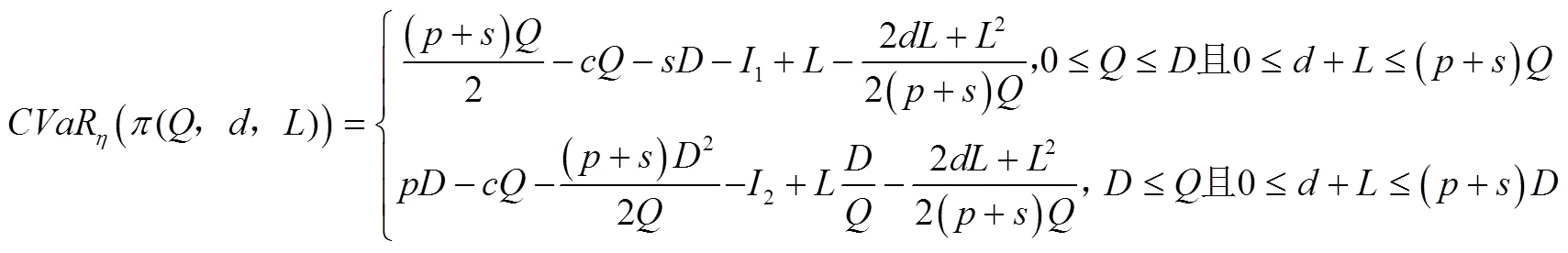
分类讨论不同取值区间下的局部最优解:

上述证明给出不同区间的局部最优解,之后要对这些局部最优解进行比较,从而找出全局最优解:

图6 农业保险策略下农副产品制造商的最优决策
Figure 6 Optimal decision of agricultural and sideline product manufacturers under agricultural insurance strategy
定理3的内容由图6给出。由图6可知,若制造商利用农业保险策略管理自然风险:

5 外部采购策略还是农业保险策略?
由定理2可知,当原材料的外部采购价格较低时,外部采购可彻底消除自然风险导致的原材料产出波动,帮助风险规避程度较高的制造商进入产品市场。由定理3可知,当保险的安全因子较低时,农业保险通过补偿不利事件造成的缺货成本、降低计划产量节约种植成本,帮助企业缓解自然风险造成的经济损失。那么,哪种策略在管理自然风险时更为有效?为了解决这一问题,本文对制造商在外部采购策略及农业保险策略下的CVaR值进行了比较。
推论1外部采购策略与农业保险策略下CVaR值的比较结果:

图7 外部采购策略与农业保险策略的比较
Figure 7 Comparison between external procurement strategy and agricultural insurance strategy
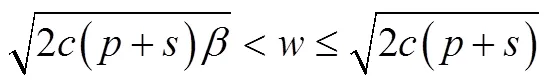
6 数值分析与管理启示
前文给出了农副产品制造商在无策略、外部采购策略及农业保险策略下的最优决策,本节将通过数值分析来验证前面的结论。Kazaz和Webster[6]在研究中以土耳其橄榄油制造商的生产参数进行数值分析。本文以此为基础对前文结论进行数值分析。
6.1 最优决策分析

图8 制造商在不同策略下的最大CVaR值
Figure 8 Manufacturer's maximum CVaR under different strategies
6.2 占优策略分析
为了更好地说明系统参数对占优策略的影响,定义农业保险策略与外部采购策略下CVaR值的变动比率为

