液压机械无级传动全功率换段过程排量比调节模型
杨树军,张 曼,曾盼文,张寅君,张 璐,田 霖
液压机械无级传动全功率换段过程排量比调节模型
杨树军1,张 曼1,曾盼文2,张寅君1,张 璐1,田 霖1
(1. 燕山大学车辆与能源学院,秦皇岛 066004;2. 江麓机电集团有限公司,湘潭 411199)
为了解决液压机械换段过程中存在的转速波动和瞬时动力中断等问题,该文以两离合器结合重叠的五阶段全功率动力换段方法为基础,分析了液压机械全功率换段过程变排量液压元件排量比调节规律。以某等差两段式液压机械为研究对象,建立了液压机械全功率换段过程变排量液压元件排量比调节模型,通过仿真分析和全功率换段过程试验,获得了换段过程液压回路压力从当前段到目标段随排量比变化的动态响应过程。结果表明,排量比变化量的仿真与试验结果基本一致,最大偏差为8.93%,验证了模型的正确性;排量比调节模型能够根据当前段状态参量和目标段压力预测出目标段排量值;阶跃排量比调节规律能有效缩短液压回路建压时间,建压时间为0.93 s,压力波动量较小,为0.64 MPa;按阶跃调节排量比至目标值,能在换段过程完成液压回路高低压侧压力平稳互换,换段前后输出转速几乎无波动、转矩连续传递。经增速机后的输出转矩为100和150 N·m时,换段时间分别为1.00和1.10 s,该转矩的最大波动量分别为6.80和6.84 N·m,换段过程中功率连续且平稳传递。研究结果可为实现液压机械无级传动全功率换段控制及后续研究提供参考。
液压机械;传动;控制;无级传动;全功率换段;排量调节
0 引 言
液压机械无级传动(hydro-mechanical variable transmission,HMT)是由液压功率传动机构和机械功率传动机构复合而成的双功率复合传动形式。具有实现大功率无级调速,传动效率高等突出优点,已经在军用车辆、工程机械和拖拉机等大功率车辆上广泛使用[1-3],成为了大功率车辆无级传动系统的主要发展方向[4-6]。
Ali H Shaker和Berger Guenter对HMT传动特性和控制方式等问题展开了深入系统的研究[7-8]。文献[9-10]开展了关于液压机械无级变速器控制技术的研究工作。文献[11]开展了关于液压机械传动特性分析以及建模仿真等方面的研究工作。文献[12]研制出了装配在M2步兵车和M3侦察车上的HMPT-500系列液压机械传动装置。其他学者和科研技术人员也都相继在HMT各构型和控制领域开展了卓有成效的理论研究和产品研制工作[13]。
国内苑士华等带领的科研团队对液压机械较早开展了研究,提出了相对完整的HMT参数设计和理论分析方法[14-16]。张明柱等研究了农用拖拉机多段液压机械无级变速器[17-18]。郭占正等建立了液压机械无级传动模型和液压路仿真模型[19]。魏超等开展了HMT段内速比跟踪策略研究,可使发动机工作在最佳区域[20-21]。王光明等分析了液压机械换段品质的影响因素[22-23]。朱镇等仿真分析了分段式液压机械变速器换挡策略,通过优化参数和换挡时序,提高换挡品质[24-25]。