腰椎间盘突出症患者突出椎间盘与相邻椎间盘退变程度的MRI探究
朱锋辉 姚爱明 崔建 张寰 仲冬 刘筱


【摘要】 目的:研究腰椎間盘突出症患者其突出椎间盘、相邻椎间盘发生退变的MRI。方法:选择2014年1月-2018年12月本院收治的86例腰椎间盘突出症患者。突出椎间盘产生在L4~5节段中共43处,在其相邻椎间盘中共86处;在L5~S1节段中共43处,在其相邻椎间盘中共43处。监测开展手术以前的腰椎部位MRI,椎间盘运用Pfirrmann分级标准加以评定,软骨终板形态运用Pappou分级标准加以评定,观察比较其结果。结果:各年龄段中L4~5、L5~S1突出椎间盘,其Pfirrmann分级均多于Ⅲ级,其Pappou分级均多于Ⅱ级(P<0.05);各年龄段中软骨终板退变结果加以比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。各年龄段中,突出椎间盘产生在L4~5、L5~S1中处于上位的相邻椎间盘,其Pfirrmann分级加以比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),处于下位的相邻椎间盘,其Pfirrmann分级加以比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),在相邻椎间盘中,其软骨终板退变结果加以比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。在L4~5突出椎间盘中的L3~4相邻椎间盘中,其Pfirrmann分级、软骨终板形态的Pappou分级评分均大于L5~S1的相邻椎间盘(P<0.05)。结论:对腰椎间盘突出症患者而言,在其突出节段中,相邻椎间盘、软骨终板所产生的退变同突出椎间盘退变程度、年龄间紧密联结,且处于上位的相邻椎间盘产生的退变多于下位。
【关键词】 MRI; 退变; 腰椎间盘突出症; 椎间盘; 影响因素
MRI Study of Degeneration Degree of Protruded Intervertebral Disc and Adjacent Intervertebral Disc in Patients with Lumbar Disc Herniation/ZHU Fenghui,YAO Aiming,CUI Jian,et al.//Medical Innovation of China,2019,16(26):-129
【Abstract】 Objective:To study the degeneration of the herniated intervertebral disc and adjacent intervertebral disc in patients with lumbar disc herniation.Method:A total of 86 patients with lumbar disc herniation in our hospital from January 2014 to December 2018 were selected.There were 43 prominent discs in L4-5 segment,86 in the adjacent intervertebral discs.43 in L5-S1 segment,and 43 in the adjacent intervertebral discs.MRI of the lumbar vertebrae before the operation was monitored.The intervertebral discs were assessed using the Pfirrmann grading standard,and the cartilage endplate morphology was assessed using the Pappou grading standard.The results were observed and compared.Result:In the various age groups,L4-5 and L5-S1 protruded from the intervertebral disc.The Pfirrmann grade was more than grade Ⅲ,and the Pappou grade was more than grade Ⅱ(P<0.05).The results of cartilage endplate degeneration in all age groups were compared,the differences were not statistically significant(P>0.05).In all ages,the intervertebral discs produced adjacent discs in the upper position in L4-5 and L5-S1,and the Pfirrmann grading was statistically significant(P<0.05).The adjacent intervertebral discs in the lower position of the Pfirrmann grading,there was no significant difference between two groups(P>0.05).There was no significant difference in the outcome of cartilage endplate degeneration between adjacent intervertebral discs(P>0.05).Pappormann grading and Pappou grading score of cartilage endplate morphology were higher in L4-5 adjacent intervertebral discs than those in L5-S1 adjacent intervertebral discs(P<0.05).Conclusion:For patients with lumbar disc herniation,the degeneration of adjacent intervertebral discs and cartilage endplates is closely related to the degree and age of the degeneration of the herniated intervertebral discs,and the degeneration of adjacent upper discs is more than that of lower discs.
