四象限探测器的信号光捕获与跟踪技术研究
鲁 倩,任 斌,边晶莹
四象限探测器的信号光捕获与跟踪技术研究
鲁 倩,任 斌*,边晶莹
西安空间无线电技术研究所,陕西 西安 710000
针对空间激光通信系统小型化设计的需求,提出了使用四象限探测器实现捕获与跟踪的方案。通过分析四象限探测器上光斑的位置分布,推导了三种光斑分布的4QD捕获牵引模型,通过对4QD光斑位置的解算以及与跟踪机构的精准标定,实现了4QD的高精度跟踪。在实验室基于一台激光终端与系统测试平台,对四象限探测器的捕获与跟踪方案及性能进行了实验验证,测试结果表明,在实验室动态条件下,用4QD作为捕获及跟踪探测器,捕获概率高达100%,跟踪精度优于3 μrad,验证了该方案的可行性,为激光终端小型化设计奠定了基础。
激光通信;四象限探测器;捕获与跟踪复用
1 引 言
相比于微波射频通信技术,卫星激光通信技术以其通信传输速率高、信息保密性好、体积小、重量轻、功耗低、无需频率使用许可、抗干扰性强等诸多优点,使其具有广泛的应用前景,目前各国新一代卫星通信技术已经将研究重点转移至小型化、系列化方向[1],不断朝着卫星激光通信技术实用方向前进。
空间激光通信系统在建立通信链路前,需要完成对目标的捕获、瞄准和跟踪(acquisition pointing tracking,APT)任务[2]。在激光通信中,通常选用电荷耦合器件(CCD)或四象限探测器件(four-quadrant detector,4QD)作为捕获、跟踪探测器来确定光斑质心,将脱靶量送给伺服系统完成捕获、跟踪任务[3]。目前,激光通信系统大都选择800 nm和1550 nm波段。与800 nm波段激光相比较,1550 nm激光具有对人体安全和大气环境影响小等优点[4];但是对于1550 nm波段激光,CCD探测器响应灵敏度低,难以满足使用要求,4QD则是理想的选择[5-6]。近几年,出现了很多4QD在激光通信领域方面的研究,例如长春工业大学的佟首峰老师研究了基于四象限探测器的跟踪与通信技术[7];中国科学院光电技术研究所马晓燠老师分析了在有噪声和死区的条件下的四象限探测器的光斑能量探测率、质心探测误差和光斑位移灵敏度[8]。目前对于4QD的应用多数仅限于桌面系统,没有进行动态试验验证,将4QD同时应用于捕获及跟踪的研究未有报道,使用4QD作为捕获、跟踪探测器的系统不需要额外增加大功率信标激光器、信标发射支路以及信标光接收探测器,可最大限度地降低系统的复杂度、功耗及体积,有助于激光载荷实现轻量化与小型化[9]。
本文针对空间激光通信系统小型化设计的需求,以及1550 nm信号光捕获、跟踪的要求,提出应用4QD探测器实现信号光捕获与跟踪技术,这不仅能提高光能利用率,还能有效降低传统激光通信终端的系统复杂度、体积及功耗。
2 四象限探测器的捕获、跟踪复用原理
4QD捕获与跟踪复用系统由激光调制发射平台、捕跟探测器、精指向机构、粗指向机构、捕跟控制单元等部分构成,如图1所示。激光器经信号发生器调制后产生强度调制信号光,经光纤耦合至光纤准直镜发出,经接收终端光学组件折转后,使信号光照射在精指向机构反射镜上,激光光束经45°反射后被光学天线接收,经透镜会聚在捕跟探测器4QD的光敏面上。QD根据各象限接收到的光能量产生相应的光电流,该电流信号在后级信号放大处理电路作用下输出电压信号。为了实现捕获与跟踪的复用,需要实时解算出光斑位置信息,与粗指向机构进行坐标标定,用以实现粗指向机构对信号光的捕获。当粗指向机构完成捕获后,需要实时解算光斑与目标位置的偏移量,驱动精跟踪机构偏转实现闭环跟踪控制,完成对光斑的实时跟踪。
3 四象限探测器捕获、跟踪策略设计
3.1 四象限探测器捕获策略
相比于跟踪,捕获过程更注重快速完成视场牵引,对于探测角分辨率没有那么严苛的要求。另外,由于光学设计上捕获要有足够大的视场,一般设计在2 mrad~5 mrad,此时焦距很短,光斑小到接近4QD沟道死区的量级,沟道损失高达7 dB~8 dB,甚至更高,导致光斑容易落入沟道。4QD作为捕获探测器时,一般光学系统会通过离焦的方式使得光斑变大,用以减小沟道损失(<1 dB);当然,光斑大小也不能太大,这样会使得4QD的探测角度分辨率降低,变得“反应迟钝”。
捕获的难度在于光斑的位置解算,只有在4QD中心区域(几百mrad)内,光斑才能分布在四个象限上,才能解算出光斑的有效位置,在其他高达90%的区域均无法解算出有效位置,光斑在QD上的位置分布有如图2所示三类。

