基于pso_FSVM的车用动力电池温度预测模型研究
刘荣 童亮 许永红
摘 要: 针对混合动力汽车在复杂工况下动力电池温度测量可靠性下降的问题,提出基于pso_FSVM的车用动力电池温度预测模型,该研究分别采集车辆key_on和key_off两种状态下的动力电池温度数据,采用粒子群优化的快速支持向量机算法,构建了稳定的动力电池温度预测模型。实验结果表明,在车辆key_on和key_off两种状态下,数据集的预测数据与实际测量数据的相关系数分别达到0.810 2和0.797 3,温度预测误差小于2 ℃,pso_FSVM模型提高了动力电池温度预测的精度和可靠性。
关键词: 混合动力汽车; 动力电池温度; 粒子群; 快速支持向量机; 预测模型; 热动力学模型
中图分类号: TN245?34; TP336 文献标识码: A 文章编号: 1004?373X(2018)12?0024?04
Abstract: In allusion to the problem of the decline of temperature measurement reliability for power battery of the hybrid electric vehicle in complicated working conditions, the temperature data of power battery at two vehicle states of Key_on and Key_off is collected respectively. A stable power battery temperature prediction model is constructed by using the particle swarm optimization based fast support vector machine algorithm. The experimental results show that the correlation coefficient between the prediction data and actual measurement data of data sets reaches 0.810 2 and 0.797 3 respectively at the two vehicle states of Key_on and Key_off, and the temperature prediction error is less than 2 ℃, which indicates that the pso_FSVM model can improve the prediction accuracy and reliability of power battery temperature.
Keywords: pso_FSVM; hybrid electric vehicle; power battery temperature; particle swarm optimization; fast support vector machine; prediction model; thermodynamics model
0 引 言
动力电池是混合动力汽车驱动系统中必不可少的能源装置,确保动力电池的性能和使用寿命尤为重要。在复杂的工况下,电池温度作为影响电池性能和使用寿命的关键因素之一,必须准确地预测电池温度以确保电池系统工作在最好状态下。因此,构建准确可靠的电池温度预测模型,实时在线地监测电池温度,为动力电池及其管理系统保驾护航,对混合动力汽车安全性能和动力电池热管理系统的研究设计同样具有重大意义。近年来对电池性能的大量研究取得了重要成果,其中Hu借助Matlab/Simulink基于神经网络对PEMFC的搭建高温稳态性能和动态性能的预测模型,预测精度较高[1]。Sun提出基于热平衡方程的电池温度在线方法[2]。Hong提出了一种基于电阻层析成像的动力电池内部温度监测新方法[3]。但是这些研究方法建立的模型过于复杂,也没有建立在动力电池处于复杂的工作工况下。本文在电池热动力学模型理论基础上,结合在车辆复杂工况下采集的测试数据集,提出一种基于pso_FSVM模型的电池温度预测模型,pso_FSVM模型能够准确可靠地预测动力电池温度,为往后更为复杂的工况和环境(极寒、极热)下预测电池温度提供可行性。
1 电池热动力学模型
电池表面温度和内部温度是表征电池性能的两个重要参数,对于广泛应用于混合动力汽车的动力电池而言,内部温度是影响电池性能的决定性因素。在研究过程中,美国伯克利大学的D.Bernardi用可逆熵变产生的热量描述化学反应热,提出了Bernardi 生热率计算模型[4];而刘伟在研究中建立一种基于递归最小二乘法估算的电池热动力学模型[5]。在车辆key_on和key_off状态下,依據物理传热定律可得动力电池热动力学模型,如下:

4 结 论
1) 依据电池热动力学数学模型,本文提出的粒子群优化算法的快速支持向量机模型在对动力电池温度预测中运算速度快,相对误差极小,为在更为复杂的工况下提供研究价值,并且可以运用于混合动力汽车/纯电动汽车电池热量管理系统对热量的最优控制。
