基于GNSS系统的整周模糊度解算算法仿真
张晟歌 程乃平 倪淑燕
摘 要: 利用载波相位观测值可以大大提高导航定位精度,但整周模糊度的存在会严重影响结果的准确性。为了解决整周模糊度对载波相位观测值的影响,对LAMBDA算法求解整周模糊度的过程进行分析和设计,提出利用协方差分解来降低模糊度组数之间相关性的算法,设计相应的Matlab仿真验证系统并进行仿真。比较分析不同分解算法下的搜索域的大小以及修正解的准确性。结果表明,下三角分解算法的整周模糊度解算算法在搜索域大小上比上三角分解算法大,且解算速度较快,能运用于后续的姿态解算。
关键词: 整周模糊度算法; Z变换; 协方差矩阵分解; LAMBDA算法; Matlab仿真; 仿真分析
中图分类号: TN911.5?34 文献标识码: A 文章编号: 1004?373X(2019)15?0131?03
Simulation of integer ambiguity resolution algorithm based on GNSS system
ZHANG Shengge, CHENG Naiping, NI Shuyan
(Department of Optoelectronic Equipment, Space Engineering University, Beijing 101400, China)
Abstract: The use of carrier phase observations can greatly improve navigation positioning accuracy, but the presence of integer ambiguities can seriously affect the accuracy of the results. In order to eliminate the influence of the integer ambiguity on the carrier phase observations, the process of solving the whole?period fuzzy of the LAMBDA algorithm is analyzed and designed in this paper. An algorithm that uses covariance decomposition to reduce the correlation between the numbers of ambiguity groups is proposed. The corresponding Matlab simulation verification system was designed and simulated. The size of the search domain of different decomposition algorithms and the accuracy of the correcting solution are compared and analyzed. The results show that the integer ambiguity resolution algorithm of the lower triangular decomposition algorithm is larger than the upper triangular decomposition algorithm in the size of the search domain, and its solution speed is faster and can be used in subsequent pose calculation.
Keywords: integer ambiguity algorithm; Z transform; covariance matrix factorization; LAMBDA algorithm; Matlab simulation; simulation analysis
0 引 言
目前整周模糊度解算算法[1]是應用最广泛且解算成功率及效率很高的一种方法,是Teunissen教授在1993年提出的LAMBDA(The Least?squares Ambiguity Decorrelation Adjustment,最小二乘去相关模糊度搜索)算法[2]。其主要思想是基于最小二乘方法的搜索方法。通过对基于最小二乘搜索法中出现的协方差矩阵进行处理,降低模糊度相关性,以此来提高搜索的效率。
本文进行了整周模糊度搜索的主要算法相应的Matlab仿真,比较了LAMBDA算法在不同协方差分解方式下整周模糊度搜索域即搜索性能,可以为整周模糊度解算方案的选择提供参考依据。
1 最小二乘搜索
载波相位观测模型[3]如式(1)所示:
整数最小二乘估计算法解算算法通常分为两步:
1) 忽略[a]的整数约束,利用一般最小二乘法估计出[a]与[b]的浮点解[a],[b]及其协方差矩阵:
2) 利用浮点解搜索使目标函数最小的整数作为整周模糊度固定解[a],搜索方式为:
在进行搜索求解时,搜索空间表示为:
式(7)是一个以[a]为中心的[n]维超椭球体,[χ2]与[Q-1a]分别控制其大小和形状。其中,假设各个模糊度之间互不相关,[Qa]为对角阵,此时搜索域所表示的椭球退化为球体。只需对[a]就近取整即为固定解[a]。但在动态定位或快速定位的应用中, 较短的观测时间及双差观测模式使得各模糊度间高度相关,[Qa]远非对角阵,此时搜索椭球被拉的很长。搜索过程异常复杂。
2 LAMBDA算法
LAMBDA算法主要采用Z变换的降相关处理方法来降低整周模糊度之间的线性关系。LAMBDA算法还利用矩阵分解原理将搜索过程中整周模糊度浮点的协方差进行分解以此来使Z变换后搜索过程中的协方差矩阵[QZ]尽量的对角化,以此来降低搜索的难度。
2.1 算法基本原理
由于在利用最小二乘法进行整周模糊度解算过程中,各模糊度间高度相关所导致的搜索椭圆过于狭长,不利于整周模糊度的解算。为了提高搜索效率,将整周模糊度未知量进行相应变换来降低相关性,使搜索椭圆更接近球体。其基本原理如下:
寻找一个[Z]矩阵满足:[Z]中所有元素为整数;det([Z])=[±]1;可逆的整数变换,即变换前后参数的整数特性保持不变。变换后参数的协因数阵尽量接近对角阵。
搜索使目标函数达到最小的[z],作为变换后的模糊度的固定解[z]反变换得到原始模糊度的固定解。
LAMBDA算法所使用的Z变换主要有:迭代算法、联合去相关算法、高斯Z变换。
