热解温度对煤泥焦燃烧及产物析出特性影响
龚德鸿,张晓婉
热解温度对煤泥焦燃烧及产物析出特性影响
龚德鸿,张晓婉
(贵州大学电气工程学院,贵州 贵阳 550025)
采用热重-质谱联用系统对不同热解温度所制煤泥焦进行燃烧实验,研究了热解温度对煤泥焦的燃烧特性及NH3、NO、SO2、CO2析出特性的影响,并运用C-R法计算煤泥焦的活化能及指前因子。结果表明:热解温度对煤泥焦的燃烧特性影响较大,可燃性指数、燃烧稳定性指数、综合燃烧指数均随热解温度升高而减小;热解温度对NH3、NO、SO2、CO2的析出特性有一定影响,其析出相对累积量均随热解温度升高而降低;煤泥焦活化能随着热解温度升高明显提高,而且煤泥焦燃烧存在动力学补偿效应。
煤泥焦;燃烧;热重-质谱;燃烧产物;动力学;补偿效应;热解温度
煤泥是煤炭洗选的副产品,由细小的煤炭颗粒、粉化矸石和水组成,具有含水率高、持水性强、粒径小、热值低等特点,在工业上使用受限[1-2]。为实现《煤炭清洁高效利用行动(2015—2020年)》提出的目标,煤泥的产量将日益增加[3],其在循环流化床锅炉中与煤大比例掺烧发电被认为是工业化综合利用的最佳处理方式[4-7]。与褐煤等低阶煤相似,煤泥也可以通过热解提质来提高其发热量,扩大利用途径。低阶煤热解实现煤炭资源化清洁高效综合利用已取得重大进展[8-9],副产品热解气和焦油可作为高品位能源使用,热解半焦用于燃烧发电[10]。不同热解条件[11-12]将对热解半焦的燃烧及产物析出特性造成影响,可通过实验研究获得燃烧产物的析出特性[13-16]、热解半焦的燃烧特性和理化特征,实现工程化应用[17-18]。但现有文献主要集中在褐煤提质研究[19-21],对煤泥制焦的研究鲜见报道,故本文采用热重-质谱联用技术对不同热解温度制取的煤泥焦进行实验研究,分析其燃烧及产物析出特性,为煤泥的热解提质产物实际应用提供依据。
1 实验装置及方法
1.1 实验装置
实验选用贵州某电厂含水率40%的煤泥,取适量煤样于105 ℃的电热鼓风箱内干燥2 h,置于空气中冷却至常温后充分研磨,装入密封瓶保存备用。煤泥的元素分析和工业分析见表1。

表1 煤泥工业分析和元素分析
实验在德国NETZSCH公司的STA409PC热分析仪和QMS403四极质谱仪组成的热重-质谱联用系统中进行,两仪器通过1根230 ℃恒温的毛细管连接。STA409PC同步热分析仪能同时记录TG和DSC信号,测量温度可由室温至1 500 ℃,精度达1 µg;反应气体可选择为还原、惰性或氧化性气体;质谱分析仪采用多离子检测(multi-ion detection,MID)方法,可实现气体产物离子流强度的在线监测。
1.2 实验方法
每次实验取(10±0.5) mg煤泥粉末于氧化铝坩埚,分别经历不同热解温度后燃烧,实验样品及条件见表2。
表2 实验样品及条件
