SS-OCTA对黑色素瘤皮肤结构和血管的成像实验
刘敬璇,樊金宇,汪 权,史国华*
SS-OCTA对黑色素瘤皮肤结构和血管的成像实验
刘敬璇1,2,樊金宇2,汪 权2,史国华2*
1中国科学技术大学,安徽 合肥 230000;2中国科学院苏州生物医学工程技术研究所,江苏 苏州 215000
扫频源光学相干层析血管成像(SS-OCTA)是一种基于分频幅去相关血管造影法(SSADA)的新型血管成像技术,在肿瘤等疾病的早期诊断方面拥有较大前景。本文在5.12 mm´5.12 mm成像视场、标准图像最大信噪比34.3 dB的SS-OCTA成像平台,对黑色素瘤C57BL6小鼠进行皮肤结构和血管成像采集。结果表明在皮肤科疾病的早期诊断方面,利用SS-OCTA系统进行血管成像优于结构成像。
扫频源光学相干层析血管成像;皮肤结构;肿瘤血管;黑色素瘤;SS-OCTA
1 引 言
近年来,光学相干层析成像(Optical coherence tomography, OCT)迅速发展,成为一种热门的新型成像技术[1]。OCT通过测量光学弱相干反射和背向散射,利用超外差探测技术提高信噪比获取生物组织断层图像[2]。在保证一定探测深度的前提下,OCT兼具非侵入、高分辨和高速成像的优点,非常适合生物医学领域的应用[2-3]。扫频源光学相干层析血管成像(swept source optical coherence tomography angiography,SS-OCTA)是一种基于分频幅去相关血管造影法(split spectrum amplitude deeorrelation angiography,SSADA)的高分辨率的新型非侵入性血管成像技术[4],主要用于血管内红细胞运动的检测和测量[5-6]。SS-OCTA依旧以迈克尔逊干涉仪作为基础光路[7],再通过测量组织后向散射光的低相干干涉信号进行断层成像,轴向分辨率可达1mm~15mm,能够清晰显示微细结构,通过对截面图进行三维重构,可以获取生物组织结构的3D图像,在眼科、皮肤科成像、肿瘤检测等领域有广泛的应用[2,8]。