但以上换段研究均是在常规换段基础上进行的,换段中离合器的分离与结合间存在一定的时间间隔或短时间的滑摩重叠,液压传动单元的压力由负载被动产生,不能从根本上消除动力中断和换段冲击。胡纪滨等探究了换段过程中双制动器结合重叠的可行性[26-27]。杨树军等分析了换段过程的影响因素,研究了换段控制方法及功率过渡特性,提出了五阶段全功率换段方法[28-30]。全功率换段过程中,两离合器结合重叠消除了常规换段过程的惯性相,通过调节排量比能主动实现液压回路高低压侧互换达到目标段压力。然而排量比调节的动态过程决定着液压回路高低压侧互换的过程及换段时间,目前关于全功率换段过程中排量比调节规律的研究未见文献报道。
本文建立了换段过程液压回路容腔模型和变排量液压元件排量调节模型,深入研究了全功率换段中排量调节特性对液压回路动态建压过程的影响规律,获得了换段过程排量的调节值和有效缩短换段时间的排量比调节规律。
1 液压机械全功率换段原理
1.1 液压机械工作原理
等差两段式液压机械无级传动样机结构简图如图1所示。HMT工作在液压段(H段)时,变排量液压元件驱动定排量液压元件,离合器H处于结合状态,行星排1工作;液压机械段(HM段)前半段时,定排量液压元件驱动变排量液压元件,离合器L处于结合状态,行星排23工作,汇流机构将液压流传动机构与机械流传动机构所传递的功率汇流输出。
1.2 液压机械全功率动力换段特性
HMT全功率动力换段过程如图2所示[31]。
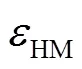
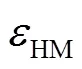
1.3 液压机械全功率换段转矩转移特性
换段过程中,两离合器结合重叠,进入换段状态,HMT各行星排、离合器和定排量液压元件的转矩存在如下关系:
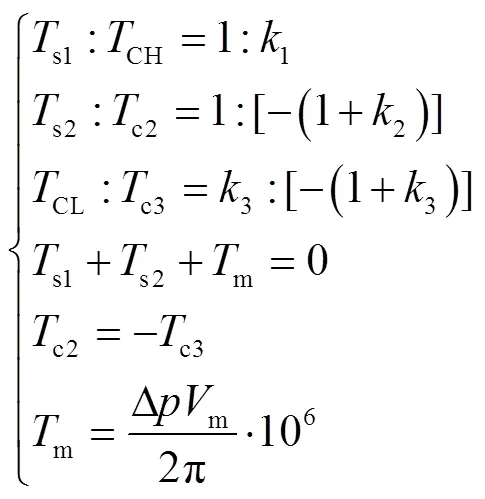
求解式(1)可得HMT全功率换段过程的转矩特性,如式(2)。
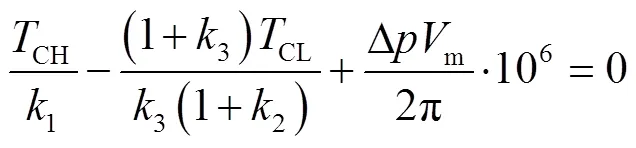
由式(2)可知,两离合器结合重叠的换段过程中,闭式液压回路高低侧压差变化,HMT当前段到目标段离合器的转矩会发生改变。根据文献[30],闭式液压回路的压力可通过调节变排量液压元件排量比控制,实现转矩转移和功率过渡。
2 液压机械全功率换段排量调节特性
2.1 全功率换段过程液压回路等效模型

两离合器结合重叠的换段过程中,定排量液压元件转速与变排量液压元件的转速之比为一个定值,液压回路低压侧容腔压力由补油压力确定且保持恒定不变,高压侧容腔压力的变化由进出容腔的油液流量决定,可表示为

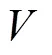

图3 HMT闭式液压回路等效模型
Fig.3 HMT hydraulic circuit equivalent model
2.2 H段至HM段全功率换段过程排量调节模型
H段至HM段换段时下腔建压,变排量液压元件进油口和定排量液压元件出油口的实际流量分别为
