颗粒化肥水平气送式螺旋组合可调定量供肥装置设计与试验
雷小龙,李蒙良,张黎骅,任万军
颗粒化肥水平气送式螺旋组合可调定量供肥装置设计与试验
雷小龙1,2,李蒙良1,张黎骅1,任万军2
(1. 四川农业大学机电学院,雅安 625014;2. 农业部西南作物生理生态与耕作重点实验室,成都 611130)
为适应不同施肥量要求和实现水平气送式集中排肥器定量变量排肥,该文设计了一种颗粒化肥螺旋组合式集中供肥装置。阐述了颗粒化肥螺旋组合式集中供肥装置的工作原理,基于颗粒化肥的机械物理特性和施肥量要求,提出了倾斜螺旋状型孔结构,确定了其主要结构参数,构建了颗粒化肥组合体在肥料充填区和投肥区的力学模型。应用台架试验研究了螺旋式排肥轮数量和转速对供肥速率及供肥稳定性变异系数的影响。结果表明:倾斜螺旋状型孔结构有利于充肥和排肥;螺旋式排肥轮数量和转速分别为1~4个和10~40 r/min条件下,供肥速率随螺旋式排肥轮数量与转速增加而增加,供肥速率范围为912.67~13 164.26 g/min。螺旋组合式集中供肥装置能适应不同机械物理特性参数的颗粒化肥,3种颗粒化肥的供肥速率之间的差值低于5%。构建了螺旋式排肥轮数量和转速与供肥速率的回归预测模型,在目标施肥量150~750 kg/hm2和拖拉机前进速度2.52~5.88 km/h条件下,供肥速率试验值与模型预测值的偏差在3%以内,供肥稳定性变异系数低于1.0%。田间试验结果表明,颗粒化肥实际施用量与模型预测值相对误差为3.54%。该研究提出的倾斜螺旋状型孔和组合排肥轮结构可满足农业生产的变量、定量集中供肥要求,可为颗粒化肥水平气送式集中排肥器结构设计提供参考。
农业机械;设计;试验;倾斜螺旋状型孔;集中排肥器;颗粒化肥
0 引 言
化肥的广泛应用为中国粮食增产做出了重要贡献[1],但存在利用率低、化肥过度施用导致土壤板结、环境污染等诸多问题[2],降低化肥施用量和提高利用率成为优质高效绿色的重要方式和途径,也是“两减一控”的核心内容[3-5]。机械化定量按需施肥成为降低化肥用量和提高化肥利用率的发展方向。
颗粒化肥在农业生产中应用广泛,具有流动性偏差、吸湿性强、架空性和粘结性等特点[6]。根据作物的营养需肥时间,施肥方式可分为基肥、追肥和穗肥等类型,不同作物和施肥方式的单位面积施肥量差异大。目前,机械化排肥方式主要包括离心式撒施和条施2种方式。离心式撒肥机以离心圆盘为核心部件,主要利用圆盘高速旋转产生的离心力将肥料均匀抛撒[7]。Edward等[8]研究了旋转圆盘式撒肥机精确定位施肥的模型,获得了肥料抛撒的运动轨迹和分布特征;通过构建颗粒肥料在旋转盘上的运动方程,确定了撒肥机的机械物理参数。Villette等采用高速摄像技术从三维角度分析了肥料的运动轨迹,确定了肥料抛撒时水平方向的出口角度[9];并应用台架试验测定水平和竖直2个方向复合肥和氮磷钾肥料的流量分布。离心式撒肥机适用于尿素、复合肥等多种颗粒化肥,但受化肥物料特性和风力的影响,施肥均匀性、精确度难以得到保证[10-11]。
条状施肥是联合播种机的重要组成部分,以外槽轮式、链条式和螺旋式等排肥器为核心部件。变量施肥机采用外槽轮式排肥器完成排肥,应用直流电机控制排肥轴转动和步进电机控制槽轮开度实现变量施肥[12-13]。齐兴源等[14]设计了一种外槽轮式排肥、气流输送肥料的稻田气力式变量施肥机,可实现施肥量在40~200 kg/hm2范围内调节。左兴健等[15]采用电机驱动排肥、风送肥料实现水稻侧位深施肥;曾山等[16]设计了同步开沟起垄施肥水稻精量旱穴直播机,排肥器的施肥量范围为300~1 500 kg/hm2。陈雄飞等[17]设计了两级螺旋排肥装置,可适用于复合肥、水稻专用肥等排肥;张睿等[18]设计了链条输送式变量施肥抛撒机,可根据处方图变量施肥。此外,叶片调节式侧深施肥装置和外槽轮排肥器用于水田深施肥[19-20],同步完成播种和侧位深施肥等工序。
为适应高速高效复式作业的要求,气力输送集排式联合播种机成为国外发展和应用的主要机型。气力输送集排式播种机采用气流输送种子和化肥,其核心部件为集中排种和排肥装置。与上述的离心式撒肥机和槽轮式排肥器相比,集中气送排肥方式精简整机和传动结构,有效提高作业效率。集中气送排肥是以“机械定量供肥+气流均匀分配成行”的方式,供肥装置是实现定量变量排肥的关键部件[21-23]。德国阿玛松公司的Primera DMC气力式播种机、美国约翰迪尔公司的1890型气吹式播种机和意大利马斯奇奥公司的Alliante Plus Drago DC Combi动力驱动耙联合气吹条播机等宽幅高速播种机均采用气流输送化肥,化肥施用量大,利用气力输肥与分配作业需配套大功率风机及拖拉机,在南方小面积田块中使用受限。集中排肥装置具有结构简单、作业高效和功耗低的特点,研制水平气送式排肥装置以适应中小田块的成为发展方向。
