基于多注意力多尺度特征融合的图像描述生成算法
陈龙杰 张钰 张玉梅 吴晓军
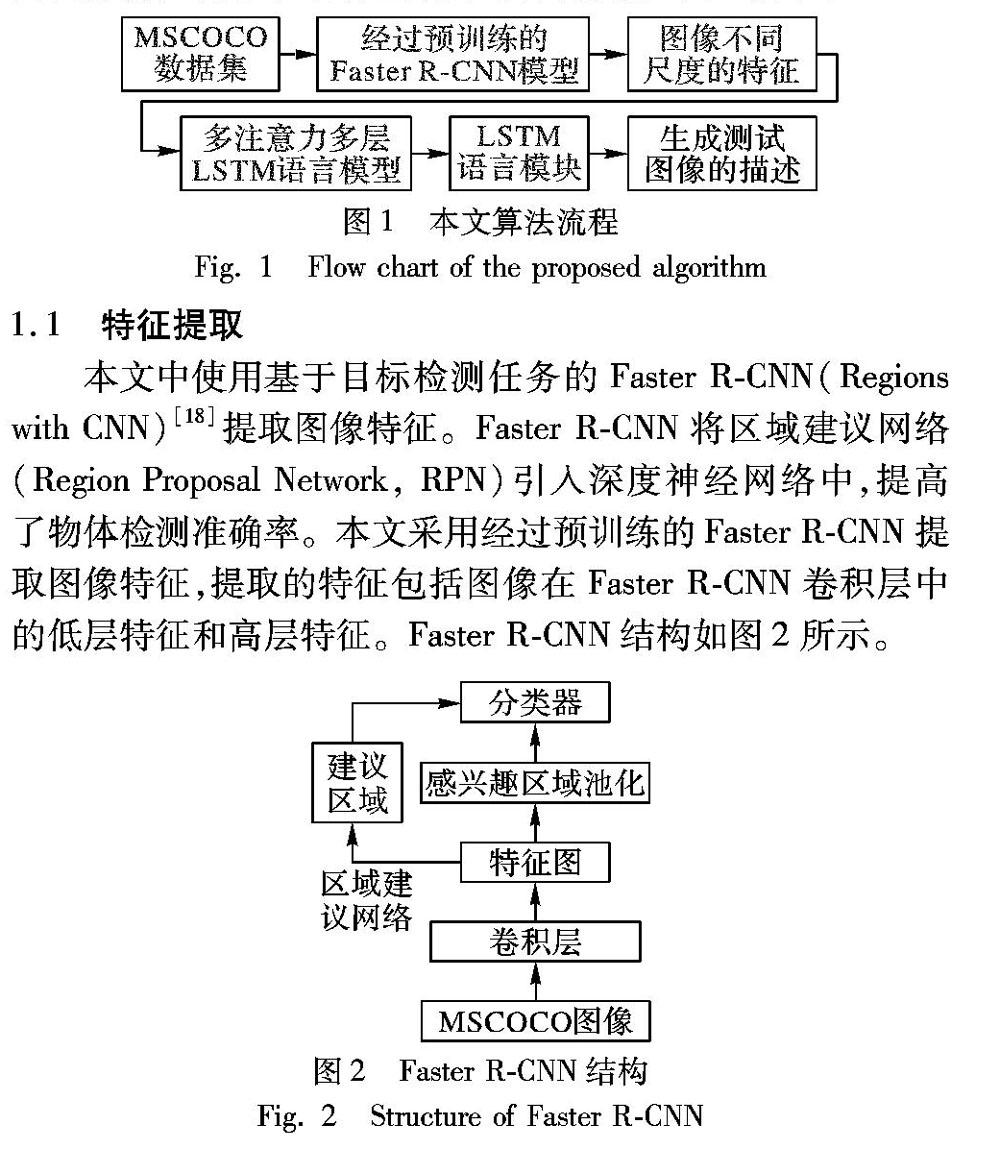

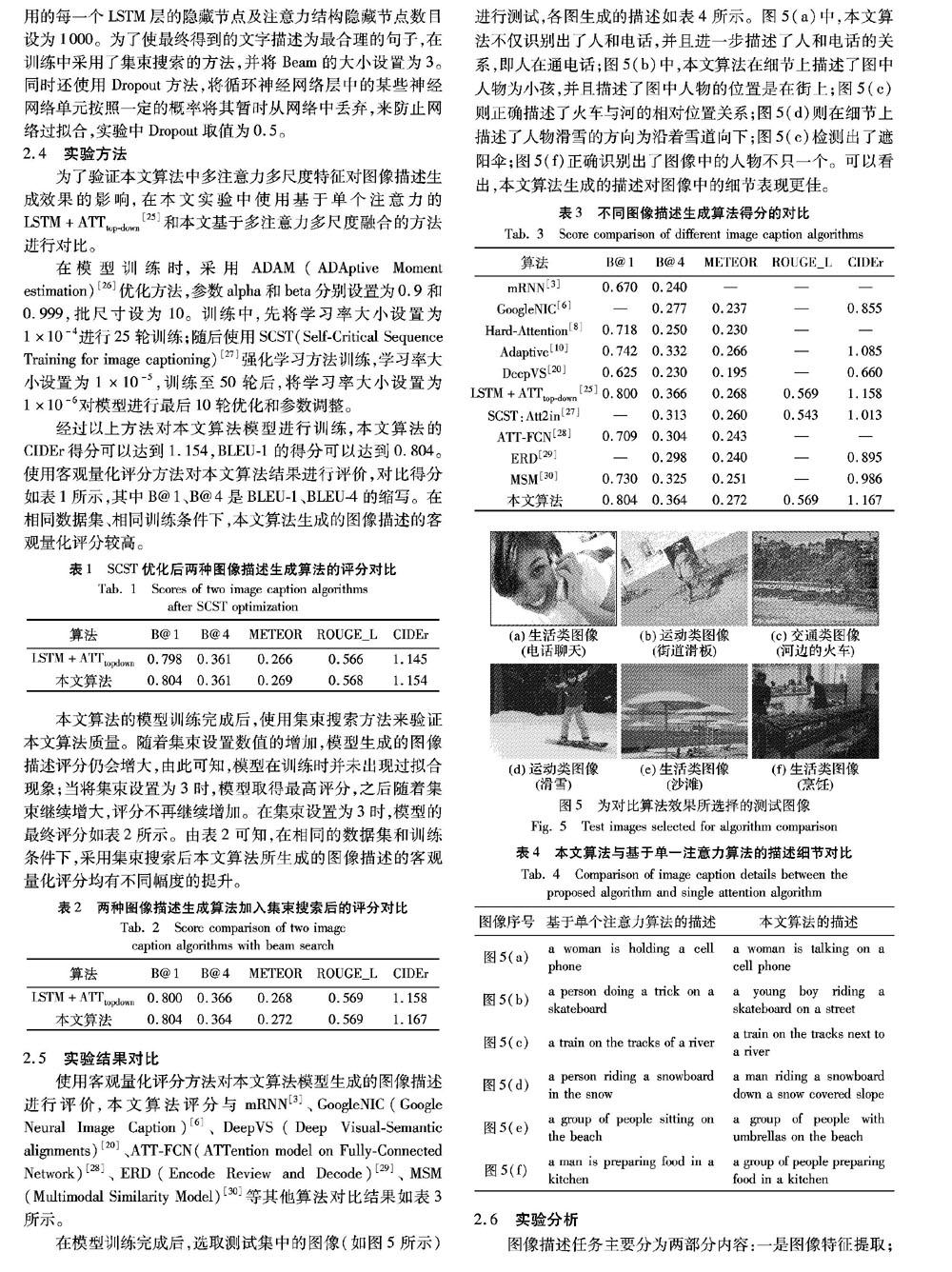
摘 要:针对图像描述生成中对图像细节表述质量不高、图像特征利用不充分、循环神经网络层次单一等问题,提出基于多注意力、多尺度特征融合的图像描述生成算法。该算法使用经过预训练的目标检测网络来提取图像在卷积神经网络不同层上的特征,将图像特征分层输入多注意力结构中,依次将多注意力结构与多层循环神经网络相連,构造出多层次的图像描述生成网络模型。在多层循环神经网络中加入残差连接来提高网络性能,并且可以有效避免因为网络加深导致的网络退化问题。在MSCOCO测试集中,所提算法的BLEU-1和CIDEr得分分别可以达到0.804及1167,明显优于基于单一注意力结构的自上而下图像描述生成算法;通过人工观察对比可知,所提算法生成的图像描述可以表现出更好的图像细节。
关键词:长短期记忆网络;图像描述;多注意力机制;多尺度特征融合;深度神经网络
中图分类号: TP391.41
文献标志码:A
Abstract: Focusing on the issues of low quality of image caption, insufficient utilization of image features and single-level structure of recurrent neural network in image caption generation, an image caption generation algorithm based on multi-attention and multi-scale feature fusion was proposed. The pre-trained target detection network was used to extract the features of the image from the convolutional neural network, then the image features were layered and put into caption model with multi-attention mechanism.which were input into the multi-attention structures at different layers. Each attention part with features of different levels was related to the multi-level recurrent neural networks sequentially, constructing a multi-level image caption generation network model. By introducing residual connections in the recurrent networks, the network complexity was reduced and the network degradation caused by