(1)种植成本的影响
(2)不利事件发生概率的影响

图9 系统参数对占优策略的影响
Figure 9 Influence of system parameters on dominant strategy
(3)最终产品单位收益的影响
(4)单位订单补偿成本的影响
6.3 管理启示
本研究对农副产品制造商如何更好管理自然风险具有如下启示:
(1)在“订单农业”的采购模式下,农副产品制造商要么完全外部采购原材料要么完全自己种植原材料,“外部采购+自己种植”的生产方式并非是应对自然风险的最优策略。对风险规避程度较高的农副产品制造商而言,当采购价格较低或期望缺货成本较高时,利用完全外部采购策略可帮助企业顺利进入市场。对风险规避程度较低的农副产品制造商而言,自己种植原材料始终是最优策略。
(2)当安全因子足够低时,农副产品制造商可利用农业保险策略管理自然风险并进行原材料的种植,最优保险策略是将缺货成本完全转移至金融机构承担。对风险规避程度较高的农副产品制造商而言,农业保险的价值主要体现在消除因合同无法交付而产生的缺货成本,并帮助企业能够以自己种植原材料的方式进入市场。这时,农业保险策略与计划产量在应对自然风险时是一种互补关系。对风险规避程度较低的农副产品制造商而言,农业保险的价值主要体现在帮助企业大幅降低计划产量,节约种植成本,改善经营状态。这时,农业保险与计划产量在应对自然风险时是一种替代关系。
(3)在农产品种植中,自然风险的不利后果体现在两个方面:一是前期投入的种植成本无法回收,二是合同无法交付产生缺货成本。当缺货成本相对种植成本较高时,农副产品制造商可借助农业保险自己种植原材料。当原材料种植成本较高时,前期投入的种植成本无法回收成为农副产品制造商面对的主要风险。这时,外部采购策略会比农业保险策略更有效。不利事件发生概率、最终产品单位收益或单位订单赔偿成本的上升意味着期望缺货成本的上升,这无疑提高了农业保险购买成本。这时,农业保险的价值逐渐减弱,而外部采购策略因其成本优势逐渐成为制造商管理自然风险的首选策略。
7 总结与展望
本文以单周期风险规避农副产品制造商的计划产量决策模型为基础,借助CVaR风险测度方法,研究了制造商规避自然风险的最优策略选择问题。
研究结果表明:(1)当制造商的风险规避程度较低时,利用外部采购策略避险是无效的。此时,如果农业保险的安全因子足够低,农业保险策略通过完全补偿缺货成本并降低计划产量节约种植成本来帮助企业提高CVaR值、改善运营状态;(2)当制造商的风险规避程度较高时,外部采购策略可完全消除自然引发的产量波动并帮助企业进入产品市场,而农业保险则是通过完全补偿不利事件引发的缺货成本帮助企业进入产品市场;(3)随着原材料单位种植成本、不利事件发生概率、最终产品单位收益及单位缺货成本的上升,外部采购策略的占优范围逐渐扩大而农业保险策略的占优范围逐渐减少。
本文在研究中仅考虑了农产品产出的不确定性,在后续研究中可同时考虑产出与需求的不确定性。此外,本文只对订单农业的采购策略进行了分析,事实上,实践中还有一些制造商通过期权合约规避风险。后续研究可对其他采购合约与农业保险之间的关系进行深入的比较分析。再者,本文只考虑随机产出率服从均匀分布的情况,其他分布下的最优决策需进一步的研究。最后,该问题可拓展至农产品供应链视角,考虑多主体下如何利用控制型风险管理策略和融资型风险管理策略来应对自然风险。
[1] Kazaz B. Production planning under yield and demand uncertainty with yield-dependent cost and price[J]. Manufacturing & Service Operations Management, 2004, 6(3): 209-224.
[2] 曾玉珍, 穆月英. 农业风险分类及风险管理工具适用性分析[J]. 经济经纬, 2011, (2): 128-132.
Zeng Y Z, Mu Y Y. Analysis of Agricultural Risk Classification and the Applicability of Risk Management Tool[J]. ECONOMIC SURVEY, 2011, (2): 128-132.
[3] Billington C, Johnson B, Triantis A.A real options perspective on supply chain management in high technology[J]. Journal of Applied Corporate Finance, 2002, 15(2):32-43.
[4] Anupindi R, Bassok Y. Supply contracts with quantity commitments and stochastic demand[M]. Boston: Quantitative models for supply chain management. Springer US, 1999: 197-232.
[5] Chen YH, Xu MH, Zhang ZG. A risk-averse newsvendor model under the CVaR criterion[J]. Operations Research, 2009, 57(4): 1040-1044.
[6] Kazaz B, Webster S. The impact of yield dependent trading costs on pricing and production planning under supply uncertainty[J]. Manufacturing & Service Operations Management, 2011, 13(3):404–417.
[7] Grosfeld-Nir A, Gerchak Y. Multiple lotsizing in production to order with random yields: Review of recent advances[J]. Annals of Operations Research, 2004, 126(1-4):43-69.
[8] 赵霞, 吴方卫. 随机产出与需求下农产品供应链协调的收益共享合同研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2009, 17(5): 88-95.
Zhao X, Wu F W. Coordination of Agri-food Chain with Revenue -sharing Contract under Stochastic Output and Demand[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2009, 17(5): 88-95.
[9] 冯颖, 余云龙, 张炎治, 等. 随机产出与随机需求下TPL介入的农产品供应链协调[J]. 管理工程学报, 2017, 31(4):156-163.
Feng Y, Yu Y L, Zhang Y Z, et al. Coordination of agri-products supply chain with TPL's participation under random yield and random demand[J]. Journal of Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management, 2017, 31(4):156-163.
[10] 张文杰, 骆建文. 随机产出随机需求下的供应链期权契约模型[J]. 管理工程学报, 2016, 30(3):121-128.
Zhang W J, Luo J W. Supply Chain Option Contract Model with Random Yield and Stochastic Demand[J]. Journal of Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management, 2016, 30(3):121-128.