为适应不同时期作物对养分的需要,本文分析颗粒化肥的机械物理特性和农艺要求,设计了颗粒化肥螺旋组合式集中供肥装置,确定了倾斜螺旋状型孔关键结构参数,并分析排肥轮数量与转速对供肥速率和供肥稳定性变异系数的影响,从而满足不同施肥时期或作物变量精确施肥需求。本研究可为颗粒化肥定量集中供肥装置设计提供参考。
1 螺旋组合式供肥装置结构与工作原理
1.1 水平气送式集中排肥器工作原理
水平气送式集中排肥器包括供肥装置、水平式分配装置、风泵、导肥管、电机、变速控制器和蓄电池等,结构示意图如图1所示。水平气送式集中排肥器工作时,蓄电池作为动力源,变速控制器调节电机的转速,从而带动供肥装置的排肥轮转动,按施肥量需求提供均匀的颗粒化肥总量;风泵提供高速正压气流,在水平式分配装置中将肥料分散均匀分配吹入6个导肥管中,从而实现一个集中排肥器同时排出6行肥料。供肥装置为控制总排肥量的机械式供肥装置,决定排肥的稳定性;水平式分配装置在正压气流的作用下将肥料均匀分配,主要影响各行排肥量一致性。颗粒化肥存在吸湿性强、流动性差的特性,供肥装置是实现变量定量提供颗粒化肥总量的关键部件。

1. 肥箱 2. 风泵 3. 供肥装置 4. 电机 5. 变速控制器 6. 蓄电池 7. 机架 8. 水平式分配装置 9. 导肥管
1.2 螺旋组合式供肥装置结构及工作过程
螺旋组合式供肥装置结构如图2所示,主要包括肥箱、供肥装置外壳、排肥轴、搅肥机构、挡板、毛刷、螺旋式排肥轮、端盖、空白轮和隔板等。肥箱安装于供肥装置外壳上方,螺旋式排肥轮、端盖、空白轮和隔板安装于排肥轴上形成排肥机构,搅肥机构安装于排肥机构正上方,搅肥机构中心与排肥机构中心距离为70 mm。挡板和毛刷呈倒锥形位于排肥机构上,供肥装置外壳、挡板和毛刷共同作用形成充肥室。螺旋式排肥轮数量可在1~4个之间调节;空白轮可替换螺旋式排肥轮,螺旋式排肥轮数量与排肥轴转速共同调节排肥量。
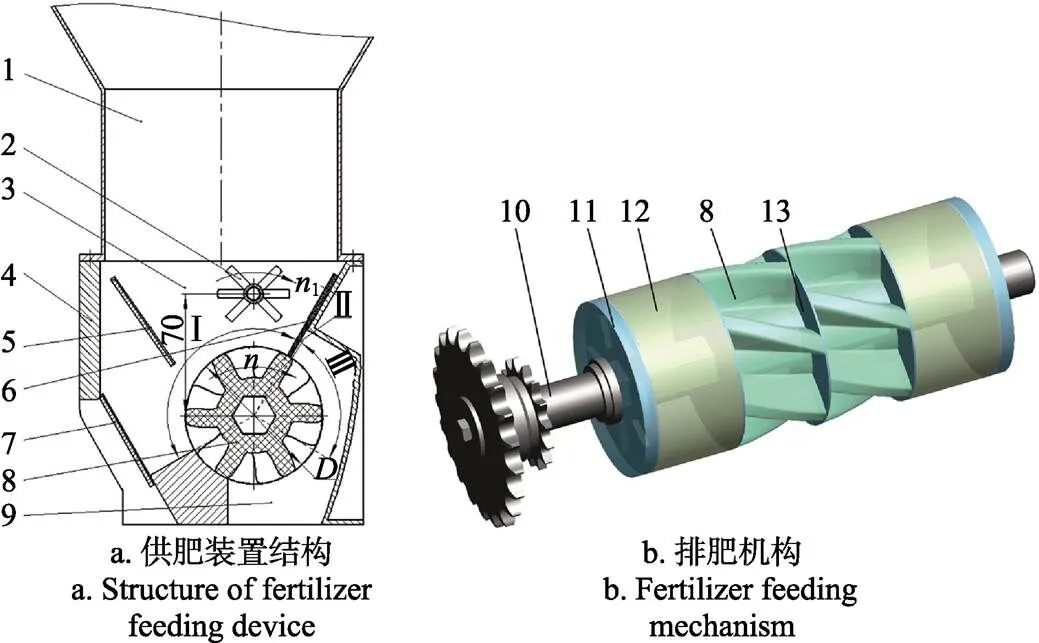
1. 肥箱 2. 搅肥机构 3. 充肥室 4. 供肥装置外壳 5. 挡板 6. 毛刷 7. 卸肥板 8. 螺旋式排肥轮 9. 排肥口 10. 排肥轴 11. 端盖 12. 空白轮 13. 隔板 Ⅰ. 肥料充填区 Ⅱ. 清肥区 Ⅲ. 投肥区
1. Fertilizer box 2. Fertilizer churning mechanism 3. Fertilizer filling room 4. Shell 5. Blocking plate 6. Brush 7. Unloaded plate 8. Screw-type fertilizer feeding unit 9. Feeding port 10. Discharging shaft 11. End cover 12. Replace wheel 13. Clapboard Ⅰ. Fertilizer filling zone Ⅱ. Fertilizer clearing zone Ⅲ. Fertilizer feeding zone
注:为螺旋式排肥轮的转速,r·min–1;1为搅肥机构的角速度,r·min–1;为螺旋式排肥轮直径,mm;下同。
Note:is rotational speed of screw-type fertilizer feeding unit, r·min–1;1is rotational speed of fertilizer churning device, r·min–1;is diameter of screw-type fertilizer feeding unit, mm; Same as below.
图2 螺旋组合式供肥装置结构示意图
Fig.2 Structure diagram of screw-type fertilizer feeding device
螺旋组合式供肥装置工作时,肥箱中的颗粒化肥进入到充肥区,排肥轴带动排肥机构和搅肥机构同步转动。搅肥机构扰动颗粒化肥增强充肥能力和防止化肥粘结、结拱等,螺旋式排肥轮将颗粒化肥从充肥区充肥经毛刷清肥进入到投肥区,颗粒化肥在重力和离心力作用下脱离螺旋式排肥轮,均匀连续的颗粒化肥通过排肥口进入水平式分配装置,完成定量排肥过程。
2 螺旋组合式供肥装置参数设计
2.1 颗粒化肥物理机械特性与农艺要求
