蛋白质Neddylation修饰与肿瘤关系的研究进展
李清梅,王淑珍
(中国药科大学生命科学与技术学院,南京 210009)
蛋白质的可逆性翻译后修饰在真核细胞生物过程的调控中发挥着重要作用,常见的修饰类型包括糖基化、乙酰化、磷酸化、甲基化和泛素化等[1]。蛋白质Neddylation修饰的机制与泛素化相似,神经前体细胞表达的发育下调蛋白8(neuronal precursor cell-expressed developmentally down-regulated protein 8,NEDD8)在其激活酶NAE(NEDD8 activing enzyme,NAE)、结合酶E2、连接酶E3催化的多步级联酶促反应下,共价结合到底物蛋白质上,从而调节靶蛋白的生物学功能[2]。近期研究表明,蛋白质Neddylation修饰异常与多种肿瘤的发生发展密切相关,因此Neddylation修饰已经成为一种新的抗肿瘤治疗的靶标[3]。小分子抑制剂MLN4924(pevonedistat)是NAE的选择性抑制剂,能通过抑制NAE的活性阻断后续蛋白质的Neddylation修饰反应,从而抑制多种肿瘤相关信号通路,在各种临床前肿瘤动物模型中表现出良好的抑瘤效果,目前已进入Ⅰ/Ⅱ期临床试验[4]。本文就蛋白质Neddylation修饰和其参与肿瘤细胞周期、凋亡、衰老、自噬、血管生成及免疫细胞调节的最新研究进展进行简要介绍。
1 蛋白质Neddylation修饰概述
1.1 蛋白质Neddylation修饰的基本过程
NEDD8是由81个氨基酸组成且与泛素相似性高达80%的小蛋白,在真核生物中高度保守[2]。蛋白质Neddylation修饰过程主要包括以下4步酶促反应(图1):(1)NEDD8在其前体加工酶的作用下,被水解为C端暴露Gly76残基的成熟NEDD8;(2)在NEDD8激活酶NAE的作用下,成熟NEDD8的Gly76与其活性位点的Cys形成一个高能量的硫酯键;(3)活化的NEDD8通过转硫醇反应被转移到NEDD8结合酶E2(UBE2M/UBE2F)上;(4)NEDD8连接酶E3将NEDD8从E2酶转移到底物蛋白上,使NEDD8通过共价键与底物的Lys残基结合完成对特定蛋白的Neddylation修饰[5]。此外,在去NEDD8修饰酶的作用下,NEDD8也可以从底物蛋白上释放出来重新进入循环,即Deneddylation,以维持蛋白质Neddylation修饰的动态平衡[2]。
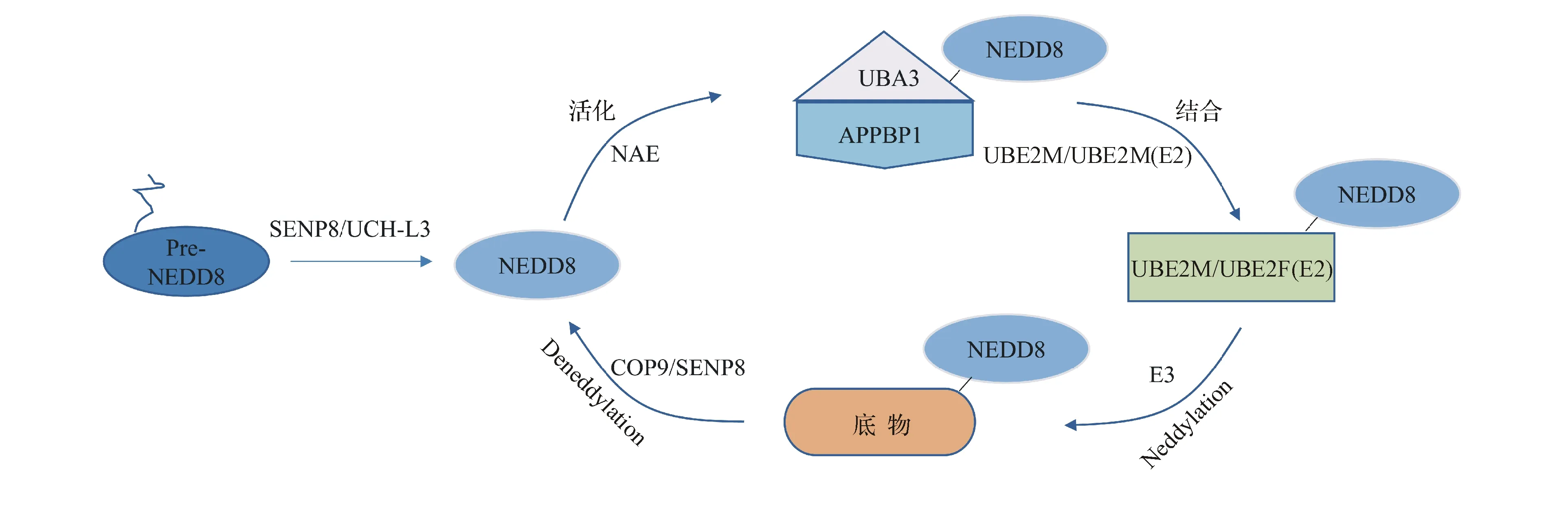
图1蛋白质Neddylation修饰过程
SENP8/UCH-L3:NEDD8前体加工酶;UBA3与APPBP1的异二聚体(NAE):NEDD8激活酶;UBE2M/UBE2F(E2):NEDD8结合酶;E3:NEDD8连接酶;COP9/SENP8:去NEDD8修饰酶
1.2 参与蛋白质Neddylation修饰的关键酶
参与蛋白质Neddylation修饰的关键酶主要包括NEDD8前体加工酶、NEDD8激活酶NAE、NEDD8结合酶E2和NEDD8连接酶E3以及去NEDD8修饰酶。