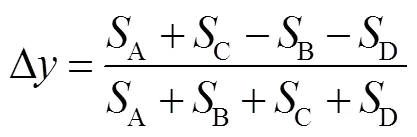
其中:A、B、C、D分别为光斑在四象限探测器A、B、C、D上各象限所占的面积。
捕获过程本质是快速实现视场牵引,将光斑快速送入跟踪视场建立稳定跟踪链路。所以,无论能否解算到有效位置信号,只要捕获探测器上探测到有效光信号就必须快速捕获,将光斑拉至中心区域,过渡到跟踪视场。根据以上分析,在第一种工况下解算出光斑有效位置,进行探测器和机构的关系标定和系统模值的标定,使得执行机构偏转方向和幅度比例均映射与探测器一致。

显然沿着这些特定方向快速收敛能够快速达到指定区域(图3彩色区域),收敛方式有三种。
在有效位置解算区域以外,除了根据光斑所在的象限和“缠绕”沟道的信息来判断并调整收敛方向,还必须设定适当的模量,设单位模量用表示,执行模量倍率用表示,则总模量a=´。为保证光斑能100%收敛调整,单位模量需要小于中间区域所对应的角度,执行模量倍率太大可能导致发散,太小可能导致收敛时间增加,需要实际实验过程中调试给出。

图2 光斑在4QD上的位置分布

图3 光斑在4QD上的收敛方式
完成执行机构(以下简称FPA)与探测器的映射后,两者的关系可由以下数学解析给出:


或


或


或

或
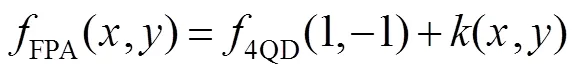
或

根据上述可知,解算结果绝对值为1,对应着多个光斑位置,为无效解。但实际中,考虑真实的位置分布,能够解算出1也分两种情况;第一种即是能够解算有效位置的中心区域边界,是一个临界区域;第二种则代表临界区以外的大片区域。前者可以称之为“真1”,后者可以称之为“假1”,在以上的解析中将变量赋值为1或者-1,就是指“真1”,以此直接生成带有方向的单位模量。
3.2 四象限探测器跟踪控制设计
四象限探测器对光斑的跟踪是通过检测光斑在光敏面上的能量变化实现的。当激光束成像于探测器的光敏面上时,形成一个光斑,光斑在探测器的4个象限中的面积分别为A、B、C、D,各象限光斑在探测器表面分别产生的光生电流为A、B、C、D。如果光斑的能量服从均匀分布,则各象限上的光功率与其象限上的分布面积成正比,因此可以根据电流的大小计算出光斑在坐标系中的位置。假设光斑的中心相对于探测器中心产生偏移时,偏移量分别为D,D,当激光光斑中心与探测器中心重合时,即D=D=0,这时四象限中的光斑面积相同,即A=B=C=D,所对应各象限产生的光生电流相等,即A=B=C=D。当激光光斑中心与探测器中心有偏移量时,光斑的偏移将改变光斑在四个象限上的投影面积,光斑的偏移量D、D与光斑在4个象限上的投影面积差成正比,即与探测器各象限的输出电流差成正比[10]。



式中为各象限上的面积,为各象限上产生的光生电流。为一个可调节系数,用于将式(12)、式(13)结果转换成光斑距离中心的偏移距离。当光束的入射角与轴成一定角度时,光束经过光学系统后,聚焦点相对于原点0产生偏移量D,D。将光斑在QD上的位置分布与精指向机构进行坐标标定,通过光斑在QD上的位置偏移量驱动精指向机构进行方位与俯仰方向的快速偏转,从而实现对光斑的跟踪。
4 模拟实验
基于一套激光载荷与系统测试平台,进行了基于4QD捕获、跟踪的模拟实验。该系统测试平台可发射1550 nm、1 M强度调制信号光,经过若干光学反射镜搭建的光学系统,将平行光发射至激光载荷。实验用激光载荷为一台捕跟探测器为4QD的激光终端,可接收1550 nm、1 M强度调制信号光。探测器视场为2 mrad,粗指向机构为潜望式结构,指向精度优于30mrad,精跟踪机构为压电陶瓷二维偏转机构,偏转范围为4 mrad,定位精度优于3mrad。
实验过程中激光终端放置在二维转台上,分别按照不确定区域为1 mrad上、下、左、右拉偏至平台平行光管,开启平台振动模拟器,振动幅度设置为10mrad@100 Hz,进行10次实验,每次实验以系统测试平台监测相机看到激光终端发出的信号光到达实验前标定的同轴点位置作为实验成功标志。成功跟踪后,开启二维转台,模拟轨道运动,轨道速度设置为0.3 °/s,此次实验捕获成功概率100%。通过系统测试平台跟踪监测子系统统计得到的跟踪精度如图4所示,图5为跟踪过程中示波器监测到4QD各象限电压信号。

