血清白细胞介素-17和白细胞介素-23在狼疮性肾炎预测中的应用
叶雅丽 赵肖丽 任应鹏
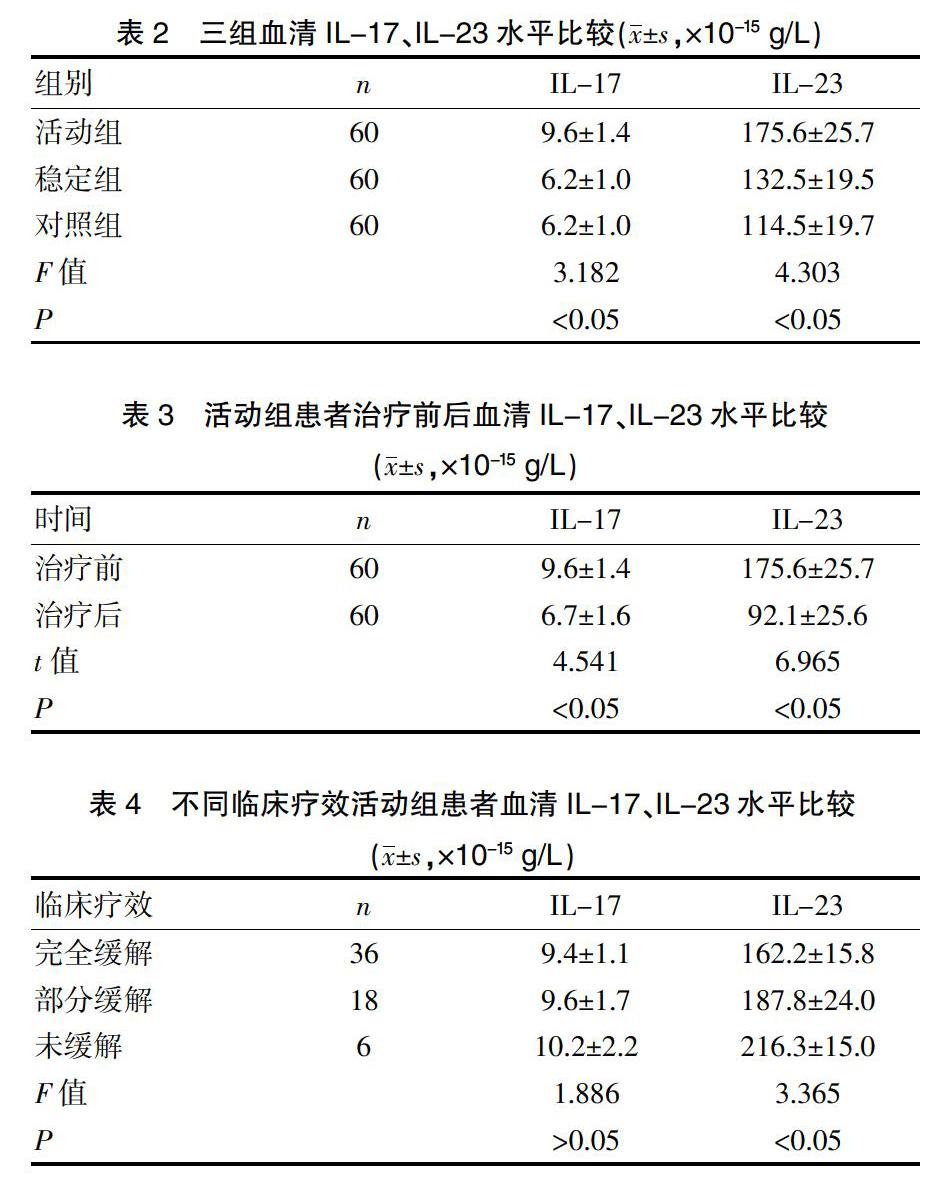

[摘要] 目的 探討血清白细胞介素-17和白细胞介素-23在狼疮性肾炎预测中的应用。 方法 对2016年8月~2018年8月我院狼疮性肾炎患者120例及健康体检者60例的临床资料进行回顾性分析,分为三组,统计分析三组人员的一般资料、血清IL-17、IL-23水平及活动组患者治疗前后的血清IL-17、IL-23水平。 结果 活动组患者的SLEDAI评分、24 h尿蛋白、AI、CI均显著高于稳定组(P<0.05),病理类型Ⅱ型、Ⅲ型比例均显著低于稳定组(P<0.05),Ⅳ型比例显著高于稳定组(P<0.05),活动组、稳定组、对照组的Scr水平逐渐降低(P<0.05),白蛋白、C3、C4水平逐渐升高(P<0.05)。活动组患者的血清IL-17水平显著高于稳定组、对照组(P<0.05);活动组患者的血清IL-23水平显著高于稳定组、对照组(P<0.05),稳定组患者的血清IL-23水平又显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。活动组患者治疗后的血清IL-17、IL-23水平均显著低于治疗前(P<0.05);完全缓解患者的血清IL-23水平显著低于部分缓解、未缓解患者(P<0.05),部分缓解患者的血清IL-23水平又显著低于未缓解患者(P<0.05)。 结论 血清白细胞介素-17和白细胞介素-23在狼疮性肾炎预测中的应用价值高。
[关键词] 血清白细胞介素-17;白细胞介素-23;狼疮性肾炎;预测
[中图分类号] R593.242 [文献标识码] B [文章编号] 1673-9701(2020)06-0158-04
[Abstract] Objective To investigate the application of serum interleukin-17 and interleukin-23 in the prediction of lupus nephritis. Methods A retrospective analysis was performed on the clinical data of 120 patients and 60 healthy examiners with lupus nephritis in our hospital from August 2016 to August 2018. The patients were divided into three groups. The general data, and serum IL-17, IL-23 levels of the three groups, and serum IL-17 and IL-23 levels in the active group before and after treatment were statistically analyzed. Results SLEDAI score, 24h urine protein, AI and CI were significantly higher in the active group than in the stable group(P<0.05). The proportion of pathological type Ⅱ and type Ⅲ were significantly lower than those in the stable group(P<0.05), and the proportion of type Ⅳ was significantly higher than that in the stable group(P<0.05). The levels of Scr in the active, stable and control group were gradually decreased(P<0.05), and the levels of albumin, C3 and C4 were gradually increased(P<0.05). The serum IL-17 level in the active group was significantly higher than that in the stable group and the control group(P<0.05); the serum IL-23 level in the active group was significantly higher than that in the stable group and the control group(P<0.05); the serum IL-23 level in the stable group was significantly higher than that in the control group(P<0.05). The levels of serum IL-17 and IL-23 after treatment in the active group were significantly lower than those before treatment(P<0.05). Serum IL-23 levels in patients with complete remission were significantly lower than those in patients with partial remission and no remission(P<0.05). Serum IL-23 levels were significantly lower in patients with partial remission than those without remission(P<0.05). Conclusion Serum interleukin-17 and interleukin-23 have a high application value in the prediction of lupus nephritis.