[11] Giri BC, Bardhan S, Maiti T. Coordinating a three-layer supply chain with uncertain demand and random yield[J]. International Journal of Production Research, 2015, 54(8):1-20.
[12] Hu F, Lim CC, Lu Z. Optimal production and procurement decisions in a supply chain with an option contract and partial backordering under uncertainties[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2014, 232(6): 1225-1234.
[13] Li J, Zhou Y, Huang W. Production and procurement strategies for seasonal product supply chain under yield uncertainty with commitment-option contracts[J]. International Journal of Production Economics, 2017, 183: 208-222.
[14] 黄琦, 陶建平, 张红梅. 农业保险市场结构,空间依赖性与农业保险条件收敛研究[J]. 中国管理科学, 2017, 25(5): 25-32.
Huang Q, Tao J P, Zhang H M. Market Structure of Agricultural Insurance, Spatial Dependence and Agricultural Insurance Conditional Convergence[J]. Chinese Journal of Management Science, 2017, 25(5): 25-32.
[15] 王国军, 王冬妮, 陈璨. 我国农业保险不对称信息实证研究[J]. 保险研究, 2017, (1): 91-100.
Wang G J, Wang D N, Chen C. An empirical study on information asymmetry of agriculture[J]. Insurance Studies, 2017, (1): 91-100.
[16] Dong L, Tang SY, Tomlin B. Production chain disruptions: Inventory, preparedness, and insurance. 2015. Working Paper..
[17] Güler MG, Bilgiç T. On coordinating an assembly system under random yield and random demand[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2009, 196(1): 342-350.
[18] 吴晨, 李怡洁, 蔡菲菲. “代工农业”的社会和环境风险—以新疆番茄制品供应链为例[J]. 中国农业信息, 2016,28(6): 142-144.
Wu C, Li Y J, Cai F F. Social and environmental risks of "OEM agriculture": a case study of tomato products supply chain in Xinjiang [J]. China Agricultural Information, 2016,28(6): 142-144.
[19] Cummins JD. Statistical and financial models of insurance pricing and the insurance firm[J].Journal of Risk and Insurance, 1991, 58(2): 261-302.
[20] Chen Y, Xu M, Zhang G.A risk-averse newsvendor model under the CVaR decision criterion[J].Operations research, 2009, 57(4):1040-1044.
[21] Rockafellar RT, Uryasev S. Conditional value-at-risk for general loss distributions[J]. Journal of Banking & Finance, 2002. 26(7): 1443-1471.
Determination of strategy against natural risks for farm and sideline products in risk-averse preference: External purchasing or agricultural insurance?
CHEN Jing1, WEI Hang2, CHEN Jingxian3
(1. School of Business Administration, Shandong Technology and Business University, Yantai 264005, China;2. College of business, Shanghai University of Finance & Economics, Shanghai 200433, China;3. School of Business, Nantong University, Nantong 226019, China)
In the agricultural and sideline products processing industry, manufacturers may plant and raise raw materials themselves, which is conducive to the company to control product quality, and access to low-cost advantages. However, with the change of global climate, adverse events such as bad weather are frequently occurring, which undoubtedly exacerbates the output uncertainty risks faced by agricultural and sideline products manufacturers. In operation practice, manufacturers can mitigate the risk using the external purchasing strategy, or the agricultural insurance strategy, to reduce the economic loss caused by the uncertainty of the raw material output for a risk-averse manufacturer. Which strategy is more effective needs further analysis. Based on the decision-making model of the planned capacity of agricultural products by a risk-averse manufacturer, this