严寒地区小型线性菲涅尔聚光集热器末端损失与补偿
闫素英,陈 壮,赵晓燕,马 靖,吴玉庭,田 瑞
严寒地区小型线性菲涅尔聚光集热器末端损失与补偿
闫素英1,2,陈 壮1,赵晓燕1※,马 靖1,吴玉庭3,田 瑞1,2
(1. 内蒙古工业大学能源与动力工程学院,呼和浩特 010051;2. 内蒙古可再生能源重点实验室,呼和浩特 010051; 3. 北京工业大学环境与能源工程学院,北京,100124)
针对严寒地区线性菲涅尔聚光集热器末端损失严重的问题,该文以呼和浩特地区小型线性菲涅尔聚光集热系统为研究对象,根据不同季节太阳位置的变化,理论分析并计算了沿水平南北轴放置的线性菲涅尔集热器自东向西跟踪过程的末端损失,得到其变化规律及补偿方法,并进行了试验验证。结果表明,一天中末端损失随时间的变化趋势与太阳高度角的变化趋势相同,与太阳方位角变化趋势相反,正午时刻末端损失最大,早晨和傍晚时刻末端损失最小;不同季节相同时间段内的末端损失,冬季最大,夏季最小,春季和秋季几乎相等;镜场调节试验结果表明,增大反射镜北端与水平面的夹角可以补偿末端损失,在夏至前后正午,当镜场北端抬高20°时,末端损失减少至集热器长度的1/10左右,瞬时集热效率达到65.9%,与反射镜调节前相比,正午瞬时集热效率提高54.5%,下午时间段内瞬时集热效率提高20%左右。研究结果可为减小严寒地区小型线性菲涅尔聚光集热器末端损失提供理论参考。
太阳能;传热;末端损失;严寒地区;线性菲涅尔聚光集热器;反射镜调节
0 引 言
线性菲涅尔式太阳能聚光集热系统具有结构紧凑、迎风面小[1]、易于制造、价格低廉等优点[2],在太阳能中温热源利用领域应用越来越广泛[3-4]。由于初级反射镜与集热器间存在一定距离,太阳光经反射后到达集热器的位置随太阳入射角变化而变化,一部分反射光线会偏离集热器端头而形成末端损失[5]。镜场的优化设计对其聚光效率影响较大[6],在大型线性菲涅尔聚光集热系统中,末端损失占集热器长度的比例较小,而对于小型线性菲涅尔系统来讲,末端损失占集热器长度的比例较大,对集热器聚光集热性能影响较大,所以减小末端损失显得特别重要[7]。目前国内外学者对线性菲涅尔集热器末端损失进行了研究,并提出一些补偿方法[8]。浦绍选等[7]计算了南北向线性菲涅尔反射镜场末端损失及其补偿办法;杜春旭等[9]利用矢量分析法说明塔高对镜场遮挡及光学损失具有一定影响;徐众等[10]采用理论计算和仿真方法分析了线性菲涅尔集热器复合抛物面反射器对镜场的遮挡情况;梁飞等[11]提出了阴影与遮挡计算模型,得出镜场布置最佳间距;邱羽等[12]优化了反射镜几何参数,提高了线性菲涅尔聚光集热系统的光学性能;Heimsath等[13]优化了2种聚焦太阳能集热器末端损失模型,利用光学损耗因子进行量化分析;Abbas等[14]提出了新型的集热器布置方式,减少了反射镜之间的遮挡和阴影问题;Buie等[15]讨论了南北向线性菲涅尔集热器末端损失,提出了正午时刻的末端损失估算公式;Xu C等[16]和Li M等[17]提出一种南北轴的太阳能集热器补偿端部损耗效应的方法;H Ajdad等[18]对线性菲涅尔太阳能集热器光学几何进行优化;Gui Q等[19]设计了一种新型CPC,增大了CPC的采光半角,提高了聚光效率;Diego等[20]提出一种用于线性菲涅尔集热器光学优化的设计方法,提高了集热器的月功率。
综上,线性菲涅尔集热器存在一定的末端损失,前人的研究主要集中在对集热器末端损失的理论分析及对补偿方法的讨论,而对严寒地区小型线性菲涅尔系统的末端损失研究及其补偿方法的试验测试少有涉及。本文在前人研究基础上,针对安装在呼和浩特高纬度严寒地区的小型线性菲涅尔聚光集热系统进行研究,并分析末端损失的影响因素及变化规律,提出了补偿方法并进行试验验证,以期为减少严寒地区小型线性菲涅尔集热器末端损失提供理论和试验依据。
1 小型线性菲涅尔聚光集热系统
1.1 试验测试系统
本文所研究的小型线性菲涅尔聚光集热试验系统如图1a所示,主要由一次反射镜、复合抛物面二次反射镜和玻璃-金属真空集热管组成。光线经过平面镜反射后,部分光线直接由真空集热管吸收,另一部分经过CPC(compound parabolic collector)二次反射后被真空集热管吸收。图1b为系统工作原理图。