3讨论
狼疮性肾炎(LN)是系统性红斑狼疮(SLE)累及肾脏所引起的一种免疫复合物性肾炎,是SLE主要的合并症和主要的死亡原因。系统性红斑狼疮(systemic lupus erythematosus,SLE)是一种临床表现为有多系统损害症状的慢性系统性自身免疫疾病,其血清具有以抗核抗体为主的大量不同的自身抗体。本病病程以病情缓解和急性发作交替为特点,有内脏(肾、中枢神经)损害者预后较差。本病在我国的患病率为1/1000,高于西方国家报道的1/2000,以女性多见,尤其是20~40岁的育龄女性。
几乎所有的SLE都可能演变为LN。诊断为SLE的患者中最终可能有高达75%的患者会出现肾脏损伤,这还并未包括隐匿性的LN。因此一旦诊断SLE就应该考虑患者未来进展为LN的可能。很可惜的是并没有前瞻性对照研究来明确LN风险。因此更多是依靠经验来判断LN风险。(1)抗核抗体滴度高 虽然抗核抗体滴度高不代表当下疾病更严重。但多数学者的经验认为高滴度往往预示未来的严重度偏高。自然来说,如果当即没有LN,那么未来进展为LN的可能性偏高。(2)ds-DNA、C1q抗体、C3抗体高 LN主要是免疫复合物损伤肾脏,这包括:A 抗双链DNA抗体(即抗dsDNA或抗DNA)攻击肾小球,并与其他抗体(如Sm、SSB、SSA)、补体结合起来损伤肾脏。B 抗C1q抗体与补体C1q结合后形成复合物后损伤肾脏。C 补体C3的自身抗体可能参与了LN。对于相对高风险的SLE患者采用超越当下疾病活动度和严重度的治疗策略是合理的,哪怕当时患者并没有明显的肾脏损伤、神经损伤等脏器受损证据。必须提醒的是,这策略并没有前瞻性临床对照试验证实,但多数专家的个人经验会倾向这样的选择。具体治疗实际上可以参考LN的维持治疗策略。落实到药物选择上,更高剂量的羟氯喹是肯定的。如果当时还未出现明显的蛋白尿,参照陈顺乐教授、杨岫巖教授的经验采用“激素+羟氯喹+甲氨蝶呤”的策略。如果有蛋白尿但还没到需要肾脏活检程度,则建议使用MMF。总之,其治疗目标不是针对当下的疾病严重度,而是针对预估性严重度治疗。
IL-17是一种前炎症细胞因子,分泌主体为T辅助细胞(T helper cells,Th17),能够促进炎症的发生。IL-17家族包括IL-17A、IL-17B、IL-17C、IL-17D、IL-17E、IL-17F 6个成员,通常情况下IL-17指IL-17A[6]。和健康人员相比,LN患者具有较高的血清IL-17水平,其可能在LN发病中发挥着极为重要的作用[7]。IL-23主要来源抗原递呈细胞,是一种新异源二聚体,形成主体为IL-12(p40p35)的p19和p40亚单位,即IL-23(p40p19)[8]。IL-23一方面能够对记忆性T细胞(Tm)形成进行诱导,另一方面还能够为Th17的分化、增殖及功能维持提供良好的前提条件[9-12]。LN患者体内的IL-23表达较高,增殖的T细胞对IL-17、IL-23受体进行高表达,在LN发病中,IL-23可能发挥着极为重要的作用[13-16]。
相关医学研究表明[17-20],在LN致病中,IL-17、IL-23可能发挥着极为重要的作用,IL-17能够对LN疾病活动及病理急性指数进行评估,IL-23能够对LN活动期治疗疗效进行预测。本研究结果表明,活动组患者的SLEDAI评分、24 h尿蛋白、AI、CI均显著高于稳定组(P<0.05),病理类型Ⅱ型、Ⅲ型比例均显著低于稳定组(P<0.05),Ⅳ型比例显著高于稳定组(P<0.05),活动组、稳定组、对照组的Scr水平逐渐降低(P<0.05),白蛋白、C3、C4水平逐渐升高(P<0.05)。活动组患者的血清IL-17水平显著高于稳定组、对照组(P<0.05);活动组患者的血清IL-23水平显著高于稳定组、对照组(P<0.05),稳定组患者的血清IL-23水平又显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。活动组患者治疗后的血清IL-17、IL-23水平均显著低于治疗前(P<0.05);完全缓解患者的血清IL-23水平显著低于部分缓解、未缓解患者(P<0.05),部分缓解患者的血清IL-23水平又显著低于未缓解患者(P<0.05),与上述相关医学研究结果一致。
总之,血清白细胞介素-17和白细胞介素-23在狼疮性肾炎预测中的应用价值高,值得推广。
[参考文献]
[1] 刘美兰,马福哲,吴昊,等.狼疮性肾炎患者血清IL-18、IL-34水平及其意义[J].中国现代医学杂志,2018, 28(2):53-56.
[2] 杨建,厉吉霞,姜虹,等.Ⅳ型和Ⅴ型狼疮性肾炎患者辅助性T细胞17和白细胞介素-17、-6的表达水平及其临床意义[J].国际输血及血液学杂志,2016,39(2):108-113.