颗粒化肥机械物理特性参数是确定螺旋组合式供肥装置结构尺寸的重要依据,本研究选取了广泛应用的住商复合肥、三宁复合肥和云顶复合肥共3种类型复合化肥为研究对象,测得不同颗粒化肥的机械物理特性参数如表1所示。3种类型的颗粒化肥的平均三轴尺寸约为3.89 mm×3.59 mm×3.32 mm,球形度均大于90%。其中,三宁复合肥的三轴尺寸和千粒质量最小,球形度和容重均最高。不同复合肥的休止角均低于34°,平均为31.84°。因此,以复合肥为代表的颗粒化肥包括氮、磷和钾等多种营养成分,球形度较高,适用于机械化排肥;但不同类型复合肥的机械物理特性参数仍有差异,本研究以3种复合肥平均值为依据进行结构参数设计,并通过试验开展不同类型颗粒化肥的适应性分析。

表1 不同颗粒化肥的机械物理特性参数
2.2 螺旋排肥轮结构参数设计
在重力和搅肥机构扰动作用下,颗粒化肥充入螺旋状型孔,通过排肥量转动将肥料排出。田间作业时,农艺要求的施肥速率为[24]
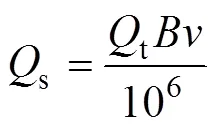
式中s为农艺要求的施肥速率,g/s;t为农艺要求的单位面积目标施肥量,kg/hm2;为施肥作业速度,m/s;为施肥幅宽,m。
供肥装置的供肥速率为
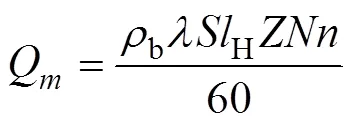
式中Q为单位时间供肥装置的供肥速率,g/s;b为颗粒化肥的容重,g/m3;为肥料充填系数;为型孔截面积,m2;H为型孔螺旋线长度,m;为排肥轮径向型孔数;为排肥轮数量;为排肥轮转速,r/min。
由式(1)、(2)可知,农艺要求的施肥速率应与供肥装置的供肥速率相同,则
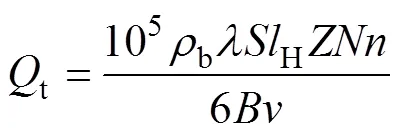
式(3)表明,若满足农艺要求的施肥量,当施肥幅宽、前进速度一定时,倾斜螺旋状型孔容积、排肥轮径向型孔数、排肥轮数量、肥料充填系数和转速之间呈负相关关系。排肥轮转速具有适宜的区间,转速和排肥轮径向型孔数均受排肥量直径的影响。增加排肥轮直径可增加排肥轮径向型孔数量,在相同供肥速率条件下降低转速,提高肥料充填性能。因此,结合外槽轮和螺旋排肥器的设计要求,确定排肥轮直径为80 mm。
型孔形状和尺寸对型孔容积以及充肥、排肥性能均有显著影响,进而影响供肥速率和稳定性。基于颗粒化肥需满足易充入、排出且连续的要求,设计了倾斜螺旋状型孔,结构如图3a所示。为提高颗粒化肥的充肥和排肥性能,保证颗粒化肥的充填度(较稳定的肥料充填系数),倾斜螺旋状型孔的截面呈倒梯形,包括型孔底槽宽度1、型孔上沿宽度2和型孔深度,型孔的左倾角和右倾角分别为和。根据型孔的几何尺寸,得
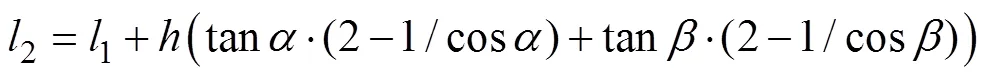
1. 型孔 2. 螺旋式排肥轮壳体 3. 螺旋式排肥轮 4. 螺旋线 5. 排肥轮圆柱
1. Model-hole 2.Shell of screw-type fertilizer feeding unit 3. Screw-type fertilizer feeding unit 4. Helix 5. Cylinder of fertilizer feeding unit
注:1为型孔底槽宽度,mm;2为型孔上沿宽度,mm;为型孔深度,mm;为型孔左倾角,(°);为型孔右倾角,(°);为螺旋线导程,mm;为排肥轮圆柱周长,mm;为螺旋式排肥轮长度,mm;为螺旋升角,(°);下同。
Note:1is the bottom width of model-hole, mm;2is the upper width of model-hole, mm;is the depth of model-hole, mm;is left inclined angle, (°);is right inclined angle, (°);is helical pitch,mm;is circumference of fertilizer feeding unit, mm;is length of fertilizer feeding unit, mm;is helix angle, (°). Same as below.
图3 倾斜螺旋状型孔结构
Fig.3 Structure of inclined screw-type model-hole
为方便颗粒化肥充入和排出型孔,左倾角和右倾角应满足
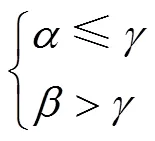
式中为颗粒化肥休止角,(°)。
为提高供肥速率,确定型孔底槽宽度1和型孔深度分别为12.0和18.0 mm。排肥轮径向型孔数与型孔上沿宽度2相关,增加倾斜螺旋状型孔数量可提高肥料容量,但需满足排肥量强度,则