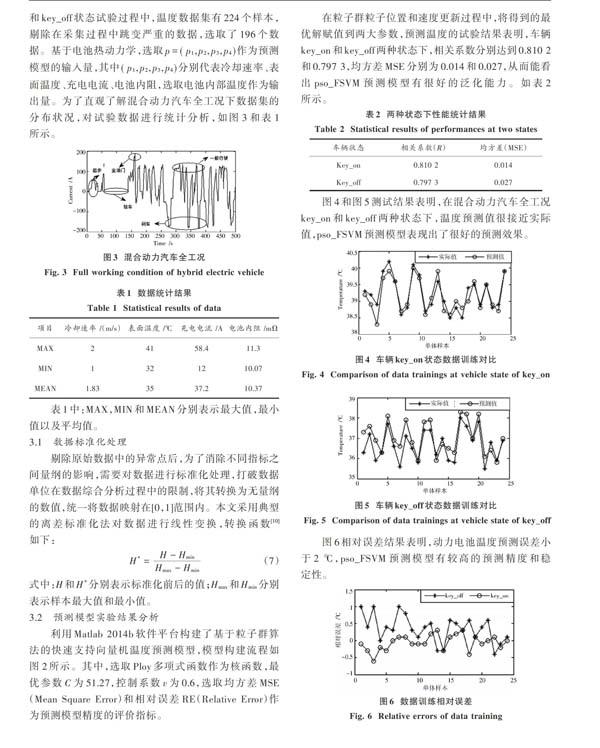
2) 在车辆全工况下,采集原始数据过程中应考虑电池均衡带来的影响,对大样本数据的综合处理以及粒子位置和速度的更新策略进行更为合理的规划,提高在大样本情况下粒子群算法的寻优能力。
注:本文通讯作者为童亮。
参考文献
[1] 胡经纬.质子交换膜燃料电池的电化学和数值模拟研究[D].大连:中国科学院,2006.
HU Jingwei. Electrochemical and mathematical model studies on PEMFC [D]. Dalian: Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2006.
[2] 孙金磊,朱春波,李磊,等.电动汽车动力电池温度在线估计方法[J].电工技术学报,2017,32(7):197?203.
SUN Jinlei, ZHU Chunbo, LI Lei, et al. Online temperature estimation method for electric vehicle power battery [J]. Transactions of China Electrotechnical Society, 2017, 32(7): 197?203.
[3] 洪晓斌,李年智,尹文伟,等.基于电阻层析成像的汽车动力电池内部温度监测[J].光学精密工程,2014,22(1):193?203.
HONG Xiaobin, LI Nianzhi, YIN Wenwei, et al. Monitoring of internal temperature of vehicle power battery based on electrical resistance tomography [J]. Optics and precision engineering, 2014, 22(1): 193?203.
[4] BERNARDI D, PAWLIKOWSKI E, NEWMAN J. A general energy balance for battery systems [J]. Journal of Electrochemical Society, 1985, 132(1): 5?12.
[5] LIU Wei. Introduction to hybrid vehicle system modeling and control [M]. Hoboken: Wiley, 2013.
[6] KENNEDY J, EBERHART R. Particle swarm optimization [C]// Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks. Piscataway: IEEE, 1995: 1942?1948.
[7] 王建国,张文兴.支持向量机建模及其智能优化[M].北京:清华大学出版社,2015:134?135.
WANG Jianguo, ZHANG Wenxing. Support vector machine modeling and intelligent optimization [M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2015: 134?135.
[8] 彭宇,彭喜元,刘兆庆.微粒群算法参数效能的统计分析[J].电子学报,2004,32(2):209?213.
PENG Yu, PENG Xiyuan, LIU Zhaoqing. Statistic analysis on parameter efficiency of particle swarm optimization [J]. Acta electronica sinica, 2004, 32(2): 209?213.
[9] 张文兴,丛宽,王建国,等.一种新的快速支持向量回归算法[J].微计算机信息,2010,26(33):208?209.
ZHANG Wenxing, CONG Kuan, WANG Jianguo, et al. A new algorithm of fast support vector regression [J]. Microcomputer information, 2010, 26(33): 208?209.
[10] HUANG Mingzhi, HAN Wei, WAN Jinquan, et a1. Multi?objective optimization for design and operation of anaerobic digestion using GA?ANN and NSGA?II [J]. Journal of chemical technology and biotechnology, 2016, 91(1): 226?233.

