高原环境条件下柴油机增压与喷油参数协同优化
焦宇飞,刘瑞林,张众杰,周广猛,杨春浩,马家明
高原环境条件下柴油机增压与喷油参数协同优化
焦宇飞1,刘瑞林2※,张众杰1,周广猛2,杨春浩3,马家明1
(1. 陆军军事交通学院,学员五大队,天津 300161;2. 陆军军事交通学院,军用车辆工程系,天津 300161;3. 海军工程大学,动力工程学院,湖北 武汉 430033)
增压与喷油是影响柴油机高海拔性能最直接的因素。为了优化柴油机不同海拔条件下增压与喷油系统协同控制策略,建立了二级可变截面增压柴油机GT-Power仿真模型,计算得到了柴油机运行各工况数据。将神经网络与仿真数据相结合,以动力性为优化目标,得到不同海拔条件下增压与喷油系统协同优化规律。研究结果表明:相比于原机,喷油参数经过优化后,最佳循环喷油量增加,增加量呈现出自最大转矩转速点向两侧逐渐增大的趋势。最佳喷油提前角,在2 500 和5 500 m低转速下平均分别增加了1和1.5 ℃A,在中高转速下,平均分别减小了25.2%和17.5%。相比于原机,最佳可变截面的涡轮增压器(variable geometry turbocharged,VGT)叶片开度增大,但增大趋势在不同海拔略有不同,0 m海拔时,增加幅度随转速增加而增大,5500 m低转速时,开度不变,中高转速时,VGT开度增加幅度随转速增加呈现先增大后减小。增压与喷油参数协同优化后,0 m海拔时,VGT叶片开度和喷油量增大,喷油提前角减小,5 500 m海拔时,低转速下VGT叶片开度不变,循环喷油量和喷油提前角增大,中高转速下VGT叶片开度和循环喷油量增大,喷油提前角减小。
柴油机;优化;高海拔;二级可调增压系统;喷油参数
0 引 言
高原条件下,受大气压力与温度影响,空气密度明显降低,柴油机在高原运行时,油与气失配使得柴油机燃烧恶化,导致柴油机动力、经济性下降、爆压超限、涡轮增压器超温、超速等一系列问题[1-5]。
改善增压与喷油系统是解决上述问题的有效途径[6-7]。对于可变截面增压柴油机,进气主要通过调节增压系统的可变几何截面增压(variable geometry turbocharged,VGT)叶片开度实现,喷油主要依靠改变喷油参数来实现。王利民等[8]提出了基于进气增压压力和位置开度的VGT多级闭环控制算法,实现了柴油机全工况增压压力的闭环控制。唐蛟等[9]提出了废气再循环系统(exhaust gas recirculation,EGR)与VGT解耦控制策略,缩短了增压压力和进气质量流量的上升时间。朱振夏[10]根据供油参数影响规律,提出了“边界适应度归零”的惩罚参数取值方法,通过优化使得柴油机4 500 m标定点功率相对原机提升了14.7%,燃油消耗率降低了9.6%。
变海拔条件下,单级增压和调节能力比较有限,难以满足柴油机不同海拔、变工况需求的状况[11],近些年来可调二级增压系统受到越来越多的关注[12-14]。吉林大学的腾鹏坤[15]研究了喷油和供气策略对二级增压柴油机瞬变性能的影响,该校的袁兴[16]提出了复合EGR控制策略对二级增压柴油机瞬变性能的影响,通过对控制策略优化有效改善了柴油机排放特性。军事交通学院的董素荣等[11]研究了不同海拔条件二级增压器与柴油机的匹配特性,得到了VGT开度对二级增压柴油机高海拔燃烧特性的影响。北京理工大学李长江[17]借助于GT-Power建立了可调二级增压系统模型,开展了二级增压器涡轮旁通流量率队增压系统的影响以及二级增压器高原条件下稳态与瞬态调节方法。但以上研究偏向于对二级增压器特性的研究,而柴油机性能受喷油与进气共同影响,单独只研究二级增压器对柴油机燃烧效率提升较为有限,对增压与喷油参数协同控制对充分发挥二级可调增压系统潜力,有效提升柴油机高海拔动力性有着重要意义。但针对不同海拔条件下,二级可调增压与喷油参数协同优化国内外还鲜有报道。