尤其在眼科领域的眼底血管成像方面,SS-OCTA除了拥有传统OCT可获得血管结构信息的优点以外,还能够分层观察视网膜脉络膜血管形态及血流改变情况,使用伪彩可区分正常与异常的血管结构,并且能够对血流信号进行探测和量化分析,将原始全频谱图像分裂为数个不同频谱图像并减少其噪声,提高信噪比,然后再将其合并,从而达到视网膜、脉络膜各层血管形态在横断面的清晰成像[5-8,15-17]。
实体瘤的生长对受到诱导所形成的血管网有较强的依赖性[9]。无论是直接研究,还是间接研究,都是肿瘤生长依赖血管的有力证据[9-10]。绝大多数的肿瘤在出现癌变现象之前处于静息期,血管不会生长;一旦进入血管期,新生血管将迅速生长,为肿瘤代谢提供了支撑,对肿瘤增殖发挥了非常关键的作用[9]。对于血管成像有不同的成像方式,如X线血管成像、计算机断层血管成像、磁共振血管成像、光学相干断层成像和血管内超声[11]。但是对于皮肤肿瘤,并不像冠状动脉疾病、眼底疾病那样具有公认的关于血管成像评估标准[8, 12]。近年来,SS-OCTA的应用领域不再局限于眼底成像,皮肤浅层血管成像也越来越得到人们的关注。由于皮肤病,如炎症、角化不全等均会引起皮肤组织微观结构的病变,而SS-OCTA技术的成像深度正好可以覆盖皮肤的全层组织结构,满足临床上的需要,更重要的是可以避免传统的组织活检所带来的损伤。同时偏转OCT还可用于组织表层的烧伤程度的检测[20]。任杰等[13]利用激光散斑成像和光学相干层析成像技术,对兔耳皮肤真皮层微血管的相关参数进行无创测量。对皮肤血管的无创实时成像,意味着将SS-OCTA技术应用在肿瘤、皮肤科等疾病上进行辅助诊断成为可能,对于一些肿瘤的早期诊断有很大应用前景。