1.2.1 NEDD8前体加工酶 NEDD8前体加工酶主要包括泛素羧基末端水解酶L3(ubiquitin carboxyl-terminal hydrolase isozyme L3,UCH-L3)和NEDD8特异性蛋白酶1(NEDD8-specific protease 1,NEDP1/DEN1/SENP8)两种。UCH-L3除了可以水解NEDD8外还可以加工泛素,但是SENP8只特异性水解NEDD8[6]。
1.2.2 NEDD8激活酶与结合酶 NEDD8激活酶NAE是由淀粉样前体蛋白结合蛋白1(amyloid precursor protein-binding protein 1,APPBP1)和泛素样修饰激活酶3(ubiquitin like modifier activating enzyme 3,UBA3)构成的异源二聚体[7]。NEDD8结合酶E2则主要包括泛素结合酶E2M(ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2M,UBE2M/UBC12)和泛素结合酶E2F(ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2F,UBE2F)两种。
1.2.3 NEDD8连接酶 与泛素化修饰的特异性一样,Neddylation修饰的特异性主要体现在NEDD8 E3连接酶催化的最后一步酶促反应上。目前已知的NEDD8 E3连接酶的数目远远少于泛素E3连接酶,包括:环指蛋白(RING-box protein,RBX)、鼠双微体2(murine double minute 2,MDM2)、c-CBL(casitas B-lineage lymphoma)、凋亡抑制因子(inhibitor of apoptosis,IAPs)和最近报道的神经突触受体相关蛋白(rapsyn)等[4,8]。其中,RBX家族的NEDD8 E3连接酶研究的最为清楚,RBX1可与UBE2M联合作用催化Cullin-RING泛素连接酶(Cullin RING ligases,CRLs)家族成员Cullin-1,-2,-3,-4A和-4B的Neddylation修饰,而RBX2可与UBE2F联合作用催化Cullin-5的Neddylation修饰[9]。
1.2.4 去NEDD8修饰酶 去NEDD8修饰酶主要包括SENP8和组成型光形态发生因子9(constitutive photomorphogenesis 9,COP9)信号复合体。SENP8发挥Deneddylation功能时倾向于将NEDD8从多聚NEDD8修饰的底物蛋白上移除而保留单NEDD8修饰形式,非Cullin底物蛋白的Deneddylation修饰一般由SENP8负责[2,6]。COP9信号复合体由8个不同的亚基(COP9 signalosome subunit,CSN)组成,其相对分子质量从大到小依次称为CSN1(57 kD)~CSN8(22 kD),其Deneddylation过程主要由CSN5负责[10]。
1.3 发生Neddylation修饰的底物蛋白质