据此,本文开展了相关研究,利用GT-Power建立柴油机仿真模型并通过试验方法进行验证。借助仿真模型计算不同海拔工况点,筛选出具有代表性的点进行神经网络的训练,得到了增压与喷油参数优化规律,提出了增压与喷油参数协同优化策略。
本文的研究为优化柴油机高海拔燃烧效率,全面提升柴油机高海拔性能提供技术支撑。
1 模型的建立与验证
试验采用一台6缸高压共轨增压中冷柴油机,主要技术参数如表1所示。
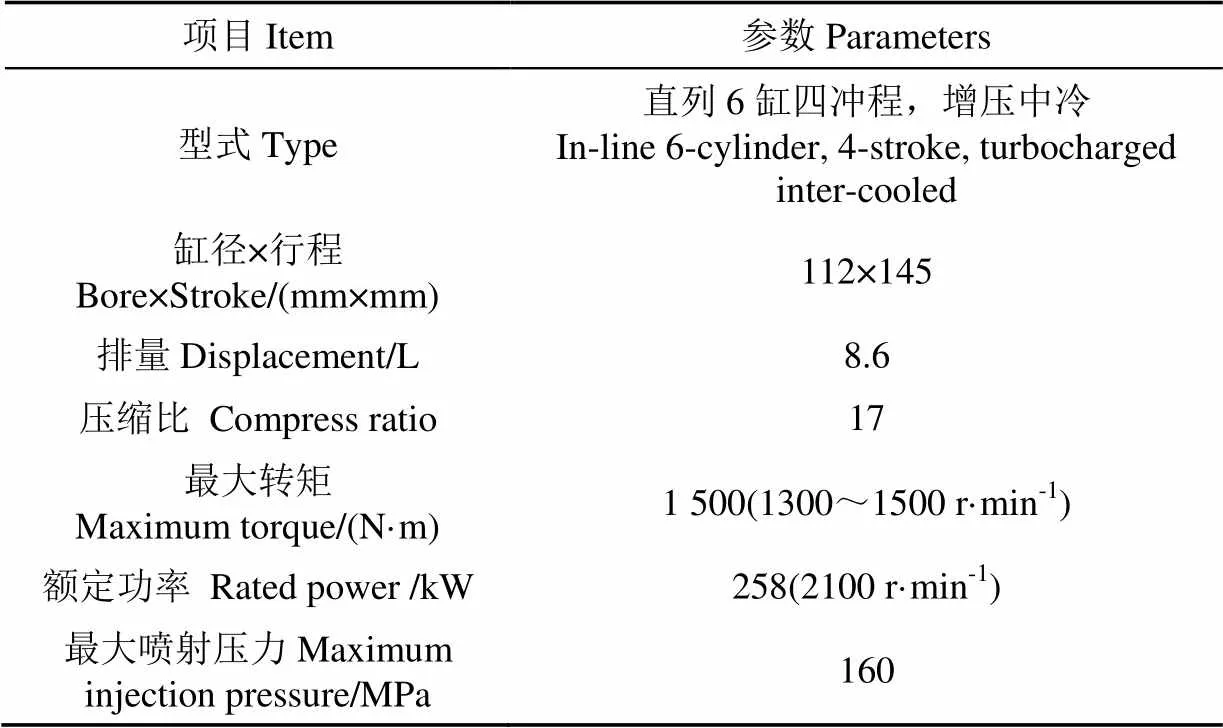
表1 柴油机主要技术参数
海拔模拟通过内燃机高原环境模拟试验台实现,该试验台通过进气节流和排气抽真空的方式能够模拟0~6 000 m海拔的大气压力,控制精度在±5%。试验设备主要包含CW440D电涡流测功机、进排气压力控制系统、AVL670燃烧分析仪、上海同圆CMFD瞬态油耗仪、上海同圆LQY600冷却液恒温系统、数据采集系统等,发动机台架详细布置如图1所示。

1.二级增压控制系统 2.进排气压力控制系统 3.发动机控制系统 4.数据采集系统 5.测功机 6.发动机 7.瞬态油耗仪 8.中冷器 9.高压级涡轮 10.高压级压气机 11.中冷器 12.低压级涡轮 13.低压级压气机 14.换热器 15.排气稳压箱 16.进气稳压箱 17.真空泵
根据内燃机实际结构,利用GT-Power建立了如图2所示的二级可调增压柴油机工作过程模型。该二级可调增压系统以普通废气涡轮增压器为低压级,以VGT为高压级,两级增压器以串联的形式相连。VGT叶片开度定义为:当前VGT叶片开度对应喷嘴环流通面积与最大VGT叶片开度对应的喷嘴环流通面积之比。燃烧模型采用GT-Power中的油滴蒸发模型进行燃烧过程模拟[18],传热模型直接采用量纲分析得到的半经验的Woschni传热模型[19],涡轮增压器模型主要根据实际涡轮机运行的速度和效率特性以及压气机运行特性进行设置。在喷油过程中的喷油定时和循环喷油量则根据实际工况直接进行设置。
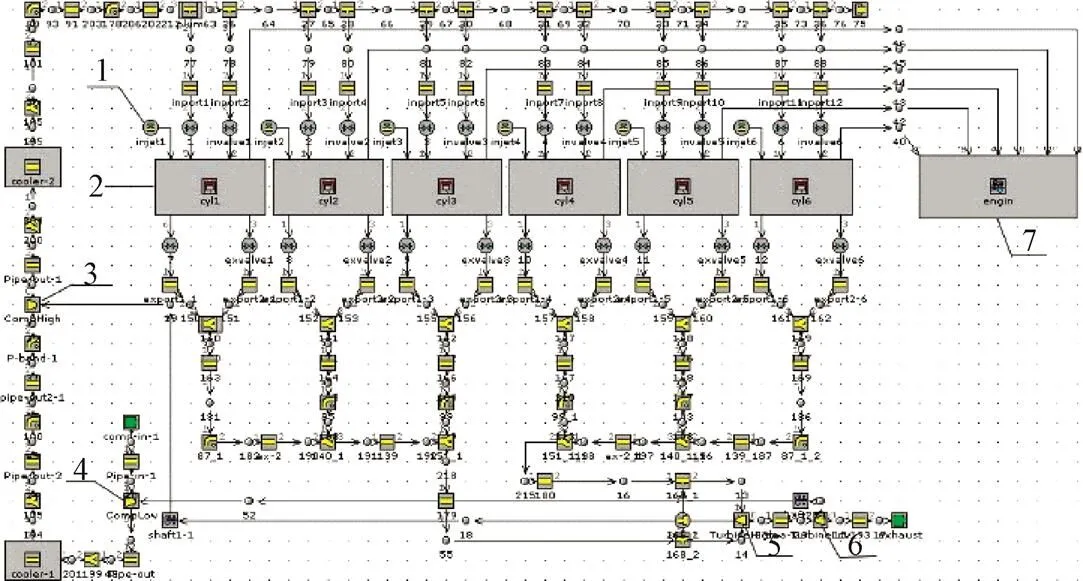
1.喷油器 2.气缸 3.高压级压气机 4.低压级压气机 5.高压涡轮机 6.低压级涡轮机 7.曲轴箱
在仿真模型的验证中,为了充分验证模型的准确性,选取具有典型的海拔与工况点进行验证,本文选取0与3 500 m为验证海拔,选取最大转矩转速点与额定功率点全负荷和部分负荷工况点作为验证工况。图3为各工况点试验与仿真结果的验证结果。由图可知,各海拔转速下,柴油机缸压与放热率的仿真值与试验值能够较好地吻合,误差在5%以内,可以用于高原柴油机性能仿真计算。

a. 部分负荷工况
a. Partial load condition

b. 全负荷工况
b. Full load condition
注:为海拔高度;为转速。Note:is the altitute;is the engine speed.