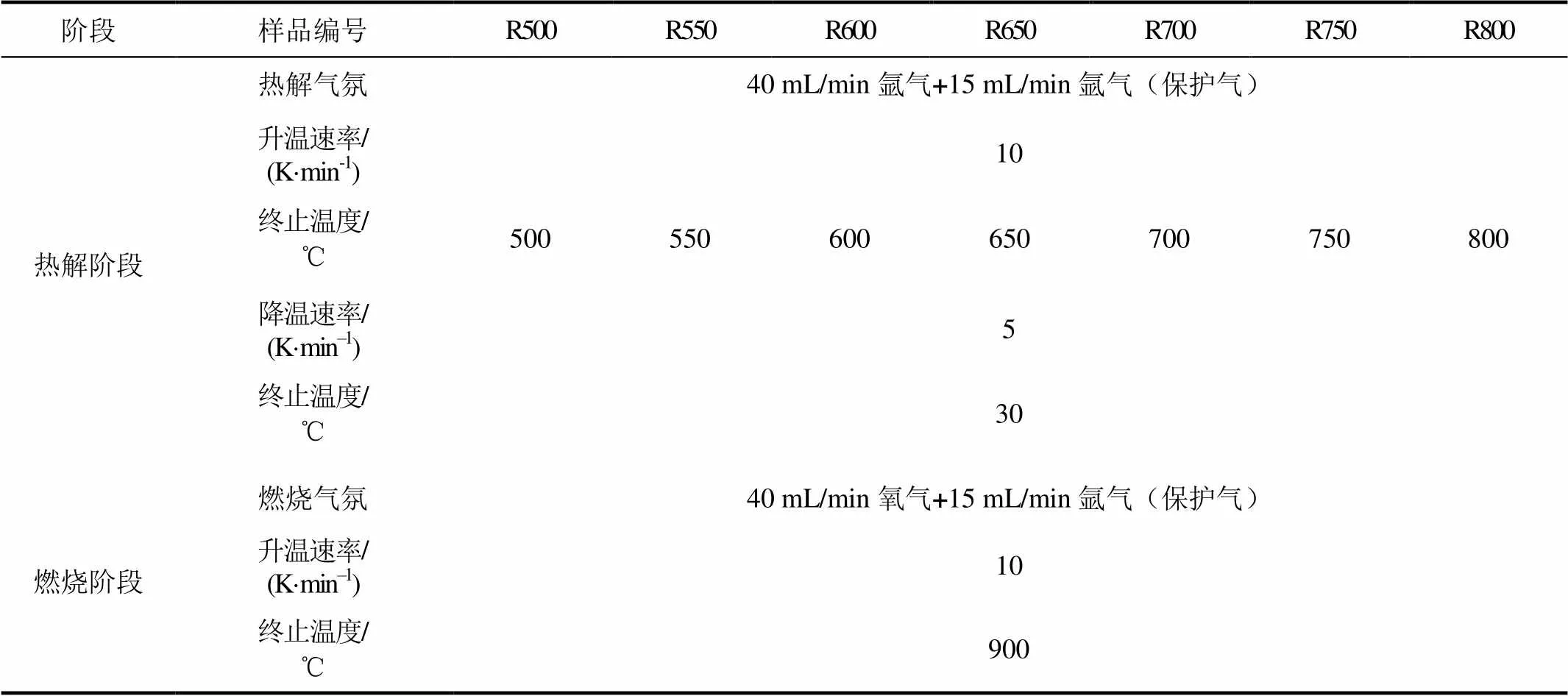
Tab.2 The experimental samples and conditions
2 实验结果及分析
2.1 热重曲线分析
图1为7种不同热解温度所制煤泥焦的燃烧TG、DTG和DSC曲线。


图1 不同热解温度所制煤泥焦燃烧的TG、DTG及DSC曲线
由图1a)可以看出:煤泥焦燃烧失重主要发生在固定碳燃烧阶段;从起始温度到着火点,TG曲线略微上升,为氧吸附在煤样表面发生氧化增重[22];着火点至燃尽点,残留的挥发分及煤焦燃烧,TG曲线急剧下降,燃尽点之后质量变化很小。
由图1b)可以看出:煤泥焦的燃烧过程包括残留挥发分的析出燃烧和固定碳的燃烧;随着热解温度升高,煤泥焦的失重份额减小,燃烧的着火温度从441.9 ℃升高到503.9 ℃,燃烧峰值温度从525.5 ℃升高到571.2 ℃,燃尽温度从488.2 ℃升高到547.3 ℃。
由图1c)可以看出:煤泥焦燃烧生成的DSC曲线表现为1个较大的吸热峰,为残留的挥发分及煤焦燃烧所贡献;放热量随着热解温度升高而减小。
2.2 煤泥焦燃烧特性指数分析
煤焦的着火温度与挥发分含量成线性关系[23-24],随着热解温度升高,煤焦中的挥发分减小,表面孔隙、总孔体积及面积增大,碳微晶结构有序化,化学稳定性增强[25-26],使得煤焦燃烧特性发生改变。采用可燃性指数b、燃烧稳定性指数和综合燃烧指数等综合燃烧指标对7种煤泥焦进行燃烧特性描述,计算式分别为[27]:
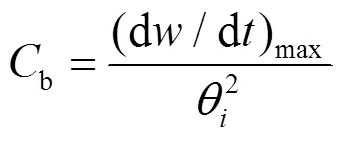

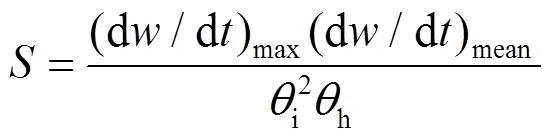
表3为计算得出的煤泥焦燃烧特性参数。由 表3可见,煤泥焦的可燃性指数、燃烧稳定性指数和综合燃烧指数均随热解温度升高而减小。这是因为在热解过程中,大部分反应活性高的物质已 析出,而残留在煤泥焦中的物质活性较低。此外,在热解过程中,挥发分析出导致煤粒表面形成 一层灰,不但形成热阻,还对氧进入煤泥焦形 成阻碍[28]。
表3 煤泥焦燃烧特性参数

Tab.3 Combustion characteristic parameters of the coal sludge chars
2.3 煤泥焦燃烧产物析出特性分析
图2为不同热解温度所制煤泥焦燃烧产物析出离子流强度曲线。
图2 不同热解温度所制煤泥焦燃烧产物析出离子流强度曲线
Fig.2 The ionic strength curves of gaseous products during combustion of coal sludge char prepared at different pyrolysis temperatures