到目前为止,已知发生Neddylation修饰的底物蛋白质大部分都是Cullin家族成员,包括Cullin-1,-2,-3,-4A,-4B和-5。Cullin被Neddylation修饰后可通过泛素-蛋白酶体系统调控多种半衰期较短的关键性调节因子的泛素化修饰与降解,如信号转导因子、细胞周期调节因子、转录因子、肿瘤抑制因子和原癌蛋白等[4]。p53是迄今为止细胞中最为重要的肿瘤抑制因子之一,MDM2不仅催化其发生泛素化修饰,也介导了其Neddylation修饰。与泛素化降解不同,p53的Neddylation修饰只会抑制p53的转录活性,而不影响其降解[11]。核糖体蛋白L11(ribosome protein L11,RPL11)和核糖体蛋白S14(ribosome protein S14,RPS14)等也可以在MDM2催化下发生Neddylation修饰,从而调节RPL11、RPS14的稳定性和亚细胞定位[12-13]。乳腺癌相关蛋白3(breast cancer-associated protein 3,BCA3)、β-淀粉样前体蛋白胞内结构域(the intracellular domain of amyloid precursor protein,AICD)和环中间的环型(RING in between RING,RBR)E3连接酶Parkin等也可以发生Neddylation修饰,参与调控各种生理或病理过程[14-16]。此外,除了常规功能性蛋白质之外,作为染色体结构的组蛋白同样也可以发生Neddylation修饰,这种表观遗传修饰与肿瘤的发生发展关系密切[4,17]。例如,在HCT116细胞中,组蛋白2A(histone 2A,H2A)会在E3连接酶RNF168的作用下发生Neddylation修饰,拮抗H2A的泛素化修饰,从而抑制DNA的损伤修复[18]。尽管还有很多其他蛋白质也可以发生Neddylation修饰,但是其对应的NEDD8 E3连接酶并不清楚,因此,目前文献报道的NEDD8 E3连接酶及其对应的底物的种类并不是很多,总结如表1所示。
表1 NEDD8 E3连接酶及其对应的底物
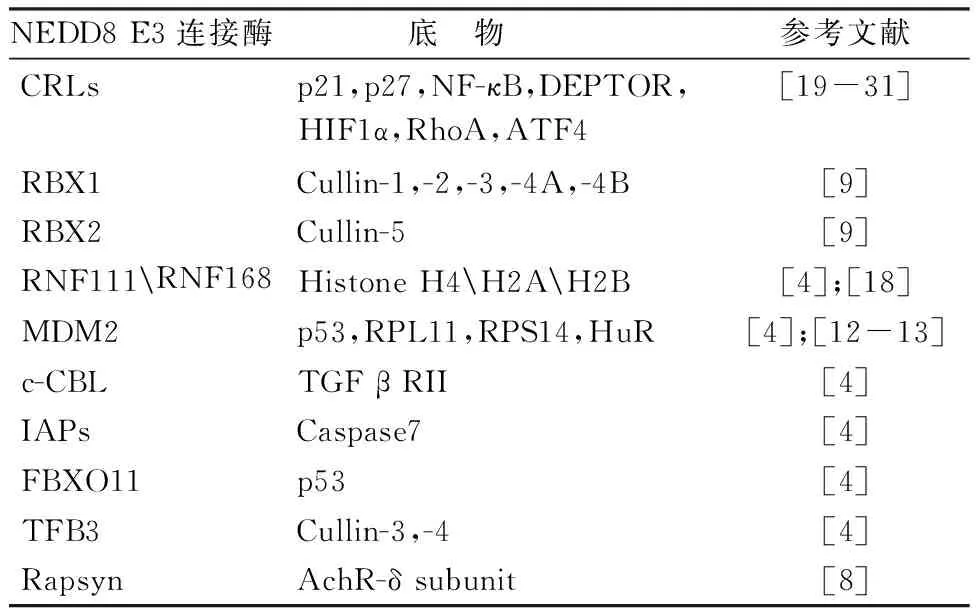
NEDD8 E3连接酶底 物参考文献CRLsp21,p27,NF-κB,DEPTOR,HIF1α,RhoA,ATF4[19-31]RBX1Cullin-1,-2,-3,-4A,-4B[9]RBX2Cullin-5[9]RNF111RNF168Histone H4H2AH2B[4];[18]MDM2p53,RPL11,RPS14,HuR[4];[12-13]c-CBLTGF β RII[4]IAPsCaspase7[4]FBXO11p53[4]TFB3Cullin-3,-4[4]RapsynAchR-δ subunit[8]
2 蛋白质Neddylation修饰与肿瘤的生物学过程
除了Neddylation修饰在肿瘤和正常组织中存在差异外,用NAE的抑制剂MLN4924处理肿瘤细胞时,会影响肿瘤细胞的多种生物学过程。目前研究Neddylation修饰涉及的肿瘤生物学内容主要包括:调控肿瘤细胞周期、参与细胞凋亡、衰老、自噬、调节血管生成及调控免疫细胞,如图2所示。
2.1 Neddylation修饰与肿瘤细胞周期