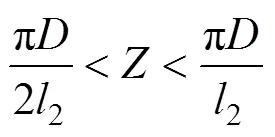
综合式(4)~(6)和颗粒化肥休止角,初步确定左倾角和右倾角分别为24°和37°,则型孔上沿宽度2为30.0 mm。求得排肥轮径向型孔数4<<8,综合考虑倾斜螺旋状排肥轮排肥量与强度要求,本文取排肥轮径向型孔数为6。
倾斜螺旋状型孔是倒梯形截面沿螺旋线方向形成,以螺旋升角绕排肥量圆柱体形成了螺旋线(图3b),螺旋升角与导程之间的关系为
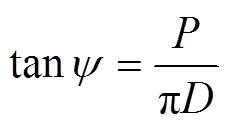
螺旋升角与导程呈正相关关系,螺旋升角太小不利于增加了自锁性,综合分析确定单一螺旋线的升角取60°,则导程为450 mm。颗粒化肥的供肥速率由转速和型孔尺寸共同决定,考虑排肥量调节范围大的要求,确定螺旋式排肥轮可在1~4个之间调节,螺旋式排肥轮和空白轮总和为4,排肥轮长度为40 mm。螺旋式排肥轮和空白轮均应用3D打印技术加工,材料为ABS(acrylonitrile butadiene styrene copolymer)工程塑料。
2.3 颗粒化肥充填过程力学分析
供肥装置工作时,在重力和搅肥机构的扰动作用下,颗粒化肥以散粒体的形式充入螺旋式排肥轮的型孔。由于颗粒化肥的尺寸小于型孔,则假设颗粒化肥以充满型孔的微小群体运动;取肥料充填区的颗粒化肥组合体为研究对象(图4a),颗粒化肥组合体的受力分析如图4b所示。颗粒化肥组合体在充填区受到肥料散粒体垂直压力Z、横向压力H、切向摩擦力F和重力,垂直压力Z和横向压力H为肥料充填室和肥箱中的压力;切向摩擦力F受搅肥机构扰动及排肥轮转动产生的颗粒化肥之间的摩擦力。基于深仓压力分布理论[25]分析颗粒化肥在肥料充填室的压力,得到颗粒化肥深度y的垂直应力:
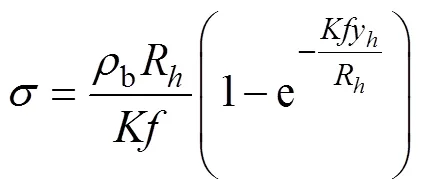
式中为垂直应力,Pa;R为肥箱的等效直径,本研究为0.088 m;为侧压系数,取0.44;为静态滑动摩擦系数,取0.5[19];y颗粒化肥的深度,m。本设计的肥箱深度为0.5 m,则肥料充填区的垂直应力为2 631.3 Pa,则垂直压力Z和横向压力H分别为
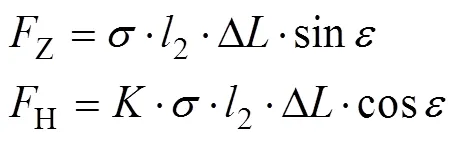
根据颗粒化肥组合体的受力分析和达朗贝尔原理,建立受力平衡方程
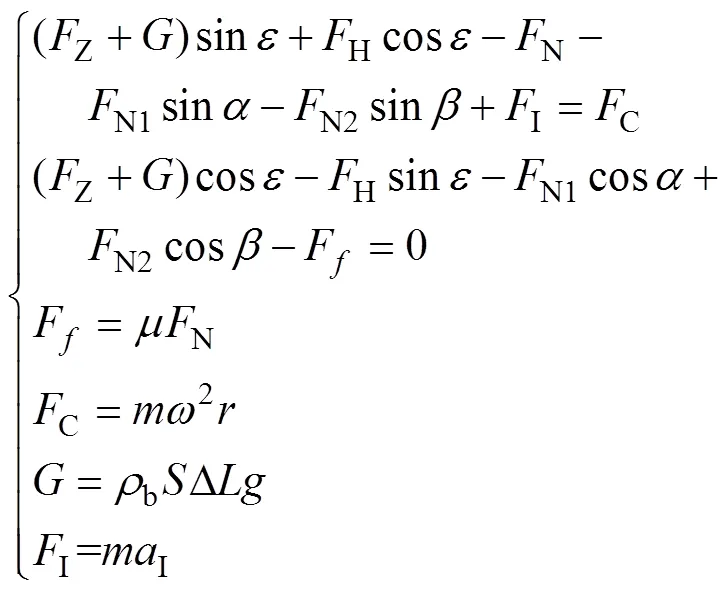
式中为颗粒化肥组合体的质量,kg;N为型孔底部对颗粒化肥组合体支持力,N;I为科氏加速度,m/s2;为排肥轮的角速度,rad/s;为重力加速度,m/s2;为颗粒化肥间的摩擦系数,取0.55;为轴与水平面的夹角,(°);为排肥轮的半径,m。
1. 螺旋式排肥轮 2. 颗粒化肥组合体
1. Screw-type fertilizer feeding unit 2. Fertilizer assemblage
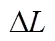
图4 颗粒化肥组合体在肥料充填区的受力分析
Fig.4 Mechanics analysis of fertilizer assemblage in fertilizer filling zone
联立式(9)和式(10),得
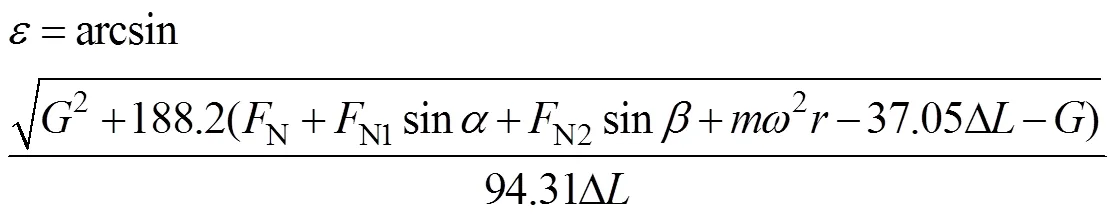
由式(11)可以看出,颗粒化肥充填初始位置与型孔左倾角、排肥轮转速和型孔右倾角等相关。当排肥轮转速一定时,颗粒化肥充填初始位置与型孔左倾角呈正相关,说明型孔左倾角增加会使充填时间缩短,降低型孔充填率;设定为0°时进行满量充填,则型孔左倾角应低于颗粒化肥休止角,即31.84°;为保证型孔保持高充填率进入清肥区,此时颗粒化肥组合体受垂直压力Z,不受横向压力H,型孔左倾角应大于清肥角,则>5°,则型孔左倾角取24°是可行的。
2.4 投肥过程力学分析
由于颗粒化肥易吸湿、粘结,设计较优的型孔结构有利于避免型孔堵塞。颗粒化肥组合体在投肥过程的受力分析如图5所示。颗粒化肥组合体处于临界投肥状态时,平衡方程如式(12)所示。

式中1为颗粒化肥与型孔间的摩擦系数,取0.5;为轴与水平面的夹角,(°)。
注:为轴与水平面的夹角,(°)。
Note:is angle betweenaxis and horizontal plane, (°).
图5 颗粒化肥组合体在投肥区的受力分析
Fig.5 Mechanics analysis of fertilizer assemblage in fertilizer feeding zone