deepening network was avoided. In MSCOCO datasets, the BLEU-1 and CIDEr scores of the proposed algorithm can achieve 0.804 and 1167, which is obviously superior to top-down image caption generation algorithm based on single attention structure. Both artificial observation and comparison results velidate that the image caption generated by the proposed algorithm can show better details.
Key words: Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) network; image caption; multi-attention mechanism; multi-scale feature fusion; deep neural network
0 引言
图像是人类社会活动中最常用的信息载体,其中蕴含了丰富的信息。随着互联网技术的发展及数码设备的普及,图像数据增长迅速,使用纯人工对图像内容鉴别已成为一项艰难的工作。因此,如何通过计算机自动提取图像所表达的信息,已成为图像理解领域的研究热点。图像描述生成是融合了自然语言处理和计算机视觉的一项较为综合的任务,目的是将视觉图像和语言文字联系起来,通过对所输入图像的特征进行提取分析,自动生成一段关于图像内容的文字描述。图像描述生成能够完成从图像到文本信息的转换,可以应用到图像检索、机器人问答、辅助儿童教育及导盲等多个方面,对图像描述生成的研究具有重要的现实意义。
图像描述生成是一种克服了人类主观认识的固有限制,借助计算机软件从一幅或多幅图像序列中生成与图像相对应文字描述的技术。图像描述的质量主要取决于以下两个方面:一是对图像中所包含物体及场景的识别能力;二是对物体间相互联系等信息的认知程度。按照图像描述模型的不同,图像描述的方法可以分为三类:1)基于模板[1]的方法,该类方法生成的图像描述依赖于模板类型,形式也较为单一;2)基于检索的方法,依赖于数据集中现存的描述语句,无法生成较为新颖的图像描述;3)基于神经网络的方法,通过将卷积神经网络(Convolutional Neural Network,CNN)[2]与循环神经网络(Recurrent Neural Network,RNN)[3]结合,使用端对端的方法训练模型,利用CNN提取特征的优势和RNN处理文字序列的优势,共同指导图像文字描述的生成。
随着深度学习的发展,以文献[4]中提出的多模态循环神经网络(multimodal RNN,m-RNN)为代表的基于神经网络的方法崭露头角。m-RNN首次将图像描述生成分割成两个分支任务,分别使用CNN提取图像特征,利用RNN建立语言模型。m-RNN中的CNN采用AlexNet[5]结构,RNN使用两层嵌入层将文字序列編码为独热表示形式,之后输入到循环层中,mRNN将CNN和RNN结合起来,使用深层CNN提取图像特征并输入到RNN循环层的多模态层中,最后经过Softmax层得到输出结果。