用MLN4924处理不同类型肿瘤细胞或动物模型,发现抑制Neddylation修饰会诱导肿瘤细胞周期阻滞,但是阻滞阶段并不相同,提示MLN4924诱导肿瘤细胞周期阻滞存在多种不同机制[32]。Milhollen等[24]用MLN4924处理弥漫大B细胞淋巴瘤(diffuse large B lymphoma,DLBCL)细胞时发现,在MLN4924诱导下激活的B细胞样(activated B-cell-like,ABC)DLBCL会快速增加磷酸化IκB-α的水平,减少p65蛋白的核内表达,通过降低NF-κB的转录活性引起G1期阻滞;但是在生发中心B细胞样(germinal center B-cell-like,GC)DLBCL模型中,MLN4924则通过增加DNA复制因子Cdt-1的累积,诱导DNA重新复制造成S期阻滞。最近暨南大学潘景轩教授课题组发现,用MLN4924阻滞Neddylation修饰,对携带T315I点突变Bcr-Abl融合的慢性粒细胞白血病细胞和白血病干细胞具有显著抑制效果。其研究也显示MLN4924可诱导多种p53野生型慢性粒细胞白血病细胞系以及CD34+干细胞中细胞周期抑制因子p27蛋白表达水平升高,引起G2/M期阻滞[22]。
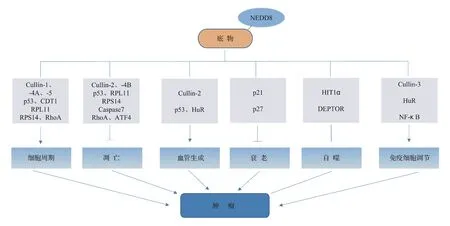
图2蛋白Neddylation修饰与肿瘤的生物学过程
2.2 Neddylation修饰与肿瘤细胞凋亡
抑制Neddylation修饰造成DNA重新复制和NF-κB信号通路失活后,不仅会诱导肿瘤细胞发生细胞周期阻滞,还会导致多种肿瘤细胞发生凋亡[25]。在慢性淋巴性白血病B细胞模型中,Godbersen等[26]发现MLN4924可通过失活NF-κB信号,调节Bcl-2家族促凋亡蛋白Bim和Noxa的水平导致细胞凋亡。在淋巴瘤细胞中,MLN4924可通过增加促凋亡相关蛋白(如Bik)和降低抗凋亡蛋白(如XIAP、c-IAP1和c-IAP2)的表达,激活内源性凋亡信号通路[23]。Chen等[31]用MLN4924处理人食管鳞状细胞癌细胞发现,抑制Neddylation修饰会增加CRLs底物激活转录因子4(activating transcription factor 4,ATF4)的稳定性,激活转录因子CHOP,诱导死亡受体5(death receptor 5,DR5)的表达,从而激活外源性凋亡信号介导的凋亡通路。此外,在急性淋巴细胞白血病细胞(acute lymphoblastic leukemic cells,ALL)模型中,MLN4924还可通过激活eIF2α和mTOR信号通路诱导内质网应激和未折叠蛋白反应(unfolded protein response,UPR)介导的细胞死亡[33]。
2.3 Neddylation修饰与肿瘤细胞衰老
衰老是一种抑制肿瘤细胞增殖的重要机制,诱导肿瘤细胞衰老已成为治疗肿瘤的策略之一。越来越多研究表明,MLN4924不仅可以诱导肿瘤细胞凋亡,还可通过诱导肿瘤细胞衰老发挥抗肿瘤作用[4]。MLN4924诱导的衰老过程是不可逆的,其机制与肿瘤抑制因子p21蛋白的持续累积以及DNA损伤反应的持续激活有关[19]。例如,Benamar等[20]研究发现,在黑色素瘤细胞中抑制Neddylation修饰后,会使CRL4-CDT2-SET8/p21轴泛素化和降解失活,从而诱导DNA重新复制和细胞衰老。在CKS1B基因特异性高表达的多发性骨髓瘤细胞中,MLN4924可以通过增加p21的蛋白稳定性诱导细胞衰老,干扰p21的表达后,会使这些细胞丧失对MLN4924的敏感性[21]。此外,在淋巴瘤细胞Raji和U937中,MLN4924可显著上调衰老标志物β-半乳糖苷酶的表达,增加肿瘤抑制因子p21/p27的蛋白稳定性,促进细胞衰老[23]。