图3 仿真结果验证
Fig.3 Verification of simulation results
2 增压与喷油系统协同优化流程
2.1 增压与喷油系统协同优化方案
全负荷工况下增压与喷油系统协同优化涉及到循环喷油量、喷油提前角及VGT叶片开度3个控制参数。控制参数与柴油机输出转矩之间没有明确的函数关系,采用传统试凑法[20]及正交试验法[21]无法满足优化要求,神经网络模型可以建立起输入与输出的映射关系,并且具有较强的预测计算能力,对于柴油机多参数优化问题具有较强的适用性[22-24]。
基于神经网络的增压与喷油系统优化主要包含3个过程:通过仿真试验筛选数据样本,神经网络模型的建立及训练与运用寻优函数实现优化[25-26]。具体流程为:在已建立的GT-Power仿真模型的基础上,设置柴油机实际工作工况点,对各工况点进行仿真试验,在试验结果中筛选出转矩较大且最高燃烧压力和空燃比符合预定要求的数据作为输入样本训练神经网络,得到输入变量与输出转矩之间的映射关系,而后扩大参数取值范围,并缩小调节步长以提高各参数调节精度,设计新的输入组合,并用导入训练好的神经网络预测输出转矩。使用Matlab软件中max函数与find函数分别求得输出转矩极大值及其对应位置,可得最大转矩对应的输入组合,将其代入仿真模型进行验证,根据限制条件作适当调整,最终确定该工况下基于动力性最优的各参数协同优化组合。
2.2 训练样本的生成
针对柴油机运行工况,选取VGT叶片开度与喷油参数进行全排列,以=2 500 m,=1 800 r/min为例,根据柴油机实际喷油参数设置仿真参数如表2所示。

表2 仿真试验参数设置
注:q为循环喷油量;为喷油提前角;VGT为VGT开度。
Note:qis the circulating fuel injection quantity;is the injection advance angle;VGTis the opening of the VGT.
柴油机运行过程中,为了防止柴油机最高燃烧压力超过限制而烧坏柴油机,最高燃烧压力限制在16 MPa。为了降低柴油机燃烧过程中热负荷过高造成柴油机拉缸,提升柴油机燃烧效率,将空燃比限定在19.5~21范围内。将所有调节参数组合作为有效输出样本,若不满足限定条件则剔除该点,共筛选出128个样本作为有效样本,部分筛选过程如表3所示。
2.3 神经网络模型的建立及训练
神经网络模型包含输入层、隐含层和输出层。输入层为柴油机协同优化控制参数,共包含循环喷油量、喷油提前角、VGT叶片开度3个参数。本文优化是以动力性最大为优化目标,因此输出层只包含1个转矩参数。为提高神经网络准确性,设置2层隐含层,第1层为3层,第2层为6层,如图4所示。
将仿真试验筛选得到的增压与喷油系统控制参数组合及其对应的转矩数据,建立成训练样本,设置学习率为1,最大校正次数为100 000,对神经网络进行训练。选取样本外的25组仿真数据,运用训练好的神经网络进行预测,得到输出转矩预测值与仿真值误差如图5所示,预测值与仿真值误差较小,神经网络模型预测精度符合要求,可用于下步预测。

表3 H=2 500 m,n=1 800 r·min-1工况下部分有效数据样本的筛选
注:图中标*为剔除掉的参数组合。T为柴油机转矩;为空燃比;max为最高燃烧压力。
