Abnormal serum carbohydrate antigen 19-9 levels in a patient with splenic retiform haemangioendothelioma concomitant with hepatic amyloidosis: A case report
Kai-Di Sun,Yu-Jie Zhang,Lan-Ping Zhu,Bo Yang,Sai-Yu Wang,Zi-Han Yu,Hai-Cheng Zhang,Xin Chen
Kai-Di Sun,Lan-Ping Zhu,Bo Yang,Sai-Yu Wang,Zi-Han Yu,Hai-Cheng Zhang,Xin Chen,Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology,Tianjin Medical University General Hospital,Tianjin 300052,China
Yu-Jie Zhang,Department of Pathology,Tianjin Medical University General Hospital,Tianjin 300052,China
Abstract
BACKGROUND
Carbohydrate antigen 19-9(CA 19-9) is a glycoprotein that is used as a reliable tool for monitoring pancreatic cancer.Serum CA 19-9 levels are increased in patients suffering from liver,lung,and other non-malignant diseases.Haemangioendothelioma is a vascular neoplasm with a borderline biological behaviour.However,no case of haemangioendothelioma has yet been reported to be associated with CA 19-9.
CASE SUMMARY
A 54-year-old Chinese man was referred to our hospital for discontinuous fatigue and unintentional weight loss for over one year.Laboratory investigations revealed an elevated serum CA 19-9 concentration of 39 IU/mL(reference interval,0-37 IU/mL) over one year before admission.Afterwards,coagulopathy appeared,and the patient's serum CA 19-9 concentration increased continuously.At the time of admission,abdominal pain and haemorrhagic shock burst occurred,and emergency medical operation was performed.Laboratory investigations conducted upon admission showed a serum CA19-9 concentration of 392.56 IU/mL.Surgical resection of the spleen was undertaken,and pathological examination showed retiform haemangioendothelioma.The patient developed jaundice ten days after surgical excision of the spleen.Pathological examination of needle biopsy samples of the liver yielded a diagnosis of hepatic amyloidosis.
CONCLUSION
We describe a rare case of splenic retiform haemangioenthelioma concomitant with hepatic amyloidosis.Physicians should note abnormal serum CA 19-9 levels with early symptoms of fatigue and unintentional weight loss.
Key words:Carbohydrate antigen 19-9;Haemangioendothelioma;Amyloidosis;Spleen;Liver;Case report
INTRODUCTION
Carbohydrate antigen 19-9(CA 19-9) is assumed to be an abundant product of cancer cells[1].For over 30 years now,CA 19-9 has been used as a prognostic indicator and reliable tool for monitoring pancreatic and gastrointestinal cancer[2,3].However,CA 19-9 is not a tumour-specific antigen because serum levels of the antigen may also be elevated in patients without malignant disease[4,5].Haemangioenthelioma is a vascular neoplasm with a borderline biological behaviour intermediate between entirely benign haemangiomas and highly malignant giosarcomas[6-8].Since the original description of the neoplasm in 1908,haemangioendothelioma cases have seldom been reported.Amyloidosis is characterised by extracellular deposition of insoluble fibrillar proteins or aberrantly folded and assembled protein fragments in a variety of tissues[9-11].To the best of our knowledge,this report is the first to describe increased serum CA19-9 with haemangioenthelioma and amyloidosis.The timeline is shown in Supplementary Table 1.
CASE PRESENTATION
Chief complaints
The patient had discontinuous fatigue and unintentional weight loss for over one year.
History of present illness
A 54-year-old Chinese man was referred to our hospital for discontinuous fatigue and unintentional weight loss for over one year.Laboratory investigations revealed an elevated,and continuously increasing,serum CA 19-9 concentration of 39 IU/mL(reference interval,0-37 IU/mL) over one year before admission.Coagulopathy appeared,but haematological disease was excluded.Four months prior to admission,the patient's serum CA 19-9 concentration was 178 IU/mL.At the time of admission,abdominal pain and haemorrhagic shock burst occurred,and emergency medical operation was performed.The patient developed jaundice ten days after surgical excision of the spleen.
History of past illness
The patient had a history of carrying inactive hepatitis B surface antigen.
Personal and family history
He denied any special personal or family history of haemangioenthelioma syndrome or other disease.
FINAL DIAGNOSIS
The patient was diagnosed with splenic retiform haemangioendothelioma and hepatic amyloidosis.
TREATMENT
After diagnosis of hepatic amyloidosis,the patient started choleretic and liver protection treatment with ursodeoxycholic acid and S-adenosylmethionine.
Physical examination
Physical examination revealed jaundice,and the remaining findings were unremarkable.