所以,本文在扫频源光学相干层析血管成像(SS-OCTA)系统的基础上,对接种黑色素瘤的C57BL6小鼠进行图像采集,并作出对比分析,发现了肿瘤早期生长时血管的发育的异常变化。在早期诊断方面,利用SS-OCTA系统进行血管成像优于结构成像,表明SS-OCTA系统在皮肤科疾病的临床诊断方面具有潜在价值。
2 理论推导
2.1 SS-OCTA系统搭建
SS-OCTA手术导航系统平台的基本设计搭建如图1所示。
扫频光源发出近红外波段的光,5%的光进入马赫-曾德尔干涉仪,其干涉信号由平衡探测器获取,用于对OCT干涉信号进行校准;95%的光经耦合器与环形器分别进入到参考臂和样品臂中,二维扫描振镜[14]将样品臂的光偏转后照射至小鼠皮肤成像区域,其部分光从样品内部各层组织原路返回,并分别与参考臂返回的光发生干涉,最终由光电平衡探测器与数字采集卡记录,经过OCT深度重构处理形成包含组织内微观结构的图像。其横向扫描可以快速获取非侵入二维和三维分辨率优于10 μm的图像。光束照射到标本上,形成显微结构反射,对反射光时间延迟起到测量作用,可对组织的纵向内部结构进行无创检测。
2.2 分频幅去相关血管造影法
本文中SS-OCTA系统的算法采用分频幅去相关血管造影法(split spectrum amplitude deeorrelation angiography,SSADA)[15],能在最大程度上降低噪声、伪影等的影响,使得信噪比得到明显提升[16-17]。
光在样品内部散射,然后通过处理形成高分辨率、高深度的图像来分析内在的微观结构。光束照射到标本上,形成显微结构反射,对反射光时间延迟起到测量作用,可对组织的纵向内部结构进行无创检测。一个光带所提供的血流信息都是独立的,对多帧扫描图像所对应的去相干图像进行计算,将不同光带去相干图像进行合并处理,就能获得平均值,使得血流信号变强,具有重要的临床研究意义[16]。
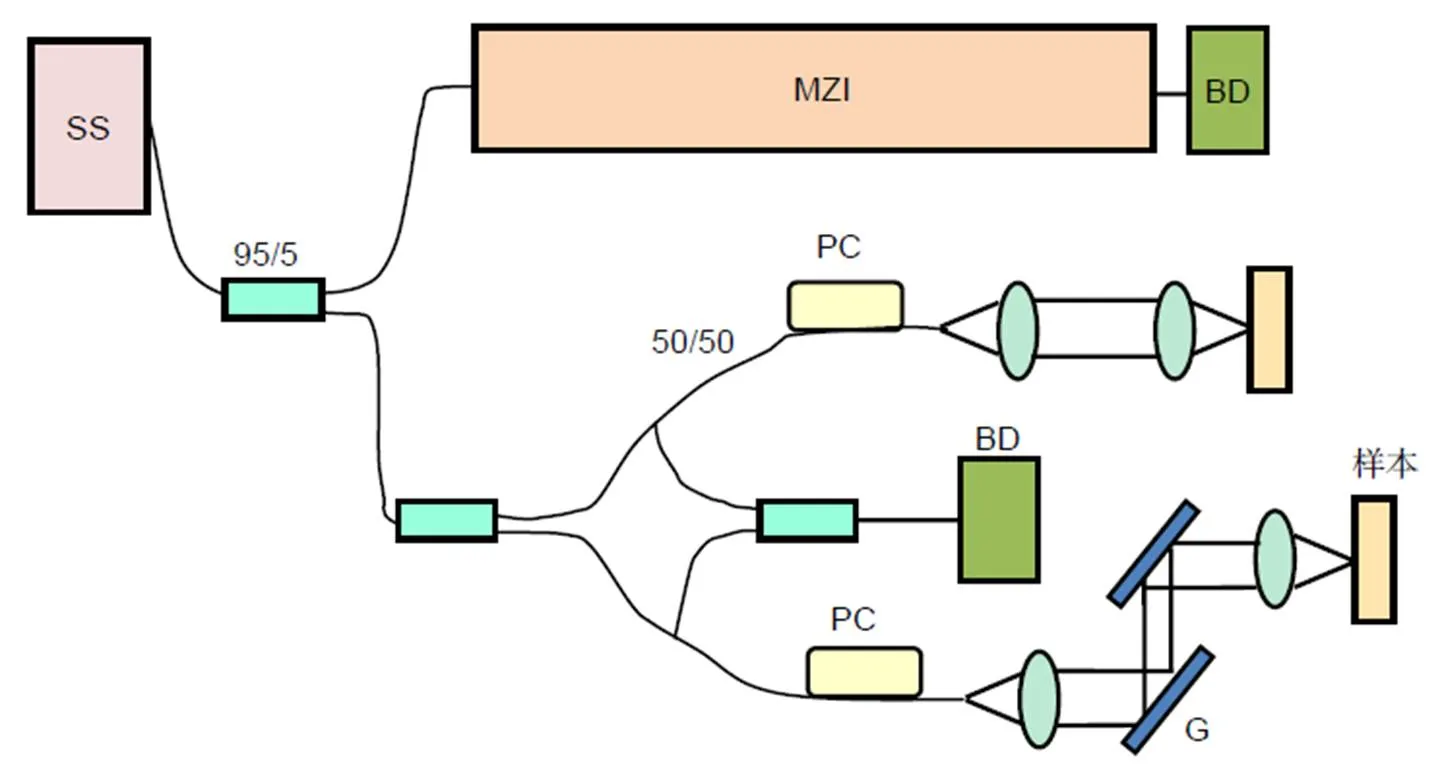