由式(12)得
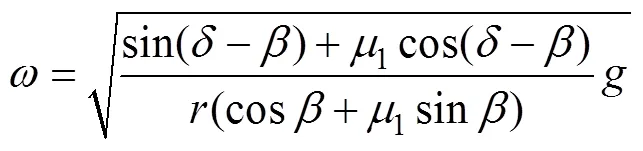
式(13)表明,投肥位置相同时,排肥轮转速随型孔右倾角增加而降低;在相同转速下,投肥位置角随型孔右倾角增加明显增加,说明右倾角适当增加可促使投肥位置提前,增加投肥时间,避免颗粒化肥堵塞型孔。综合考虑清肥区位置和投肥时间,投肥位置角Î[0°, 30°],排肥轮转速为10~60 r/min时,得右倾角的范围为17.43°~47.97°,本研究取右倾角为37°是合理的。
3 螺旋组合式供肥装置供肥性能试验
3.1 试验材料与装置
本试验以住商复合肥、三宁复合肥和云顶复合肥3种颗粒化肥为试验材料,其机械物理特性参数见表1。应用自制的供肥装置试验台开展供肥性能试验研究,供肥装置试验台如图6所示。
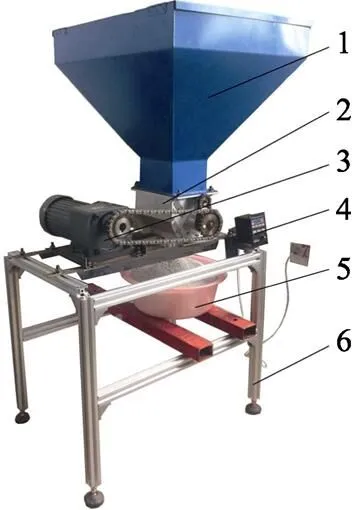
1. 肥箱 2. 螺旋组合式供肥装置 3. 减速电机 4. 调速系统 5. 盛肥容器 6. 系统台架
3.2 试验设计与方法
为确定螺旋组合式供肥装置供肥速率以适应不同施肥量要求和拖拉机作业速度,以住商复合肥为试验材料开展了螺旋式排肥轮数量和转速的双因素试验,根据施肥量要求,螺旋式排肥轮数量设1、2、3和4共4个水平,排肥轮转速设10~40 r/min共4个水平,增量为10 r/min。为验证螺旋组合式供肥装置对不同颗粒化肥的适应性,以3种类型的颗粒化肥(住商复合肥、三宁复合肥和云顶复合肥)为试验材料,分析转速为10、20和30 r/min条件下的供肥性能。试验中均以供肥速率[26-28](1 min内供肥装置的供肥量)和供肥稳定性变异系数为评价指标。
试验按照GB/T 9478-2005“谷物条播机试验方法”进行供肥装置供肥性能试验和测定[29]。用容器收集供肥口排出的颗粒化肥,称量颗粒化肥质量,采集时间为1 min,重复3次,计算不同处理下供肥速率和供肥稳定性变异系数,按式(14)~(15)计算。
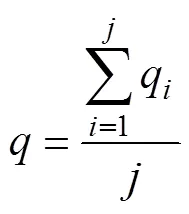
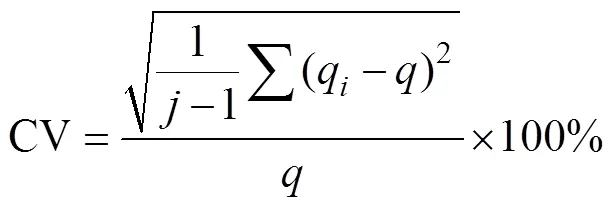
式中为供肥速率,g/min;q为第次1 min内供肥量,g/min;为试验次数;CV为供肥稳定性变异系数,%。
3.3 试验结果与分析
3.3.1 螺旋式排肥轮数量与转速对供肥性能的影响
螺旋式排肥轮数量与转速对供肥性能影响结果表明(图7),供肥速率随螺旋式排肥轮数量与转速增加而增加,供肥速率范围为912.67~13 164.26 g/min,供肥速率变化范围大,可满足不同的施肥量要求。供肥稳定性变异系数随转速和螺旋式排肥轮数量增加均呈先降后升趋势,均低于0.6%。稳定性变异系数在螺旋式排肥轮数量和转速分别为2~3个和20~40 r/min时较低。应用Matlab软件对供肥速率进行二次多元回归拟合,得到螺旋式排肥轮数量和转速与供肥速率的回归方程为
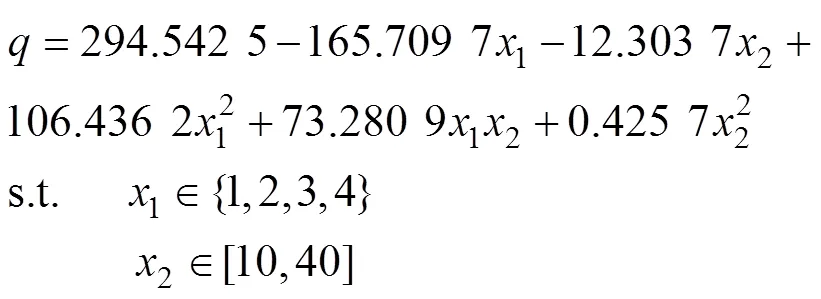
式中1为螺旋式排肥轮数量;2为螺旋式排肥轮转速,r/min。
经显著性检验分析,该模型决定系数为0.995 8(<0.001),表明该回归模型显著且回归方程失拟性不显著,能够较好地描述试验结果,说明使用式(16)可预测给定供肥速率求解螺旋式排肥轮数量和转速。
3.3.2 供肥装置对颗粒化肥的适应性分析
在2个螺旋式排肥轮数量条件下,不同类型的颗粒化肥试验材料和转速对供肥性能的影响结果如表2所示。颗粒化肥类型、转速及其交互作用对供肥速率均有极显著影响(<0.01)。在相同转速下,供肥速率以三宁复合肥最高,住商复合肥次之,云顶复合肥最低,但3种颗粒化肥的供肥速率之间的相对最大差值低于5%,这是由于颗粒化肥的三轴尺寸和容重差异较大引起的。颗粒化肥类型和转速对供肥稳定性变异系数影响不显著,不同处理的供肥稳定性变异系数低于0.8%。综上所述,螺旋组合式供肥装置能够适应不同物理机械特性的颗粒化肥,并能保证较低的供肥稳定性变异系数。
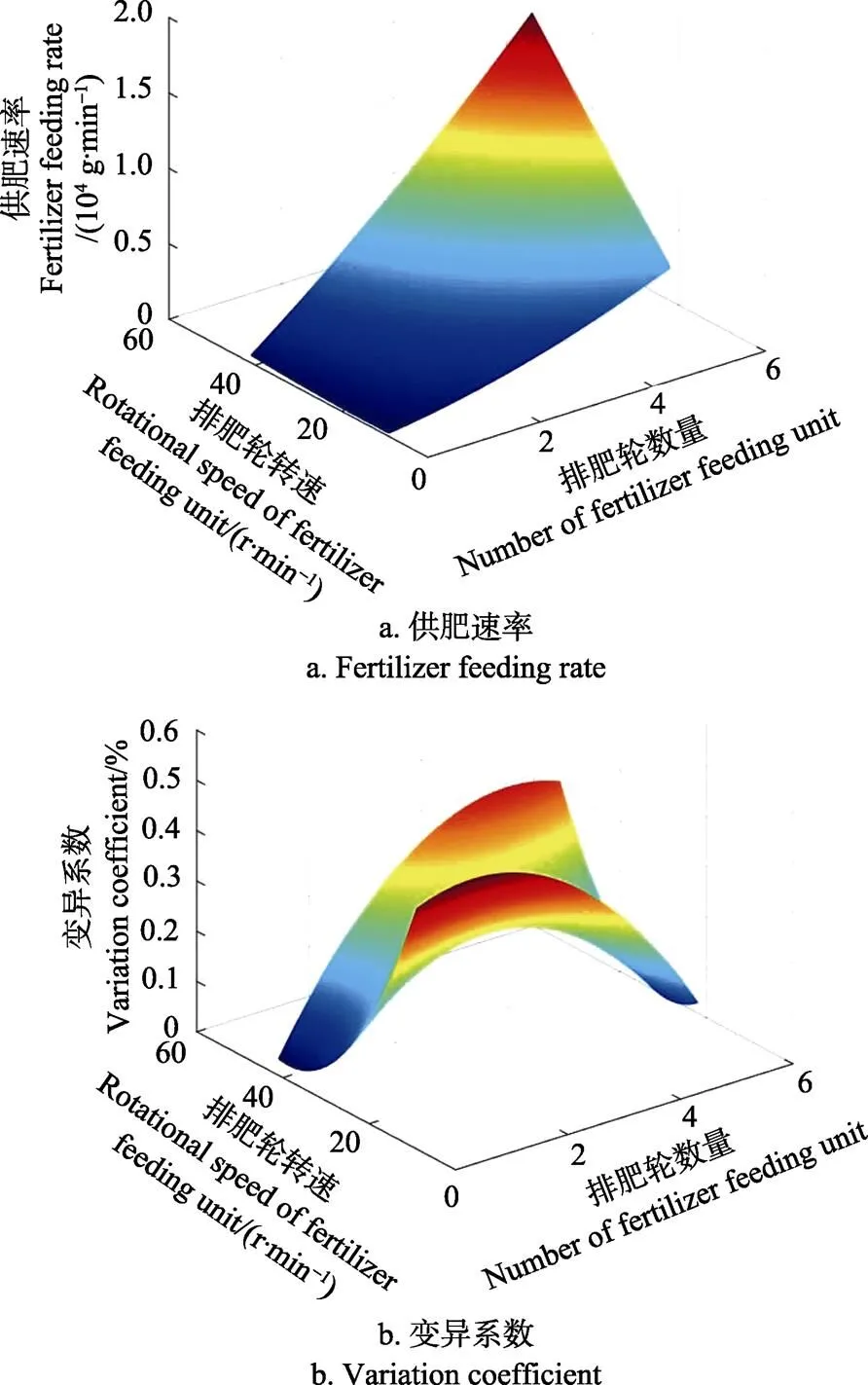
图7 螺旋式排肥轮数量与转速对颗粒化肥供肥性能的影响

表2 供肥装置对颗粒化肥的适应性分析
注:*和**分别表示方差分析在0.05和0.01水平上差异显著。
Note: * and ** denotes significance of variance analysis at the 0.05 and 0.01 levels, respectively.