2.4 Neddylation修饰与肿瘤细胞自噬
自噬作为一种双功能的细胞信号途径,既可以在药物作用时作为一个促凋亡信号发挥作用,也可以作为促生存的信号引起肿瘤细胞耐药[34]。研究发现MLN4924可以降低磷酸化mTOR的蛋白水平,通过抑制mTOR活性引起细胞自噬。Zhao等[29]在研究中发现,MLN4924可通过调节HIF1-REDD1-TSC1-mTORC1-DEPTOR信号轴诱导多种肿瘤细胞系(例如,人宫颈癌HeLa细胞、乳腺癌SK-BR3和MDA-MB-231细胞)发生时间和剂量依赖性的细胞自噬。深入分析发现抑制Neddylation修饰后,引起CRLs的底物低氧诱导因子HIF1α和mTOR的抑制因子DEPTOR的水平升高,从而抑制mTOR活性[29]。此外,MLN4924还可通过提高活性氧自由基(reactive oxygen species,ROS)水平引发自噬[35]。
2.5 Neddylation修饰与肿瘤血管生成
恶性肿瘤的发生和发展依赖于新生血管增殖与形成,新生血管可为不断增殖的肿瘤细胞提供营养,抑制新生血管生成策略在临床上已表现出了显著的抗肿瘤效果。研究表明,Neddylation修饰不仅对内皮细胞的正常生理功能(例如,屏障功能和血管内皮通透性)的调节非常重要[36],也参与了肿瘤新生血管的生成[30]。Yao等[30]用MLN4924处理人脐静脉血管内皮细胞(human umbilical vein endothelial cells,HUVECs)发现,抑制Neddylation修饰后很快会引起Rho GTP酶家族成员RhoA的累积,破坏血管内皮细胞的血管生成活性,随后会造成其他肿瘤抑制性CRLs蛋白底物的累积,引发DNA损伤反应、细胞周期阻滞和凋亡。之后,他们在大鼠主动脉环实验、鸡胚绒毛尿囊膜实验和基质胶栓等经典的血管生成实验模型中也证明了MLN4924的有效性[30]。Jin等[27]发现抑制Neddylation修饰可破坏肿瘤干细胞特征,干扰NF-κB介导的VEGF-C的旁分泌,抑制新生血管生成,从而有效抑制葡萄膜恶性黑色素瘤的肝脏转移。
2.6 Neddylation修饰与免疫细胞调节
肿瘤微环境中存在多种类型的免疫细胞,它们在肿瘤发生、发展、侵袭与转移过程中发挥着极为重要的作用[37]。研究表明,Neddylation修饰可以通过调节CRLs的底物(如NF-κB等转录因子)的活性影响巨噬细胞、树突状细胞和T细胞等免疫相关细胞的功能,参与调节肿瘤微环境的形成和重塑[28]。Chang等[38]课题组用MLN4924处理脂多糖(lipopolysaccharide,LPS)刺激的巨噬细胞样THP-1细胞,或用siRNA干扰巨噬细胞中NEDD8或UBC12的表达后,显著降低了TNF-α和IL-6等促炎细胞因子的产生,证明Neddylation修饰对于LPS诱导巨噬细胞炎性细胞因子的分泌是必需的。Asare等[39]的最新研究结果表明,MLN4924处理LPS刺激的巨噬细胞会使其从促炎的M1型向抗炎的M2型极化。同样,MLN4924也能降低LPS诱导的树突状细胞促炎细胞因子的产生,还能使未成熟的树突状细胞发生坏死性死亡[40-41]。此外,用MLN4924处理或敲除UBC12也都能降低效应T细胞的激活、增殖和细胞因子的释放[42-43]。