[3] 杨进山,雍春娥.中药组方联合环磷酰胺治疗狼疮性肾炎的临床疗效及对血清IF N-γ、TGF-β1、IL-4水平的影响[J].中西医结合研究,2017,9(4):179-182.
[4] 乔建芬,张瑶琳,颜帅,等.肾肝宁胶囊联合来氟米特治疗狼疮性肾炎的临床研究[J].现代药物与临床,2018,33(8):2091-2094.
[5] 顾丽萍,杨贵丽,陈幼发,等.Th22细胞及其功能分子IL-22在狼疮性肾炎中的作用研究[J].中国免疫学杂志,2017,33(5):755-758.
[6] 袁一孟,郑戈.连续血液净化辅助甲基强的松龙及环磷酰胺联合冲击对狼疮性肾炎合并狼疮性肺炎患者Th1/Th2细胞因子失衡的影响[J].临床肺科杂志,2017, 22(8):1427-1430.
[7] 吴立波,文静,赵铖,等.系统性红斑狼疮患者血清中白细胞介素-33的表达及其临床意义[J].中华临床医师杂志(电子版),2016,10(5):656-662.
[8] 武彩虹,銀广悦,钱成荣,等.可溶性E-钙粘蛋白(SE-CAD)在系统性红斑狼疮中的临床研究[J].中国实验诊断学,2016,20(4):595-597.
[9] 谢鸣部,王芳.尿MCP-1、细胞免疫水平检测对狼疮性肾炎患者病情评估的价值及相关性研究[J].中国现代医生,2017,55(34):4-6.
[10] 邱宏芬,张萍.狼疮性肾炎患者并发感染的相关临床特点及护理[J].中国现代医生,2014,52(36):70-72.
[11] Von Visger J,Cassol C,Nori U,et al. Complete biopsy-proven resolution of deposits in recurrent proliferative glomerulonephritis with monoclonal IgG deposits (PGNMIGD) following rituximab treatment in renal allograft[J].BMC Nephrol,2019,20(1):53.
[12] Yang J,Yang X,Yang J,et al. Baicalin ameliorates lupus autoimmunity by inhibiting differentiation of Tfh cells and inducing expansion of Tfr cells[J].Cell Death Dis,2019,10(2):140.
[13] Parodis I,Ding H,Zickert A,et al. Serum Axl predicts histology-based response to induction therapy and long-term renal outcome in lupus nephritis[J].PLoS One,2019, 14(2):e0212068.
[14] Masoodi I,Sirwal IA,Anwar SK,et al. Predictors of mortality in pulmonary haemorrhage during SLE:A single centre study over eleven years[J].Open Access Maced J Med Sci,2019,7(1):92-96.
[15] Shao M,He J,Zhang R,et al. Interleukin-2 deficiency associated with renal impairment in systemic lupus erythematosus[J].J Interferon Cytokine Res,2019,39(2):117-124.
[16] He S,Liu X,Lin Z,et al. Reversible SAHH inhibitor protects against glomerulonephritis in lupus-prone mice by down regulating renal α-actinin-4 expression and stabilizing integrin-cytoskeleton linkage[J].Arthritis Res Ther,2019,21(1):40.
[17] Deng J,Xie H,Zhu L,et al. Maintenance therapy for lupus nephritis with mycophenolate mofetil or azathioprine. A meta-analysis[J]. Clin Nephrol,2019,91(3):172-179.
[18] Zhang M,Yao C,Cai J,et al. LRRK2 is involved in the pathogenesis of system lupus erythematosus through promoting pathogenic antibody production[J].J Transl Med,2019,17(1):37.
[19] Rovin BH,Caster DJ,Cattran DC,et al. Management and treatment of glomerular diseases(part 2):Conclusions from a kidney disease:Improving global outcomes(KDIGO) controversies conference[J].Kidney Int,2019,95(2):281-295.
[20] Hax V,Moro ALD,Piovesan RR,et al. Human immunodeficiency virus in a cohort of systemic lupus erythematosus patients[J].Adv Rheumatol,2018,58(1):12.
(收稿日期:2019-02-18)

