改良的两次屏气扫描方案联合100 kV管电压行减影CCTA的临床可行性
过伟锋 Tripathi Pratik 杨 姗 张利军 曾蒙苏△
(1复旦大学附属中山医院放射科 上海 200032; 2上海市影像医学研究所 上海 200032)
Due to high negative predictive value,coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) has been able to replace invasive coronary angiography (ICA) and be the first choice of examination for the diagnosis of coronary artery disease (CAD)[1].However,severe calcification and stent-induced partial volume effect and beam-hardening artifacts in coronary artery result in poor diagnostic accuracy and still remains a big challenge in CCTA[2-5].To address these problems,Yoshiokaetal[6]proposed subtraction technique in the application of CCTA for the first time in 2012.
In subtraction CCTA,severe calcified plaques in the coronary artery segments are removed by subtracting pre-contrast CT image volume data from post-contrast CCTA image volume data.With subtraction CCTA using 320-detector CT,the diagnostic accuracy of significant stenosis (>50%) with severe calcification has been increased distinctly[7-9].
To minimize the misregistration artifacts during the subtraction process between pre- and post-contrast volume data,some studies have determined one hold breath scanning method for subtraction CCTA.Up to date,although the breath holding time in latest modified scan protocol is almost 15 sec[10],this is still a limitation for the patients who are unable to hold breath for such long time.In the conventional double breath-hold subtraction scanning protocol (conventional CCTA scan) with minimum breath holding time,the subtraction imaging is obtained by subtracting the mask image (Agatston score scanning) data from post contrast image data (Fig 1A).In the scanning protocol mentioned above,the breath holding pattern is same as conventional CCTA.The biggest disadvantage of this protocol is the high probability of misregistration artifact,which is almost 50%[8].
We hypothesized that a pre-contrast volume data acquired betweenAgatston score scan and post-contrast scan in single breath-hold would reduce the rate of misregistration artifact and maintain minimum breath-holding time (Fig 1B).In this study,we present our initial experience with a modified double breath hold scanning method in subtraction CCTA.

A:Conventional subtraction CCTA.The bolus-tracking technique is used.The mask scan is obtained from the Agatston score scan.The post-contrast scan is triggered when the CT number in the ascending aorta reaches 250 Hounsfield units (HU).B:Modified subtraction CCTA.The bolus-tracking technique is used.Pre-contrast scan is obtained between Agatston score scan and post-contrast scan in single breath-hold.The post-contrast scan is triggered when the CT number in the ascending aorta reaches 250 HU in second breath hold.
Fig1Overviewoftheconventionalandmodifiedsubtractioncoronarycomputedtomographyangiographyindoublebreath-holdingmethod
Methods and materials

Beta-blockers were given when the resting heart rate was above 65 bpm,unless patients had contraindications.The patients with heart rate >65 bpm even after oral intake of beta-blocker were excluded from this study.
The calcification score scan was performed before the modified subtraction CCTA as described by Agatston,etal[13].The tube voltage was 120 kV and the padding was just 75%.The pre-contrast and post-contrast volume data acquisition was obtained in two single breath hold (Fig 1B).All patients were scanned with the use of prospective ECG-triggered without current modulation.The acquisition phase window was 65%-80% of the RR interval for both pre- and post-contrast scans.Tube voltage of 100 kV was used for pre- and post-contrast data acquisition.Iodinated contrast Iopamidol (Isovue 370;Bracco Diagnostics) was administered intravenously at a rate of 4 or 5 mL/s,followed by a 30 mL saline chaser bolus with a dedicated triphasic protocol.Image acquisition was triggered automatically at threshold of 250 HU in the descending aorta using bolus-tracking method.
Images were reconstructed with a 512×512 matrix,0.5-mm-thickness by using kernel FC09,iterative reconstruction (Adaptive Iterative Dose Reduction 3D,AIDR 3D,Toshiba Medical Systems) standard.First,the series of pre- and post-contrast images were reconstructed in the interval of 5 ms in the whole scanning period.Then,the visually optimal registrated volume data images were selected from these two series reconstructed images in which motion artifacts were minimal.Finally,the accurate registration and subtraction of coronary images were performed using a dedicated algorithm,volumetric CT digital subtraction angiography,on the scanner console[14].