3 结 语
Neddylation修饰是蛋白质翻译后修饰方式之一,它不仅可以造成多种Cullin家族的底物蛋白泛素化降解,还可通过修饰其他非Cullin家族的底物蛋白,广泛参与多种信号传导途径的调节。越来越多研究结果证明Neddylation修饰与肿瘤发生发展关系密切,参与调控肿瘤的细胞周期、凋亡、衰老、自噬、血管生成以及免疫细胞等多种过程。因此,进一步对Neddylation修饰中未知NEDD8 E3连接酶、蛋白底物及其调控各种细胞生物学过程机制的研究将对肿瘤治疗具有十分重要的临床意义及应用前景。
参 考 文 献
[1] Karve TM,Cheema AK.Small changes huge impact:the role of protein posttranslational modifications in cellular homeostasis and disease[J].JAminoAcids,2011,2011(2):207691.
[2] He S,Zhang LQ,He FC.Research progress on the function and regulation mechanism of ubiquitin-like Neddylation[J].ProBiochemBiophys(生物化学与生物物理进展)2009,36(9):1089-1094.
[3] Jiang Y,Jia L.Neddylation pathway as a novel anti-cancer target:mechanistic investigation and therapeutic implication[J].AnticancerAgentsMedChem,2015,15(9):1127-1133.
[4] Zhou L,Zhang W,Sun Y,etal.Protein neddylation and its alterations in human cancers for targeted therapy[J].CellSignal,2018,44:92-102.
[5] Wang X,Li L,Liang Y,etal.Targeting the neddylation pathway to suppress the growth of prostate cancer cells:therapeutic implication for the men′s cancer[J].BiomedResInt,2014,21(17):2383-2400.
[6] Coleman KE,Békés M,Chapman JR,etal.SENP8 limits aberrant neddylation of NEDD8 pathway components to promote cullin-RING ubiquitin ligase function[J].Elife,2017,6:e24325.