半焦燃烧产生NO的主要前驱物是NH3和HCN,NH3在慢速热解产物中所占比例较大,主要来源于胺的分解和HCN的二次反应[29]。从图2a)可以看出:煤泥焦燃烧时NH3有两个析出峰,分别在50~240 ℃和300~600 ℃区间,为煤泥焦中残留挥发分N随着温度升高迅速析出转换和焦炭N燃烧所贡献[30];两个析出峰的峰值温度皆随着热解温度的升高向高温区移动,但析出NH3的相对累积量随着热解温度的升高明显下降。
煤中的N分为挥发分N和焦炭N,热解温度的升高有利于挥发分析出,煤焦燃烧产生的NO有90%以上为NO,其生成与氧化、还原两个因素相关[31]。从图2b)可以看出:NO析出峰在400 ℃开始生成,457 ℃达到峰值,610 ℃终止;随着热解温度升高,对应煤泥焦燃烧产生NO析出的起始温度、峰值温度和终止温度均向高温区移动;煤泥焦燃烧产生NO的相对累积量随着热解温度的升高明显下降,主要原因是热解温度的升高使得煤泥焦中总的含N量减少。
从图2c)可以看出:煤泥焦燃烧产生的SO2只有一个析出峰,这与原煤燃烧析出2个SO2峰的特性不同[32-33];随着热解温度升高,煤泥焦燃烧产生SO2的析出峰起始温度由R500的340 ℃增加到R700的440 ℃,峰值温度由R500的470 ℃增加到R700的496 ℃,终止温度均在560 ℃左右,但R800煤泥煤并未出现析出峰。由煤中的含硫组分可知,硫铁矿的分解温度一般为600 ℃[34],有机硫在1 000 ℃基本分解完毕。随着热解温度升高,残留在焦炭中的硫呈下降趋势,这也可以解释R800煤泥焦燃烧未出现明显SO2析出峰,以及SO2析出强度和相对累积量均随着热解温度升高而减小。
从图2d)可以看出:煤泥焦燃烧产生的CO2离子流强度曲线只有1个析出峰,R500煤泥焦燃烧析出的CO2在260 ℃时开始增强,487 ℃时达到最大析出强度,600 ℃终止;热解温度每升高100 ℃,CO2析出峰的起始温度分别以60 ℃的跨度向高温区移动,析出峰值温度分别为7.8、16.5、32.6 ℃向高温区递增,而析出峰的终止温度几乎相同;热解温度对煤泥焦燃烧析出的CO2相对累积量存在很大影响,R500、R600、R700、R800煤泥焦燃烧析出的CO2相对累积量为50:28:15:7。
2.4 煤泥焦燃烧动力学参数分析
通过热失重曲线的变化,利用不同化学反应机理方程的拟合程度可以判断反应的动力学特征[35]。本文采用Coats-Redfern积分法[36],机理函数选用随机成核、随后生长Avrami-Erofeev方程模型,分别对=3/2、2、3、4进行计算,并取相关系数最高的=3/2模型求取样品的动力学参数,这也与刘建忠等人的研究结果相吻合[37]。动力学参数的计算式为


表4为计算所得7种煤泥焦的活化能、指前因子及拟合相关系数。
表4 煤泥焦的动力学参数
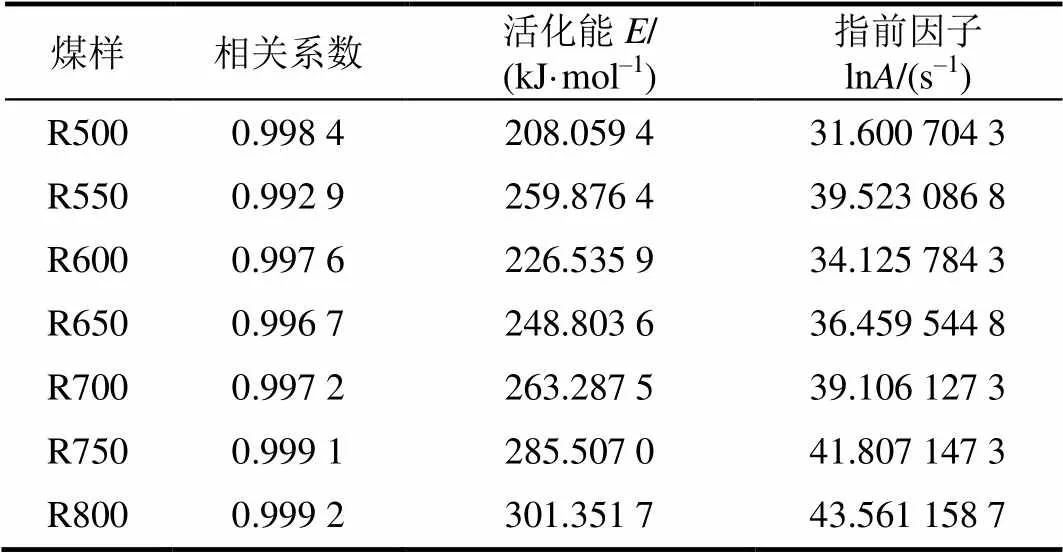