The effective radiation dose was estimated based on the dose-length product (DLP,mGy×cm) using the formula effective radiation dose=DLP×k,where k=0.014 mSv× mGy-1×cm-1.
The image quality assessment of subjective segment was performed.The coronary arteries were divided into 17 segments according to the American Heart Association Classification[15].Only segments with severe calcification were evaluated.Severe calcified plaque was characterized with arc more than 180° in cross-section of each coronary segment[16].The stented segments were excluded from the evaluation.A 4-point scale was used to evaluate Image quality for each calcified segment on conventional and subtraction CCTA[9-11]:1-uninterpretable,2-poor image quality,3-fair image quality,and 4-good image quality.The segments with score 1 or 2 were considered to reflect non-diagnostic image quality.The evaluation was performed by two experienced cardiac radiologists with more than 8 years of experience.

Results
This modified subtraction CCTA protocol was successfully performed in all 17 patients.Their characteristics are listed in Tab 1.The average coronary calcium score was 871 (range:405-1 915).Heart rate during the pre-contrast scan was (57.66±4.43) bmp (range:45-63 bmp) and the post-enhanced scan was (57.44±5.04) bmp (range:43-63 bmp) with no significant difference in heart rate between the pre-contrast and post-contrast scan (P=0.57).The average BMI was 21.4 (range:18.3-23.4).The average tube current was (150±27) mA (range:120-200 mA).The estimated total effective radiation dose of subtraction CCTA was (2.80±0.64) mSv (range:1.58-4.00 mSv).
A total of 53 segments with severe calcification were included for subjective image quality evaluation.The average image quality of conventional CCTA was 2.51±0.95 (Tab 2).The inter-observer kappa score (K) for convention CCTA image quality score was 0.885.The total number of non-diagnostic segments that was caused by severe calcification was 23 (43.4%).The average image quality of subtraction CCTA was 3.36±0.92 (Tab 2),which was significantly higher than conventional CCTA (P<0.001).The inter-observer kappa score (K) for subtraction CCTA image quality score was 0.786.A total of 6(11.3%) segments were judged as non-diagnostic that was caused by misregistration artifact.The segments with non-diagnostic image quality of subtraction CCTA was significantly lower than conventional CCTA (P<0.001).Case examples are provided in Fig 2 and 3.
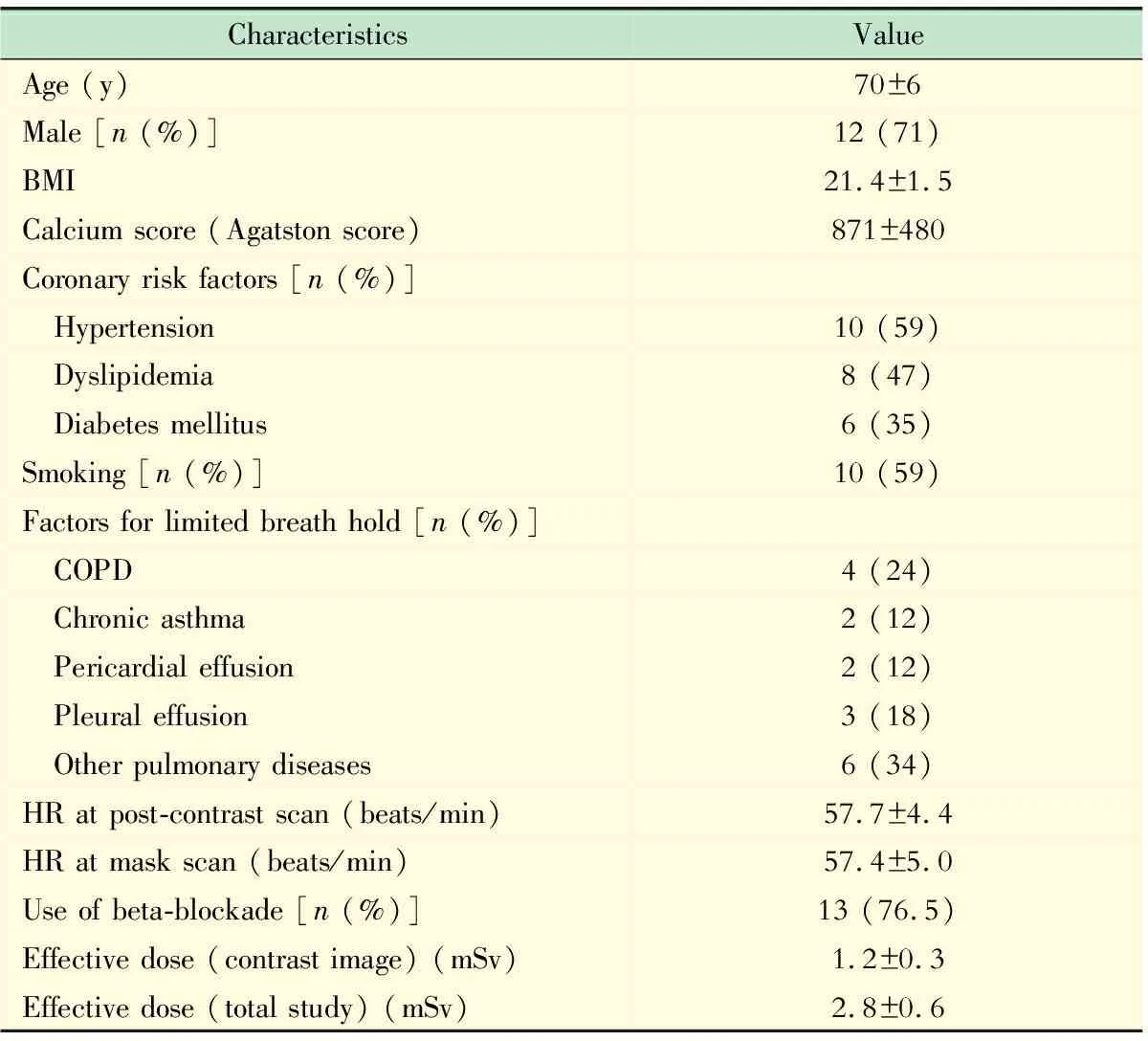
Tab 1 Patients’ characteristics and image parameters of the study group (n= 17)
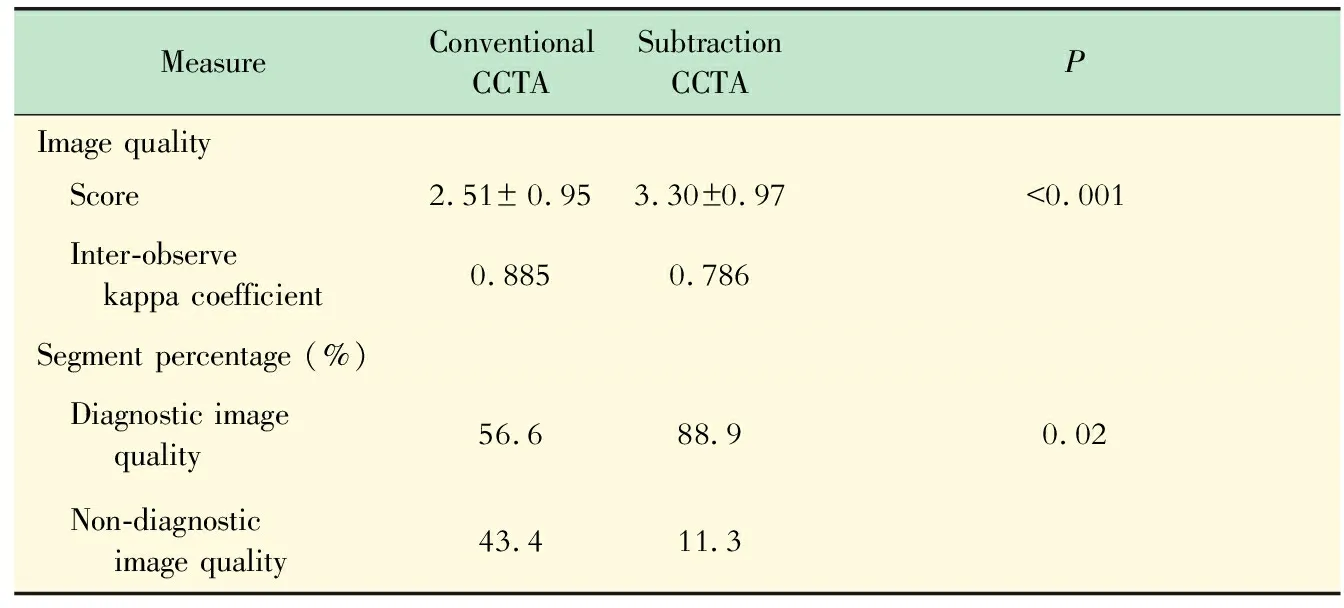
Tab 2 Image quality scores and percentages of diagnostic vs.non-diagnostic image quality
CCTA:Coronary computed tomography angiography;SD:Standard deviation.