[7] Walden H,Podgorski MS,Huang DT,etal.The structure of the APPBP1-UBA3-NEDD8-ATP complex reveals the basis for selective ubiquitin-like protein activation by an E1[J].MolCell,2003,12(6):1427-1437.
[8] Li L,Cao Y,Wu H,etal.Enzymatic activity of the scaffold protein rapsyn for synapse formation[J].Neuron,2016,92(5):1007-1019.
[9] Enchev RI,Schulman BA,Peter M.Protein neddylation:beyond cullin-RING ligases[J].NetRevMolCellBiol,2015,16(1):30-44.
[10] Li P,Xie L,Gu Y,etal.Roles of Multifunctional COP9 signalosome complex in cell fate and implications for drug discovery[J].JCellPhysiol,2017,232(6):1246-1253.
[11] Bailly A,Perrin A,Bou Malhab LJ,etal.The NEDD8 inhibitor MLN4924 increases the size of the nucleolus and activates p53 through the ribosomal-Mdm2 pathway[J].Oncogene,2016,35(4):415-426.
[12] Sundqvist A,Liu G,Mirsaliotis A,etal.Regulation of nucleolar signalling to p53 through NEDDylation of L11[J].EMBORep,2009,10(10):1132-1139.
[13] Zhang J,Bai D,Ma X,etal.HCINAP is a novel regulator of ribosomal protein-HDM2-p53 pathway by controlling NEDDylation of ribosomal protein S14[J].Oncogene,2014,33(2):246-254.
[14] Gao F,Cheng J,Shi T,etal.Neddylation of a breast cancer-associated protein recruits a class III histone deacetylase that represses NFκB-dependent transcription[J].NatCellBiol,2006,8(10):1171-1177.
[15] Lee MR,Lee D,Shin SK,etal.Inhibition of APP intracellular domain (AICD) transcriptional activity via covalent conjugation with Nedd8[J].BiochemBiophysResCommun,2008,366(4):976-981.
[16] Kane LA,Lazarou M,Fogel AI,etal.PINK1 phosphorylates ubiquitin to activate parkin E3 ubiquitin ligase activity[J].JCellBiol,2014,205(2):143-153.
[17] Shanmugam MK,Arfuso F,Arumugam S,etal.Role of novel histone modifications in cancer[J].Oncotarget,2017,9(13):11414-11426.
[18] Li T,Guan J,Huang Z,etal.RNF168-mediated H2A neddylation antagonizes ubiquitylation of H2A and regulates DNA damage repair[J].JCellSci,2014,127(10):2238-2248.
[19] Jia L,Li H,Sun Y,etal.Induction of p21-dependent senescence by an NAE inhibitor,MLN4924,as a mechanism of growth suppression[J].Neoplasia,2011,13(6):561-569.
[20] Benamar M,Guessous F,Du K,etal.Inactivation of the CRL4-CDT2-SET8/p21 ubiquitylation and degradation axis underlies the therapeutic efficacy of pevonedistat in melanoma[J].EBioMedicine,2016,10:85-100.
[21] Huang J,Zhou Y,Thomas GS,etal.NEDD8 inhibition overcomes CKS1B-induced drug resistance by upregulation of p21 in multiple myeloma[J].ClinCancerRes,2015,21(24):5532-5542.
[22] Liu C,Nie D,Li J,etal.Antitumor effects of blocking protein neddylation in T315I-BCR-ABL leukemia cells and leukemia stem cells[J].CancerRes,2018,78(6):1522-1536.
[23] Wang Y,Luo Z,Pan Y,etal.Targeting protein neddylation with an NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 induced apoptosis or senescence in human lymphoma cells[J].CancerBiolTher,2015,16(3):420-429.
[24] Milhollen MA,Traore T,Adams-Duffy J,etal.MLN4924,a NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor,is active in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma models:rationale for treatment of NF-κB-dependent lymphoma[J].Blood,2010,116(9):1515-1523.
