Direction navigability analysis of geomagnetic field based on Gabor filter
XIAO Jing,DUAN Xiusheng,*,QI Xiaohui,and WANG Jianchen
1.Army Engineering University,Shijiazhuang 050003,China;2.Government Representative Office,Northwestern Polytechnical University,Xi’an 710065,China
Direction navigability analysis of geomagnetic field based on Gabor filter
XIAO Jing1,DUAN Xiusheng1,*,QI Xiaohui1,and WANG Jianchen2
1.Army Engineering University,Shijiazhuang 050003,China;
2.Government Representative Office,Northwestern Polytechnical University,Xi’an 710065,China
Direction navigability analysis is a supplement to the navigability analysis theory,in which extraction of the direction suitable-matching features(DSMFs)determines the evaluation performance.A method based on the Gabor filter is proposed to estimate the direction navigability of the geomagnetic field.First,the DSMFs are extracted based on the Gabor filter’s responses.Second,in the view of pattern recognition,the classification accuracy in fault diagnosis is introduced as the objective function of the hybrid particle swarm optimization(HPSO)algorithm to optimize the Gabor filter’s parameters.With its guidance,the DSMFs are extracted.Finally,a direction navigability analysis model is established with the support vector machine(SVM),and the performances of the models under different objective functions are discussed.Simulation results show the parameters of the Gabor filter have a significant influence on the DSMFs,which,in turn,affects the analysis results of direction navigability.Moreover,the risk of misclassification can be effectively reduced by using the analysis model with optimal Gabor filter parameters.The proposed method is not restricted in geomagnetic navigation,and it also can be used in other fields such as terrain matching and gravity navigation.
geomagnetic navigation,navigability analysis,direction navigability,Gabor filter,direction suitable-matching feature.
10.21629/JSEE.2018.02.18
Manuscript
February 27,2017.
.
This work was supported by the Key Project of Military Research on Weapons and Equipment(2014551).
1.Introduction
Geomagnetic navigation is based on geographic information,which is passive and has the characteristics of no radiation and good concealment.Aboveall,its location error does not accumulate over time[1].As a result,geomagnetic navigation can be used in all weather and all regions,especially in sea-crossing navigation.Acquiring accurate position is the core of geomagnetic navigation,which is influenced not only by the navigation algorithms,but also by the features of the magnetic map[2,3].Generally speaking,the more obvious the magnetic field fluctuates,the better navigation precision and real-time performance will be obtained in that area.Navigability analysis is such a method that evaluates whether the geomagnetic characteristics can fully represent the geographical locations in the matching process.
Navigability analysis of the geomagnetic field can draw lessons from the relevant achievements in image matching.And the decision-making analysis,model prediction and classification method can be used to evaluate the navigability[4–6].However,unlike image matching,the geomagnetic matching method is based on one-dimensional sequence,whose performance is also closely related to the carrier’s motion direction.Thus strictly speaking,the navigability analysis of a magnetic area only reflects the mean matching suitability in all directions.As a magnetic area whose mean matching suitability is indifferent may have an excellent matching direction,research on regional suitability may lead to missing some directions with good navigability.Direction navigability can describe the matching performance in any direction of the area,which not only improves the navigability analysis theory,but also provides guidance for the path planning of the carrier.
Research on direction navigability of the geomagnetic field has aroused tremendous attention among scholars.In[7],the gray level co-occurrence matrix(GLCM)was preliminarily used to analyze the direction navigability,but it was based on statistical theory and cannot extract features in any direction in practice.Wang established a hierarchical decision-making scheme for direction navigability analysis with the GLCM features and the standard deviation extracted by the Gabor filter.However,it is only capable of evaluating the navigability in four main directions and the analysis accuracy requires to be further improved[8,9].
A 2-D Gabor filter can obtain the optimum resolution in both space and frequency domains[10].It is widely used in the fields such as feature extraction and image recogni-tion.Given its good property of orientation selectivity,a direction feature set is built in this paper based on it to describe the direction navigability of the geomagnetic field.Then the problem of direction navigability analysis can be transformed into a pattern classification problem.It needs to be noted that the navigability analysis method and parameter optimization method proposed in the paper also can be used in other fields such as image matching,terrain matching and gravity navigation.