Discussion
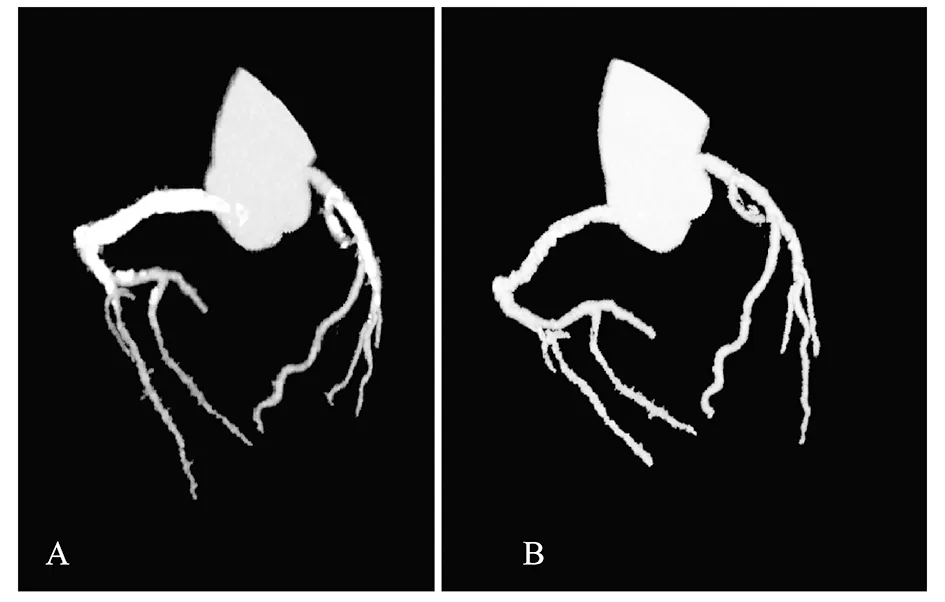
The total Agatston score was 1912 units in both LAD and RCA.After the subtraction of the calcified deposition,the coronary segments were revealed distinctly with no significant stenosis.
Fig2A71-year-oldmanwithsuspectedcoronaryarterydisease:post-contrastimage(A)andsubtractioncoronarycomputedtomographyangiography(B)angiographicview
We demonstrated the preliminary experience regarding the feasibility of this modified two breath-hold scan protocol.As we all know,one breath hold scan protocol is the best for data acquisition to eliminate the misregistration artifact that results from the position shift between pre- and post-contrast volume data.But the long breath hold might be difficult for some patients to maintain;it might also result in fluctuation of heart rate and blur the post-contrast imaging,which can increase the possibility of misregistrated artifact.

A:Conventional CCTA.Curved planar reformation (CPR) image of the left descending artery.Severe calcifications make it difficult to assess the lumen (arrow).B:Subtraction CCTA.Curved planar reformation (CPR) image at the same position as in A.The severe calcifications were eliminated,making the segment assessable (arrow).C:Conventional CCTA.A cross-sectional image of the left descending artery at the site of severe calcification.The circular calcification made it difficult to assess the lumen (arrow).D:Subtraction CCTA.A cross-sectional image at the same position as in C.The calcification was eliminated,making it possible to assess the lumen (arrow).