虽然m-RNN成功地将CNN引入图像描述任务中,但其RNN结构较为单一,网络学习能力较弱。文献[6]则使用长短期记忆(Long Short-Term Memory,LSTM)网络代替普通的RNN,并使用了带有批标准化层的CNN提取图像特征,算法精度和速度均有提升。在视频自然语言描述任务中,文献[7]使用AlexNet模型及牛津大学视觉几何组(Visual Geometry Group,VGG)提出的VGG16模型分别提取视频空间特征,采用多种特征融合的方法,将空间特征与通过提取相邻帧的光流得到的运动特征与视频时间特征融合后输入LSTM自然语言描述模型,提升了视频自然语言描述的准确性。
3 结语
本文设计了基于多注意力多尺度融合深度神经网络的图像描述生成算法,该算法通过使用Faster R-CNN目标检测模型提取图像不同尺度上的特征,然后将图像不同尺度上的特征依次输入多个注意力结构,并最终连入多层循环网络语言模型中。本文通过在多层语言模型中加入残差映射来增加网络学习效率。在实验中采用ADAM优化方法,并通过在训练过程逐步降低学习率,可以有效地促进网络收敛。本文算法的图像描述效果和BLEU、ROUGE_L、METEOR、CIDEr等评价指标皆取得较高得分,其中BLEU-1、CIDEr得分可以达到0.804和1.167。实验结果表明,基于多注意力多尺度融合的神经网络模型在图像描述生成任务上能取得出色的表现,通过加入多个注意力结构可以有效提高对图像细节及位置关系等的描述效果。下一步,将结合现有图像描述的方法,在视频描述及图像问答等相关任务方面展开进一步研究。
参考文献:
[1] FANG H, GUPTA S, IANDOLA F, et al. From captions to visual concepts and back [C]// CVPR2015: Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society, 2015: 1473-1482.
[2] LeCUN Y, BENGIO Y, HINTON G. Deep learning[J]. Nature, 2015, 521(7553): 436-444.
[3] HOPFIELD J J. Neural networks and physical systems with emergent collective computational abilities [J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 1982, 79(8): 2554-2558.
[4] MAO J, XU W, YANG Y, et al. Explain images with multimodal recurrent neural networks[EB/OL]. [2018-06-10]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1410.1090v1.pdf.
