压裂液长期滞留对低渗透储层的伤害试验研究
薛蕾 丁小军 马青莲

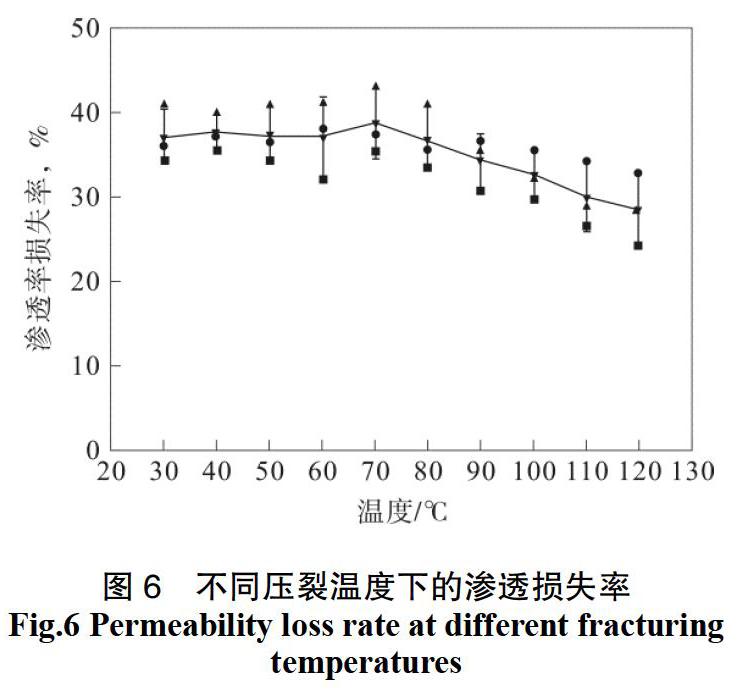

摘 要: 针对当前低渗透油藏中大量使用的压裂液给储层带来的伤害,导致开采量降低的问题,以羟丙基瓜尔胶压裂液作为研究对象,以适应充填装置作为储层模拟,以渗透损失率作为评价指标,探讨不同因素对羟丙基瓜尔胶滞留的影响。结果表明,不同羟丙基瓜尔胶压裂液浓度、pH值和温度对渗透损失率和压裂液滞留量都有着影响。其中浓度越大,对渗透损失率的影响越大,但随着浓度的持续增加,其影响也逐步变小;pH值越大,对渗透损失率的影响越小;温度与渗透损失率和滞留量呈现为正相关关系。由此通过上述的研究,为石油开采中压裂液的配比提供了参考,对减少压裂液对储层的损害具有可借鉴性。
关 键 词:低渗透油藏;羟丙基瓜尔胶;伤害;渗透损失率
中图分类号:TE348 文献标识码: A 文章编号: 1671-0460(2019)10-2331-04
Abstract: In view of the reservoir damage caused by fracturing fluids widely used in low permeability reservoirs, resulting in the reduction of production, the hydroxypropyl guar gum fracturing fluid was taken as the research object, the suitable filling device was taken as simulated reservoir, and the permeability loss rate was taken as evaluation index,the different factors affecting hydroxypropyl guar gum retention were investigated. The results showed that different HPG fracturing fluid concentration, pH value and temperature had influence on the permeability loss and fracturing fluid retention. The higher the concentration, the greater the impact on the permeability loss rate; the higher the pH value, the smaller the impact on the permeability loss rate; there was a positive correlation between the temperature with the permeability loss rate and fracturing fluid retention. Therefore, the research can provide reference for the proportion of fracturing fluids in oil exploitation, and can also provide reference for reducing the damage of fracturing fluids to reservoirs.
Key words: Low permeability reservoir; Hydroxypropyl guar gum; Damage; Permeability loss rate
随着我国油气田资源的大量开发,使得我国低渗透油藏开采成为当前的主流。在低渗透油藏开发中,如何確保低渗透油藏的产量,一直以来是油气开采的重点。但是在低渗透油藏压裂施工中,随着压裂液的加入,使得高分子稠化剂进入到储层岩石的内部,进而在储层孔道中滞留,从而形成堵塞,并给储层带来损害,最终影响给低渗透油藏的改造效果。因此,为解决这类问题,人们开始就压裂液在储层中滞留问题进行研究。徐兵威(2013)则探讨了压裂液对致密性油藏的损害机理,在研究中深入探讨了敏感性损害、液相圈闭等不同因素对储层的损害问题[1]。结果表明,储层悟性越差,在储层中滞留越严重,对储层带来的损害也就越严重;游利军则从储层油藏敏感性的角度入手,就压裂液对页岩储层的影响进行了探讨[2]。作者认为压裂液与储层作用,会在一定程度上降低表面强度,使得裂缝更容易压缩闭合,同时支撑剂可有效降低页岩的应力敏感性。因此,合理的压裂液配比是关键;徐林静(2016)则研究了当前比较主流的胍胶压裂液长期滞留在储层对储层渗透率的影响[3];李春颖(2016)则探讨了压裂液在储层长期滞留和吸收的机理[4]。上述的研究都为本文奠定了理论与实践基础。本文则模拟低下储层压裂液滞留环境,以石英充填层作为主要的研究对象,探讨羟丙基瓜尔胶压裂液滞留对储层的影响。
1 羟丙基瓜尔胶在储层中的吸附机理
羟丙基瓜尔胶作为当前常用的一种压裂液中,其结构式如图1所示。羟丙基瓜尔胶是一种长链结构的高分子聚合物,当注入储层后,会与岩石表面发生吸附,进而吸附在岩石表面。周含浩(2016)通过研究后认为,在储层岩层中,石英是主要的组成成分[5],羟丙基瓜尔胶在进入储层后,其吸附与溶液的浓度、温度和pH值等有着很大的关系。同时作者还通过试验得出,之所以会产生吸附,一个重要的原因是氢键。当其中的氢键没有被破坏时,吸附在储层表面的量大,相反则较小。
由此看出,从反应条件来讲,羟丙基瓜尔胶在储层中吸附的与温度、pH值等有着很大的关系。而从分子作用力来讲,与羟丙基瓜尔胶结构中的氢键有着很大的关系。