Note: The dots marked with * in the figure are the deleted parameter combinations. Tis the engine torque;is the air-fuel ratio;maxis the maximum cylinder pressure.
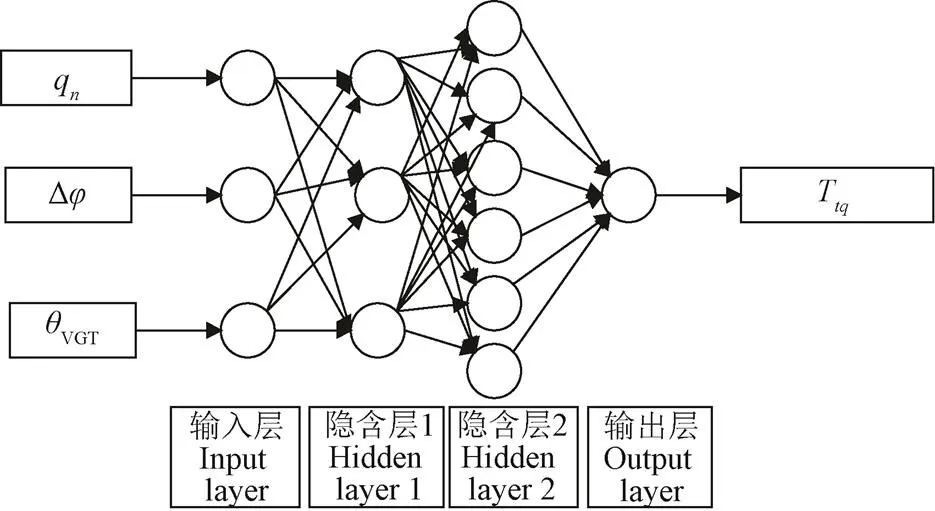
图4 神经网络模型的建立
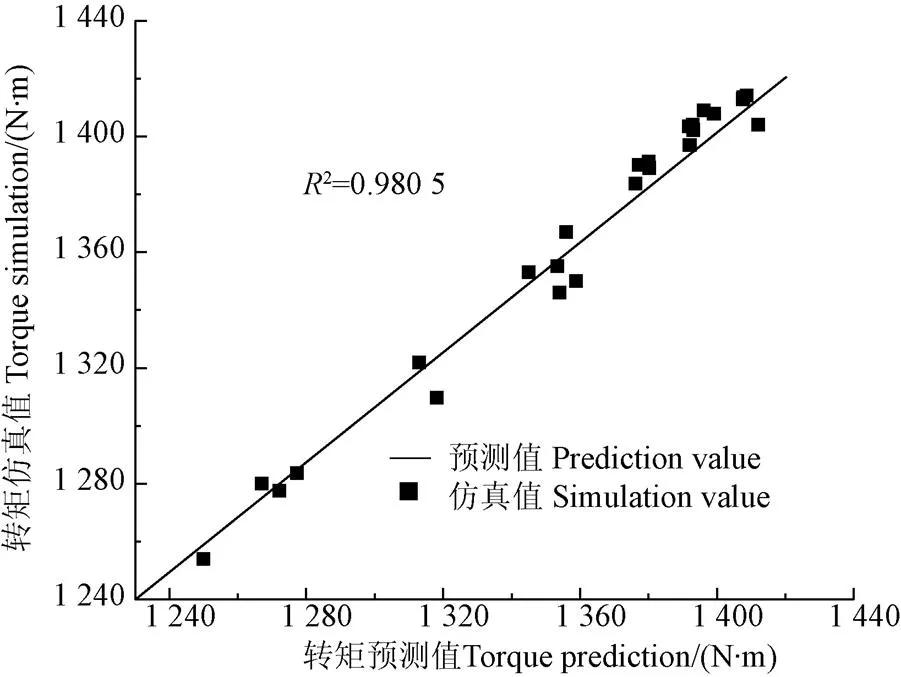
图5 模型预测准确性验证
2.4 协同优化组合的确定
通过神经网络建立起增压和喷油系统控制参数与转矩之间的映射关系。基于训练好的神经网络,取表4中3个参数取值的全排列,建立新的输入组合共21×11×13=3 003组,输入神经网络中可预测出3 003组输出,在Mtalab中对输出转矩数组调用max函数,可得到极值点转矩为1 364.2 N·m,再调用find函数,可得转矩极大值对应位置为第44组序列,即最大转矩对应第44组输入,神经网络预测的转矩极大值及对应位置如图6所示。
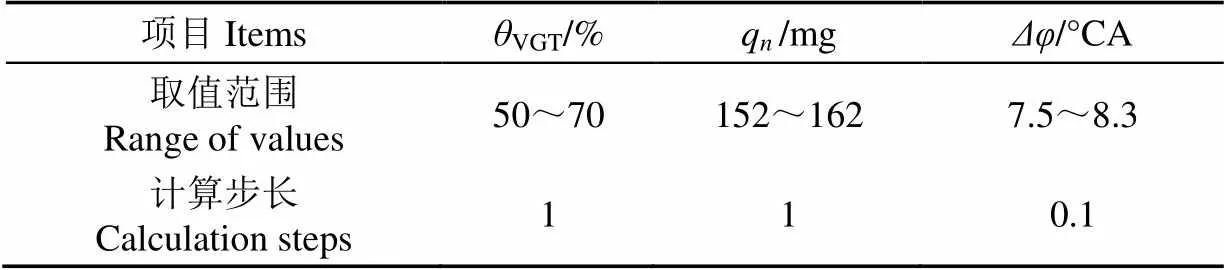
表4 输入组合参数设置

图6 预测转矩极值点及对应位置
通过在二级可调增压柴油机仿真模型中设置柴油机不同海拔与工况,用上述协同优化方法可得出0~5 500 m海拔,1 000~2 100 r/min转速全负荷条件下,喷油量、喷油提前角及VGT叶片开度协同优化组合如表5所示。
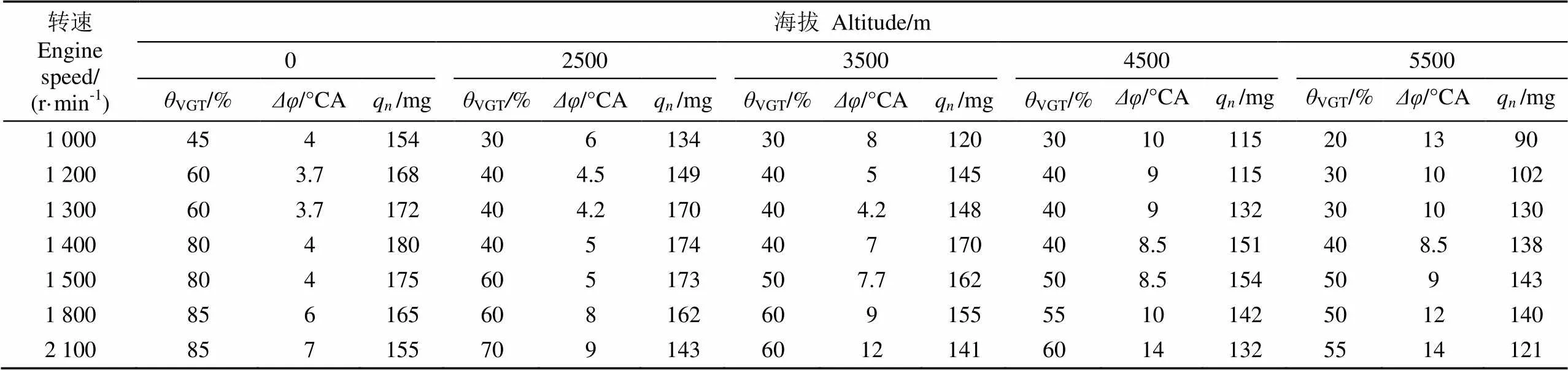
表5 不同海拔控制参数优化值
3 增压与喷油系统控制参数协同优化变化规律
基于神经网络得到不同海拔不同转速下增压与喷油控制参数的协同优化组合后,分析喷油量、喷油提前角及VGT叶片开度随海拔及转速的变化规律,为增压与喷油系统控制参数协同控制策略的制定提供参考依据。
图7a为优化后各转速下最佳循环喷油量随海拔变化规律。由图可知,同一海拔条件下,柴油机最佳循环喷油量随转速增加先增大后减小,随海拔升高,柴油机最佳循环喷油量逐渐减小,减小趋势随海拔增加逐渐递增,由0至3 500 m不同转速下循环喷油量平均降低了10.96%,由3 500至5 500 m平均降低了16.99%。图7b为2 500和5 500 m条件下优化前后最佳循环喷油量对比图。由图可知,海拔一定时,优化后循环喷油量随转速的变化规律与原机基本一致,但相比原机优化后各转速下的最佳循环喷油量都有所增加,低转速时循环喷油量增加幅度最大,中高转速下循环喷油量增加幅度减小,在最大转矩转速附近循环喷油量增加量最小,呈现出增加量自最大转矩转速点向两侧逐步增大的趋势。相比于单级增压,二级增压增大了柴油机缸内进气量,缓解了高原环境引起的空气密度的下降,适当增大循环喷油量,有利于柴油机高海拔动力性能的提升,但为了保证最高燃烧压力和排温不超限,循环喷油量增加量需要得到限制,越靠近最大转矩转速点,增加值越小。

图7 最佳循环喷油量随转速的变化规律