SS: 扫频光源(swept-source);MZI: 马赫-曾德尔干涉仪(Mach-Zehnder interferometer);BD: 平衡探测器(balance detector);PC: 偏振控制器(polarize controller);M: 反射镜(mirror);G: 振镜(galvanometer)
因为SSADA只对信号强度信息进行干涉,所以其算法就能对动态物质背景进行分离,使得抖动影响大大变小,对流场检测的信噪比明显增强,然后利用幅值去相关技术提取流动信息,如下式[16]:
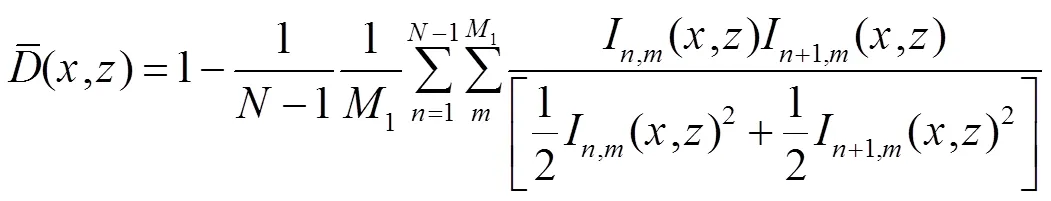
式中:为相同位置实现多帧重复扫描的帧数索引;为分光谱帧数索引用;1、分别为分光谱数和多帧重复扫描数。当采集时间间隔不增加时,增加1就可导致信噪比大大提升。
本文利用SSADA算法对SS-OCTA系统进行成像检测,结果如图2所示。图中显示的噪声基底为70.3 dB,最大信号强度为104.6 dB,标准图像的最大信噪比为34.3 dB。
3 成像实验
本次实验使用的实验动物为C57BL6小鼠。小鼠经麻醉、脱毛后,左背部后肢部位皮下注射0.2 ml B16F10单细胞悬液,注射细胞量为105个,接种5天后进行成像。
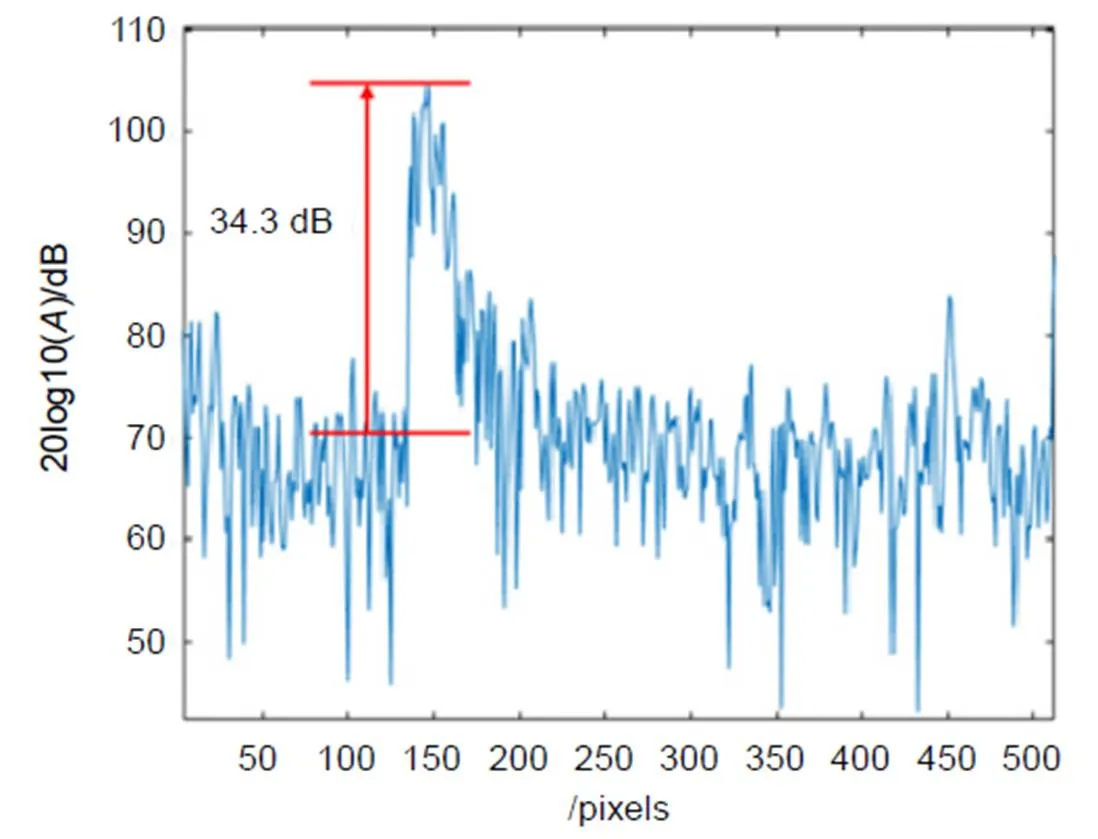
图2 利用SSADA算法对SS-OCTA系统进行成像检测的结果
本次成像实验设定SS-OCTA实验平台的采集视场为5.12 mm´5.12 mm,黑色素瘤因体积大于采集视场,无法单次采集整个肿瘤的血管图像。为此,本次实验以不同方向与角度进行采集,将采集到的结构、血管图像进行拼接,形成完整的皮肤黑色素瘤的结构图与血管图。图3分别展示了小鼠肿瘤处的实物图、SS-OCTA扫描的结构图和血管图。
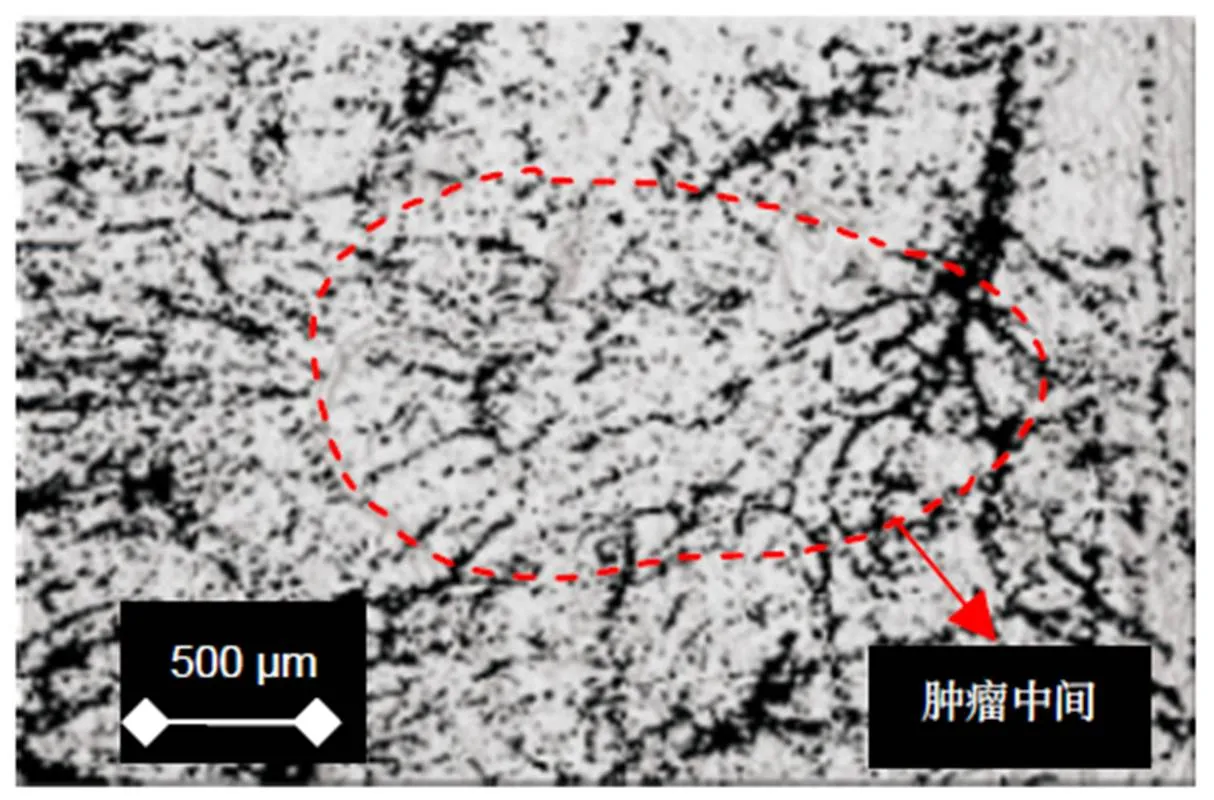