【Key words】 MRI; Degeneration; Lumbar disc herniation; Intervertebral disc; Influencing factors
First-authors address:Affiliated Hospital of Xuzhou Medical University,Xuzhou 221000,China
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2019.26.034
腰椎间盘突出症在临床中十分普遍,在这其中,突出就是十分普遍的种类,而脱出十分罕见,且其病情十分隐匿,较易对患者带来十分不利的影响[1]。有研究人员指出,脱出、突出指的就是腰椎间盘突出症产生进展的两大步骤,而脱出最为严重,会引发腰腿酸痛,甚至让下肢无法活动[2]。现阶段,对腰椎间盘突出症的各大种类与其椎体产生退变的MRI加权像相关的分析与研究依旧不多[3]。本文主要对比与分析了腰椎间盘突出症患者其突出椎间盘、相邻椎间盘发生退变的MRI,现报道如下。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取2014年1月-2018年12月本院收治的86例腰椎间盘突出症患者。纳入标准:均符合腰椎间盘突出症的诊断标准。排除标准:重度肺部、心脏等关键脏器功能障碍;有药物过敏史;中途退出;妊娠期與哺乳期女性;传染疾病、精神疾病、恶性肿瘤。86例患者中,男52例,女34例;年龄22~77岁,平均(49.00±16.34)岁,其中<40岁11例,40~50岁23例,51~60岁37例,>60岁15例;突出椎间盘产生在L4~5节段中共43处,在其相邻椎间盘中共86处;在L5~S1节段中共43处,在其相邻椎间盘中共43处。
1.2 方法 开展手术前,全部患者腰椎实施MRI监测,采用美国GE公司Signa 1.5T Infinity TwinSpeed型超导磁共振成像系统,以SE型自旋回波序列,作矢状面T1加权(TR/TE为440/10.7 ms)、
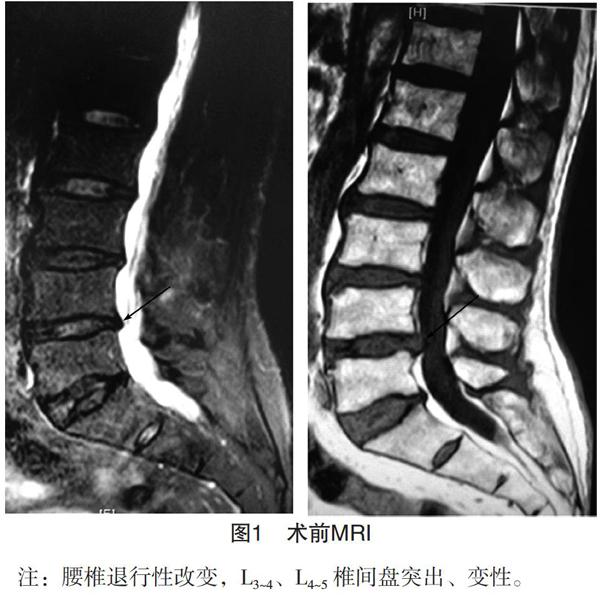
T2加权(TR/TE为2400/103 ms),层厚4 mm,层距1 mm,矩阵320×256[4]。全部MRI结果与资料采用双盲法,由一位放射科室医生与一位外科医生评定分级,再总体实施评分。术前MRI见图1;术后MRI,见图2。
1.3 观察指标 对椎间盘中的L3~4、L4~5、L5~S1节段而言,应用Pfirrmann分级方式,共五级,Ⅰ、Ⅱ级为正常,Ⅲ级及以上为退变;依据分级标准加以评分,Ⅰ级为1分,Ⅱ级为2分,Ⅲ级为3分,Ⅳ级为4分,Ⅴ级为5分,总分越高退变越严重。对于软骨终板形态而言,运用Pappou分级标准,总共三级,Ⅰ级即为正常,Ⅱ、Ⅲ级为退变;依据分级标准加以评分,凹面为Ⅰ级(1分),平坦为Ⅱ级(2分);不规则为Ⅲ级(3分),总分越高退变越严重。
1.4 统计学处理 采用SPSS 19.0软件对所得数据进行统计分析,计量资料用(x±s)表示,比较采用t检验。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 各年龄段突出节段与其相邻节段退变评分比
较 各年龄段L4~5、L5~S1突出椎间盘,其Pfirrmann分级均多于Ⅲ级,其Pappou分级均多于Ⅱ级(P<0.05);在各个年龄阶段中,软骨终板退变结果加以比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。在各个年龄阶段中,突出椎间盘产生在L4~5、L5~S1中处于上位的相邻椎间盘,其Pfirrmann分级加以比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);处于下位的相邻椎间盘,其Pfirrmann分级加以比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);在相邻椎间盘中,其软骨终板退变结果加以比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表1、2。
2.2 相邻椎间盘比较 L3~4中的相邻椎间盘,其Pfirrmann分级评分为(3.37±0.18)分,L5~S1为(2.87±0.60)分,两者比较差异有统计学意义(t=5.234 1,P=0.019 7);L3~4中的软骨终板形态,其Pappou分级评分为(1.65±0.11)分,L5~S1为(1.34±0.20)分,两者比较差异有统计学意义(t=8.905 9,P=0.000 0)。
3 讨论
MRI是无辐射且无创的影像学监测方法,因为椎间盘中的成分不一致,其髓核、纤维环等处于MRI中的信号表现不一致,所以MRI变成了临床中对椎间盘退变性病症诊断的首要方式[5-6]。同时,因为椎间盘中各个成分在MRI中表现的差别,产生了Pfirrmann分级体系,这一体系可以凸显出椎间盘的相关情况,已经被大量地运用到评定椎间盘产生的退变[7-8]。此外,在椎间盘产生退变后,软骨终板也会产生某种程度上的改变,以适应这一退变[9-10]。有研究人员指出,软骨终板形态与椎间盘产生的退变紧密联结,并提示了凹面、平坦、不规则三大种类;同时软骨终板形态自凹面至平坦至不规则,腰椎间盘产生的退变逐步加剧,能够间接且全面地凸显出腰椎间盘产生的退变。
椎间盘退变相应的机制包括细胞凋亡、营养等因素[11-12]。现阶段,有关突出椎间盘的分析与研究十分普遍,然而相邻椎间盘具有相似的退变与否有关的分析与研究不多[13-14]。对腰椎间盘突出症患者而言,在对其治疗的总有效率实施长时间的回访后,指出了在突出椎间盘中相邻节段椎间盘处于MRI也会产生程度不一的退变,比如,椎间盘信号处于T2加权像中表现为低信号、椎间盘产生轻度膨出等[15-16]。现阶段许多主流观点指出,相邻节段椎间盘产生的退变同腰椎运动所担负的负荷与其应力分布具有的变化相关[17-18]。突出椎间盘产生的退变提升了各周围节段椎间盘的内压,特别是对部分产生退变的周围节段,会提升周围节段椎间盘产生退变的速度[19]。