图8为不同海拔条件下最佳喷油提前角的变化规律。由图8a可知,同一海拔条件下,柴油机最佳喷油提前角随转速增加呈现先减小后增加的趋势,最佳喷油提前角平均值随海拔升高而增大,海拔每升高1 000 m,喷油提前角平均增大1.15 °CA。随着海拔升高,大气压力与温度降低导致进气终了缸内空气密度降低,反应物分子之间的碰撞概率减小,着火之前混合气的物理和化学反应时间延长,滞燃期延长,滞燃期累积的混合气增多,大量准备好的混合气,几乎同时开始燃烧,增大了速燃期内放热速率,缸内压力与温度急剧上升,增加了柴油机燃烧粗暴度,因而随海拔升高要相应增加柴油机喷油提前角[27-28]。相比于原机,优化后的喷油提前角在低速时略有增加,在海拔2 500和5 500 m,转速在1 000~1 500 r/min时最佳喷油提前角平均分别增加了1和1.5 °CA,随转速升高,最佳喷油提前角减小,在2 500和5 500 m海拔下1 500~2 100 r/min平均分别减小了25.2%和17.5%,如图8b所示。低转速时,增压器效率较低,增大喷油提前角有利于油气充分混合,提高燃烧效率,进而改善柴油机低速动力、经济性。随着转速增加,增压器效率升高,相比于单级增压器,二级增压器增大了缸内进气量,适当减小喷油提前角,能够降低缸内最高燃烧压力和燃烧粗暴度。
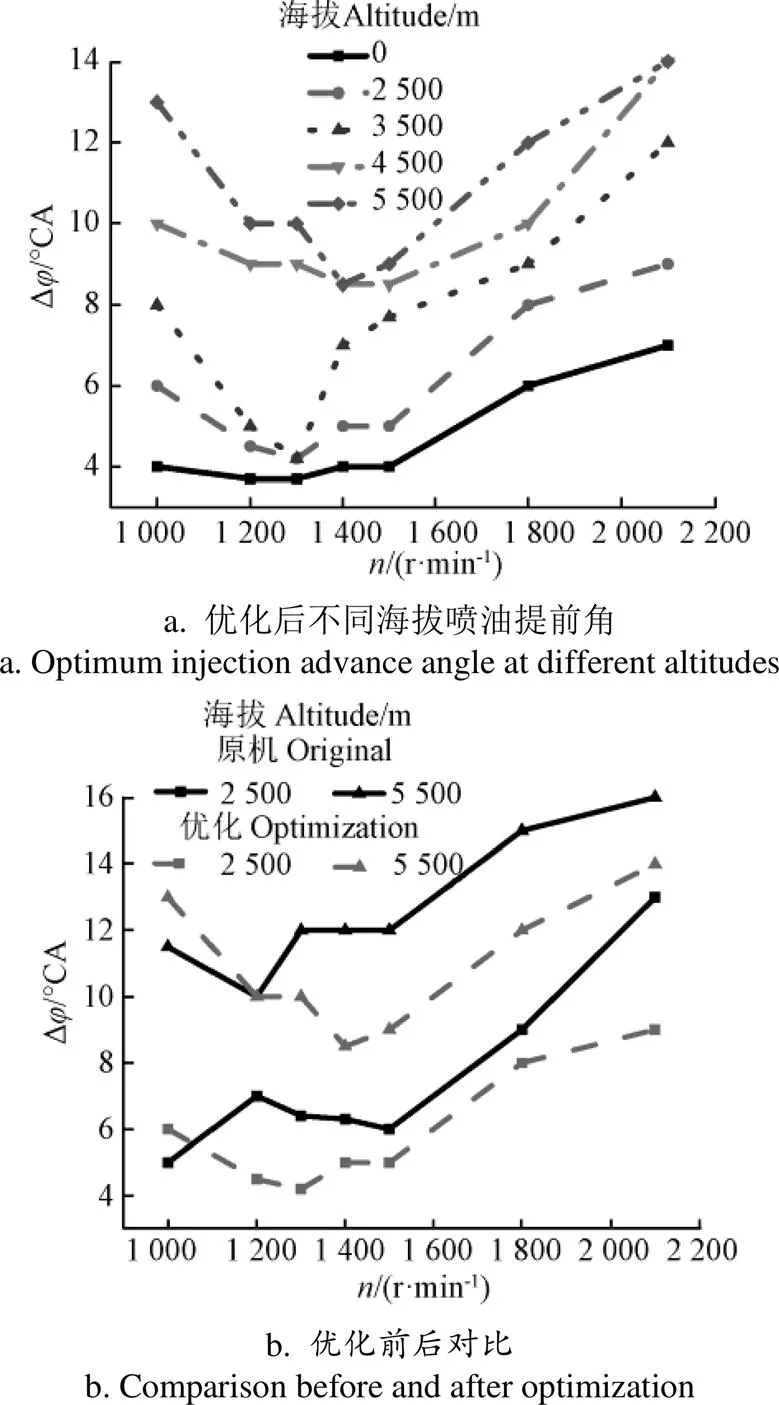
图8 最佳喷油提前角随转速的变化规律
图9a为0 m~5 500 m海拔条件下最佳VGT叶片开度随转速的变化规律。由图可知,在同一海拔高度下,柴油机最佳VGT叶片开度,随转速的增加而逐渐增大,随海拔升高,最佳VGT叶片开度逐渐减小,相比于平原,5 500 m海拔条件不同转速工况下最佳VGT叶片开度平均降低了44.44%。海拔升高和转速的降低都会导致进气压力降低,通过减小VGT叶片开度减少涡轮流通面积,使得排气背压和流速增大,可用排气能量升高,进而提高增压器转速,增加柴油机进气流量,随着海拔降低和转速增加,需要增大VGT开度以防止增压器超速。由图 9b可知,相比于原机,柴油机优化后最佳VGT开度呈现增大趋势,但增大趋势在不同海拔条件下有所差异。在平原条件下,优化后的VGT开度增大幅度随转速增加而增大,在海拔5 500 m条件下,低速时VGT叶片开度与原机相同,随着转速升高,VGT叶片开度增加幅度呈现先增大后减小的趋势,在2 100 r/min时,优化后的VGT开度相比于原机略有下降。相比于单级增压器,二级增压器增压比较高且随着转速增加效率升高,平原条件下,较大的VGT开度已经能够满足柴油机燃烧需求,因此优化后VGT开度增加,增大幅度随转速升高而增大。在海拔5 500 m条件下,低速工况下,VGT叶片开度减小,一方面减少了流通面积,提高了增压器转速,另一方面VGT叶片开度减少使得泵气损失增大,减少了缸内进气量,因此在低速下,VGT开度变化较小。在中高转速下,增压器效率较高,适当增大VGT开度增大涡轮流通面积,来降低排气背压和流速以避免增压器超速。额定转速工况下,原机最高燃烧压力距离限制值仍有一定余量,减小VGT叶片开度可进一步提升柴油机额定功率[29]。
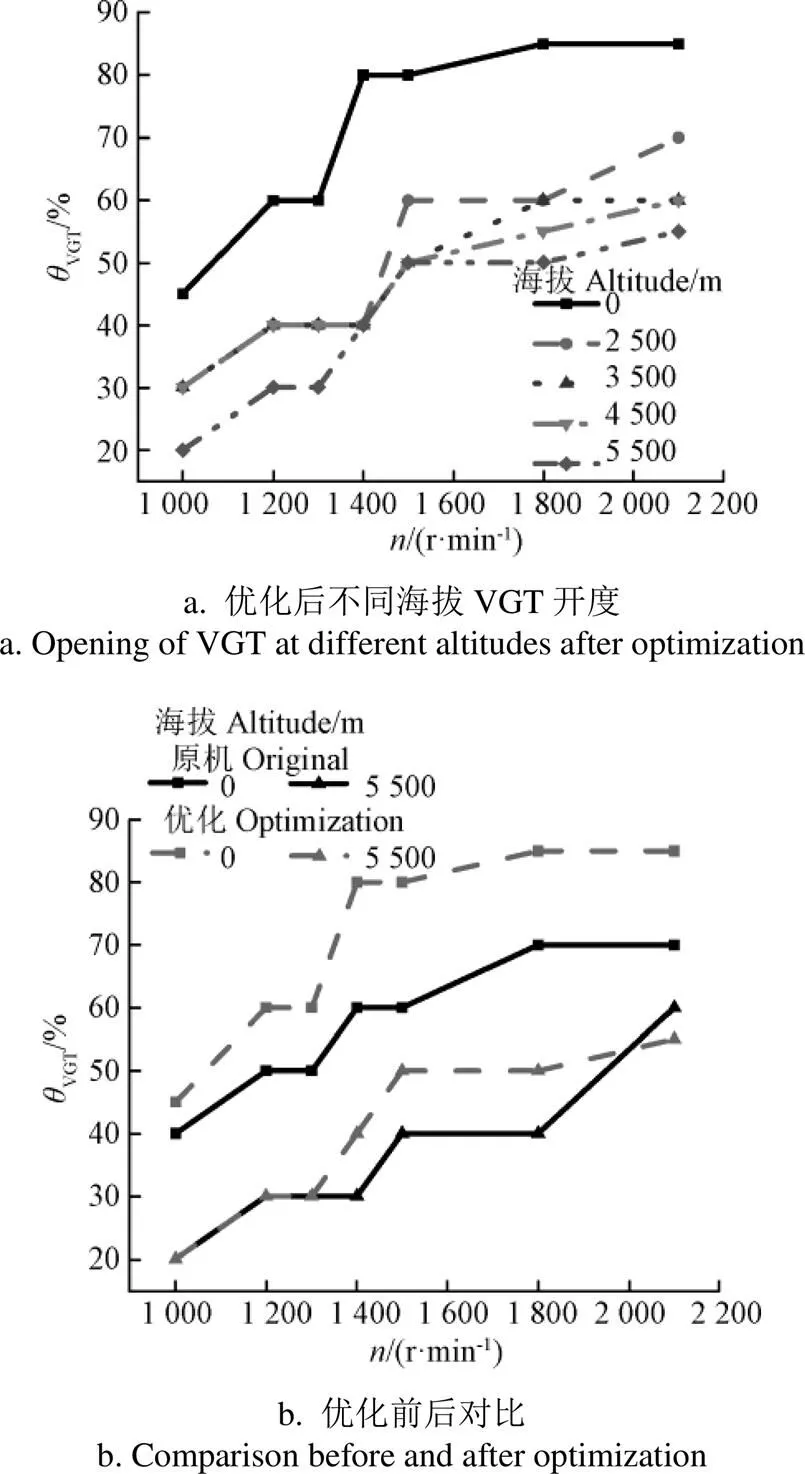
图9 最佳VGT叶片开度随转速的变化规律