Laboratory examinations
Laboratory tests showed alanine aminotransferase of 105U/L,aspartate aminotransferase of 59 U/L,alkaline phosphatase of 180 U/L,direct bilirubin of 130µmol/L,total bilirubin of 180 µmol/L,gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase of 127U/L,alpha-1-antitrypsin of 146mg/dL,and ceruloplasmin of 28 mg/dL.The patient's serum CA 19-9 concentration was 392.56 IU/mL.Leukocyte count,lymphocyte count,and C-reactive protein were normal.Tests for antinuclear,smooth muscle,antimitochondrial,and liver-kidney microsomal antibodies and hepatitis B virus(HBV) DNA were negative.Immunoelectrophoresis was negative for immune globulin,monoclonal immunoglobulin kappa light chain,and monoclonal immunoglobulin lambda light chain.Hepatotropic viruses(except HBV) and nonhepatotropic viruses were negative.Urinalysis results were negative for protein(reference range negative,0 g/L).Ultrasound cardiogram was normal.
Imaging examinations
Computed tomography(CT) performed 4 mo before admission confirmed the presence of haepatomegaly and diffuse hypodense liver lesions,uneven enhancement after intravenous contrast,and the absence of mass effects.CT also showed lowdensity plaques in the spleen,uneven enhancement after intravenous contrast,and the absence of mass effects(Figure 1A).CT was repeated after surgical excision of the spleen and after the appearance of jaundice.Findings were identical to previous liver results,but the volume of the liver was larger than that recorded in the previous 4 mo(Figure 1B and C).
Pathologic findings
Pathological examination showed that the spleen was 17 cm × 13 cm × 5 cm in size.Several cracks measuring 3-7 cm in length and a solid-cystic lesion were seen on the cut surface.The capsular structure of the spleen had nearly disappeared.Histologically,elongated arborising vessels arranged in an anastomosing pattern were seen.Immunohistochemically,neoplastic cells were platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule-1 [cluster of differentiation(CD) 31]+,friend leukemia integration 1+,cytokeratin-,and CD34 antigen(CD34)-;a Ki-67 antigen index of 15% was also noted(Figure 2).Retiform haemangioendothelioma was thus confirmed.
The presence of persistent bilirubin elevation could not be explained despite serologic investigation.Thus,needle biopsy of the liver was performed.Sampled areas were Congo red stain- and methyl violet stain-positive on polarising microscopy,thus suggesting amyloid deposits.Haepatocytes and bile capillary cholestasis with compressed haepatocytes were observed.Sinusoidal cells were positive for CD31,and vascular endothelial cells were positive for CD34(Figure 3).
Gastrointestinal biopsy was performed.Gastroscopy showed mild atrophic gastritis and mild intestinal metaplasia with dysplasia in the gastric antrum.Sampled areas were Congo red stain- and methyl violet stain-negative(Supplementary Figure 1A and B).Colonoscopy showed mucosa chronic inflammation and mild dysplasia in focal glands with lymphoid tissue increasing in the lamina propria.Sampled areas were Congo red stain- and methyl violet stain-negative(Supplementary Figure 2A and B).Evidence of amyloid deposits was not found basedon the above histological findings.Moreover,no evidence of involvement of the gastrointestinal tract,kidneys,heart,and bone marrow was observed.

Figure 1 Computed tomography images.
OUTCOME AND FOLLOW-UP
Four months after resection of the spleen,the patient was in good condition without recurrence or any other symptoms.Laboratory data revealed alanine aminotransferase of 35 U/L,aspartate aminotransferase of 42 U/L,alkaline phosphatase of 135 U/L,direct bilirubin of 5.3 µmol/L,total bilirubin of 11.5 µmol/L,gammaglutamyltranspeptidase of 166 U/L,and serum CA 19-9 concentration of 107.71 IU/mL.Magnetic resonance imaging showed diffuse hepatomegaly and even signals(Figure 4).The size of the liver was larger than that noted during the duration of the patient's hospital stay.
DISCUSSION
CA 19-9 is a tumour-associated antigen originally isolated from a human colorectal cancer cell line in 1979 by Koprowskiet al[12].To date,148 studies related to CA 19-9 have been searched on PubMed.In these studies,CA 19-9 was used to monitor various cancer types and as a prognostic marker in pancreatic,colon,and stomach adenocarcinoma[13,14].Giorgioet al[15]reported a case of large benign epidermoid splenic cyst with serum CA 19-9 levels increasing to 3103 IU/mL.However,no article reporting splenic haemangioma or hepatic amyloidosis associated with increased concentrations of serum CA 19-9 has yet been published.