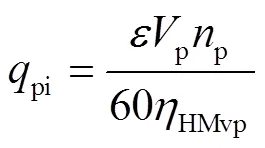
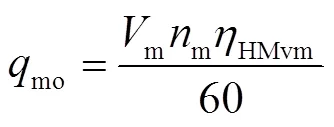
当HMT工作在H段至HM段换段后稳定阶段时,变排量液压元件和定排量液压元件容积效率分别为

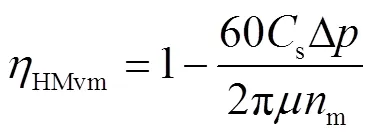
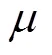
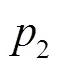
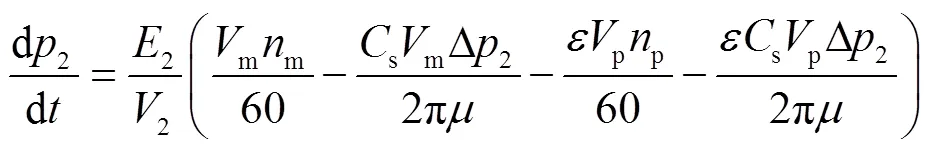

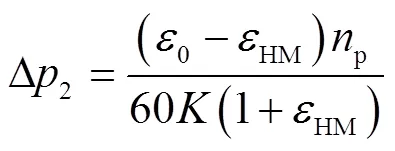
由式(2)、式(10)可得H段至HM段全功率换段过程转矩转移机理表达式。

H段换至HM段的换段过程中通过调节变排量液压元件的排量比控制压力动态变化过程,排量比按一定规律由当前值调节至目标值,使换段过程中闭式液压回路的压力从当前段状态向目标段压力过渡,控制转矩从当前段离合器向目标段离合器转移。
2.3 HM段至H段全功率换段过程排量调节模型
HM段至H段换段时上腔建压,变排量液压元件出油口和定排量液压元件进油口的实际流量分别为
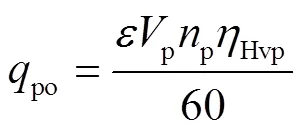

HMT工作在HM段至H段换段后稳定阶段时,变排量液压元件和定排量液压元件容积效率分别为
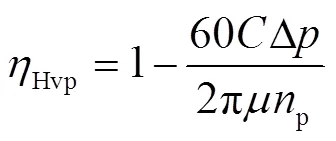


程慧(2013)等采取实证研究的方法,通过对证券市场近年数据建模研究显示,研发支出相关会计规定的修订,提升了企业在年报对于研发支出的发布要求然而对于细节实施方面,如研发项目信息公开的表现形式,明细增减变动,研发资金的现金流等仍欠缺行业认可和统一的披露发方法。
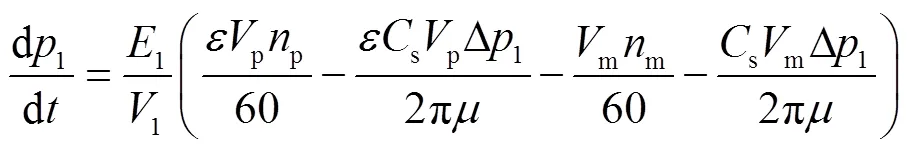
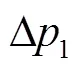

将式(17)简化,得到HM段换至H段闭式液压回路压力差与排量比的关系为

由式(2)、式(18)得HM段至H段全功率换段过程转矩转移机理表达式。
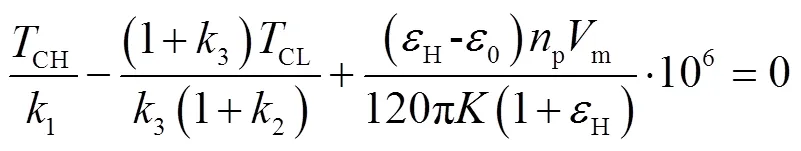
HM段换至H段的换段过程中通过调节变排量液压元件的排量比控制压力动态变化过程,调节排量比至目标值时,HMT从当前段过渡至目标段,从而实现转矩平稳转移。
2.4 全功率换段过程排量调节特性仿真分析
为了分析全动率换段过程排量比特性,本文建立的HMT全功率换段过程闭式液压回路容腔模型和排量比调节模型的参数如表1。
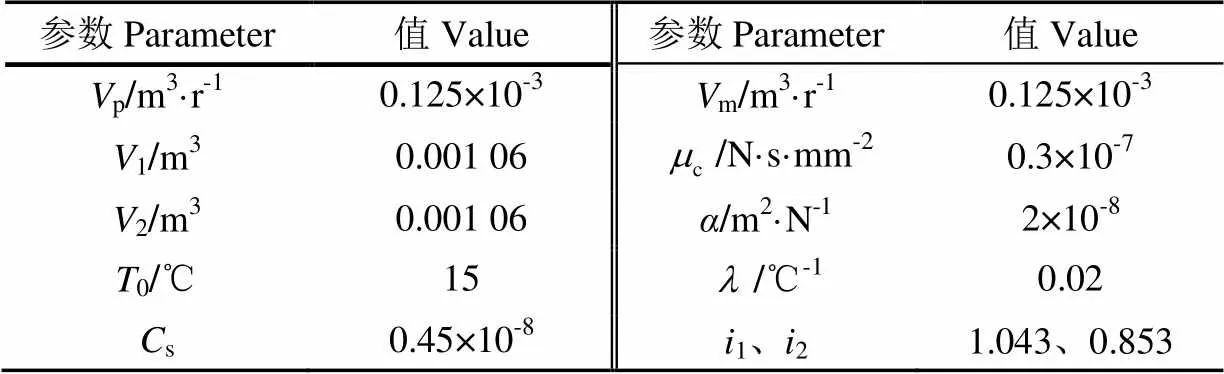
表1 液压回路仿真模型参数 Table 1 Parameters of simulation model for hydraulic circuit
排量比调节分别采用阶跃和线性2种调节,对应的液压回路压力响应过程如图4所示。

