The Validity Study on the Reading Comprehension of JSGT in Xiamen
陈慧端


【Abstract】Junior Secondary Graduation Test is an important test that is used to select qualified students to get higher education. Reading comprehension plays a major part in the entrance exams. This paper is designed to examine the validity of reading comprehension tests of JSGT in Xiamen. Judging and analyzing from the data, the author finds that the comprehension parts have conformed to the two syllabus and have reached a high content validity. However, the author also finds some insufficiency and puts forward several suggestions so as to improve the future reading comprehension tests.
【Key words】Content validity; reading comprehension of JSGT in Xiamen (2012, 2013, 2016)
1. Introduction
Reading is a basic and crucial skill in our daily life. And reading comprehension is critical to the development of all students reading skills. This is particularly true in the upper grades in the senior high school, where the curriculum requires that students comprehend increasingly complex texts. Furthermore, the total score of JSGT is 150, and reading comprehension part accounts for 50. Therefore, it can be safely concluded that the content validity study on Junior Secondary Graduation Test reading comprehension is of great value, typical and representative. This article will focus on the content validity of reading comprehension in 2012, 2013, and 2016 JSGT aiming to find out whether the tests conforms to the requirements of the National English Curriculum Standard and Blooms cognitive taxonomy and offer useful suggestions for improving the design of the test and reflections on how to upgrade students reading comprehension in Junior High school.
2. Research Design
The author analyses the reading comprehension parts of 2012, 2013, 2016 JSGT in Xiamen, then uses the framework of task characteristics and content validity study theories put forward by Bachman and Palmer (1999) and combines with the junior high English teaching syllabus and also gives specific examples. The data was collected from 24700 participants in 2012 and 24388 participants in2013 and 28624 participants. .
2.1 Results and Discussions
2.1.1 Content validity analysis
A. Topics
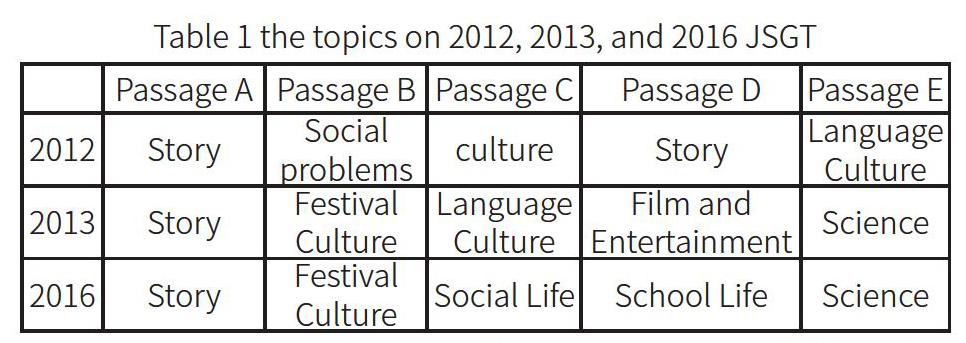
Teaching syllabus and test syllabus states the following themes can be included in the English test: social life, culture, geography, history, science, politics, education, biography, etc.There are 15 articles in total and 3 in total.
As Table 1 shows, among the 15 passages, social life takes up 13%, science takes up 13%, culture takes up33%, school life takes up 6%, film and entertainment takes up 6%. However, the author finds out that there are no topics on biography, history, or geography in these three papers. Alderson(2000) believes that good reading tests and good evaluation procedures will ensure that readers can understand various texts theme. Weir(1993, P67) pointed out that this topic should not be culturally biased, nor should it be biased towards some test groups.Thus, by analyzing Table 1, its obvious that the themes are not involved completely. Its suggested that JSGT should select various topics to ensure the diversity and extensive of reading materials. However, Most of the topics can stimulate students interest in reading to a great extent. for example, the introduction of the famous TV program-A Bite of China. Some topics can make the test takers actuate their prior experience, like the introduction of Chinese traditional 24 solar term-grain rain.
B. Types of genres
With the syllabus and the examination syllabus as the fundamental basis, narratives, arguments, discourses, application texts, and newspapers should appear in the English test paper.
The narrative describes what happened and the events were performed in a meaningful order.
The debate seeks to convince through evidence or emotional appeal.
Exposition explains, defines analyses, illustrates, or compares.
The essay is a essay that is often used in everyday life. (Zhang Shukui, 2014 ).
Generally speaking, from the Table 2 above, the three papers cover different genres. But there are no argumentation texts and practical writing genre texts in the paper. Exposition and news reports occupy a large proportion, and both of them are considered as the two most commonly used genres in the reading comprehension part of the three papers. For the ninth graders, the proportion for narration is proper and suitable. News report also accounts for a large proportion in the three papers, which encourage students to pay more attention to the latest news report and use English to know whats happening around the world. However, the three papers didnt cover the argumentation and practical writing genres. In summary, it is clear that it does not fit the syllabus very well. A suggestion can be made that the genres like argumentation, practical writing should get equal attention in the future JSGT test so as to have a positive impact on English teaching and learning.