Tab.4 Kinetic parameters of the coal sludge chars
由表4可见,R500煤泥焦活化能为208 kJ/mol,随着热解温度升高,煤泥焦活化能提高,与燃烧特征指数的变化趋势相对应。这是由于热解温度升高促进了碳结构的有序化,使煤焦表面活性位点减少,矿物质熔融加快导致其催化能力降低所致[38]。
通常将ln与呈线性关系的现象称为动力学补偿效应,是热分析动力学研究中的一个重要内容,数学表达式为
ln=+(5)
式中,、为补偿参数,可通过已知预测,也可以通过已知预测[37]。
对7种煤泥焦燃烧时C-R法得到的参数进行动力学补偿效应分析,得动力学补偿表达式为ln=0.130 44+4.606 87。图3为动力学补偿效应拟合曲线。由图3可以得出,拟合曲线的相关性系数为0.993 0,说明煤泥焦燃烧存在动力学补偿效应。

图3 动力学补偿效应拟合曲线
3 结 论
1)热解温度对煤泥焦的燃烧特性影响较大。煤泥焦燃烧的着火温度、燃烧峰值温度、燃尽温度均随热解温度升高向高温区移动,可燃性指数、燃烧稳定性指数、综合燃烧指数均随热解温度升高而减小。
2)热解温度对NH3、NO、SO2、CO2的析出特性存在一定影响。析出峰的起始温度、峰值温度均随热解温度升高向高温区移动,析出峰的终止温度不受热解温度的影响;煤泥焦燃烧产生的NH3、NO、SO2、CO2相对累积量均随热解温度升高而降低。
3)煤泥焦活化能随着热解温度升高明显提高,存在动力学补偿。R500煤泥焦活化能为208 kJ/mol,当热解温度增加到800 ℃时,煤泥焦活化能增加到301 kJ/mol。
[1] 刘彦鹏, 李建民, 余永生, 等. 300 MW循环流化床锅炉掺烧煤泥试验研究[J]. 热力发电, 2010, 39(10): 60-64. LIU Yanpeng, LI Jianmin, YU Yongsheng, et al. Test study on mixedly burning coal slime in 300 MW CFB boiler[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2010, 39(10): 60-64.
[2] 杨婷婷, 邸小慧, 洪烽, 等. 掺烧煤泥循环流化床锅炉床温动态建模[J]. 热力发电, 2018, 47(2): 43-48. YANG Tingting, DI Xiaohui, HONG Feng, et al. Dynamic modeling for bed temperature of circulating fluidized bed boilers co-firing coal slime[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2018, 47(2): 43-48.