图4 跟踪精度

图5 4QD跟踪过程中各象限电压信号
由图4可看出,本次试验使用4QD作为跟踪探测器,在跟踪监测系统上监测到的和方向跟踪精度均优于3mrad。由图5可看出,跟踪过程中示波器监测到的4QD探测器各象限的电压值相等,即光斑位于4QD中心,为本次试验的跟踪目标位置,且跟踪稳定。
5 结 论
针对空间激光通信系统轻小型化和低功耗要求,本文提出了采用4QD探测器实现捕获与跟踪复合探测的方案。对系统的设计方案进行了详细分析,设计了试验方案并进行了试验验证。测试结果表明,在实验室动态条件下,用4QD作为捕获探测器,捕获概率高达100%,跟踪精度优于3mrad,验证了该方案的可行性。
[1] Wang X G, Wang S M, Chen D D,. Design of laser tracking system with quadrant detector[J]., 2017, 47(4): 432–436.
王选钢, 王仕明, 陈丹丹, 等. 采用四象限探测器的激光跟踪系统设计[J]. 激光与红外, 2017, 47(4): 432–436.
[2] Deng K, Wang B Z, Zhao G H,. Principle and performance analysis of coherent tracking sensor based on local oscillator beam nutation[J]., 2014, 22(19): 23528–23538.
[3] Zhang Y L, Jiang H L, Zhang L,. Research on tracking and communication technology base on the four-quadrant detector[J]., 2017, 41(10): 27–29.
张艺蓝, 姜会林, 张磊, 等. 基于四象限探测器的跟踪与通信技术研究[J]. 光通信技术, 2017, 41(10): 27–29.
[4] Han C, Bai B X, Yang H M,. Study four-quadrant detector in the free space laser communication[J]., 2009, 36(8): 2030–2034.
韩成, 白宝兴, 杨华民, 等. 自由空间激光通信四象限探测器性能研究[J]. 中国激光, 2009, 36(8): 2030–2034.
[5] Song Z Y, Fu Y, Fan X K,. Analysis and simulation of positioning accuracy of four-quadrant detector[J].(), 2018, 41(2): 41–44.
宋哲宇, 付芸, 范新坤, 等. 四象限探测器定位精度的分析与仿真[J]. 长春理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 41(2): 41–44.
[6] Lin X, Guo Y, Han M Z,. Research on two-dimensional laser beam scanning and tracking system based on four quadrant detector[J]., 2018, 39(3): 425–430.
林鑫, 郭迎, 韩明珠, 等. 基于四象限探测器的激光束二维扫描跟踪系统的研究[J]. 半导体光电, 2018, 39(3): 425–430.
[7] Fan X K, Zhang L, Song Y S,. Simultaneous detection technology of tracking and communication based on four-quadrant detector[J]., 2017, 44(9): 0906009.
范新坤, 张磊, 宋延嵩, 等. 四象限探测器的跟踪与通信复合探测技术[J]. 中国激光, 2017, 44(9): 0906009.
[8] Gu Y. Research on the multiplexing technology of tracking and communication based on the four quadrant detector[D]. Changchun: Changchun University of Science and Technology, 2016: 1–7.
谷野. 基于四象限探测器的跟踪与通信复用技术研究[D]长春: 长春理工大学, 2016: 1–7.
[9] Zhao X, Song Y S, Tong S F,. Dynamic demonstration experiment of acquisition, pointing and tracking system in space laser communication[J]., 2014, 2014, 41(3): 0305005.
赵馨, 宋延嵩, 佟首峰, 等. 空间激光通信捕获、对准、跟踪系统动态演示实验[J]. 中国激光, 2014, 41(3): 0305005.
[10] Guo X K, Zhang Y M, He S J. Study on high precision positioning algorithm of spot center based on the four-quadrant detector[J]., 2017, 47(11): 1353–1357.
郭小康, 张彦梅, 贺仕杰. 基于四象限探测器的光斑中心高精度定位算法[J]. 激光与红外, 2017, 47(11): 1353–1357.
Research on acquisition and tracking technology for the four-quadrant detector
Lu Qian, Ren Bin*, Bian Jingying
Xi¢an Institute of Space Radio Technology, Xi¢an, Shaanxi 710000, China