由以上结论可以得到不同转速下优化前后增压与喷油参数协同优化控制策略。0 m海拔条件下,相比于原机,优化后柴油机VGT叶片开度和喷油量增大,喷油提前角减小。主要由于0 m海拔条件下,进气流量和过量空气系数较大使得缸内密度增加,增大喷油量与VGT叶片开度减小喷油提前角,能够在保证最高燃烧压力不超限的前提下有效提升柴油机动力性。5 500 m海拔条件下,相比于原机,柴油机优化后低转速下VGT叶片开度不变,循环喷油量和喷油提前角增大,中高转速下VGT叶片开度和循环喷油量增大,喷油提前角减小。相比于单级增压,柴油机匹配二级增压后在低速条件下能够改善涡轮增压器的效率,在VGT叶片开度不变条件下,增大循环喷油量和喷油提前角有利于增加滞燃期内混合气,进而提高柴油机低速时动力性能[30]。随着转速增加,一方面涡轮增压器效率升高,进气量增加明显,柴油机增加循环喷油量,增大了混合气浓度,有利于动力性提升,但柴油机排温与增压器转速也会增加,为了防止这些超限,必须增大VGT开度,减小喷油提前角。
4 结 论
1)将仿真模型与神经网络相结合,有效构建增压和喷油参数与输出转矩之间联系,所构建模型的预测值和仿真值之间相关度较高,能够用于增压与喷油参数协同优化研究。
2)相比于原机,优化后最佳循环喷油量增加,增加量呈现出自最大转矩转速点向两侧逐渐增大的趋势。最佳喷油提前角,在海拔2 500和5 500 m低速时分别增加了1和1.5 °CA,随转速升高,最佳喷油提前角平均分别减小了25.2%和17.5%。最佳VGT开度在海拔0 m时,增大幅度随转速增加而增大,在海拔5 500 m时,低速时最佳VGT开度不变,中高转速VGT增加幅度随转速先增大后减小。
3)通过增压与喷油参数协同优化后,在0 m海拔条件下,VGT叶片开度和喷油量增大,喷油提前角减小。5 500 m海拔条件下,低速下VGT叶片开度不变,循环喷油量和喷油提前角增大,中高转速下VGT叶片开度和循环喷油量增大,喷油提前角减小。
[1] 倪计民,刘越,石秀勇,等.可变喷嘴涡轮增压及废气再循环系统改善柴油机排放性能[J].农业工程学报,2016,32(16):82-88. Ni Jimin, Liu Yue, Shi Xiuyong, et al. Variable nozzle turbine combined with Venturi exhaust gas recirculation system improving emission performance of diesel engines[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(16):82-88. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] Liu R, Zhang Z, Dong S, et al. High-altitude matching characteristics of regulated two-stage turbocharger with diesel engine[J]. Journal of Engineering for Gas Turbines and Power, 2017, 139(9):094501-094509.
[3] Jiao Y, Liu R, Zhang Z, et al. Comparison of combustion and emission characteristics of a diesel engine fueled with diesel and methanol-Fischer-Tropsch diesel-biodiesel-diesel blends at various altitudes[J]. Fuel, 2019, 224(5):52-59.