[25] Wu S,Yu L.Targeting cullin-RING ligases for cancer treatment:rationales,advances and therapeutic implications[J].Cytotechno-logy,2016,68(1):1-8.
[26] Godbersen JC,Humphries LA,Danilova OV,etal.The Nedd8-activating enzyme inhibitor MLN4924 thwarts microenvironment-driven NF-kappaB activation and induces apoptosis in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B cells[J].ClinCancerRes,2014,20(6):1576-1589.
[27] Jin Y,Zhang P,Wang Y,etal.Neddylation blockade diminishes hepatic metastasis by dampening cancer stem-like cells and angiogenesis in uveal melanoma[J].ClinCancerRes,2017.doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1703.
[28] Jin JY,Jing ZF,Wang J,etal.Regulation of immune cells by ubiquitin- like neddylation[J].ChinJImmunol(中国免疫学杂志),2017,33(5):777-780.
[29] Zhao Y,Xiong X,Jia L,etal.Targeting cullin-RING ligases by MLN4924 induces autophagy via modulating the HIF1-REDD1-TSC1-mTORC1-DEPTOR axis[J].CellDeathDis,2012,3(9):e386.
[30] Yao WT,Wu JF,Yu GY,etal.Suppression of tumor angiogenesis by targeting the protein neddylation pathway[J].CellDeathDis,2014,5(2):e1059.
[31] Chen P,Hu T,Liang Y,etal.Neddylation inhibition activates the extrinsic apoptosis pathway through ATF4-CHOP-DR5 axis in human esophageal cancer cells[J].ClinCancerRes,2016,22(16):4145-4157.
[32] Zhao Y,Sun Y.Cullin-RING ligases as attractive anti-cancer targets[J].CurrPharmDes,2013,19(18):3215-3225.
[33] Leclerc GM,Zheng S,Leclerc GJ,etal.The NEDD8-activating enzyme inhibitor pevonedistat activates the eIF2α and mTOR pathways inducing UPR-mediated cell death in acute lymphoblastic leukemia[J].LeukRes,2016,50:1-10.
[34] Singh SS,Vats S,Chia AY,etal.Dual role of autophagy in hallmarks of cancer[J].Oncogene,2018,37(9):1142-1158.
[35] Chen P,Hu T,Liang Y,etal.Synergistic inhibition of autophagy and neddylation pathways as a novel therapeutic approach for targeting liver cancer[J].Oncotarget,2015,6(11):9002-9017.
[36] Sakaue T,Fujisaki A,Nakayama H,etal.Neddylated cullin 3 is required for vascular endothelial-cadherin-mediated endothelial barrier function[J].CancerSci,2017,108(2):208-215.
[37] Quail DF,Joyce JA.Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis[J].NatMed,2013,19(11):1423-1437.
[38] Chang FM,Reyna SM,Granados JC,etal.Inhibition of neddylation represses lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory cytokine production in macrophage cells[J].JBiolChem,2012,287(42):35756-35767.
[39] Asare Y,Ommer M,Azombo FA,etal.Inhibition of atherogenesis by the COP9 signalosome subunit 5invivo[J].ProcNatlAcadSciUSA,2017,114(13):E2766-E2775.
[40] EI-mesery M,Seher A,Stühmer T,etal.MLN4924 sensitizes monocytes and maturing dendritic cells for TNF-dependent and -independent necroptosis[J].BrJPharmacol,2015,172(5):1222-1236.
[41] Mathewson N,Toubai T,Kapeles S,etal.Neddylation plays an important role in the regulation of murine and human dendritic cell function[J].Blood,2013,122(12):2062-2073.
[42] Mathewson ND,Fujiwara H,Wu SR,etal.SAG/Rbx2-dependent neddylation regulates T-cell responses[J].AmJPathol,2016,186(10):2679-2691.
[43] Jin HS,Liao L,Park Y,etal.Neddylation pathway regulates T-cell function by targeting an adaptor protein Shc and a protein kinase Erk signaling[J].ProcNatlAcadSciUSA,2013,110(2):624-629.