3.3.3 供肥速率模型的验证分析
为验证供肥速率理论公式(式2),比较了排肥轮数量为1~4个和转速为10~40 r/min条件下理论值与试验值之间的差异(表3)。以理论分析得到的结构参数为依据,得到供肥速率理论值,供肥速率理论值与试验值之间的偏差总体在10%以内,这主要与肥料充填系数的取值相关。肥料充填系数随转速增加呈降低趋势,在搅肥机构的作用下肥料充填系数均较高。说明该理论公式(式2)可以为结构参数设计和理论分析提供参考,但由于肥料充填系数无法准确测定,生产实践则需依据台架试验预测(式15)的结果开展。
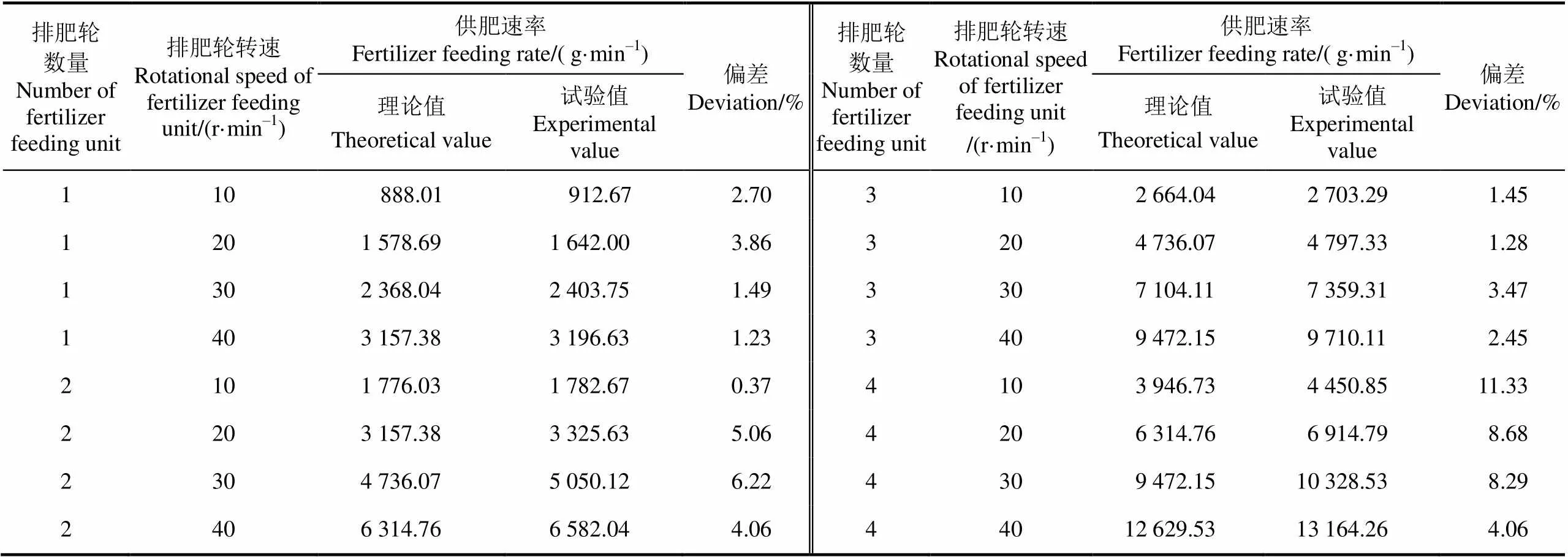
表3 供肥装置供肥速率模型预测值与试验值的比较
注:理论值计算中肥料充填系数在转速为10 r×min-1时取0.9,20~40 r×min-1为0.8[31]。
Note: The filling coefficient of fertilizeris 0.9 for 10 r×min-1of rotational speed and 0.8 for 20-40 r×min-1of rotational speed in theoretical value's calculation.
为适应不同施肥量要求、工作条件及检验供肥速率预测模型的准确性,以幅宽2 m的直播机为平台和住商复合肥为试验材料,选取东方红-LX854拖拉机的4个前进速度(2.52、3.09、4.91、5.88 km/h)为条件,分别以目标施肥量150、300、450、600和750 kg/hm2计算供肥速率理论值,将结果带入式(15)得预测的螺旋式排肥轮数量和转速。根据施肥量和拖拉机前进速度所需的螺旋式排肥轮数量和转速开展供肥性能试验,每组试验重复3次取平均值,结果如表4所示。
由表4可知,供肥速率试验值与模型预测值之间的偏差在3%范围内,说明该供肥速率模型较精确。螺旋组合式供肥装置能够适应较大范围的施肥量和拖拉机前进速度,且供肥稳定性变异系数均低于1.0%,满足JB/T 6274.1-2001“谷物条播机技术条件”[30]中对总排肥量稳定性变异系数的要求。该供肥速率模型能够根据施肥量要求和前进速度实时调节螺旋式排肥轮数量和转速,为适应不同施肥需求和变量施肥提供参考。试验尚未出现颗粒化肥粘结和架空现象,说明供肥装置采用上方充肥和搅肥机构扰动的方式可防止化肥粘结、结拱的发生。

表4 螺旋组合式供肥装置供肥速率预测模型验证结果
4 田间试验
为进一步验证台架试验结果,考察颗粒化肥螺旋组合式集中供肥装置的供肥性能,于2018年5月14日在四川省崇州市四川农业大学现代农业研发基地开展了水稻直播同步施肥试验(图8),前茬为小麦。颗粒化肥为三宁复合肥,作基肥施用,目标施肥量为600 kg/hm2。试验以久保田M954KQ拖拉机为牵引动力,机组平均前进速度为2.48 km/h,幅宽2 m,采用化肥带状混施方式,施肥6行,行距为300 mm。试验中应用12 V蓄电池提供直流电机的动力源,通过直流电机调速器驱动并调节螺旋式排肥轮转速,转速为31 r/min,螺旋式排肥轮数量为2个。试验田面积为0.090 3 hm2,预测施肥量为54.18 kg,实际施肥量为56.10 kg,实际施肥量与模型预测值的相对误差为3.54%,满足水稻种植对基肥的施用要求[32]。

1. 拖拉机 2. 肥箱 3. 供肥装置 4. 导肥管 5. 颗粒化肥 6. 直流电机调速器 7. 蓄电池
5 结论与讨论
本文通过分析颗粒化肥的机械物理特性和施肥量要求,提出了倾斜螺旋状型孔结构,设计了一种颗粒化肥螺旋组合式集中供肥装置,确定了型孔和排肥轮的主要结构参数,构建了颗粒化肥组合体在肥料充填区和投肥区的力学模型,验证了倾斜螺旋状型孔结构参数的合理性。
1)排肥性能台架试验表明:螺旋式排肥轮数量和转速分别为1~4个和10~40 r/min条件下,供肥速率随螺旋式排肥轮数量与转速增加而增加,供肥速率范围为912.67~13 164.26 g/min。3种类型颗粒化肥适应性结果表明,螺旋组合式集中供肥装置能适应不同机械物理特性参数的颗粒化肥,不同颗粒化肥的供肥速率之间的差值低于5%。
2)构建了螺旋式排肥轮数量和转速与供肥速率的回归预测模型,其决定系数为0.995 8。试验研究了目标施肥量150~750 kg/hm2和拖拉机前进速度2.52~5.88 km/h条件下的供肥速率,供肥速率试验值与模型预测值之间的偏差在3%以内,供肥稳定性变异系数均低于1.0%。田间试验表明,颗粒化肥实际施用量与模型预测值相对误差为3.54%,该颗粒化肥螺旋组合式集中供肥装置可实现变量、定量、集中排出颗粒化肥,满足农业生产中对变量精量施肥及排肥稳定性要求。
本研究以含N、P、K多元素的复合肥为试验材料,未对尿素、过磷酸钙和氯化钾等单元素的化肥开展研究,且这些肥料偏粉状,本研究的供肥装置对粉状化肥的适应性尚需进一步分析。研究中采用12 V蓄电池作动力源和直流电机主动驱动的方式,可以简化传动机构,但拖拉机同步测速反馈控制系统尚需完善以提高同步性和智能化。
[1] 李忠芳,徐明岗,张会民,等. 长期施肥下中国主要粮食作物产量的变化[J]. 中国农业科学,2009,42(7):2407-2414. Li Zhongfang, Xu Minggang, Zhang Huimin, et al. Grain yield trends of different food crops under long-term fertilization in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2009, 42(7): 2407-2414. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 彭少兵,黄建良,钟旭华,等. 提高中国稻田氮肥利用率的研究策略[J]. 中国农业科学,2002,35(9):1059-1003. Peng Shaobing, Huang Jianliang, Zhong Xuhua, et al. Research strategy in improving fertilizer-nitrogen use efficiency of irrigated rice in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2002, 35(9): 1059-1003. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 王伟妮,鲁剑巍,李银水,等. 当前生产条件下不同作物施肥效果和肥料贡献率研究[J]. 中国农业科学,2010,43(19):3997-4007. Wang Weini, Lu Jianwei, Li Yinshui, et al. Study on fertilization effect and fertilizer contribution rate of different crops at present production conditions[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 43(19): 3997-4007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 谷洁,高华. 提高化肥利用率技术创新展望[J]. 农业工程学报,2000,16(2):17-20. Gu Jie, Gao Hua. Prospects on the technical innovation to increase fertilizer use efficiency[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2000, 16(2): 17-20. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] Yang Xianlong, Lu Yongli, Ding Yan, et al. Optimising nitrogen fertilisation: A key to improving nitrogen-use efficiency and minimising nitrate leaching losses in an intensive wheat/maize rotation (2008-2014)[J]. Field Crops Research, 2017, 206: 1-10.
[6] 李宝筏. 农业机械学[M]. 北京:中国农业大学出版社,2003.
[7] 陈书法,张石平,孙星钊,等. 水田高地隙自走式变量撒肥机设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(11):16-21. Chen Shufa, Zhang Shiping, Sun Xingzhao, et al. Design and experiment of self-propelled high-ground-clearance spreader for paddy variable-rate fertilization[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(11): 16-21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] Edward D, Engelbert T, Robert O, et al. Calibration of a spinning disc spreader simulation model for accurate site-specific fertiliser application[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2004, 88(1): 49-62.