注:、分别表示液压回路高低压侧压力,MPa。下同。
图4a是H段换向HM段压力动态响应过程,H段压力为11.07 MPa,排量比从0.972调节为0.804,调节后的HM段压力为9.07 MPa。排量比阶跃调节时,建压所需时间为0.93 s,压力波动量为0.39 MPa,相对偏差为4.30%;排量比线性调节时,建压所需时间为1.68 s,压力波动量为0.19 MPa,相对偏差为2.09%。图4b是HM段换向H段压力动态响应过程,排量比从0.804调节为0.972,压力从HM段9.07 MPa调节为H段11.11 MPa。排量比阶跃调节的建压时间为0.85 s,压力波动量为0.64 MPa,相对偏差5.76%;排量比线性调节的建压时间为1.63 s,压力波动量为0.46 MPa,相对偏差为4.14%。
从建压时间分析,排量比阶跃调节明显优于线性调节;从液压回路压力波动量看,线性调节优于阶跃调节;与排量比线性调节相比,阶跃调节有效减小了建压时间,高压侧压力波动量无明显变化,为了减小换段时间,可采用排量比阶跃调节。
3 液压机械全功率换段过程排量调节试验
3.1 试验设备
为研究HMT全功率换段过程变排量液压元件排量比调节特性,搭建了HMT全功率动力换段试验台架,试验原理和实物照片如图5所示。
试验台主体部分为洛阳凯迈机电的变速箱电封闭传动试验台。HMT动力源为CJ250变频电机(额定功率为250 kW),动力输出端经转速转矩仪与HMT样机输入端相连接;HMT输出端经增速机(增速比1∶3)、T40转速转矩仪(额定转矩为1 000 N·m,转矩精度为0.5%F.S)与加载装置相连,加载装置为CJ200电力测功机(额定功率为200 kW);试验台离合器润滑控制油液由泵站提供,闭式液压回路中所用油液与润滑系统所用油液分开供给,并在定排量液压元件输出轴加装转速传感器(OD9011-NPN),在液压回路高低压侧油路加装压力传感器(HDA3844-A-600,量程0~60 MPa,精度为0.2%F.S)、补油压力传感器、壳体温度传感器,离合器控制回路加装压力传感器(JYB-K0-HAG,量程2.5 MPa,精度为0.5%F.S)和温度传感器(JWB23/2e/A,量程-50~150 ℃,精度为0.2%F.S)。试验台测控系统由试验台控制柜和HMT控制器组成。HMT控制器输出两路开关量控制离合器电磁阀,输出2路比例电流(含颤振)驱动变排量液压元件排量调节机构比例阀,并进行数据采集。比例阀电流从当前值阶跃调节为目标值时,改变伺服阀两端控制油压,使伺服缸运动至目标位置,变量泵调节至目标排量。
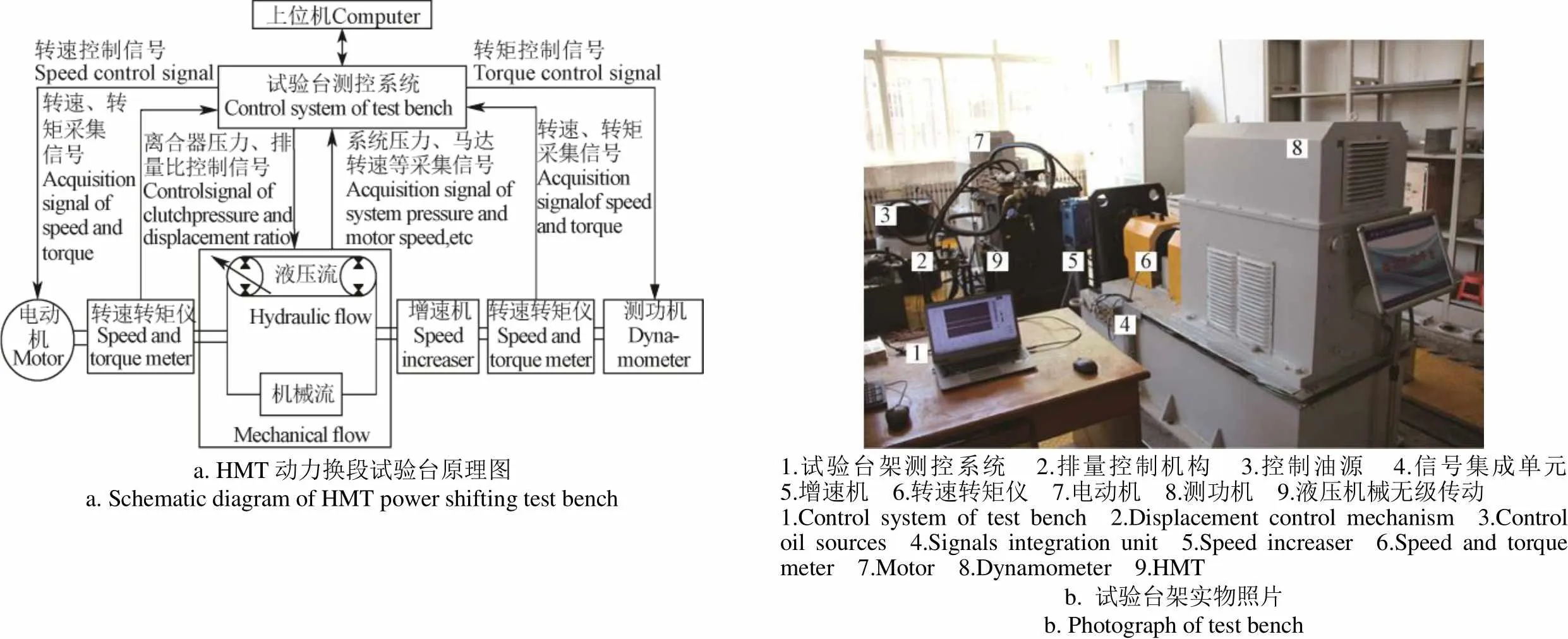