[5] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E. ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks [C]//NIPS 2012: Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Lake Tahoe, Nevada: Curran Associates Inc. 2012: 1097-1105.
[6] VINYALS O, TOSHEV A, BENGIO S, et al. Show and tell: a neural image caption generator [C]//CVPR 2015: Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society, 2015: 3156-3164.
[7] 梁锐,朱清新,廖淑娇,等.基于多特征融合的深度视频自然语言描述方法[J].计算机应用,2017,37(4):1179-1184. (LIANG R, ZHU Q X, LIAO S J, et al. Deep natural language description method for video based on multi-feature fusion[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2017,37(4):1179-1184.)
[8] XU K, BA J L, KIROS R, et al. Show, attend and tell: Neural image caption generation with visual attention[EB/OL]. [2018-06-08]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1502.03044.pdf.Computer Science, 2015: 2048-2057.没找到
[9] BAHDANAU D, CHO K H, BENGIO Y. Neural machine translation by jointly learning to align and translate [EB/OL]. [2018-06-10]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.0473.pdf.Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2015
[10] LU J, XIONG C, PARIKH D, et al. Knowing when to look: adaptive attention via a visual sentinel for image captioning [C]//CVPR2017: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society, 2017: 3242-3250.
[11] VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[EB/OL]. [2018-05-10]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1706.03762.pdf.