[4] 毕玉华,唐成章,申立中,等.VNT与EGR耦合对不同气压下燃用含氧燃料柴油机性能的影响[J].农业工程学报,2018,34(17):38-45. Bi Yuhua, Tang Chengzhang, Shen Lizhong, et al. Effect of VNT and EGR coupling on performance of diesel engine fueled with oxygenated fuel under different atmospheric pressures[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(17):38-45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 周广猛,刘瑞林,焦宇飞,等. 柴油机高原燃烧特性研究进展[J]. 车用发动机,2018(4):17-21. Zhou Guangmeng, Liu Ruilin, Jiao Yufei, et al. Research progress of diesel engine combustion characteristics in plateau environment[J]. Vehicle Engine, 2018 (4):17-21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 黄粉莲,纪威,周炜,等.车用涡轮增压柴油机加速工况瞬态特性仿真[J].农业工程学报,2014,30(3):63-69. Huang Fenlian, Ji Wei, Zhou Wei, et al. Simulation of transient performance of vehicle turbocharged diesel engine during acceleration process[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(3):63-69. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 王俊,申立中,杨永忠,等.基于响应曲面法的非道路用高压共轨柴油机设计点优化标定[J].农业工程学报,2017,33(3):31-39. Wang Jun, Shen Lizhong, Yang Yongzhong, et al. Optimizing calibration of design points for non-road high pressure common rail diesel engine base on response surface methodology[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(3):31-39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 王利民,韩义勇,裴海俊.基于多级闭环的柴油机VGT控制策略的研究[J].汽车与配件,2018(20):72-74. Wang Limin, Hang Yiyong, Pei Haijun. Research on control strategy of diesel VGT based on multi-level closed loop[J]. Automobile & Parts, 2018(20): 72-74. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 唐蛟,李国祥,王志坚,等.基于欧Ⅵ柴油机EGR阀与VGT阀解耦控制策略研究[J].内燃机工程,2015,36(3):63-67. Tang Jiao, Li Guoxiang, Wang Zhijian, et al. Study of EGR/VGT decoupling control strategy based on euroⅥ diesel engines[J]. Chinese Internal Combustion Engine Engineering, 2015, 36(3): 63-67. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 朱振夏. 增压柴油机高原环境下的供油与进气调节研究[D].北京:北京理工大学,2015. Zhu Zhenxia. Investigation on Parameters Adjustment of Fuel Supplying and Air-Intaking Systems for Diesel Engines Working at Plateau Environment[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 董素荣,刘瑞林,周广猛,等. VGT叶片开度对二级增压柴油机高海拔燃烧特性与性能的影响[J]. 内燃机学报,2017,35(3): 231-237. Dong Surong, Liu Ruilin, Zhou Guangmeng, et al. Effects of VGT blade opening on combustion and performance on a two-stage turbocharging diesel engine at high altitude[J].Transactions of CSICE, 2017, 35 (3):231-237. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 陈贵升,陈春林,狄磊,等.可变二级增压柴油机变海拔工作特性数值模拟[J].内燃机学报,2018,36(4):305-313. Chen Guisheng, Chen Chunlin, Di Lei, et al. Numerical simulation on performance of diesel engine equipped with regulated two stage turbocharging systems at different altitudes[J]. Transactions of CSICE, 2018, 36 (4):305-313. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 徐思友,潘丽丽,杨磊,等.二级增压系统不同旁通结构流阻特性仿真分析[J].车用发动机,2017(4):68-72. Xu Siyou, Pan Lili, Yang Lei, et al. Simulation on flow resistance characteristics of different bypass structures for two-stage turbocharger[J]. Vehicle Engine, 2017(4):68-72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 董素荣,刘卓学,熊春友,等.二级可调增压共轨柴油机的高海拔燃烧特性[J].燃烧科学与技术,2017,23(1):36-40. Dong Surong, Liu Zhuoxue, Xiong Chunyou, et al. High altitude combustion characteristics of common rail diesel engine with two-stage regulated turbocharging system[J]. Journal of Combustion Science and Technology, 2017, 23(1):36-40. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 腾鹏坤. 喷油与供气策略对二级增压柴油机瞬变性能的影响[D].长春:吉林大学,2017. Teng Pengkun. The Influence of Injection and Intake Parameters On the Two-Stage Turbocharges Diesel Engine Under Transient Operations[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 袁兴.复合EGR对二级增压柴油机瞬变性能的影响[D].长春:吉林大学,2018. Yuanxing. Effect of Hybrid EGR on Transient Performance of a Two-Stage Turbocharged Diesel Engine[D].Changchun: Jilin University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 李长江. 柴油机高原可调二级增压系统的匹配与调节[D].北京:北京理工大学,2016. Li Changjiang. The Study of Matching and Adjusting of Regulated Two-Stage Turbocharging System for Diesel Working at Plateau[D].Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] Hiroyasu H, Arai M. Structure of Fuel Sprays in Diesel Engine[C]// Society of Automotive Engineers: International Congress & Exposition. Detroit: SAE International in United States, 1990.
[19] Woschni G.A applicable equation for the instantaneous heat transfer coefficient in the internal combustion engine[C] // Society of Automotive Engineers: National Fuels and Lubricant &Transportation Meetings. Detroit: SAE International in United States, 1967.
[20] 王明露. 国Ⅴ共轨柴油机逐点模型标定研究[D].秦皇岛:燕山大学,2017. Wang Minglu. Study on Point by Point Model Base Calibration for CN V Common Rail Diesel Engine[D]. Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 周广猛. 高压共轨柴油机高海拔标定和燃烧过程研究[D].武汉:海军工程大学,2012. Zhou Guangmeng. Research on High Altitude Calibration and Combustion Process of Common Rail Diesel Engine[D]. Wuhan: Naval University of Engineering, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 牛晓晓,王贺春,李旭,等.基于神经网络的柴油机性能预测模型优化[J].内燃机学报,2018,36(6):561-568. Niu Xiaoxiao, Wang Hechun, Li Xu, et al. Optimization of diesel engine responses prediction model based on neural network[J].Transactions of CSICE, 2018, 36 (6):561-568. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 王森,赵金星,刘双寨,等.基于神经网络和遗传算法的Atkinson循环发动机几何压缩比优化[J].内燃机学报,2015,33(4):370-377. Wang Sen, Zhao Jinxing, Liu Shuangzhai, et al. Optimization of geometrical compression ratio for an atkinson cycle engine based on artificial neural network and genetic algorithm[J]. Transactions of CSICE, 2015, 33 (4):370-377. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 朱振夏,张付军,吴滔滔,等.基于神经网络的零维预测燃烧模型及建模方法[J].内燃机学报,2015,33(2):163-170. Zhu Zhenxia, Zhang Fujun, Wu Taotao, et al. Zero-D predictable combustion model based on neural network and modeling[J]. Transactions of CSICE, 2015, 33 (2):163-170. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] Meng X, Jia M, Wang T. Neural network prediction of biodiesel kinematic viscosity at 313 K[J]. Fuel, 2014, 121:133-140.