[3] 陈红, 周安鹂, 耿向瑾, 等. W火焰锅炉低负荷条件下掺烧煤泥的数值模拟[J]. 广东电力, 2018, 31(3): 15-20. CHEN Hong, ZHOU Anli, GENG Xiangjin, et al. Numerical simulation on burning blended coal slime under the condition of low load in W-flame boiler[J]. Guangdong Electric Power, 2018, 31(3): 15-20.
[4] 张娟丽, 郝雪弟, 朱大科, 等. 循环流化床锅炉掺烧煤泥发电技术及其应用[J]. 煤炭加工与综合利用, 2016(7): 70-73. ZHANG Juanli, HAO Xuedi, ZHU Dake, et al. Circulation fluidized bed boiler blended coal slime power generation technology and its application[J]. Coal Processing & Comprehensive Utilization, 2016(7): 70-73.
[5] 张琦. 掺烧煤泥对循环流化床锅炉床温床压的影响[D].保定: 华北电力大学, 2017: 5. ZHANG Qi. The effect on the bed temperature and pressure of the coal slime CFB boiler[D]. Baoding: North China Electric Power University, 2017: 5.
[6] 李丞亮. 煤泥掺烧循环流化床锅炉机组运行分析与经济性研究[D]. 北京: 华北电力大学, 2017: 5.LI Chengliang. Operation analysis and economic research on blending combustion with coal slime in circulating fluidized bed boiler[D]. Beijing: North China Electric Power University, 2017: 5.
[7] 侯志鹏, 肖凯华, 俞志鹏, 等. 煤泥循环流化床锅炉NO排放特性研究[J]. 热能动力工程, 2017, 32(11): 68-72. HOU Zhipeng, XIAO Kaihua, YU Zhipeng, et al. Study on NOemission characteristics of coal slurry circulating fluidized bed boilers[J]. Journal of Engineering for Thermal Energy and Power, 2017, 32(11): 68-72.
[8] 王建国, 赵晓红. 低阶煤清洁高效梯级利用关键技术与示范[J]. 中国科学院院刊, 2012, 27(3): 382-388. WANG Jianguo, ZHAO Xiaohong. Demonstration of key technologies for clean and efficient utilization of low-rank coal[J]. Bulletin of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2012, 27(3): 382-388.
[9] 本刊通信员. 1500万t/a大庆林源煤炭分质清洁利用项目开工[J]. 化肥设计, 2016, 54(5): 14. Publication Messenger. 15 million t/a Daqing Linyuan coal quality clean utilization project started[J]. Chemical Fertilizer Design, 2016, 54(5): 14.
[10] 巩志强. 低阶煤热解半焦的燃烧特性和NO排放特性试验研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2016: 3. GONG Zhiqiang. Experimental study on combustion and NOemission characteristics of char from pyrolysis of low rank coal[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2016: 3.
[11] 李艳昌, 吴晓宇, 韩光. 抚顺油页岩半焦燃烧特性[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2017, 23(5): 67-71. LI Yanchang, WU Xiaoyu, HAN Guang. Combustion characteristics research of Funshun oil shale semi-coke[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2017, 23(5): 67-71.
[12] 梁鼎成, 解强, 党钾涛, 等. 不同煤阶煤中温热解半焦微观结构及形貌研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2016, 45(4): 799-806. LIANG Dingcheng, XIE Qiang, DANG Jiatao, et al. Microcrystalline structure and morphology of chars derived from medium-temperature pyrolysis of coals with different metamorphisms[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology, 2016, 45(4): 799-806.
[13] JAYARAMAN K, KOK M V, GOKALP I. Pyrolysis, combustion and gasification studies of different sized coal particles using TGA-MS[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017, 125: 1446-1455.
[14] 武俊智, 杨凤玲, 程芳琴. 煤泥与玉米芯混燃过程TG-MS研究[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2017, 23(5): 72-76. WU Junzhi, YANG Fengling, CHENG Fangqin. TG-MS analysis of co-combustion of coal sludge and corncobs[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2017, 23(5): 72-76.
[15] KANDASAMY J. Thermogravimetric and mass spectrometric (TG-MS) analysis and kinetics of coal-biomass blends[J]. Renewable Energy, 2017, 101: 293-300.