paper, with the help of the CVaR risk measurement method, deals with the problem of selection of a strategy for natural risk management. The external purchasing strategy and the agricultural insurance strategy are compared with each other in terms of application conditions as well as the optimal strategies so that the implementation conditions of each of the two strategies are discovered. The dominant strategy for manufacturers to manage natural risk leads to the raw materials output uncertainty, and the conditions in which one strategy is dominant to the other are given.
The specific issues in the study include: (1) Under what conditions can manufacturers use external purchasing strategies to manage the natural risk? And in the case of external purchasing strategy, how should the manufacturer's optimal planning output and external purchasing quantity be formulated? (2) Under what conditions can manufacturers use agricultural insurance strategy to manage natural risk? In the case of an agricultural insurance strategy, how should the manufacturer's optimal planning output and insurance strategy be formulated? (3) Under what conditions are the external purchasing strategy dominant to the agricultural insurance strategy? And under what conditions is the agricultural insurance strategy dominant to the external purchasing strategy?
The results of the study show that when the manufacturer's risk aversion is low, it is ineffective to hedge risks with external purchasing strategy. At this point, if the safety factor of agricultural insurance is low enough, the agricultural insurance strategy can help enterprises improve the CVaR value and better the operation state by fully compensating the shortage cost and reducing the planned output and saving the planting cost. When the manufacturer's risk aversion is high, the external purchasing strategy can eliminate the profit fluctuation caused by output uncertainty and help the company to enter the market, whereas the agricultural insurance is to help enterprises to enter the market in the way of completely compensating the shortage cost caused by adverse events. Which strategy is more effective is dependent on the relationship between the external purchasing price and the security factor. (3) With the increases of unit raising cost of raw material, the probability of adverse events, the unit revenue of a final product, and unit shortage costs, the dominating range of external purchasing strategy gradually expands, while the dominating range of agricultural insurance strategy gradually reduces. In the end, the problems, methods, and results discussed in this study have practical implications for manufacturers to manage the natural risks better, causing the raw material output uncertainty and provide theoretical basis and strategic recommendations for the manufacturers of agricultural and sideline products to manage natural risk.
Natural risk management of agricultural products; Agricultural insurance strategy; External purchasing strategy; CVaR method; Production Decision
2018-02-06
2018-06-28
F253.4
A
1004-6062(2020)03-0175-016
10.13587/j.cnki.jieem.2020.03.019
2018-02-06
2018-06-28
国家自然科学基金资助项目(71771127、71401082);山东工商学院博士启动基金资助项目(BS201725)
陈静(1983—),女,湖北潜江人;山东工商学院工商管理学院讲师,博士;研究方向:运营与供应链管理,风险管理。
Funded Project:Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (71771127, 71401082) and the Doctoral Research Start-up Project of Shandong Technology and Business University (BS201725)
中文编辑:杜 健;英文编辑:Charlie C. Chen