[26] Wu B, Filipi Z, Kramer D, et al. Using neural networks to compensate altitude effects on the air flow rate in variable valve timing engines[C]// Society of Automotive Engineers: SAE 2005 World Congress & Exhibition. Detroit: SAE International in United States, 2005.
[27] 王宪成,郭猛超,和穆,等.高原环境大功率柴油机性能综合改进技术研究[J].内燃机工程,2014,35(2):113-118. Wang Xiancheng, Guo Mengchao He Mu, et al. Study on improvement of high power diesel engine performance in plateau environment[J]. Chinese Internal Combustion Engine Engineering, 2014, 35(2): 113-118. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 刘瑞林.柴油机高原环境适应性研究[M].北京:北京理工大学出版社,2013:151-159.
[29] 邹泽宇. 不同增压系统对重型柴油机性能和排放影响的试验研究[D].天津:天津大学,2017. Zhou Zeyu. Effect of Different Turbocharging Systems on Performance and Emissions of a Heavy-duty Diesel Engine[D].Tianjin: Tianjin University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] 杨春浩,刘瑞林,张众杰,等.基于VGT控制参数的柴油机低速变海拔热平衡试验[J].热科学与技术,2019,18(3):206-213. Yang Chunhao, Liu Ruilin, Zhang Zhongjie, et al. Exper imental study on thermal balance of diesel engine at low speed affected by VGT control parameters at variable altitudes[J]. Journal of Thermal Science and Technology, 2019, 18(3): 206-213. (in Chinese with English abstract)
Optimization of supercharger and injection parameters for diesel engine at plateau environment
Jiao Yufei1, Liu Ruilin2※, Zhang Zhongjie1, Zhou Guangmeng2, Yang Chunhao3, Ma Jiaming1
(1.,,300161,; 2.,,300161,; 3.,,430033,)
Supercharge and fuel injection are direct factors to improve the performance of diesel engines at plateau. When diesel engines are used at higher altitudes, especially in the Qinghai-Tibet plateau region with the altitude ranging from 3000 to 5000 m, the decreasing ambient pressure and temperature reduce the air inflow resulting in deteriorating combustion, reducing power output, increasing fuel consumption, worsening emissions, exceeding cylinder pressure, cylinder pressure, thermal load and turbocharger speed limits. The optimization of injection parameters can improve the plateau combustion process of diesel engine to some extent, however, optimization of injection parameters alone cannot fundamentally solve the problem of insufficient intake and power decline of diesel engines at plateau. Two-stage variable geometry turbocharge (VGT) system is an effective way to increase the intake pressure effectively. However, only optimizing the control parameters of the supercharging system without adjusting the injection parameters will lead to the problem of "improper oil and gas coordination" at high altitude, and the plateau application potential of the two-stage variable geometry turbocharge system cannot be fully play. Recent researches mainly focused on optimizing injection parameters or two-stage variable geometry turbocharge system, there was few about the comprehensive optimization of supercharger and injection parameters, therefore, the paper focused on optimizing the compositive control strategy of supercharge and injection parameters. In the paper, a GT-Power model of a two-stage variable geometry turbocharged (VGT) diesel engine was built and verified by experiment on engine plateau environment simulating testing bed. The simulation performance date of the engine was obtained from the model. What’s more, the neural network was established and then trained with these simulation values to improve the power performance of the engine, and finally the optimization rules and comprehensive control strategy of supercharge and injection parameters were obtained. The results showed that: The optimized circulating fuel injection quantity had similar variation trend with the original parameters. What was different was that the circulating fuel injection quantity increased after optimizing, the increment came to its maximum at lower speed and its minimum at speed of maximum torque, and it showed a trend that the increment quantity gradually increased from the speed point of the maximum torque to both sides. With the increase of altitude, the optimal cycle fuel injection quantity of the engine decreased gradually, and the decreasing trend increased gradually with altitude increasing. The circulating fuel injection quantity decreased by 10.96% on average from 0 to 3500 m, and by 16.99% on average from 3500 to 5500 m. At a certain altitude, the optimal injection advance angle of the engine decreased first and then increased with the increase of speed, and the average value of the optimal injection advance angle increased with altitude increasing. Compared with the original parameters, the optimum injection advance angle increased by 1 and 1.5℃A, respectively, at low speed conditions of 2500 and 5500 m, however, when it came to higher speed, the optimum injection advance angle decreased by 25.2% and 17.5%, respectively. The optimum VGT opening increased large gradually with the increase of the speed at 0 m, while when it came to 5500 m, it kept invariable at lower speed, and increased firstly and then decreased at higher speed. After comprehensive optimizing of supercharge and fuel injection, the VGT opening and circulating fuel injection quantity increased and the injection advance angle decreased at 0 m. When it came to low speed of 5500 m, the VGT opening kept invariable, the circulating fuel injection quantity and injection advance angle increased, however, the VGT opening and circulating fuel injection quantity increased, the injection advance angle decreased at high speed.
diesel engine; optimization; high altitudes; two-stage variable geometry turbocharged system; injection parameters
2019-05-05
2019-08-28
国防预研资助项目(30105190501)
焦宇飞,博士生,主要研究方向含氧燃料高原环境适应性。Email:jiaoyufei2016@163.com
刘瑞林,教授,博士生导师,主要从事内燃机高原环境适应性研究。Email:163lrl@163.com
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.17.009
TK427
A
1002-6819(2019)-17-0066-08
焦宇飞,刘瑞林,张众杰,周广猛,杨春浩,马家明.高原环境条件下柴油机增压与喷油参数协同优化[J]. 农业工程学报,2019,35(17):66-73. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.17.009 http://www.tcsae.org
Jiao Yufei, Liu Ruilin, Zhang Zhongjie, Zhou Guangmeng, Yang Chunhao, Ma Jiaming. Optimization of supercharger and injection parameters for diesel engine at plateau environment[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2019, 35(17): 66-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.17.009 http://www.tcsae.org