2.Extraction of direction suitable-matching features(DSMFs)based on Gabor filter
2.1 The 2-D Gabor filter
In 1985,the 2-D Gabor filter was first put forward by Daugnan.In the space domain,it. can be regarded as a Gaussian function which is modulated by a complex sinusoidal function.The definition of the 2-D Gabor filter[11]is
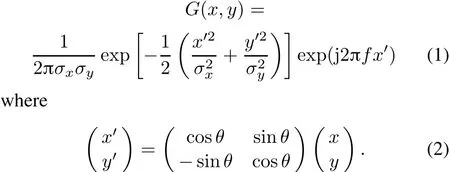
(x,y)is a position in the space coordinate system,σxandσyare the standard deviations of the Gaussian function inx-axis andy-axis directions,which determine the size of the filter.fis the center frequency of the Gabor filter.θcontrols the filter’s direction,which ranges from 0°to 360°.
Obviously,(1)consists of two parts:the real part and the imaginary part,so it can be rewritten[12]as
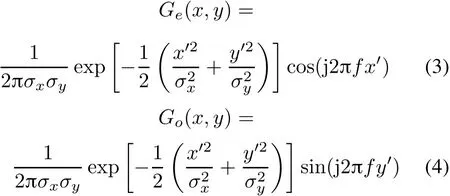
whereGe(x,y)andGo(x,y)respectively correspond to the Gabor filter’s real part and imaginary part.The former is even symmetric and the latter is odd symmetric, and their phases are orthogonal to each other.In feature extraction,the two parts play different roles.
2.2 Extraction of DSMFs of geomagnetic field
Researches show that the real part of the 2-D Gabor filter is good at detecting spot features and the imaginary part does well in edge detection[13].In order to obtain effective features,both parts of the Gabor filter are used to extract the DSMFs in different directions.
Suppose the magnetic intensity of a magnetic area isI(x,y),then the responses of the Gabor filter in this area can be calculated by executing a convolution ofI(x,y)andGe(x,y)orGo(x,y):

whereTe(x,y)andTo(x,y)are the original responses corresponding to the real part and imaginary part of the Gabor filter,representing the filtering results of the magnetic area in the filter’s direction.T(x,y)is the amplitude of the filter and “∗”is the convolution operator.In this paper,the DSMFs of the geomagnetic field is extracted based onTe(x,y),To(x,y)andT(x,y).
According to different functions,the DSMFs can be divided into three types:(i)the one that describes the fluctuation of the magnetic area;(ii)the one that represents the information of the area;(iii)the one that reflects the uniqueness of the area.From another perspective,these features also can be divided into macroscopic and microscopic features,representing the global and local changes.Sixteen common features are shown in Table 1.
Table 1 DSMFs in different directions of a magnetic area
DSMF Macroscopic feature Microscopic feature Roughness,eastward roughness,westward roughness,roughness/variance,standard deviation/mean,mean gradient,gradient standard deviation,fractal dimension Information Fisher information Entropy Uniqueness Correlation coefficient Fluctuation Mean,standard deviation,accumulative mean gradient,kurtosis coefficient,skewness coefficient
By choosing a group of Gabor filters in different directionsand selecting proper parameters for them, the original filtering responses in the given directions can be obtained.Then,the DSMFs in Table 1 can be computed.
Here,in order to keep the paper reasonably concise,only the formula of computing the magnetic stand arddeviation withTe(x,y)is given.Other concepts in Table 1 can be referred to[14].

whereX,Yrespectively represent the dimension in axesxandy;is the mean value ofTe(x,y).
3.Design of the Gabor filter
Design of the Gabor filter is the key to extract the DSMFs in different directions of a magnetic area,which directly influences the evaluation results of the direction navigability.This section focuses on selecting proper parameters for the Gabor filter.