根据式(7),式(9)可以描述出搜索空间是一个[n]维的超椭球体,[χ2]与[Q-1a]分别控制其大小和形状。为了解决由于[Qa],[Qz]中元素相关性较高所导致的搜索椭圆被拉得过长的问题。将协方差[Qz]进行一定的处理,将其分解成一个固定的组合。使分解后的搜索方程的协方差尽量逼近对角阵,降低整周模糊度搜索的难度。
2.2 协方差分解算法
协方差分解方式主要分为上三角分解[5]([UD])与下三角分解[6]([LDLT]),这两类都是将对称正定矩阵分解成单位三角矩阵与对角线矩阵之间的组合乘积。以此对协方差矩阵去相关化,降低搜索的难度。
协方差分解算法的主要步骤是通过已知的协方差矩阵先计算出对应的对角线矩阵。通过对角线矩阵,将协方差矩阵分为两个部分,分别为上三角部分和下三角部分,再获得单位三角矩阵。
3 仿真分析
为了进行整周模糊度解算仿真实验,利用式(10)中的方式构造整周模糊度浮点解及协方差矩阵:
设置最大[n=15],整周模糊度备选解的个数为3。
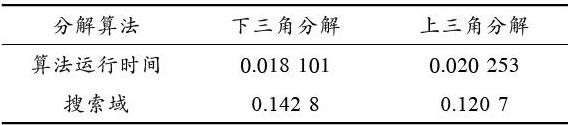
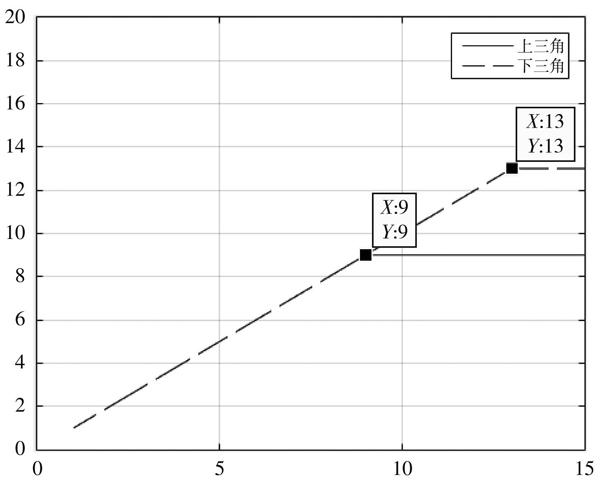
对协方差分解的两种方式以及后续的整周模糊度解算进行仿真,结果如图1所示。并记录算法的运行时间以及搜索域的大小,见表1。
表1 整周模糊度算法搜索域与搜索时间

图1 整周模糊度解算组数

通过图1和表1可以看出,下三角分解算法的整周模糊度解算算法在搜索域大小上比上三角分解算法大,且解算速度相对较快,可以用于将来的研究。
4 结 语
协方差分解是LAMBDA算法中重要的一步,是算法中核心的一个部分。文章较为细致地阐述了在解算过程中对角线矩阵形成的两种不同的分解算法的基本实现过程,并设计了Matlab仿真实验。经过验证,发现将协方差阵的对角线元素作为分解后对角阵元素的分解方式,能有效地提高整周模糊度解算的精确度以及降低搜索过程的范围以及时间。但是,随着整周模糊度位数的不断增加,在解算过程中出现计算量过大的问题。需要进一步的研究来提高高维模糊度解算速率问题。
参考文献
[1] COUNSELMAN C C, GOUREVITCH S A. Miniature interfe?rometer terminals for earth surveying: ambiguity and multipath with global positioning system [J]. IEEE transactions on geo?science & remote sensing, 1981, 19(4): 244?252.
[2] TEUNISSEN P J G. Least?squares estimation of the integer GPS ambiguities [C]// General Meeting of the International Association of Geodesy. Beijing: [s.n.], 1993: 1?16.
[3] 李建文,郝金明,李军正,等.GPS/GLONASS载波相位测量模糊度解算方法[J].测绘科学技术学报,2004,21(3):163?165.
LI Jianwen, HAO Jinming, LI Junzheng, et al. Ambiguity solution methods in gps/glonass carrier phase measurement [J]. Journal of institute of surveying and mapping, 2004, 21(3): 163?165.
[4] 王冰.基于GNSS的实时姿态确定算法研究[D].郑州:解放军信息工程大学,2013.
WANG Bing. Research on real?time attitude determination algorithms utilizing global navigationsatellite system [D]. Zhengzhou: The PLA Information Engineering University, 2013.
[5] 刘朝功.三种整周模糊度搜索方法对比[J].北京测绘,2015(2):50?54.
LIU Chaogong. The comparison of three methods in search of ambiguity [J]. Beijing surveying and mapping, 2015(2): 50?54.
[6] 宋福成.GNSS整周模糊度估计方法研究[D].北京:中国矿业大学,2016.
SONG Fucheng. Research on GNSS integer ambiguity estimation methods [D]. Beijing: China University of Mining and Technology, 2016.
[7] RIZOS C, HAN S W. A new method for constructing multi?satellite ambiguity combinations for lmproved ambiguity resolution [C]// Proceedings of the 8th International Technical Meeting of the Satellite Division of the Institute of Navigation. Palm Springs: Institute of Navigation, 1995: 1145?1153.
[8] GREWAL M S, ANDREWS A P. Kalman filtering: theory and practice using matlab [M]. NJ: Prentice Hall, 2001.
[9] TEUNISSEN P J G. The least?squares ambiguity decorrelation adjustment: a method for fast GPS integer ambiguity estimation [J]. Journal of geodesy, 1995, 70(1): 65?82.
[10] 赵蓓,王飞雪,孙广富,等.LAMBDA整周模糊度解算方法中的整数Z变换算法[J].弹箭与制导学报, 2008,28(3):254?257.
ZHAO Bei, WANG Feixue, SUN Guangfu, et al. Analysis of integer Z?transformation in the LAMBDA method [J]. Journal of projectiles, rockets, missiles and guidance, 2008, 28(3): 254?257.