图3(a)可以看到,接种后,小鼠肿瘤处皮肤呈黑色,与粉色的正常皮肤有明显差异。图3(b)为SS-OCTA扫描采集的结构图经过拼接后的完整皮肤表面。由图可知肿瘤皮肤表面不平整,存在一些凹凸不平的现象,猜测应该是皮肤表面的粗糙程度,并没有明显的异常现象。图3(c)为SS-OCTA扫描采集的血管图像经过拼接后的黑色素瘤处完整血管图像,由图红色虚线区域可知,肿瘤部位血管呈现不均匀分布,并且血管分支复杂、紊乱,很多微血管结构不完整,这些特征跟周围正常皮肤血管相比尤为突出(红色箭头)。并且肿瘤新生的毛细血管主要分布在肿瘤生长活跃的边缘,呈现由外向内的生长趋势。
4 分析讨论
将小鼠肿瘤处的皮肤结构图和血管图进行叠加,得到图4。在图4中,可以更清晰看到,小鼠黑色素瘤处的皮肤与其皮下异常生长的血管丛并无太大关系。单单看皮肤结构图,很难判别皮肤是否异常、是否存在肿瘤。而在看血管图片时,则很容易看出血管生长、分布和结构的异常。这说明本文设计搭建的SS-OCTA成像系统在对皮肤黑色素瘤成像时,可以从血管特征方面对早期的黑色素瘤进行简要判定,而在皮肤结构界面则很难起到早期判定的作用。相比较而言,SS-OCTA对于血管特征的分辨要高于对皮肤组织结构的分辨。
与内窥式OCT相比较,在实时无创成像的同时,还可以基本给出肿瘤血管与正常血管的边界线,这将有助于在手术切除肿瘤的同时更少地切除周边正常组织[18]。相比较对黑色素瘤进行早期辅助诊断的普遍性手段皮肤镜而言,SS-OCTA成像不仅可以进行皮肤表面结构成像,而且还可以进行更深层次的皮下血管成像,并且同样可以做到实时、无创成像[19]。同时,本实验也证明SS-OCTA可以对生物组织结构、血管进行无创成像,对一些肿瘤的早期诊断有很大应用前景。
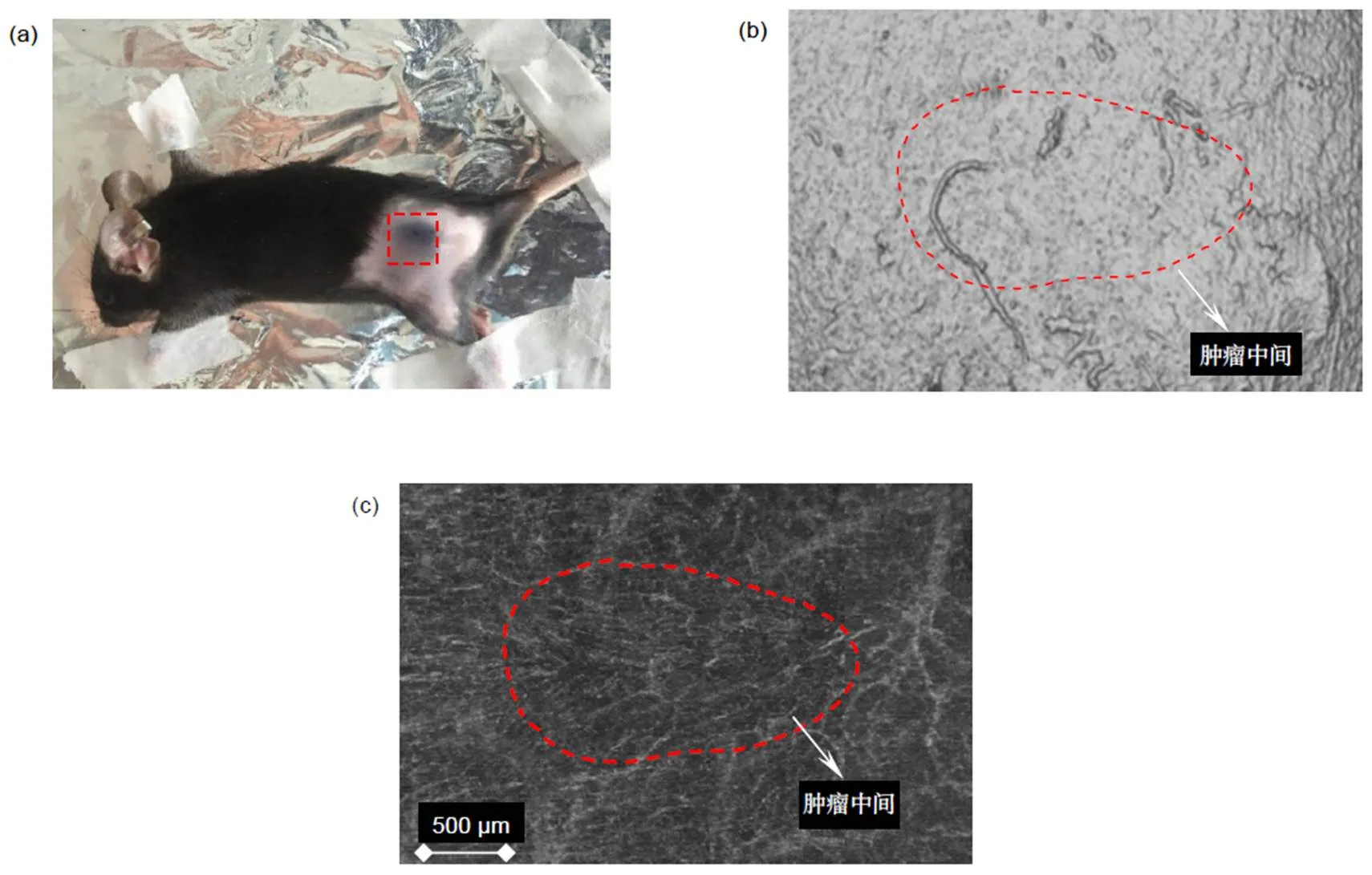
图3 小鼠肿瘤处的皮肤结构图、血管图。(a) 小鼠皮肤实物图;(b) 小鼠皮肤结构图;(c) 小鼠皮肤血管图
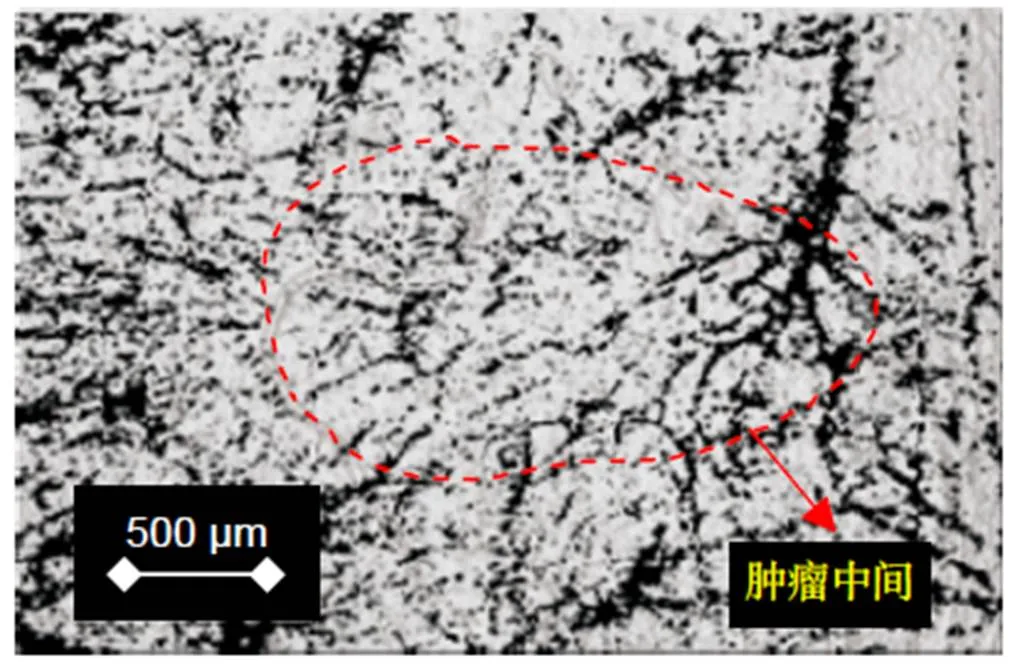
图4 结构图与血管图的叠加
5 结 论