a. HMT动力换段试验台原理图 a. Schematic diagram of HMT power shifting test bench 1.试验台架测控系统 2.排量控制机构 3.控制油源 4.信号集成单元 5.增速机 6.转速转矩仪 7.电动机 8.测功机 9.液压机械无级传动 1.Control system of test bench 2.Displacement control mechanism 3.Control oil sources 4.Signals integration unit 5.Speed increaser 6.Speed and torque meter 7.Motor 8.Dynamometer 9.HMT b. 试验台架实物照片 b. Photograph of test bench
3.2 试验方案
在给定转速和转矩的换段过程中,按调节规律调节排量,主动控制液压回路高低压侧压力互换,使HMT从当前段过渡到目标段。按上述方法,进行由H段向HM段、HM段向H段往复换段试验,实时采集输入输出转速、转矩、定排量液压元件转速、变排量液压元件排量比、液压回路高低压侧压力、补油温度和离合器控制油压等试验参数,并与相同条件下的仿真结果进行对比分析,探究全功率换段的功率转移机理及换段过程排量比调节的影响规律。
负载大小决定换段前后液压回路的工作压力和全功率换段过程的排量调节量,转速影响HMT传动效率,但这2个参数都不影响排量调节规律和功率转移机理。装备HMT的5 t装载机,在典型工作工况(ZZJ/07B01-2017《土方机械轮胎式装载机能效试验及评价方法》)中,HMT换段时的发动机转速范围为800~1 200 r/min,液压回路最高压力为8~14 MPa,限于试验台条件,本文试验时HMT输入转速选择1 000 r/min,测功机加载转矩选择100和150 N·m,通过增速机后,液压段压力约为9和11 MPa,属装载机HMT的换段典型工况点,液压回路试验油温80 ℃。由于试验设备的限制,被试HMT和测功机间设置了增速机,转速转矩仪安装在增速机之后,故本文所提及的“输出转矩”均为HMT经增速机后的输出转矩,即测功机的加载转矩。
3.3 结果与分析
输入转速为1 000 r/min,输出转矩为100 N·m时,排量比阶跃调节化下对应的液压机械由H段向HM段和由HM段向H段的换段过程试验与仿真结果如图6、图7所示。

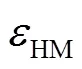
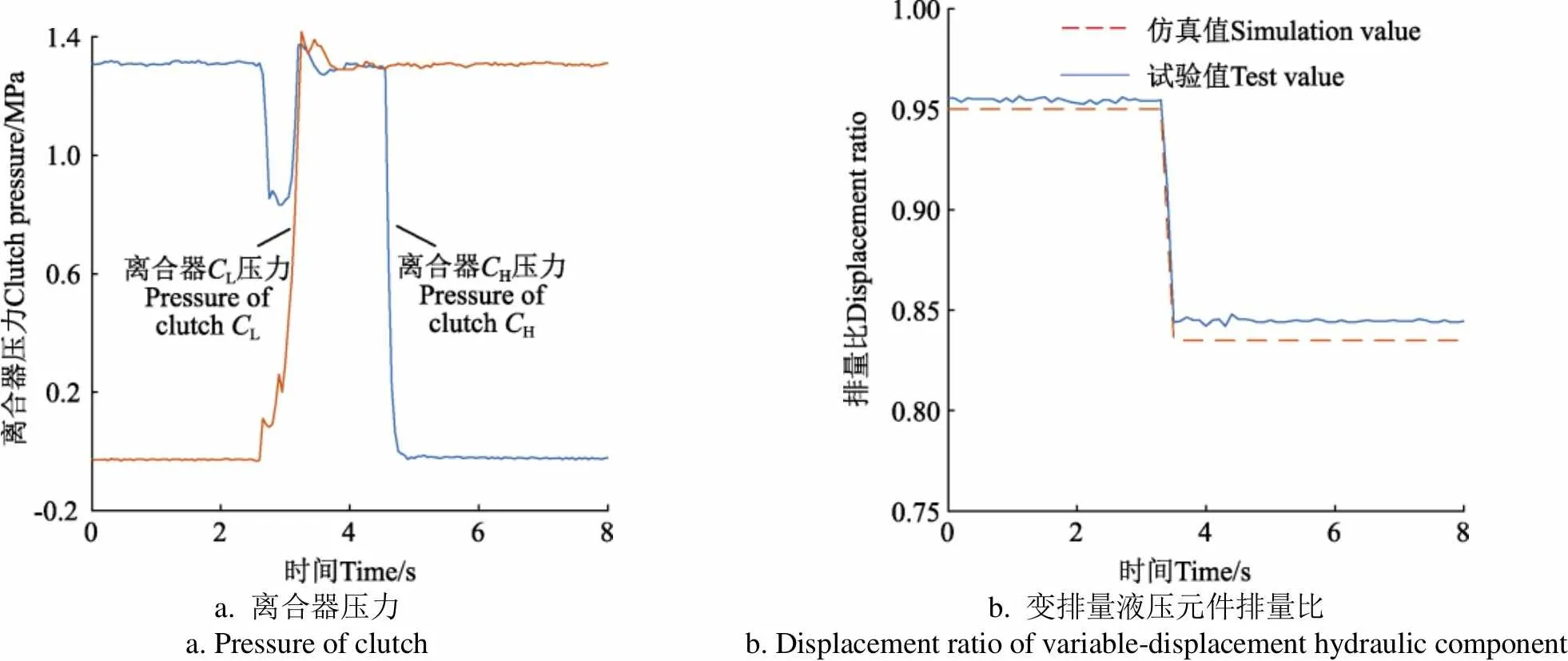
a. 离合器压力 a. Pressure of clutchb. 变排量液压元件排量比 b. Displacement ratio of variable-displacement hydraulic component
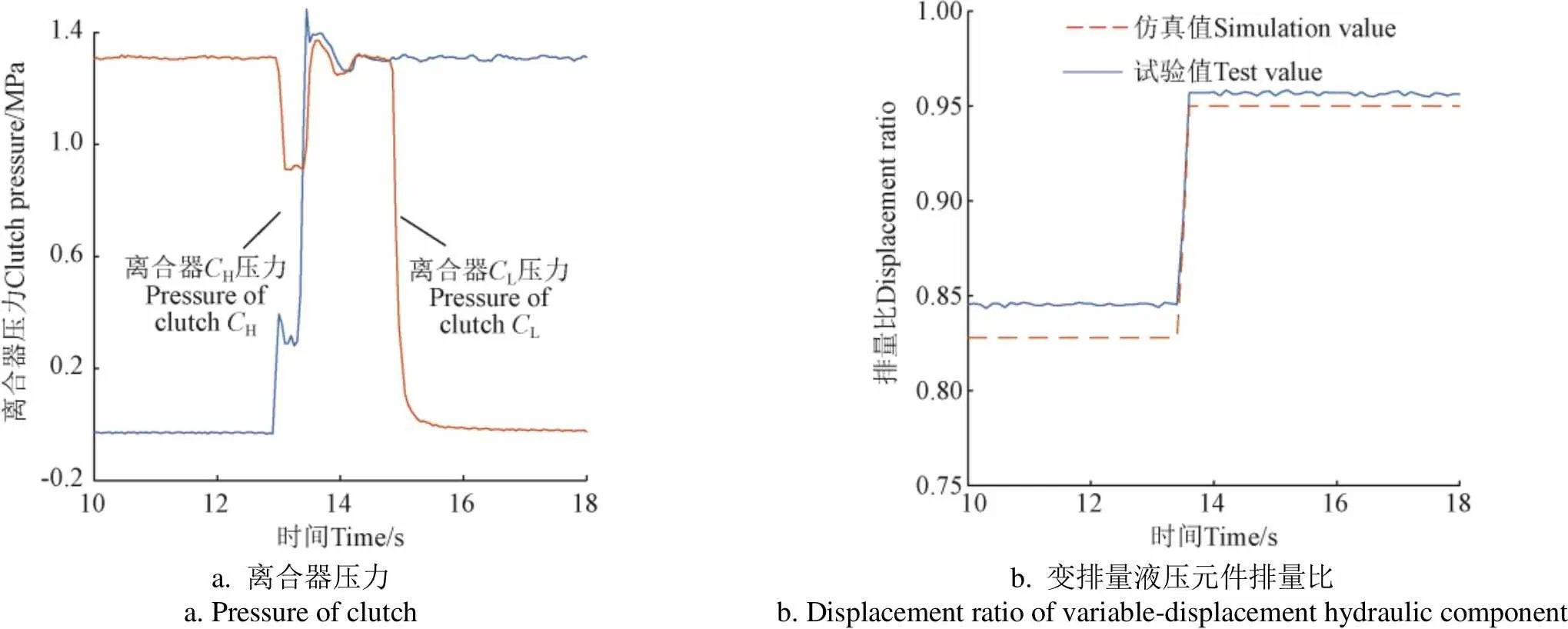
a. 离合器压力 a. Pressure of clutchb. 变排量液压元件排量比 b. Displacement ratio of variable-displacement hydraulic component
输入转速1 000 r/min、输出转矩150 N·m,排量比阶跃调节的换段过程试验结果如图8、图9所示。H、L两离合器结合重叠过程仍为2 s。