[9] Villette S, Cointault F, Piron E, et al. Centrifugal spreading: An analytical model for the motion of fertiliser particles on a spinning disc[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2005, 92(2): 157-164.
[10] Simon R C, Jan G P, Joris V A, et al. Determining the effect of wind on the ballistic flight of fertiliser particles[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2016, 151: 425-434.
[11] Sylvain V, Emmanuel P, Richard M, et al. Estimation of two-dimensional fertiliser mass flow distributions by recording granule impacts[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2013, 115: 463-473.
[12] 施印炎,陈满,汪小旵,等. 稻麦精准变量施肥机排肥性能分析与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2017,48(7):97-103. Shi Yinyan, Chen Man, Wang Xiaochan, et al. Analysis and experiment of fertilizing performance for precision fertilizer applicator in rice and wheat fields[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2017, 48(7): 97-103. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 金鑫,李倩文,苑严伟,等. 2BFJ-24型小麦精量播种变量施肥机设计与试验[J].农业机械学报,2018,49(5):84-92. Jin Xin, Li Qianwen, Yuan Yanwei, et al. Design and test of 2BFJ-24 type variable fertilizer and wheat precision seed sowing machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(5): 84-92. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 齐兴源,周志艳,杨程,等. 稻田气力式变量施肥机关键部件的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(6):20-26.Qi Xingyuan, Zhou Zhiyan, Yang Cheng, et al. Design and experiment of key parts of pneumatic variable-rate fertilizer applicator for rice production[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(6): 20-26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 左兴健,武广伟,付卫强,等. 风送式水稻侧深精准施肥装置的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(3):14-21. Zuo Xingjian, Wu Guangwei, Fu Weiqiang, et al. Design and experiment on air-blast rice side deep precision fertilization device[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(3): 14-21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 曾山,汤海涛,罗锡文,等. 同步开沟起垄施肥水稻精量旱穴直播机设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(20):12-19. Zeng Shan, Tang Haitao, Luo Xiwen, et al. Design and experiment of precision rice hill-drop drilling machine for dry landwith synchronous fertilizing[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(20): 12-19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 陈雄飞,罗锡文,王在满,等. 两级螺旋排肥装置的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(3):10-16. Chen Xiongfei, Luo Xiwen, Wang Zaiman, et al. Design and experiment of a fertilizer distribution apparatus with double-level screws[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(3): 10-16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 张睿,王秀,赵春江,等. 链条输送式变量施肥抛撒机的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(6):20-25. Zhang Rui, Wang Xiu, Zhao Chunjiang, et al. Design and experiment of variable rate fertilizer spreader with conveyor chain[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(6): 20-25. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 王金峰,高观保,王金武,等. 叶片调节式水田侧深施肥装置设计与试验[J]. 农业机械学报,2018,49(3):68-76. Wang Jinfeng, Gao Guanbao, Wang Jinwu, et al. Design and test of adjustable blades side deep fertilizing device for paddy Field[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(3): 68-76. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] Wang Jinwu, Li Shuwei, Zhang Zhao, et al. Design and experiment of electrical drive side deep hill-drop fertilization system for precision rice hill-direct-seeding machine[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(8): 43-54.
[21] Yatskul A, Lemiere J P, Cointault F. Influence of the divider head functioning conditions and geometry on the seed's distribution accuracy of the air-seeder[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2017, 161: 120-134.
[22] Maleki M R, Mouazen A M, Ketelaere B D, et al. On-the-go variable-rate phosphorus fertilisation based on a visible and near-infrared soil sensor[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2008, 99(1): 35-46.