沒找到NIPS2017: Proceedings of the 2012 International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems. Long Beach, USA. 2017: 6000-6010.
[12] LI J, MEI X, PROKHOROV D, TAO D. Deep neural network for structural prediction and lane detection in traffic scene[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017,28(3): 690-703.
[13] QU Y, LIN L, SHEN F, et al. Joint hierarchical category structure learning and large-scale image classification[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(9): 4331-4346.
[14] SHELHAMER E, LONG J, DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(4): 640-651.
[15] GONG C, TAO D, LIU W, LIU L, YANG J. Label propagation via teaching-to-learn and learning-to-teach[J]. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2017, 28(6): 1452-1465.
[16] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition [C]// CVPR2016: Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society, 2016: 770-778.
[17] WANG P, LIU L, SHEN C, et al. Multi-attention network for one shot learning [C]// CVPR2017: Proceedings of the 2017 Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society, 2017: 22-25.
[18] REN S, HE K, GIRSHICK R, et al. Faster R-CNN: towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6): 1137-1149.https://arxiv.org/pdf/1506.01497v3.pdf
[19] LIN T-Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S, et al. Microsoft COCO: Common Objects in COntext [C]//ECCV2014: Proceedings of the 2014 European Conference on Computer Vision. Cham: Springer, 2014: 740-755.
[20] KARPATHY A, LI F-F. Deep visual-semantic alignments for generating image descriptions [C]//CVPR2015: Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society, 2015: 3128-3137.
[21] PAPINENI K, ROUKOS S, WARD T, et al. BLEU: a method for automatic evaluation of machine translation [C]// ACL2002: Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting on Association for Computational Linguistics. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2002: 311-318.
[22] LIN C-Y. Rouge: a package for automatic evaluation of summaries [C]//ACL2004: Proceedings of the ACL 2004 Workshop on Text Summarization. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2004: 74-81.
[23] BANERJEE S, LAVIE A. METEOR: an automatic metric for MT evaluation with improved correlation with human judgments [C]//ACL2005: Proceedings of the 2005 ACL Workshop on Intrinsic and Extrinsic Evaluation Measures for Machine Translation and/or Summarization. Stroudsburg, PA: ACL, 2005: 65-72.https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/METEOR
[24] VEDANTAM R, ZITNICK C L, PARIKH D. CIDEr: consensus-based image description evaluation [C]//CVPR2015: Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Computer Vision and PatternRecognition. Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society, 2015: 4566-4575.https://arxiv.org/pdf/1411.5726v2.pdf
[25] ANDERSON P, HE X, BUEHLER C, et al. Bottom-up and top-down attention for image captioning and VQA[EB/OL]. [2018-05-07]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1707.07998.pdf.
[26] KINGMA D P, BA J. ADAM: a method for stochastic optimization [EB/OL].[2018-04-22]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1412.6980.pdf.Published as a conference paper at ICLR 2015
[27] RENNIE S J, MARCHERET E, MROUEH Y, et al. Self-critical sequence training for image captioning [C]//CVPR2017: Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Computer Vision and PatternRecognition. Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society, 2017: 1179-1195.https://arxiv.org/pdf/1612.00563.pdf
[28] YOU Q, JIN H, WANG Z, et al. Image captioning with semantic attention [C]//CVPR2016: Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Washington, DC: IEEE Computer Society, 2016: 46514659.https://www.cvfoundation.org/openaccess/content_cvpr_2016/papers/You_Image_Captioning_With_CVPR_2016_paper.pdf
[29] YANG Z, YUAN Y, WU Y, et al. Encode, review, and decode: Reviewer module for caption generation[EB/OL]. [2018-06-10]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1605.07912v1.pdf.
[30] YAO T, PAN Y, LI Y, et al. Boosting image captioning with attributes[EB/OL]. [2018-03-10]. https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.01646.pdf.未查到OpenReview, 2016, 2(5): 8.,應该是 ICLR 2017https://arxiv.org/pdf/1611.01646.pdf