Fig3A75-year-oldmanwithseverecoronaryarterycalcification(Agatstonscore=944)
In the early protocol,the breath-holding time for 20-40 s was applied for subtraction CCTA by some feasibility studies[9,17].Later in some studies,with some changes in the scanning protocol,the breath-holding time was controlled from about 25 s to <20 s[18-19].Recently,the breath-holding time was shortened to around 15 s in the latest modified protocol by reversing the scan order combined with bolus tracking[10].The inadequate intra-arterial enhancement of the coronary segment caused by the residual of the contrast in mask image is one of the major limitations for that modified subtraction CCTA protocol.Breath hold for 15 s is considerable time for general patients,but for the patients with special conditions that affect normal breathing (such as severe pulmonary edema,pleural effusion,chronic asthma etc.);it is still difficult to hold breath for such long time.
In this scenario,we introduced this modified two breath-hold scanning protocol for those patients with clinical abnormalities who have severe limited breath hold capacity (Fig 1B).This preliminary study has some advantages compared to the above-mentioned protocols.
Using present modified protocol,clear and sharper contrast image is obtained and the heart rate uniformity between the pre- and post-contrast acquisition is also maintained.Moreover,as pre- and post-volume data was acquired both in the 65%-80% of R-R interval,we could select the most registrated images from the two group volume data to compensate the position shift induced by two breath holds.The subjective image quality was significantly improved in subtraction CCTA compared to conventional CCTA (2.51±0.95vs.3.36±0.92,P<0.01).The percentage of non-diagnostic segment in subtraction CCTA was 17%,while 38% in conventional CCTA.There was an improvement in the image quality and diagnostic evaluation of the severe calcified segments in subtraction CCTA compared to conventional CCTA.
The radiation dose of subtraction CCTA is obviously higher than conventional CCTA because subtraction CCTA requires scanning twice.Some studies proved that there is no significant difference in image quality between 100 and 120 kV settings but with obvious reduction of radiation dose (approximately 57%)[20].To reduce the effective scanning radiation dose,it is the first study that attempted to complete pre- and post-contrast data acquisition using 100 kV for subtraction CCTA.Compared to previous studies using 120 kV voltage for subtraction CCTA,the radiation dose in this study showed a remarkable reduction compared with that of previous studies (2.80±0.64vs.5.2±2.2,12.0±4.7,5.1±2.9)[10,17-18].It means that scanning with 100 kV voltage in patients with BMI <25 kg/m2would largely decrease the total effective radiation dose for subtraction CCTA.
Although this modified two breath-hold scan protocol has shown the preliminary feasibility but there are still some limitations in our study,misregistration artifact being the major limitation.The rate of misregistration artifact was seen in 43% of the segments,including 9 (17%) non-diagnostic segments and 14(26%) diagnostic segments.But in the clinical practice,contrast images should be added to the subtracted images for accurate evaluation of the severe calcified segments.
To reduce the radiation dose and maintain the image quality,100 kV was applied to the selected patient with BMI <25 kg/m2.Patients with higher BMI were excluded from this study.In future,more scan parameter should be optimized to reduce the radiation dose for more patients.Another approach with dual-energy CT system generating virtual non-enhanced image could potentially contribute to subtraction.
Another important limitation of the present study was the selective limited patients and targeted coronary segments.The purpose of this preliminary investigation was to demonstrate the feasibility in patients with special conditions who couldn’t hold their breath for such long interval of time and obtain initial experience with our modified subtraction CCTA protocol using a two breath-hold method.As a next step,we will investigate the diagnostic accuracy of this modified subtraction CCTA in patients with a limited breath-holding capability and severe coronary artery calcifications by comparing to invasive coronary angiography as the gold standard.
Our initial study proved the applicability of this modified subtraction CCTA scan protocol.In clinical practice,using this modified two breath-hold method would be an optimal supplement for patients with limited breath hold (chronic asthma,pleural effusion,COPD etc.) who are not qualified for the one breath hold scan protocol.Additionally,a combination of 100 kV scanning voltage can significantly reduce the total effective radiation dose in patients with BMI <25 in subtraction CCTA.