注:为太阳入射光线与水平面的夹角,(°);为反射镜与水平面夹角,(°);为相邻反射镜间距离,m;为第n个反射镜距镜场中心的水平距离,m;为反射镜宽度,m;为CPC的开口宽度,m;为集热器高度,m;为CPC的最大采光半角,(°)。
1.2 镜场参数
线性菲涅尔系统的镜场布置需要考虑相邻镜面的阴影与遮挡问题[7],以本试验的基础参数为依据进行集热器高度的计算,试验测试系统结构参数如表1所示。

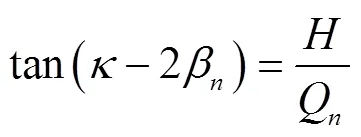
同理,当镜场与太阳位于集热器异侧时,有:


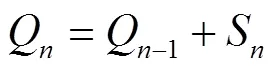
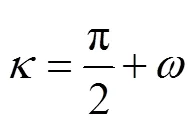

表1 小型线性菲涅尔系统结构参数及光学参数

在实际工程应用中,为保证系统在一定时间内无阴影遮挡下运行,反射镜与镜场中心的距离Q应尽可能小,以增加系统的地面覆盖率、降低集热器高度,进而降低系统成本。
2 集热器末端损失计算与分析
2.1 末端损失计算

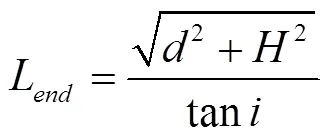

根据式(7),可得
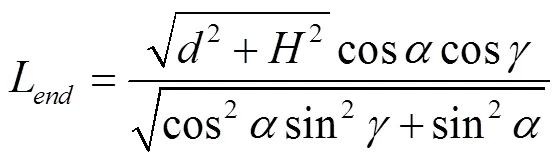


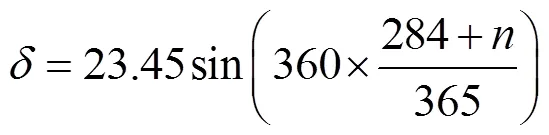

2.2 末端损失规律分析
本文根据文献[7]的方法计算不同季节呼和浩特地区的小型线性菲涅尔聚光试验系统的末端损失。呼和浩特位于东经111.65°,北纬40.87°,选取2017年不同季节(春分、夏至、秋分和冬至日)太阳真时9:00-16:00时,根据式(10)~(13),计算得到一天中各时刻的太阳方位角、高度角,结果如图2所示。由图2可知,在测试时间段,以当地太阳真时的12:30为节点,太阳高度角、方位角(负号表示下午太阳方位角方向)均在上午和下午呈现对称变化趋势,高度角先升高后降低,方位角先下降后升高,最大高度角和最小方位角均出现在12:30,该结果与文献[25]吻合。
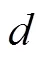