a. 离合器压力 a. Pressure of clutchb. 变排量液压元件排量比 b. Displacement ratio of variable -displacement hydraulic component
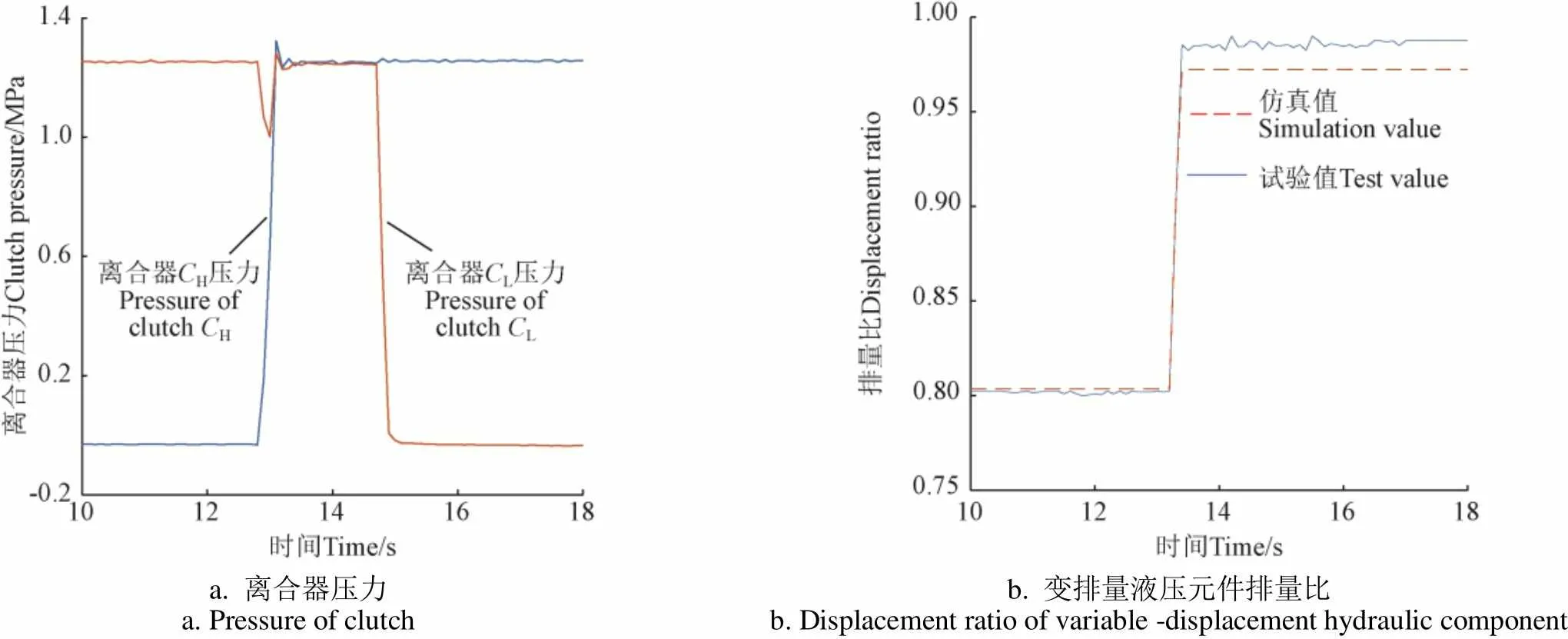
a. 离合器压力 a. Pressure of clutchb. 变排量液压元件排量比 b. Displacement ratio of variable -displacement hydraulic component
如图8,试验中排量比从0.985调至0.802(仿真值为0.972和0.803,试验和仿真结果偏差为7.65%)时,液压回路压力从H段11.07 MPa调节为HM段9.13 MPa,建压时间1.05 s,输出转速无波动,转矩波动6.70 N·m,为输出转矩的4.50%;如图9,排量比0.803调至0.988(仿真值为0.804和0.973,仿真和试验结果偏差为8.65%)时,液压回路压力从HM段9.11 MPa调节为H段11.11 MPa,建压时间1.10 s,转矩波动6.84 N·m ,为输出转矩的4.60%。
图6~图9中换段试验与仿真结果对比可知,换段过程排量比试验结果变化量和仿真结果变化量最大偏差为8.93%,仿真和试验结果基本一致,证明本文所建立的HMT全功率换段过程排量调节模型可以准确计算目标段排量值,能准确反映液压回路高低压侧压力互换过程。在两离合器结合重叠过程中合理调节变排量液压元件排量,能够使转矩在离合器间快速转移,负载为100和150 N·m时,最大建压时间分别为1.00和1.10 s,转矩波动量最大分别为6.80和6.84 N·m,分别为输出转矩的6.80%和4.60%。
4 结 论
本文以HMT全功率换段为目标,开展了换段过程排量变化规律、液压回路动态响应过程的理论分析和试验研究,得到如下结论:
1)获得全功率换段转矩转移机理表达式,闭式液压回路的压力可以通过调节排量比控制,改变闭式液压回路压力,使转矩从当前段离合器向目标段离合器转移。
2)对比排量比阶跃和线性调节规律响应特性,阶跃调节规律能有效减小建压时间,换段时间为0.93 s,压力波动量为0.64 MPa,与线性调节相比,高压侧压力波动无明显变化。为有效减小换段时间,可采用排量比阶跃调节规律。
3)在相同工况下,从当前段到目标段排量调节量的仿真与试验结果基本相同,偏差为8.93%,建压时间基本一致,表明本文所建立的排量比调节模型能准确计算排量比目标值,并能准确反映建压过程。
4)在当前段和目标段离合器结合重叠时,通过合理调节排量比控制液压回路高低压侧压力完成释压、建压过程,能够使转矩在离合器间快速转移,换段前后输出转速平稳无变化、转矩连续传递。输出转矩为100和150 N·m时,建压时间分别为1.00和1.10 s,转矩波动量最大分别为6.80和6.84 N·m,分别为输出转矩的6.80%和4.60%,实现了全功率换段。
[1] 刘修骥.车辆传动系统分析[M]. 北京:国防工业出版社,1998.