Convergence mode of light spots on the four-quadrant detector
Overview:Before establishing the communication link, acquisition, pointing and tracking (APT) is needed to complete in the space laser communication system. Charge coupled device (CCD) or four-quadrant detector (4QD) are usually selected as capture and tracking detectors to determine the spot center, and miss distance is sent to the servo system to complete the capture and tracking tasks. At present, most laser communication systems choose 800 nm and 1550 nm. Compared with the 800 nm, 1550 nm laser has the advantages of having little impact on human safety and atmospheric environment. However, CCD detector has low response sensitivity and cannot meet the requirements for the 1550 nm, so 4QD is the ideal choice. In recent years, there have been many researches on 4QD in the field of laser communication. For 4QD applications mostly limited to the desktop system, not to dynamic test, 4QD is applied to capture and tracking studies did not report. Using 4QD as capture and tracking detector, laser communication system does not need to be high power beacon laser, the beacon transmitting branch and beacon capture detector. It can reduce the complexity of the system, power and volume.
Aiming at the space laser communication system requirement of miniaturization, this paper proposes a scheme of using the four-quadrant detector to complete the acquisition and tracking. By analyzing the position distribution of the spots on the 4QD, the acquisition models are derived for the three kinds of spots distribution. Through the calculation of the position of the spots and the accurate calibration of the tracking mechanism, the high precision tracking is realized. Then besed on the laserteco and system test platform the capture and tracking scheme and detection performance of the 4QD are experimentally verified. The laser terminal used in the experiment is a laser terminal with a tracking detector of 4QD, which can receive 1550 nm and 1 M intensity modulation signal light. The detector's field of view is 2 mrad, the coarse pointing mechanism is a latent looking structure, and the pointing accuracy is better than 30mrad. The fine tracking mechanism is a two-dimensional deflection mechanism of piezoelectric ceramics. Its deflection range is 4mrad and positioning accuracy is better than 3mrad. The test results show that under the laboratory dynamic conditions, using 4QD as the capture and tracking detector, the capture probability is up to 100%, and tracking accuracy is better than 3mrad, which verifies the feasibility of the scheme and lays a foundation for the miniaturization design of the laser terminal.
Citation: Lu Q, Ren B, Bian J YResearch on acquisition and tracking technology for the four-quadrant detector[J]., 2020, 47(3): 190559
Research on acquisition and tracking technology for the four-quadrant detector
Lu Qian, Ren Bin*, Bian Jingying
Xi¢an Institute of Space Radio Technology, Xi¢an, Shaanxi 710000, China
Aiming at the space laser communication system requirement of miniaturization, this paper proposes a scheme of using the four-quadrant detector to complete the acquisition and tracking. By analyzing the position distribution of the spots on the four-quadrant detector (4QD), the acquisition models are derived for the three kinds of spots distribution. Through the calculation of the position of the spots and the accurate calibration of the tracking mechanism, the high precision tracking is realized. Then besed on the laserteco and system test platform the capture and tracking scheme and detection performance of the 4QD are experimentally verified. The test results show that under the laboratory dynamic conditions, using 4QD as the capture and tracking detector, the capture probability is up to 100%, and tracking accuracy is better than 3 μrad, which verifies the feasibility of the scheme and lays a foundation for the miniaturization design of the laser terminal.
optical communication; four-quadrant detector; acquisition and tracking multiplexing
TB872;TN929.1
A
10.12086/oee.2020.190559
: Lu Q, Ren B, Bian J Y. Research on acquisition and tracking technology for the four-quadrant detector[J]., 2020,47(3): 190559
2019-09-20;
2019-12-16作者简介:鲁倩(1986-),女,硕士研究生,工程师,主要从事激光通信捕获与跟踪技术的研究。E-mail:qlu1986@126.com
任斌(1986-),男,硕士,高级工程师,激光通信捕获与跟踪技术的研究。E-mail:renbin.0934@163.com
鲁倩,任斌,边晶莹. 四象限探测器的信号光捕获与跟踪技术研究[J]. 光电工程,2020,47(3): 190559
* E-mail: renbin.0934@163.com