图2 呼和浩特不同季节太阳方位角和高度角随时间变化
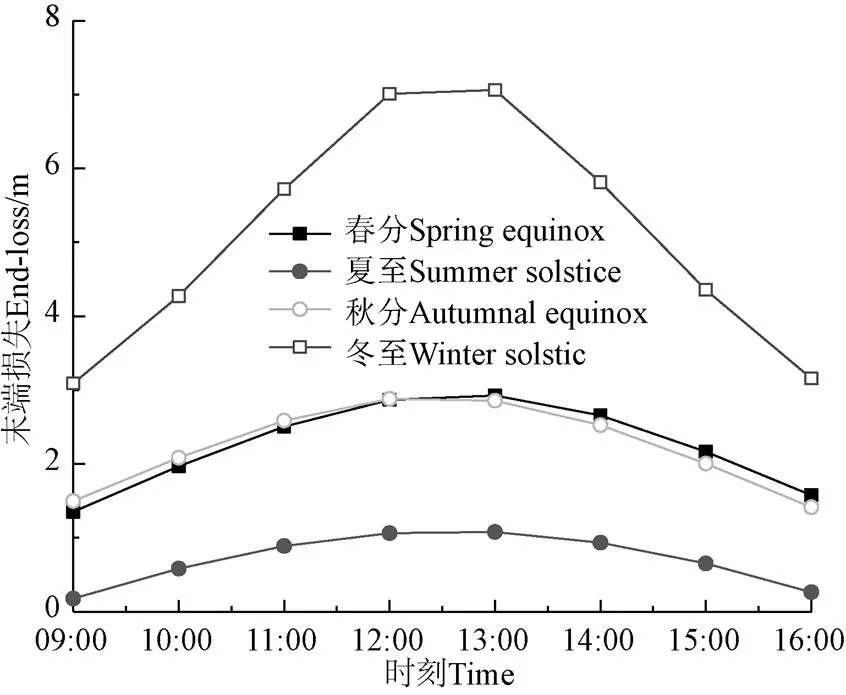
图3 不同季节集热器末端损失随时间变化
本试验系统集热器长2 m,在夏至正午时刻,集热器有55%的末端损失,即损失1.1 m;在冬至正午时刻,由于高度角变小,集热器末端损失7.1 m,2 m的集热器长度全部损失,即集热器长度越短,损失比例越大,如果不进行调节将全部损失,即对于小型线性菲涅尔聚光集热系统,末端损失影响较大,必须根据季节变化进行调节。如果线性菲涅尔反射式聚光集热系统的集热器长50 m,则在夏至正午时刻集热器有2.2%的末端损失;若集热器长100 m,有1.1%的末端损失。因此为了减少末端损失,应尽可能增加集热器的长度。
依据式(9)计算6月21日(夏至)太阳真时9:00-16:00,集热器距反射镜场高0~4.5 m时的末端损失,结果如图4所示。由图4可知,末端损失随集热器高度呈增大趋势,并且集热器越高,其末端损失越大。根据1.2节中的计算,为了避免阴影遮挡,本试验系统集热器距反射镜场高度应在2.45 m以上。以正午时刻为例,集热器高度为2.5 m时反射镜的末端损失为0.8 m,集热器高度为4.5 m时末端损失为1.4 m,两者相差0.6 m,该结果与文献[25]一致。这表明在搭建线性菲涅尔反射式聚光集热系统时,应尽可能降低集热器高度,同时也要考虑采取该措施会增大相邻反射镜间的阴影遮挡面积[23]。
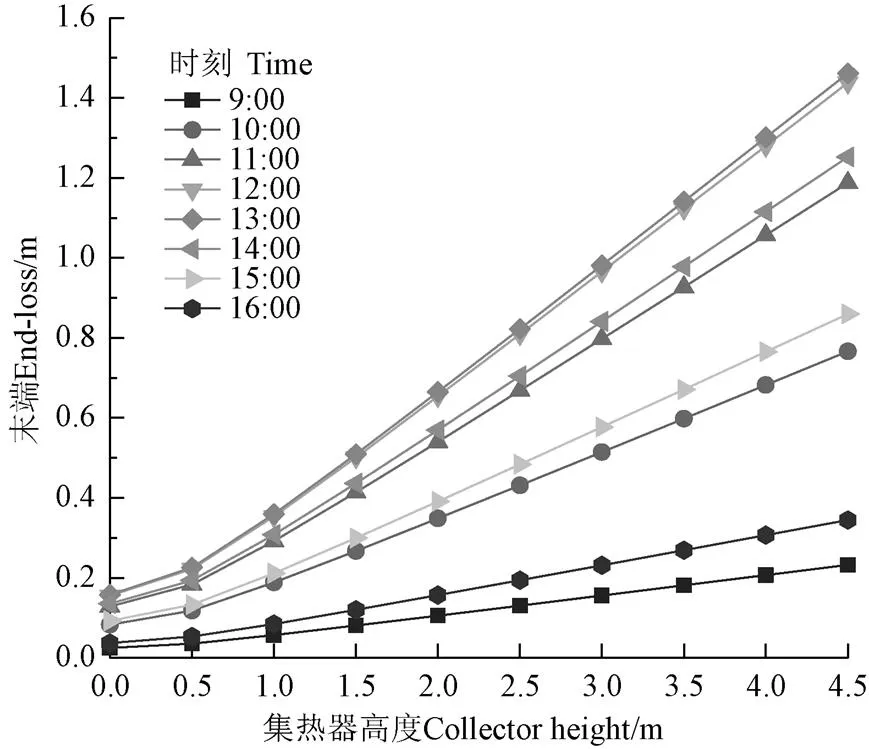
图4 不同时刻末端损失随集热器高度的变化
3 末端损失补偿调节
3.1 反射镜调节补偿原理与计算
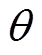