本文利用扫频源光学相干层析血管成像(SS-OCTA)系统完成了对皮肤的结构成像,并对黑色素瘤小鼠进行肿瘤部位的皮肤结构和血管成像。证明了本文的SS-OCTA系统能发现肿瘤早期生长时血管发育的异常变化。同时,在早期诊断方面,利用SS-OCTA系统进行血管成像优于结构成像,表明SS-OCTA系统在皮肤科疾病的临床诊断方面具有潜在价值。
[1] Liang L, Jia Y L, Takusagawa H L,.Optical coherence tomography angiography of the peripapillary retina in Glaucoma[J].,2015, 133(9): 1045–1052.
[2] Zhao S Y, Yu X, Huang N Y,. Rat ear blood vessels imaging by optical coherence tomography[J]., 2011, 20(3): 137–140, 202.
赵士勇, 俞信, 黄乃艳,等.大鼠耳部微血管光学相干层析成像研究[J]. 中国激光医学杂志,2011, 20(3): 137–140, 202.
[3] Zhang Y M, Yang L, Dai P D,. Application of optical coherence tomography in otology[J]., 2018, 18(4): 285–288.
张玉梅, 杨琳, 戴培东, 等. 光学相干层析成像技术在耳科学研究中的应用[J]. 中国眼耳鼻喉科杂志,2018, 18(4): 285–288.
[4] Di Y, Ye J J. Application of optical coherence tomography angiography in ophthalmology[J]., 2017, 53(1): 65–72.
狄宇, 叶俊杰. 光学相干层析扫描血管成像检查在眼科的应用[J]. 中华眼科杂志,2017, 53(1): 65–72.
