腹腔镜切口疝修补术与开放式切口疝修补术治疗腹壁切口疝的疗效对比
郭驰
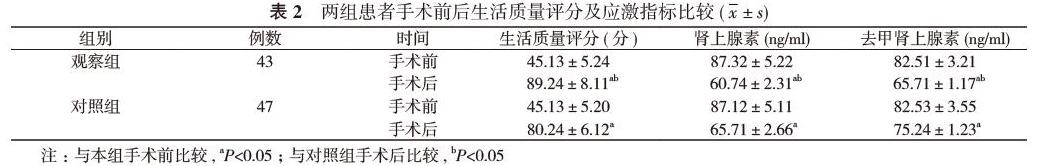

【摘要】 目的 探讨腹腔镜切口疝修补术与开放式切口疝修补术治疗腹壁切口疝的疗效。方法 90例腹壁切口疝患者 ,采用随机数字表法分为对照组 (47例 )和观察组 (43例 )。对照组进行开放式切口疝修补术 ,观察组进行腹腔镜切口疝修补术。比较两组患者的治疗效果 ,手术实施时间、术后抗生素使用时间、术后住院时间 ,手术前后生活质量评分及应激指标 ,并发症发生情况。结果 观察组患者的治疗总有效率 97.67%显著高于对照组的 72.34%,差异具有统计学意义 ( P<0.05)。观察组患者手术后的生活质量评分、肾上腺素水平、去甲肾上腺素水平, 手术实施时间、术后抗生素使用时间、术后住院时间均优于对照组 ,差异具有统计学意义 ( P<0.05)。观察组患者的并发症发生率为 9.30%, 低于对照组的 27.66%, 差异具有统计学意义 ( P<0.05)。结论 腹壁切口疝患者行腹腔镜切口疝修补术疗效明显 ,可更好的改善生活质量、应激指标, 加速康复, 减少相关并发症的发生。
【关键词】 腹腔镜切口疝修补术;开放式切口疝修补术;腹壁切口疝
DOI:10.14163/j.cnki.11-5547/r.2019.03.003
【Abstract】 Objective To discuss the efficacy of laparoscopic incisional hernia repair and open incisional hernia repair in the treatment of abdominal incisional hernia. Methods A total of 90 patients with abdominal incisional hernia were divided by random number table method into control group (47 cases) and observation group (43 cases). The control group was treated with open incisional hernia repair, and the observation group was treated with laparoscopic incisional hernia repair. Comparison were made on treatment effect, operative implementation time, postoperative antibiotic use time, postoperative hospitalization time, quality of life scores and stress indicators before and after operation and occurrence of complications between the two groups. Results The observation group had significantly higher total treatment effective rate as 97.67% than 72.34% in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). After operation, the observation group had better quality of life score, adrenaline and norepinephrine levels, operative implementation time, postoperative antibiotic use time, postoperative hospitalization time than the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). The observation group had lower incidence of complications as 9.30% than 27.66% in the control group, and the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05). Conclusion Laparoscopic incisional hernioplasty provides obvious efficacy for patient with abdominal incisional hernia, and it can better improve the quality of life, stress indicators, accelerate recovery and reduce the occurrence of related complications.
【Key words】 Laparoscopic incisional hernia repair; Open incisional hernia repair; Abdominal incisional hernia
腹壁切口疝在臨床发生率较高 ,是腹部手术常见的并发和观察组 (43例)。观察组中男 26例, 女 17例;年龄 32~75岁 , 症 ,尤其是术后有切口感染的患者 ,往往腹壁切口疝的发生平均年龄 (50.22±8.26)岁;切口疝在腹部中间 34例 , 在边率也较高。以往对于腹壁切口疝的治疗一般采用开放式人工缘区域 9例;复发时间距离上次手术 5~17个月 ,平均时间补片进行修补或者采用缝合修补手术进行治疗[1]。本研究分(7.22±3.26)个月。对照组男 29例, 女 18例;年龄 32~76岁 , 析腹腔镜切口疝修补术与开放式切口疝修补术治疗腹壁切口平均年龄 (50.65±8.45)岁;切口疝在腹部中间 37例 , 在边疝的疗效, 报告如下。 缘区域 10例;复发时间距离上次手术 5~17个月 ,平均时间1 资料与方法 (7.25±3.25)个月。两组患者的一般资料比较 ,差异无统计学