a 反射镜调节补偿末端损失原理示意图
a Schematic diagram of reflector adjustment compensation end-loss

b 反射镜调节后实物图


图6 集热器末端损失随反射镜调节角的变化
3.2 末端损失调节补偿验证试验
为了验证本文末端损失补偿方法的准确性,进行了系统验证试验。试验地点为呼和浩特市某高校4层办公楼顶,试验时间是2017年6月20日和6月21日的上午10:30至下午15:30,2 d的试验时间段内天气晴朗、无风,工况近似相同,太阳直射辐照度在720~900 W/m2之间,温度在23~25℃之间,传热工质为导热油,密度为868 kg/m3(20℃),流量为0.18 kg/s。根据3.1节的补偿调节原理及计算结果,夏至日时的补偿调节方法是将反射镜和集热器北端同时抬高20°(即镜场南北轴线与水平面夹角为20°),试验系统图5b所示。试验中采用Fluke Ti55FT红外热成像仪(具体参数如表2)拍摄反射镜调节前后集热器聚光焦斑长度变化情况,根据聚光焦斑长度计算末端损失,采用线性菲涅尔聚光集热系统的数据采集系统记录集热器进出口温度,计算瞬时集热效率。

表2 Ti55FT红外热成像仪主要技术参数
3.3 试验结果与分析


图7 反射镜调节前后集热器聚光焦斑变化

注:DSI1 、DSI2分别为反射镜调节前后太阳直射辐照度,W·m-2;△t1 、△t2分别为反射镜调节前后工质进出口温差,℃。
根据图7和图8结果,反射镜调节前开始测试时,其末端损失发生在工质出口端一侧,上午10:30集热器末端损失约为0.4 m;随着太阳高度角和方位角的变化,在12:30时末端损失达到1 m,损失部位处于工质出口端,此时末端损失达到最大,与前文理论分析计算结果一致,并随着太阳高度角的减小,集热器末端损失逐渐减小直至聚光焦斑完全覆盖整个集热器。反射镜调节后开始测试时,其末端损失发生在工质进口端一侧,与反射镜调节前变化趋势相反,中午12:00至13:00时间段内太阳高度角最大,呼和浩特地区受纬度影响,该地区真太阳时为12:30左右,此时聚光焦斑最长,末端损失最小,仅占集热器长度的1/10左右,约为0.2 m,与前文3.1中的理论计算相一致,同时在该时间段前后均有末端损失发生;上午9:00至12:00时间段内随着太阳高度角的增加,末端损失最大,约为0.7 m;下午13:00至16:00时间段太阳高度角减小,末端损失逐渐减小,到15:30左右,末端损失约为0.5 m,太阳高度角对系统末端损失影响较大。综上,补偿后的线性菲涅尔聚光集热器在早晚时刻末端损失最大,约为0.7 m;正午时刻最小,约为0.2 m。