[2] Satyam R, Tewari V K, Mukhopadhyay S. Simulation of components of a power shuttle transmission system for an agricultural tractor[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture, 2015, 3(6): 114-124.
[3] 李东民,黄德杰,李翠赟. 车用液压机械无级变速器研究及应用[J]. 液压与气动,2016(9):44-48. Li Dongmin, Huang Dejie, Li Cuiyun. Study and application on hydro-mechanical variable transmission[J] Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics, 2016(9): 44-48. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] Michael Sprengel, Monika Ivantysynova. Recent development in a novel blended hydraulic hybrid transmission[R]. SAE Technical Paper 2014-01-23.
[5] Lloyd. High efficiency, hydro-mechanical passenger vehicle transmission using fixed displacement pump/motors and digital hydraulics[J]. SAE International Journal of Passenger Cars-Mechanical Systems. 2012, 5(2): 833-855.
[6] 王铁军. 工程机械上液压机械传动的应用探究[J]. 液压与气动,2012(6):61-63. Wang Tiejun. The application of the hydraulic mechanical transmission on the construction machine[J] Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics, 2012(6): 61-63. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] Ali H Shaker. Stufenlose Hydrostatische Koppelgetriebe fuer Kraftfahrzeuge[D]. Bochm: Ruhr Universitat, 1981.
[8] Berger Guenter. Automatische Stufenlos Wirkends Hudrostatisches Lastschaftgetriebe Fuer Kraftfahrzeuge[D]. Bochum: Ruhr Universitat, 1986.
[9] Cheong K L, Li P Y, Chase T R. Optimal design of power-split transmission for hydraulic hybrid passenger vehicles[C]// American Control Conference. IEEE, 2011: 3295-3300.
[10] Cheong K L, Du Z, Li P Y, et al. Hierarchical control strategy for a hybrid hydro-mechanical transmission (HMT) power-train[C]// American Control Conference. IEEE, 2014(6):4599-4604.
[11] Kumar R. A Power Management Strategy for Hybrid Output Coupled Power-Split Transmission to Minimize Fuel Consumption[D]. West Lafayette: Purdue University, 2010.
[12] 马志远. HMT车辆动力传动综合控制技术研究[D]. 北京:北京理工大学,2015. Ma Zhiyuan. Study on Power Driveline Integrated Control Technology of Vehicle Equipped with Hydro-Mechanical Continuously Variable Transmission[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] Tanelli M, Panzani G, Savaresi S M, et al. Transmission control for power-shift agricultural tractors: Design and end-of-line automatic tuning[J]. Mechatronics, 2011, 21(1): 285-297.
[14] 苑士华. 多段液压机械双流无级传动的理论与试验研究[D].北京:北京理工大学,1999. Yuan Shihua. Theoretical and Experimental Research of Multi-Range Hydro-Mechanical Double-Flow CVT[D]. Beijing: Beijing Institute of Technology, 1999. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 苑士华,杜玖玉,胡纪滨,等. 两段式分速汇矩式液压机械传动设计[J]. 农业工程学报,2008,24(11):109-113. Yuan Shihua, Du Jiuyu, Hu Jibin, et al. Design of two-rang input split hydrostatic mechanical transmission[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2008, 24(11): 109-113. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 杜玖玉,苑士华,胡纪滨,等. 两段式分矩汇速式液压机械传动设计[J]. 农业工程学报,2009,25(4):86-94. Du Jiuyu, Yuan Shihua, Hu Jibin, et al. Design of two-rang torque split hydrostatic mechanical transmission[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2009, 25(4): 86-94 (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 张明柱,周志立,徐立友,等. 农业拖拉机用多段液压机械无级变速器设计[J]. 农业工程学报,2003,19(6):118-121. Zhang Mingzhu, Zhou Zhili, Xu Liyou, et al. Design of a multi-range hydrostatic mechanical transmission for farm tractors[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2003, 19(6): 118-121. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] Zhang Mingzhu, Zhou Zhili, Xu Liyou. Efficiency analysis of an innovative multi-range hydro-mechanical continuously variable transmission[C]// International Conference on Automation and Logistics, 2009: 170-174.
[19] 郭占正,苑士华,荆崇波,等. 基于AMESim的液压机械无级传动换段过程建模与仿真[J]. 农业工程学报,2009,25(10):86-91. Guo Zhanzheng, Yuan Shihua, Jing Chongbo, et al. Modeling and simulation of shifting process in hydraulic machinery stepless transmission based on AMESim[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2009, 25(10): 86-91. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 魏超,胡纪滨,荆崇波,等. HMT变速器速比跟踪控制对发动机转速的调节规律研究[J]. 北京理工大学学报,2012,32(5):455-459. Wei Chao, Hu Jibin, Jing Chongbo, et al. Reasearch of engine speed governing rule based on the speed ratio follow-up control of hydro-mechanical transmission[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2012, 32(5): 455-459. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 魏超,马志远,尹旭峰,等. 液压机械无级变速器换段冲击影响因素研究[J]. 北京理工大学学报,2015,35(11):1122-1127. Wei Chao, Ma Zhiyuan, Yin Xufeng, et al. Research on the influencing factors of the range-shifting impact on HMT[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2015, 35(11): 1122-1127. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 王光明,张晓辉,朱思洪,等. 拖拉机液压功率分流无级变速器换段规律研究[J]. 农业机械学报,2015,46(10):7-15.Wang Guangming, Zhang Xiaohui, Zhu Sihong, et al. Shift performance of tractor hydraulic power-split continuously variable transmission[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(10): 7-15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 王光明. 拖拉机液压机械无级变速箱的特性、控制与故障诊断研究[D]. 南京:南京农业大学,2014. Wang Guangming. Study on Characteristics, Control and Fault Diagnosis of Tractor Hydro-Mechanical CVT[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] 朱镇,高翔,潘道远,等. 液压机械无级变速器换挡控制策略研究[J]. 机械科学与技术,2017,36(4):527-534. Zhu Zhen, Gao Xiang, Pan Daoyuan, et al. A shifting control strategy for hydro-mechanical continuously variable transmission[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering, 2017, 36(4): 527-534. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 朱镇,陈龙,曹磊磊,等. 液压机械无级变速器换挡品质因素分析[J]. 机械设计,2018,35(1):39-45. Zhu Zhen, Chen Long, Cao Leilei, et al. Analysis on the shift quality of hydro-mechanical continuously variable transmission[J]. Journal of Machine Design, 2018, 35(1): 39-45. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 胡纪滨,魏超,杜玖玉,等. 液压机械无级变速器速比跟踪控制系统研究[J]. 北京理工大学学报,2008,28(6):481-485. Hu Jibin, Wei Chao, Du Jiuyu, et al. A study on the speed ratio follow-up control system of hydro-mechanical transmission[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology, 2008, 28(6): 481-485. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] Hu Jibin, Wei Chao, Yuan Shihua, et al. Characteristics on hydro-mechanical transmission in power shift process[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2009, 22(1): 50-56.