[5] Gołębiewska J, Olechowski A, Wysocka-Mincewicz M,.Optical coherence tomography angiography vessel density in children with type 1 diabetes[J].,2017, 12(10): e0186479.
[6] Zhang Q, Jonas J B, Wang Q,.Optical coherence tomography angiography vessel density changes after acute intraocular pressure elevation[J].,2018, 8(1): 6024.
[7] 孟庆刚. 迈克尔逊干涉仪的应用[J]. 黑龙江科技信息,2011(36): 62.
[8] Skalet A H, Li Y, Lu C D,.Optical coherence tomography angiography characteristics of iris melanocytic tumors[J].,2017, 124(2): 197–204.
[9] Folkman J. Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications[J].,1971, 285(21): 1182–1186.
[10] Balch C M, Murad T M, Soong S J,.A multifactorial analysis of melanoma: prognostic histopathological features comparing Clark's and Breslow's staging methods[J].,1978, 188(6): 732–742.
[11] Fazlali H R, Karimi N, Soroushmehr S M R,.Vessel segmentation and catheter detection in X-ray angiograms using superpixels[J].,2018, 56(9): 1515–1530.
[12] Kato S, Kitagawa K, Ishida N,.Assessment of coronary artery disease using magnetic resonance coronary angiography: a national multicenter trial[J].,2010, 56(12): 983–991.
[13] Ren J, Wang Y, Gu Y. Basic research on noninvasive detection of skin microvasculature by laser speckle imaging and optical coherence yomography[J].,2012, 21(5): 309.
任杰, 王颖, 顾瑛. 激光散斑成像和光学相干层析成像用于皮肤微血管无创检测的基础研究[J]. 中国激光医学杂志,2012, 21(5): 309.
[14] 喻超. 二维振镜式扫描系统在激光扫描成像中的应用[D]. 北京: 北京邮电大学, 2011.
[15] Wang Q, Wei W B. Optical coherence tomography angiography with split-spectrum amplitude decorrelation angiography[J]., 2016, 40(2): 112–116.
王倩, 魏文斌. 分频幅去相干血管成像[J]. 国际眼科纵览,2016, 40(2): 112–116.
[16] Gao F, Fan J Y, Kong W,. Research progress on optical coherence tomography in detecting vascular flow field[J]., 2018, 45(2): 0207019.
高峰, 樊金宇, 孔文, 等. 光学相干层析技术在血管流场检测方面的研究进展[J]. 中国激光,2018, 45(2): 0207019.
[17] Jia Y L, Tan O, Tokayer J,.Split-spectrum amplitude-decorrelation angiography with optical coherence tomography[J].,2012, 20(4): 4710–4725.
[18] Luo S T, Fan Y W, Chang W,.Boundary region of stomach mucinous carcinoma with swept source optical coherence tomography[J].,2018, 38(5): 0507001.
罗斯特, 范应威, 常玮, 等.扫频光学相干层析成像应用于判断黏液型胃癌边界区域[J]. 光学学报,2018, 38(5): 0507001.
[19] Cozzani E, Chinazzo C, Ghigliotti G,.Cutaneous angiosarcoma: the role of dermoscopy to reduce the risk of a delayed diagnosis[J].,2018, 57(8): 996–997.
[20] Schoenenberger K, Colston B W, Maitland D J,. Mapping of birefringence and thermal damage in tissue by use of polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography[J]., 1998, 37(25): 6026–6036.
Imaging of skin structure and vessels in melanoma by swept source optical coherence tomography angiography
Liu Jingxuan1,2, Fan Jinyu2, Wang Quan2, Shi Guohua2*
1University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui 230000, China;2Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Suzhou, Jiangsu 215000, China
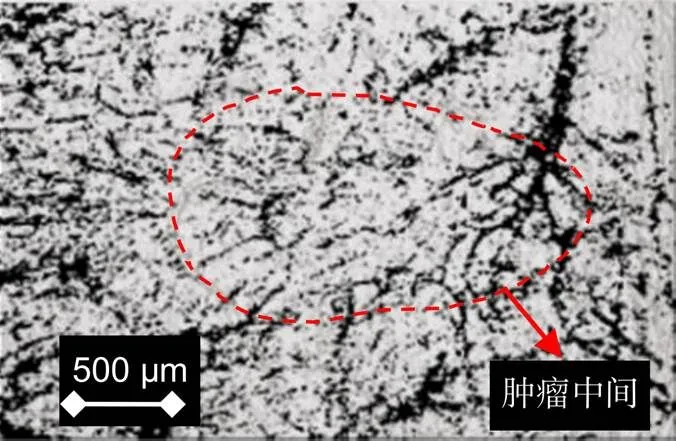
The superimposition of the structure map and the vascular map
Overview:In recent years, optical coherence tomography (OCT) has developed rapidly and become a new imaging technology. OCT weakens coherent reflection and backscattering. Super heterodyne detection technique was used to improve the signal-to-noise ratio of biological tissue tomography. OCT has the advantages of non-invasive, high resolution, and high-speed imaging, and thus it is very suitable for biomedical applications. Scanning source optical coherence tomography (SS-OCTA) is a frequency-domain OCT technology and can support a high resolution in vivo angiography. As a new angiography technique, SS-OCTA still uses the Michelson interferometer's basic optical path and can achieve axial resolution of 15 microns by measuring the back scattering of light from low-coherent interference signals in tissue. Cross sectional images of 3D reconstruction of 3D images of biological tissues can be obtained, which are widely used in ophthalmology, dermatology imaging, tumor detection, and other fields. In addition to imaging biological