C. Item Difficulty Index
According to Heaton (2000), many test constructors may be ready to accept items with facility values between 0.3 and 0.7. An item should be excluded if its FV is below 0.2 or if its FV is above 0.9. Ideally items FVs should fall between 0.4 and 0.8 (Zou Shen 1997, p18). We can see from the above four tables that most of the facility values range from 0.4 to 0.8, except Item 43 in 2012 is above 0.9 and Item 54 is below 0.4. However, what should be of concern to us is that the layout of the reading paragraphs usually has some weak points. In general, the ordering of reading paragraphs should be from easy to difficult, but some papers do not follow this logic.such as in Paper 2016, the difficulty index of five passages are almost the same. Students get the best scores in Passage B, and the lowest ones in Passage A. Furthermore, In Paper 2012, students did poorly in Passage C. The passage is a news report about a widely-known TV program ‘The bite of China. In fact, the readability of this passage is moderate. The structure and vocabulary difficulty of an article are combined to form the readability of this article. But schemata and background knowledge are also important variables that affect the nature of reading. Alderson mentions that when readers process text, they integrate the new information from the text into their preexisting schemata (2000, p33). Thus, its suggested that teachers should constantly elevate their culture cultivation and professional knowledge to meet the requirements of new NECS. During teaching process, teachers can integrate the culture knowledge, current events into their class and provide more access for students to various English reading materials.
C. Reading skills
A survey of the distribution of the reading skills of the main contents of these three papers are shown in Table 5:
As the above table shows, the overall reading skills coverage is not very all-rounded and well-balanced. There are 75 questions in these 3 papers in total. The six specific reading skills take up various proportions in the three tests. Based on the data above, the author can reach the following conclusions:
Among the 3 papers, the largest proportion of micro-skills that understand explicit information in the total number of projects. It has a ratio of 50.7%. It means that great importance has been attached to the surface or literal understanding of the passage, which are considered as the basic requirement for reading comprehension in Junior Middle School.
Micro-skill of making simple judgment and inference takes up 21.3%. The reader must make inferences based on what he believes to be true, otherwise the decision cannot be made easily.Its a higher level reading skill that students need in the daily life as well as in the reading comprehension tests.
Apart from the above two skills, these three papers pay little attention to the structure of the passage and writers intention and attitude. They only take up 2.7% and 4%. Its not well-balanced. Therefore, in the future tests, the developer should keep a good balance among six reading skills.
3.Conclusions and suggestions
Generally speaking, based on the analysis of a large amount of data collected from the students participated in the 3 yearsJSGT in Xiamen, the standards for the syllabus and test syllabus apply to reading comprehension tests.The characteristics of these three papers and the suggestions are as following:
First, the topics of the reading materials mainly cover culture, hot-spot news and reports home and abroad, science and so on. Some topics are quite novel and vivid. They are close to students daily life or modern social life. The topics are extensive and push students to apply English to read more English magazines and newspapers. Furthermore, teachers need to constantly elevate their culture awareness and upgrade themselves. Meanwhile, teachers should integrate the current events with their teaching and encourage students to do more reading besides textbooks.
Second, as for the genres of the passages, narration, exposition and news report are distributed in these papers. In the future tests, argumentation and practical should also be included in t he tests so as to improve the diversification of types of literature.
Third, most of the passages are selected with proper difficulty. The item difficulty Index is well under controlled. But the layout of the reading paragraph usually has some weak links. In a certain sense, the author suggests that the reading channels be arranged in order according to the principle of “from easy to difficult”.
Fourth, tests developer should take six micro skills into full consideration.
Last but not least, the test format should be enriched. Weir (1993) mentioned in the article that multi-selection testing almost completes the reliability of the markup, which is faster than other forms of written tests, and it also has a relatively low cost. However, the MCQ formats also have some disadvantages.
References:
[1]Alderson, J. C.. Accessing Reading[M]. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press,2000.
[2]Alderson, J. C.. Testing reading comprehension skills (Part One)[J]. Reading in a Foreign Language,19906(2):425-438.
[3]Bloom, B. et al. Taxonomy of Educational Objectives: The classification of Educational Goals (Handbook 1: Cognitive domain) [J]. New York: Longman,1956.
[4]Hennig, G.. Development, evaluation and research, A Guide to Language Testing, Cambridge[J]. Massachusetts, Longman, 1987:89.
[5]Heaton, J. B.. Writing English Language tests[M]. Beijing: Foreign Language Teaching and Research Press,2000:159.
[6]Lyle F. Bachman, Fundamental Considerations in Language Testing,1990:25.
[7]Messick, S.A..‘Validity in Linn[J].1989:13-103.
[8]Munby, J.. Read and think, Harlow: Longman[J].1968.
[9]Spolsky, B.. Measured words: The Development of Objective Language Testing[M]. Oxford, Oxford University Press,1995.
[10]Weir, C. J.. Understanding and Developing Language Tests [J]. Hemel Hempstead: Prentice Hall International (UK) Ltd,1993.
[11]中華人民共和国教育部.义务教育课程标准[M].北京:人民教育出版社,2011.
[12]张书奎.Diachronic Validity Study on NMET Reading Comprehension Part (2001-2010)[J].2014.
[13]邹申.TEM考试效度研究[M].上海外语教育出版社,1997.