注:η1、η2分别为反射镜调节前后的系统瞬时集热效率,%。
4 结 论
严寒地区小型线性菲涅尔聚光集热系统的末端损失严重,本文基于南北向线性菲涅尔反射镜场,首先对集热器末端损失进行分析,以搭建在呼和浩特地区(北纬40.87°)的线性菲涅尔聚光系统为例,计算了不同季节和不同集热器高度时,末端损失的变化情况,提出一种末端损失反射镜调节补偿方法并进行了试验验证,利用红外热成像仪拍摄末端损失补偿前后集热器不同时刻聚光焦斑长度变化,并分析调节前后系统瞬时集热效率的变化,得到以下结论:
1)末端损失的大小主要与反射镜到集热器的水平距离、集热器高度、太阳高度角和方位角有关,在避免反射镜间阴影遮挡损失的前提下,可通过降低集热器高度减小末端损失;
2)采用东西方向跟踪的线性菲涅尔聚光集热系统,可根据季节变化增加反射镜与南北方向水平面的夹角来减小末端损失,反射镜场与南北方向水平面的夹角应保持在理论计算值范围内,其值根据当地纬度计算得到;
3)反射镜调节后末端损失变化趋势发生改变,正午时聚光焦斑完全覆盖集热器,瞬时集热效率为65.9%,较补偿前正午时的瞬时集热效率增加54.5%,验证了本文补偿方案的有效性,对减小严寒地区小型线性菲涅尔聚光集热系统集热器末端损失提供了理论参考。
[1] 魏博斌,孔令刚,蒋庆安,等. 细多管CPC线性菲涅尔聚光系统仿真及实验研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展,2019,56(3):66-73. Wei Bobin, Kong Linggang, Jiang Qingan, et al. Simulation and experimental study of a thin multi-tube compound parabolic condenser linear fresnel spot system[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2019, 56(3): 66-73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 闫素英,马晓东,王峰,等. 菲涅尔聚光CPVT系统光热输出特性研究[J]. 工程热物理学报,2017,38(6):1178-1183.Yan Suying, Ma Xiaodong, Wang Feng, et al. Study on photothermal output characteristics of Finel CPVT system[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2017, 38(6): 1178-1183. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] Nicholas Kincaid, Greg Mungas, Nicholas Kramer, et al. An optical performance comparison of three concentrating solar power collector designs in linear Fresnel,parabolic trough,and central receiver[J]. Applied Energy, 2018(231): 1109-1121.
[4] 闫素英,吴泽,王峰,等. 菲涅尔高倍聚光PV/T系统热电输出性能模拟与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(20):197-203.Yan Suying, Wu Ze, Wang Feng, et al. Simulation and test of thermoelectric output performance of Fresnel high concentration PV/T system[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(20): 197一203. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 徐众,浦绍选,夏朝凤. 线性菲涅耳集热器的能损分析[J]. 能源研究与利用,2012(1):40-43. Xu Zhong, Pu Shaoxing, Xia Chaofeng. Energy loss analysis of linear Fresnel collector[J]. Energy Research & Utilization, 2012(1): 40-43. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] Roostaee A, Ameri M. Effect of linear Fresnel concentrators field key parameters on reflectors configuration, Trapezoidal Cavity Receiver dimension, and heat loss[J]. Renewable Energy, 2019(134): 1447-1464.
[7] 浦绍选,夏朝凤,线聚光菲涅耳集热器的端部损失与补偿[J]. 农业工程学报,2011,27(13):282-285. Pu Shaoxuan, Xia Chaofeng. End-loss and compensation of linear fresnel collectors[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE),2011, 27(13): 282一285. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 戴静,郑宏飞,冯朝卿. 三运动复合线性菲涅耳反射式太阳聚光系统的性能研究[J]. 北京理工大学学报,2016,36(5):464-469,479. Dai Jing, Zheng Hongfei, Feng Chaoqing. Performance of linear Fresnel reflector system combined three—movement[J]. Transactions of Beijing Institute of Technology. 2016, 36(5): 464-469,479. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 杜春旭,王普,马重芳,等. 线性菲涅耳聚光系统无遮挡镜场布置的光学几何方法[J]. 光学学报,2010,30(11):3276-3282. Du Chunxu, Wang Pu, Ma Chongfang, et al. Optical geometric method for LFR mirror field arrangement without shading and blocking[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2010, 30(11): 3276-3282. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 徐众,万书权,韩洪波,等. 线性菲涅耳集热器接收器对镜场的遮挡研究[J]. 新能源进展,2015,3(4):261-264. Xu Zhong, Wan Shuquan, Han Hongbo, et al. Discussion of mirror field shelter from linear Fresnel collector receiver[J]. Advances in new and renewable energy, 2015, 3(4): 261-264. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 梁飞,张娜. 线性菲涅尔式聚光系统阴影与遮挡计算分析模型[J/OL]. 激光与光电子学进展,1-12[2019-01-28]. http//kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/31.1690.TN.20190125.1300.002. html. Liang Fei,Zhang Na. Calculation and analysis model of shadow and block for Linear Fresnel Concentrator System[J/OL]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress:1-12[2019-01-28].