tissue, SS-OCTA can also image surface blood vessels such as fundus and skin. SS-OCTA can observe the changes of retinal blood vessel morphology and blood flow in the choroid retina in the field of ophthalmology such as retinal angiography. Furthermore, it can also use pseudo-color to distinguish normal and abnormal vascular structures, blood flow signal detection and quantitative analysis, split different spectral images of the original full-spectrum image, reduce noise, improve signal-to-noise ratio, and then merge, so as to achieve retinal, choroidal vascular formation of any layer of significant cross-sectional imaging. Finally, we use laser speckle imaging and optical coherence tomography to noninvasive measurement of animal skin irritation and obtain dermal microvascular parameters. Angiography provides a possibility for the applications of SS-OCTA in the diagnosis of tumors, skin diseases, and other diseases. In fact, solid tumor growth is strongly dependent on the induced vascular network. Direct and indirect studies can support a strong evidence that tumor growth depends on blood vessels. Most tumors remain inactive until they become cancerous, and blood vessels no longer grow. Once entering the vascular phase, new blood vessels will grow rapidly to support tumor metabolism and play an important role in tumor proliferation. SS-OCTA can perform noninvasive imaging of biological tissues and blood vessels. This is of great significance for the early diagnosis of some tumors. Therefore, skin structure and angiography of melanoma C57BL6 mice were collected and compared with the SS-OCTA system. To observe the changes of the vascular development and biological tissue structure in the early stage of tumor growth, SS-OCTA is better at distinguishing vascular functional structures than the structural imaging.
Citation: Liu J X, Fan J Y, Wang Q,Imaging of skin structure and vessels in melanoma by swept source optical coherence tomography angiography[J]., 2020, 47(2): 190239
Imaging of skin structure and vessels in melanoma by swept source optical coherence tomography angiography
Liu Jingxuan1,2, Fan Jinyu2, Wang Quan2, Shi Guohua2*
1University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei, Anhui 230000, China;2Suzhou Institute of Biomedical Engineering Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Suzhou, Jiangsu 215000, China
Sweep source optical coherence tomographic angiography (SS-OCTA) is a kind of angiography technologies based on split spectrum amplitude deeorrelation angiography (SSADA). It has a great prospect in the early diagnosis of tumors and other diseases. In this paper, skin structure and angiography of melanoma C57BL6 mice were collected on the basis of the SS-OCTA imaging platform with an imaging field of 5.12 mm´5.12 mm and a standard image maximum signal-to-noise ratio of 34.3 dB. The results show that the SS-OCTA system is superior to the structural imaging in early diagnosis of dermatological diseases.
scanning frequency source optical coherence tomography; skin structure; tumor vessels; melanoma; SS-OCTA
Supported by Key Research and Development Plan of the Ministry of Science and Technology - Digital Diagnosis and Treatment Equipment (2017YFC0108201, 2017YFC0108200, 2017YFB0403700), Key Research Project of Frontier Science of Chinese Academy of Sciences (QYZDB-SSW-JSC03), and Key Projects for Inter-governmental International Scientific and Technological Innovation Cooperation (2016YFE0107700)
A
10.12086/oee.2020.190239
: Liu J X, Fan J Y, Wang Q,. Imaging of skin structure and vessels in melanoma by swept source optical coherence tomography angiography[J]., 2020,47(2): 190239
2019-05-13;
2019-11-23
科技部重点研发计划-数字诊疗装备(2017YFC0108201, 2017YFC0108200, 2017YFB0403700);中国科学院前沿科学重点研究项目(QYZDB-SSW-JSC03);政府间国际科技创新合作重点专项(2016YFE0107700)
刘敬璇(1993-),女,硕士研究生,主要从事光学生物成像的研究。E-mail:ljx1216@126.com
史国华(1981-),男,博士,研究员,主要从事新型在体光学成像与检测的研究。E-mail:ghshi_lab@126.com
刘敬璇,樊金宇,汪权,等. SS-OCTA对黑色素瘤皮肤结构和血管的成像实验[J]. 光电工程,2020,47(2): 190239
R732.2;TP391
* E-mail: ghshi_lab@126.com