[16] WANG Z T, GONG Z Q, WANG Z B, et al. A TG-MS study on the coupled pyrolysis and combustion of oil sludge[J]. Thermochimica Acta, 2018, 663: 137-144.
[17] 张建, 侯影飞, 周洪洋, 等. 活性半焦用于油田含油污水除油的研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2010, 4(2): 355-359.ZHANG JIAN, HOU Yingfei, ZHOU Hongyang, et al. Study on oil removal from oilfield wastewater using activated semicoke[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2010, 4(2): 355-359.
[18] 于英民, 郭瑞莉, 李春虎. 半焦吸附剂烟气脱硫脱硝性能[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2011, 39(5): 385-389.YU Yingmin, GUO Ruili, LI Chunhu. Flue gas desulfurization and denitrification performance of the semi-coke adsorbents[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2011, 39(5): 385-389.
[19] 刘建忠, 吴君宏, 王智化, 等. 水热提质褐煤的转化利用研究进展[J]. 热力发电, 2017, 46(11): 7-12. LIU Jianzhong, WU Junhong, WANG Zhihua, et al. Research progress of conversion and utilization of upgraded lignite by hydrothermal dewatering[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2017, 46(11): 7-12.
[20] 王卫东, 涂亚楠, 孙阳阳, 等. 微波吸收剂对褐煤微波提质的影响规律[J]. 煤炭学报, 2018, 43(5): 1440-1447. WANG Weidong, TU Ya’nan, SUN Yangyang, et al. Enhancement of microwave absorbents on quality of microwave dehydrated lignite[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2018, 43(5): 1440-1447.
[21] 阎军, 鞠文斐, 于秀举. 滚筒式褐煤干燥提质技术及经济性分析[J]. 煤炭工程, 2012(12): 64-65. YAN Jun, JU Wenfei, YU Xiuju. Analysis on drum type dry upgrading technology and economy of lignite[J]. Coal Engineering, 2012(12): 64-65.
[22] 张佳丽, 张如意, 谌伦建. 用热重法研究型煤燃烧特性[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2005, 11(3): 65-68.ZHANG Jiali, ZHANG Ruyi, CHEN Lunjian. Study on combustion character of briquette with thermogravimetry[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2005, 11(3): 65-68.
[23] JIA L, ANTHONY E J, LAU I, et al. Study of coal and coke ignition in fluidizebeds[J]. Fuel, 2006, 85(5): 635-642.
[24] 胡文斌, 杨海瑞, 吕俊复, 等. 煤着火特性的热重分析研究[J]. 电站系统工程, 2005, 21(2): 8-9. HU Wenbin, YANG Hairui, LU Junfu, et al. Study on ignition properties of coals by using thermogravimetry[J]. Power System Engineering, 2005, 21(2): 8-9.
[25] 周军, 张海, 吕俊复. 不同升温速率下石油焦燃烧特性的热重分析[J]. 煤炭转化, 2006, 29(2): 39-43.ZHOU Jun, ZHANG Hai, LV Junfu. Study on combustion characteristics of a petroleum coke at different heating rates by using thermongravimetry[J]. Coal Conversion, 2006, 29(2): 39-43.
[26] 徐朝芬, 向军, 孙路石, 等. 热解温度对淮南煤热解与CO2气化特性的影响[J]. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 38(11): 100-103. XU Chaofen, XIANG Jun, SUN Lushi, et al. Effect of the pyrolysis and CO2gasification characteristics of coal from Huainan on pyrolysis temperature[J]. Journal of Huazhong University of Science & Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(11): 100-103.
[27] 孙学信. 燃煤锅炉燃烧试验技术与方法[M]. 北京: 中国电力出版社, 2001: 75.SUN Xuexin. Coal-fired boiler combustion test technology and method[M]. Beijing: China Electric Power Press, 2001: 75.
[28] 刘典福, 魏小林, 盛宏至. 煤焦燃烧特性的热重试验研究[J]. 工程热物理学报, 2007, 28(增刊2): 229-232.LIU Dianfu, WEI Xiaolin, SHENG Hongzhi. Thermogravi- metric test study on combustion characteristics of coal char[J]. Jurnal of Egineering Termophysics, 2007, 28(Suppl.2): 229-232.
[29] LEPPÄLAHTI J, KOLJONEN T. Nitrogen evolution from coal, peat and wood during gasification: literature review[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 1995, 43(1): 1-45.