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/31.1690.TN. 20190125.1300.002.html. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 邱羽,何雅玲,程泽东. 线性菲涅尔太阳能系统光学性能研究与优化[J]. 工程热物理学报,2015,36(12):2551-2556. Qiu Yu, He Yaling, Cheng Zedong. Optical performance investigation and optimization of a Linear Fresnel Reflector Solar Collector[J]. Journal of Engineering Thermophysics, 2015, 36(12): 2551-2556. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] Heimsath A, Bern G, Van Rooyen D, et al. Quantifying optical loss factors of small linear concentrating collectors for process heat application[J]. Energy Procedia,2014(48): 77-86.
[14] Abbas R, Montes M J, Rovira A, et al. Parabolic trough collector or linear fresnel collector? A comparison of optical features including thermal quality based on commercial solutions[J]. Solar Energy, 016(124): 198-215.
[15] Buie D, Dey C J, Mills D. Optical considerations inline focus fresnel concentrators[C] Zürich,Switzerland,Proceedings of the 11th Solar PACES International Symposium on Concentrating Solar Power and Chemical Energy Technologies,2002,197-203.
[16] Xu Chengmu, Chen Zhiping, Li Ming, et al. Research on the compensation of the end loss effect for parabolic trough solar collectors[J]. Applied Energy,2014 (115): 128-139.
[17] Li Ming, Xu Chengmu, Ji Xu, et al. A new study on the end loss effect for parabolic trough solar collectors[J]. Energy, 2015(82): 382-394.
[18] H Ajdad, Y Filali Baba, A Al Mers, et al. Particle swarm optimization algorithm for optical-geometric optimization of linear fresnel solar concentrators[J]. Renewable Energy,2019( 130): 992-1001.
[19] Li Guiqiang. Design and development of a lens-walled compound parabolic concentrator-a review[J]. Journal of Thermal Science, 2019, 28(1): 17-29.
[20] Diego P I, Loreto V, Serrano-Aguilera Juan-José, et al. Optimized design of a Linear Fresnel Reflector for solar process heat applications[J]. Renewable Energy, 2019(131): 1089-1106.
[21] 周小泉,周海妮,谭永超,等. 线性菲涅尔反射式太阳能集热系统镜场优化布置及光学性能开发与应用研究[J]. 实验室研究与探索,2012,31(10):306-309,367. Zhou Xiaoquan,Zhou Haini,Tan Yongchao,et al. The optimal layout of mirror field and optical properties of linear Fresnel concentrator[J]. Research and Exploration in Laboratory, 2012, 31(10): 306-309,367. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 宋固. 线性菲涅尔反射式太阳能集热系统研究[D]. 济南:山东大学,2011. Song Gu. Research on Linear Fresnel Reflector Solar Collector System[D]. Jinan:Shandong University,2011. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] Duffie J A, Beckman W A. Solar Engineering of Thermal Processes (3nd ed )[M]. New York: John Wiley and Sons,Inc, 2006.
[24] Cooper P I. The absorption of solar radiation in solar stills[J]. Solar Energy, 1969, 12(3): 333-346.
[25] 车淑平. 线性菲涅尔反射系统光学和集热性能研究[D]. 济南:山东大学,2012. Che Shuping. Research of Optical and Thermal Properties of Linear Fresnel Reflector[D]. Jinan:Shandong University,2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
End-loss and compensation for small linear Fresnel collectors in severe cold area
Yan Suying1,2, Chen Zhuang1, Zhao Xiaoyan1※, Ma Jing1, Wu Yuting3, Tian Rui1,2
(1.,,010051,;2.,,010051,;3.,,100124,)
The linear Fresnel solar concentrating collector has been widely used in the field of solar heat source utilization due to its compact structure, easy manufacture and low price. Because there is a certain distance between the primary mirror and the collector, the position of the sunlight after reaching the collector changes with the incident angle of the sun, and a part of the reflected light will run out of the collector end to form the end-loss. For the large linear Fresnel collector systems, the end-loss length accounts for a small proportion of the length of the collector, while for the small linear Fresnel systems, the end-loss length accounts for a large proportion of the length of the collector, it has a