[23] Maleki M R, Ramon H, Baerdemaeker J D, et al. A study on the time response of a soil sensor-based variable rate granular fertiliser applicator[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2008, 100(2): 160-166.
[24] 中国农业机械化科学研究院. 农业机械设计手册(上册)[M]. 北京:中国农业科学技术出版社,2007.
[25] 刘宏新,徐晓萌,郭丽峰,等. 具有复合充填力的立式浅盆型排种器充种机理[J]. 农业工程学报,2014,30(21): 9-16. Liu Hongxin, Xu Xiaomeng, Guo Lifeng, et al. Research on seed-filling mechanism of vertical shallow basin type seed-metering device with composite filling force[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2014, 30(21): 9-16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 雷小龙,廖宜涛,李兆东,等. 油麦兼用型气送式集排器供种装置设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2015,31(20):10-18. Lei Xiaolong, Liao Yitao, Li Zhaodong, et al. Design and experiment of seed feed device in air-assisted centralized metering device for rapeseed and wheat[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2015, 31(20): 10-18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 雷小龙,廖宜涛,李兆东,等. 种层厚度对油麦兼用集排器供种装置充种性能的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(6):11-19. Lei Xiaolong,Liao Yitao,Li Zhaodong,et al. Effects of seed layer thickness on seed filling performance of seed feeding device for rapeseed and wheat[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(6): 11-19. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 雷小龙,廖宜涛,李兆东,等. 油菜小麦兼用气送式集排器搅种装置设计及充种性能试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(18):26-34. Lei Xiaolong, Liao Yitao, Li Zhaodong, et al. Design of seed churning device in air-assisted centralized metering device for rapeseed and wheat and experiment on seed filling performance[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016, 32(18): 26-34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 谷物条播机试验方法国家标准:GB/T 9478-2005[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2005.
[30] 谷物播种机技术条件机械标准:JB/T 6274.1-2001[S]. 北京:机械科学研究院,2001.
[31] 李凯. 变量施肥系统的设计与研究[D]. 石河子:石河子大学,2017.
Li Kai. Design and Research of Variable Rate Fertilization System[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] 水稻覆土直播机国家标准:GB/T 25418-2010[S]. 北京:中国标准出版社,2010.
Design and experiment of horizontal pneumatic screw combination adjustable quantitative fertilizer feeding device for granular fertilizer
Lei Xiaolong1,2, Li Mengliang1, Zhang Lihua1, Ren Wanjun2
(1.625014,; 2.611130,)
Nutrients including the elements of N, P and K are beneficial to the growth and yield of crops. Reducing the application amount of chemical fertilizer and increasing the utilization rate have become the important ways and means of high quality and high efficiency green agriculture. Granular fertilizer has been widely used in agricultural production because of its low fluidity, strong hygroscopicity and cohesion. Meanwhile, the amount of fertilizer applied depends on the crops, the fertilization application time, and the fertilizer varieties. In order to adjust the requirements of fertilization and precision fertilization, the horizontal pneumatic centralized feeder of fertilizer was developed. The fertilizing device is the core part of the horizontal pneumatic centralized feeder. According to the mechanical and physical properties, and fertilizer requirements of granular fertilizers, the inclined screw-type model-hole and combined fertilizer feeding unit was designed. The main structural parameters of the inclined screw-type model-hole and the fertilizing unit were determined. The bottom width, upper width and depth of model-hole were 12.0 mm, 30.0 mm and 18.0 mm, respectively. The left inclined angle, right inclined angle and number of screw-type model-hole was 24°, 37° and 6, respectively. The helical pitch,helix angle and length of fertilizer feeding unit were450mm, 60° and 40 mm, respectively. The number of fertilizing unit could be adjusted from 1 to 4. The amount of fertilizer applied varied with the number of fertilizing units and the rotational speed. The mechanical models of fertilizer combination in fertilizer filling and feeding zone were established. The results showed that filling and feeding performance of fertilizer could be improved significantly by tilting angle between left and right. The fertilization performance experiments were performed in the bench test. The effects of fertilization unit number of and rotation speed on fertilizer application and coefficient of variation were studied using Zhushang Fertilizer. Furthermore, the fertilizer adaptability of fertilization device was studied with Zhushang Fertilizer, Sanning Fertilizer and Yunding Fertilizer. The results showed that: 1) When the fertilization unit number and rotational speed were 1-4 and 10-40 r/min, respectively, the fertilization amount increased with the increase of number of fertilization unit number and rotational speed. The range of fertilizer feeding rate was 912.67-13 164.26 g/min. 2) The amount of fertilizer application was significantly affected by the fertilizer types, rotation speed and interaction between fertilizer types and rotation speed. With the same rotation speed of 10-30 r/min, the fertilizer feeding rate of Sanning Fertilizer was the largest, while that of Yunding Fertilizer was the lowest. The difference of fertilizer feeding rate among three fertilizer types was less than 5%. It indicated that the fertilizer feeding device could be applied to different compound granular fertilizer. 3) The quadratic regression predicted model of fertilizer amount was established with the factors of fertilization unit number and rotational speed. The determination coefficient of the regression prediction model was 0.995 8, which indicated that the prediction model was feasible. The fertilizer feeding rate was studied under the condition of target fertilizer application range of 150-750 kg/hm2and tractor velocity of 2.52-5.88 km/h. The deviations between the experimental value and the predicted value of fertilizer feeding rate were not more than 3%. In addition, the coefficients of variation of fertilizer feeding rate in each treatment were less than 1.0%. The results showed that the model can accurately predict the fertilizer feeding rate and calculate the fertilizer feeding unit number and rotational speed. The field experiment showed that the relative error between the fertilizer feeding amount and the theoretical value was 3.54%. The structure of the inclined screw-type model-hole and combined fertilizer feeding unit can realize the adjustment of fertilizer feeding rate in a wide range for granular fertilizer. The fertilizer feeding performance of fertilizer feeding device could meet the requirements of fertilizer application amount and fertilizer feeding stability. This research can provide the basis for the structue design of horizontal pneumatic centralized feeder and variable-rate precision fertilization.
agricultural machinery; design; experiments; inclined screw-type model-hole; pneumatic centralized feeder; granular fertilizer
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.19.002
S223.2+3
A
1002-6819(2018)-19-0009-10
2018-06-15
2018-08-21
十三五国家重点研发计划项目(2018YFD0301204, 2017YFD030171);国家玉米产业体系专项资助项目(CARS-02-29)
雷小龙,博士,讲师,主要从事现代农业装备设计与测控研究。Email:leixl1989@163.com
雷小龙,李蒙良,张黎骅,任万军.颗粒化肥水平气送式螺旋组合可调定量供肥装置设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(19):9-18. doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.19.002 http://www.tcsae.org
Lei Xiaolong, Li Mengliang, Zhang Lihua, Ren Wanjun. Design and experiment of horizontal pneumatic screw combination adjustable quantitative fertilizer feeding device for granular fertilizer[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2018, 34(19): 9-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2018.19.002 http://www.tcsae.org