[28] 杨树军,焦晓娟,鲍永,等. 油液含气量对液压机械换段性能的影响[J]. 机械工程学报,2015,51(14):122-130. Yang Shujun, Jiao Xiaojuan, Bao Yong, et al. Fluid air content affecting the power shift performance of the hydro-mechanical variable transmission[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 51(14): 122-130. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] Yang Shujun, Bao Yong, Tang Xianzhi, et al. Integrated control of hydromechanical variable transmissions[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2015(7): 1-11.
[30] 杨树军,鲍永,范程远. 液压机械全功率换段方法及功率过渡特性[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(5):63-72. Yang Shujun, Bao Yong, Fan Chengyuan. Full power shift method of hydro-mechanical transmission and power transition characterstics[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(5): 63-72. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[31] 杨树军,鲍永,杨得青,等. 液压机械无级传动全功率动力换段控制方法,201610656305.7[P]. 2016-12-21.
Model of regulating displacement ratio in full power shifting process of hydro-mechanical variable transmission
Yang Shujun1, Zhang Man1, Zeng Panwen2, Zhang Yinjun1, Zhang Lu1, Tian Lin1
(1.,,066004,; 2.,,411199,)
Hydro-mechanical variable transmission (HMT) is a kind of double power flow transmission system constituted by hydraulic branch and mechanical branch in parallel. HMT has the ability to realize high-power CVT and high transmission efficiency, and is suitable for high-power automobiles. In general power shift process, there are load reversal in hydraulic transmission unit, power flow reversal in hydraulic branch, and function interchange in hydraulic components. At the same time, the speed of fixed displacement hydraulic component changes abruptly, and there is a short time power interruption. To solve the problems of speed fluctuation and power interruption in power shift, based on the five-stage full power shift method by overlapping the double clutches, the displacement regulating law of variable displacement hydraulic component is studied in this paper. An arithmetic type two-range HMT is taken as the research object, and the pressure responses to different displacement regulation are analyzed. The torque characteristic equation in full power shift is derived. The cavity model of closed hydraulic circuit is established, in which the closed hydraulic circuit is simplified to two cavities. Considering the influence of the volumetric efficiency of the hydraulic transmission unit, the mathematical model of the displacement ratio regulation of variable displacement hydraulic component is derived. The step change and linear change of displacement ratio are adopted respectively, and the pressure response is obtained by simulation. The results show that the regulation law of displacement ratio has a great influence on the time of pressure building-up and pressure fluctuation. The step change of displacement ratio can effectively reduce the time of pressure building-up, and there is no obvious increase of pressure fluctuation compared with that of the linear change. The power shift time is 0.93 s and pressure fluctuation is 0.64 MPa. In order to reduce the power shift time, the step change of displacement ratio could be adopted. Through the displacement regulation characteristic test of HMT in full power shift process, the pressure response is obtained. The results show that the simulation results of displacement ratio change are in accordance with the test results, and the maximum deviation is 8.93% under the same working conditions. Based on the state parameters of current range and the target range pressure, the mathematical model of the displacement ratio regulation proposed in this paper can predict the displacement ratio target value, and accurately describe the pressure interchange between the high and low pressure circuits. During the double clutches overlapping, the displacement ratio is adjusted to the target value. The pressure interchange between the high and low pressure circuits can be completed in the full power shift process, and the torque is transferred from current clutch to target clutch. The output speed remains unchanged, and the output torque is continuous. When the output torque after speed increaser is 100 and 150 N·m, the power shift time is 1.00 and 1.10 s respectively, it’s the maximum fluctuation is 6.80 and 6.84 N·m respectively. The problems such as speed fluctuation and power interruption in the shift process are solved, this study provides a reference for the realization of HMT full power shift control and subsequent research.
hydro-mechanical; transmission; control; variable transmission; full power shift;displacement regulation
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.13.007
U463.2
A
1002-6819(2019)-13-0064-11
2019-01-25
2019-03-03
国家自然基金面上项目(51675462,51175449);河北省高校科技支撑项目(ZD2016012)
杨树军,博士,教授,主要从事车辆新型传动及其控制技术研究。Email:ysj@ysu.edu.cn
杨树军,张 曼,曾盼文,张寅君,张 璐,田 霖. 液压机械无级传动全功率换段过程排量比调节模型[J]. 农业工程学报,2019,35(13):64-73. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.13.007 http://www.tcsae.org
Yang Shujun, Zhang Man, Zeng Panwen, Zhang Yinjun, Zhang Lu, Tian Lin. Model of regulating displacement ratio in full power shifting process of hydro-mechanical variable transmission[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2019, 35(13): 64-73. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.13.007 http://www.tcsae.org