great influence on the heat collection performance of the collector, so it is particularly important to reduce the end loss. According to the geographical location, the end-loss length of a north-south linear Fresnel mirror field is difference. Based on this, aiming at the serious end- loss of linear Fresnel collector in severe cold area, taking the small linear Fresnel collector system in Hohhot area(north latitude 40.87°) as the research object, the end-loss of linear Fresnel collector placed along the horizontal north-south axis and its adjustment and compensation method were studied and verified by experiments in this paper. The experiment bench was developed on a building roof. The linear Fresnel experimental system was mainly composed of a primary mirror, a compound parabolic secondary mirror and a glass-metal vacuum heat collecting tube. After the light reflected by the plane mirror, part of the light was directly absorbed by the vacuum heat collecting tube, and the other part was absorbed by the vacuum heat collecting tube after the secondary reflection of CPC(compound parabolic collector). The change of end-loss in different seasons and different collector heights was analyzed and calculated theoretically, a method of adjusting reflectors to compensate end-loss was proposed. The focal spot length of collector at different time before and after end-loss compensation was captured by infrared thermal imager, and the change of instantaneous heat collection efficiency before and after reflectors adjustment was analyzed. The results showed that the end-loss length was mainly caused by the horizontal distance from the mirror field to the collector, the height of the collector, the solar azimuth angle and height angle. The end-loss length could be reduced by raise the height of the collector under the premise of avoiding the occlusion and shadow loss between the mirror elements. Meanwhile, the end loss could be reduced by increasing the angle between the mirror and the north-south horizontal plane according to the seasonal variation, and the angle should be kept within the theoretical range. The length of the end-loss decrease to about 1/10 of the collector length after the northern end of the mirror field was raised to 20°at summer solstice afternoon, and the instantaneous heat collecting efficiency increased to 65.9% at noon, which was 54.5% higher than that of before compensation. The change trend of the end-loss with time was the same as that of the sun altitude angle in the middle of the day, contrary to the change trend of the sun azimuth angle, the end-loss at noon was the largest, and the en-loss at morning and evening was the smallest. In the same period of time, the end-loss was the largest in winter, the smallest in summer, and almost the same in spring and autumn. The study provided a theoretical reference for reducing the loss-end length of small linear Fresnel concentrating collectors in severe cold area.
solar energy; heat transfer; end-loss; severe cold area; linear Fresnel concentrating collector; reflector adjustment
2018-12-04
2019-01-30
国家自然科学基金资助项目(No.51766012);内蒙古财政创新资助项目(2017年度);内蒙古工业大学科学研究项目(A类)(No.X201606)
闫素英,教授,博士,主要从事太阳能光热、光电利用技术的研究。Email:yan_su_ying@aliyun.com.
赵晓燕,博士生,实验师,主要从事传热传质强化及能源利用技术方面的研究。Email:NGZXY@imut.edu.cn
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.06.025
K515
A
1002-6819(2019)-06-0206-08
闫素英,陈 壮,赵晓燕,马 靖,吴玉庭,田 瑞. 严寒地区小型线性菲涅尔聚光集热器末端损失与补偿[J]. 农业工程学报,2019,35(6):206-213. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.06.025 http://www.tcsae.org
Yan Suying, Chen Zhuang, Zhao Xiaoyan, Ma Jing, Wu Yuting, Tian Rui. End-loss and compensation for small linear Fresnel collector in severe cold area[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2019, 35(6): 206-213. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.06.025 http://www.tcsae.org