[30] SMOOT L D, SMITH P J. Coal combustion and gasification[M]. New York: Plenum Press, 1985: 91-95.
[31] 岑可法. 燃烧理论与污染控制[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2004: 410. CEN Kefa. Combustion theory and pollution control[M]. Beijing: Mechanical Industry Press, 2004: 410.
[32] 刘建忠, 周俊虎, 程军, 等. 长广煤燃烧硫析出动态特性研究[J]. 燃料化学学报, 2001, 29(4): 368-370.LIU Jianzhong, ZHOU Junhu, CHENG Jun, et al. Study on dynamic characteristic of sulfur release during Changguang Coal combustion[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology, 2001, 29(4): 368-370.
[33] 任强, 刘建忠, 周俊虎, 等. 石煤燃烧硫析出动态特性[J].煤炭学报, 2006, 31(1): 99-103.REN Qiang, LIU Jianzhong, ZHOU Junhu, et al. Dynamic characteristic of sulfur release during stone coal combustion[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2006, 31(1): 99-103.
[34] PATRICK J W. Sulphur release from pyrites in relation to coal pyrolysis[J]. Fuel, 1993, 72(3): 281-285.
[35] 平传娟, 周俊虎, 程军, 等. 混煤热解反应动力学特性研究[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2007, 27(17): 6-10.PING Chuanjuan, ZHOU Junhu, CHENG Jun, et al. Research on the pyrolysis kinetics of blended coals[J]. Proceedings of the Chinese Society for Electrical Engineering, 2007, 27(17): 6-10.
[36] 胡荣祖. 热分析动力学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2008: 55.HU Rongzu. Thermal analysis kinetics[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2008: 55.
[37] 刘明强, 刘建忠, 王睿坤, 等. 煤泥燃烧动力学机理研究的新方法探讨[J]. 煤炭学报, 2012, 37(增刊2): 444-448. LIU Mingqiang, LIU Jianzhong, WANG Ruikun, et al. Discussion of a new approach to study kinetic mechanism of coal slurry combustion[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2012, 37(Suppl.2): 444-448.
[38] 董爱霞, 张守玉, 王健, 等. 煤焦燃烧特性及反应活性探究[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2013, 19(1): 87-91. DONG Aixia, ZHANG Shouyu, WANG Jian, et al. Combustion performance and reaction activity of coal char[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2013, 19(1): 87-91.
Effect of pyrolysis temperature on coal sludge char combustion and products emission characteristics
GONG Dehong, ZHANG Xiaowan
(Electrical Engineering College, Guizhou University, Guiyang 550025, China)
The combustion experiments of coal sludge chars produced at different pyrolysis temperatures were carried out through thermogravimetric-mass spectrometry (TG-MS). The coal sludge chars’ combustion characteristics and the emission characteristics of NH3, NO, SO2and CO2at different pyrolysis temperatures were studied. Moreover, the C-R method was employed to calculate the coal sludge chars’ activation energies and pre-exponential factors. The results show that, the pyrolysis temperature had great influence on combustion performance of the sludge chars. The flammability index, combustion stability index and comprehensive combustion characteristic parameters of the sludge chars decreased with the increasing pyrolysis temperature. The pyrolysis temperature had a certain influence on precipitation characteristics of NH3, NO, SO2and CO2. The relative precipitation accumulation of these gases decreased with the increasing pyrolysis temperature. The activation energy of the sludge char increased obviously with the pyrolysis temperature, and kinetic compensation effect exists in the coal sludge char’s combustion process.
coal sludge char, combustion, TG-MS, combustion product, kinetics, compensation effect, pyrolysis temperature
The Guizhou Science and Technology Cooperation Foundation (QKHJC[2019]No.1059)
龚德鸿(1977—),男,博士,副教授,主要研究方向为清洁燃烧技术,gdh191@163.com。
TK16
A
10.19666/j.rlfd.201812230
龚德鸿, 张晓婉. 热解温度对煤泥焦燃烧及产物析出特性影响[J]. 热力发电, 2019, 48(6): 84-89. GONG Dehong, ZHANG Xiaowan. Effect of pyrolysis temperature on coal sludge char combustion and products emission characteristics[J]. Thermal Power Generation, 2019, 48(6): 84-89.
2018-12-24
贵州省科技计划项目(黔科合基础[2019]1059号)
张晓婉(1994—),女,硕士研究生,1109539318@qq.com。
(责任编辑 马昕红)