CA 19-9 is a glycoprotein that is widely present in normal glandular epithelial cells with secretory effects[11,16-18].The CA 19-9 epitope has been identified to be a glycan containing a sialylated Lewis-a structural motif[19,20];it may be elevated in the bile,pancreatic juice,and intestinal digestive juice under non-malignant physiological conditions[21].During the progressive course of neoplastic disease,hypoxia induces the synthesis of sialyl-Lewis antigens in hypoxia-resistant cells[22].CA 19-9 accumulates in high-grade neoplastic cells and is released to the blood circulation due to serious cell damage[4,5].In the present case,we observed a corresponding change in CA 19-9 level between the development of splenic retiform haemangioenthelioma and in the followup period after surgical excision of the lesion.CA 19-9 levels peaked during rupture of the spleen.The mechanism responsible for increased CA 19-9 levels in splenic retiform haemangioenthelioma has yet to be defined.Retiform haemangio-endothelioma is an infiltrative neoplasm composed of elongated arborising vessels arranged in an anastomosing pattern.Vessels in narrow lumina are lined by a single layer of hobnail-like endothelial cells[7].Hypoxia plays a critical role in the pathogenesis of vascular proliferation;it is also a driving force for vascular remodelling in various pathological situations,especially haemangioenthelioma[23,24].Thus,the presence of a hypoxic environment during the development of haemangioenthelioma is hypothesised to result in increased CA 19-9 synthesis and release to the blood.

Figure 2 Microscopic appearance and immunophenotypes of the spleen.
After surgical excision of the spleen,the patient developed jaundice and was diagnosed with hepatic amyloidosis by biopsy.Amyloidosis involving two or more organs/systems may portend a poor prognosis.However,the condition of the patient was not as poor as expected.Little is known about the relationships amongst CA 19-9,haemangioenthelioma,and amyloidosis.Amyloid deposits would compressed bile ductules in hepatic amyloidosis[25,26].Several studies observed an obvious correlation between CA-19-9 and cholestasis[16,27,28].CA19-9 is secreted in a mucin bound form by the biliary and gallbladder mucosa and is exclusively excreted in bile.In the cholestatic situation,overload bile lead CA 19-9 epitope to release to the blood circulation[29].
Secondary amyloidosis may develop in the setting of chronic infection such as tuberculosis[30].However,we thought that such possibility is slim in this case.First,the patient did not present any clinical manifestation of chronic infection such as fever,local swelling,pain,and vomiting.Second,markers of the inflammatory response including leukocyte count,lymphocyte count,C-reactive protein,and autoimmune rheumatic indicators were normal.Lastly,infection with bacteria or virus(except HBV) was ruled out through serologic investigation and biopsy.The patient had a history of carrying inactive hepatitis B surface antigen but HBV DNA was negative.
Lesions of the liver and spleen were observed at the same time.Although the patient's CA 19-9 level decreased after surgical excision of the spleen,it did not reach the normal range.Therefore,we speculated that a potent mechanism of hepatic amyloidosis may be related with CA 19-9.Haemorrhagic shock burst and emergency medical operation may be inducements aggravating hepatic amyloidosis.Taking these considerations together,we recommend a diagnosis of primary hepatic amyloidosis rather than secondary hepatic amyloidosis.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion,we describe a rare case of splenic retiform haemangioentheliomaconcomitant with hepatic amyloidosis.Although the clinical specificity of CA 19-9 is weak,subsequent investigations of the underlying lesion are required once continuously increasing serum CA 19-9 is detected,especially when accompanied with early symptoms of fatigue and unintentional weight loss.Further studies are needed to fully elucidate the biological mechanisms underlying this syndrome.

Figure 3 Microscopic appearance and immunophenotypes of liver biopsy.
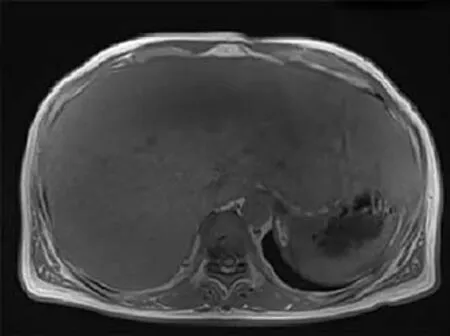
Figure 4 Magnetic resonance imaging showing diffuse haepatomegaly and even signals.
 World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年5期
World Journal of Clinical Cases2020年5期
- World Journal of Clinical Cases的其它文章
- Gut microbiota and nutrient interactions with skin in psoriasis: A comprehensive review of animal and human studies
- Microbiota-gut-brain axis and its affect inflammatory bowel disease:Pathophysiological concepts and insights for clinicians
- Distal esophageal spasm: Update on diagnosis and management in the era of high-resolution manometry
- Clinical course of percutaneous cholecystostomies: A crosssectional study
- Clinical characteristics and 28-d outcomes of bacterial infections in patients with hepatitis B virus-related acute-on-chronic liver failure
- Application of hybrid operating rooms for treating spinal dural arteriovenous fistula