A method called half-peak magnitude iso-curves(HMI)was used in[8]to convert the parameter selection problem into finding a proper frequency or standard deviation for the Gabor filter.However,it needs to introduce an auxiliary empirical threshold to draw conclusion and is dependent on prior knowledge.Reference[15]applied an intelligent algorithm to design the Gabor filter.By choosing a proper objective function,the dependence on the empirical threshold can be avoided.Enlightened by their thoughts,the hybrid partial swarm optimization(HPSO)algorithm is introduced to design the Gabor filter’s parameters on basis of analyzing their constraint relations.Meanwhile,the classification accuracy in fault diagnosis is used as the objective function to ensure the accuracy of navigability analysis.In this way,the Gabor filter is designed to extract the DSMFs in any direction of the magnetic area.
3.1 Constraint relations of the Gabor filter’s parameters
As is shown in(1)and(2),the Gabor filter has four parameters in total,namelyσx,σy,fandσ.It has been noted that the Gabor filter is able to extract the DSMFs in any direction.Here,six directions,namely 0°,30°,60°,90°,120°and 150°are taken as examples to design the filter and analyze their direction navigability.
Generally,when designinga Gabor filter,its aspect ratio is usually set to 1,i.e.σ=σx=σy.As a result,the Gabor filter’s parameters to be designed are reduced tofandσ.
In fact,fandσare not independent,they are constrained with each other[16],as is in(7):
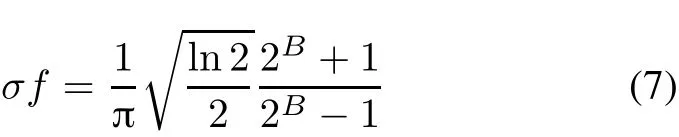
whereBis the frequency bandwidth of the Gabor filter.WhenB=1,it is closest to animals’visual receiving system.Thus(7)is rewritten as
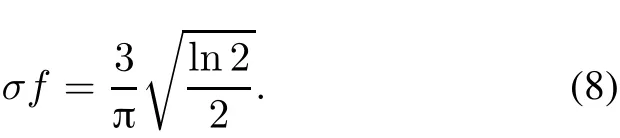
Thus,the Gabor filter’s parameters to be designed are simplified to find properσorf.
3.2 Basic principle of optimizing Gabor filter’s parameters
The constraints of the Gabor filter’s parameters have been discussed above and the design of the filter is turned into finding a properσorf.As the spectrum energy of the geomagnetic field is mainly concentrated in low frequency[9],oncefis fixed,other parameters of the filter are determined.Finally,design of the Gabor filter is transformed into the optimization off.
The particle swarm optimization(PSO)algorithm uses the cooperation and competition mechanism among the swarms to guide the optimization process,and it has the global optimization ability.If the PSO algorithm is combined with the genetic algorithm(GA),the crossover and mutation mechanism will be introduced to the HPSO method,and it will avoid the standard PSO falling into local convergence.Thus,the HPSO algorithm is applied to optimize the Gabor filter’s parameters.
To ensure more effective DSMFs are extracted by the filter,the classification accuracy is introduced as the objective function of the HPSO algorithm.Assume a direction is divided into two kinds:suitable for matching(denoted as category “1”)and unsuitable for matching(denoted as category “0”),then the classification accuracy is defined as

whereCAirepresents the classification accuracy of a single category,AAis the average accuracy,andOAis the overall accuracy.ωiequals 0 or 1,representing the category of the sample;N(Real C=ωi)is the number of the samples whose real category isωi;N(Prediction C=ωi∩Real C=ωi)counts the samples whose real category and prediction category are bothωi.
Fig.1 shows the schematic diagram of optimizing the filter’s parameters with the HPSO algorithm.As is shown,in the HPSO algorithm,positions of the swarms represent possible values off,so a group of Gabor filters at different frequencies are generated to extract different DSMFs.The back propagation neural network(BPNN)is used to calculate the value of the objective function.Parameters of the Gabor filter influence the DSMFs,and different DSMFs affect the classification results of BPNN. Thus taking the classification accuracy as the HPSO algorithm’s objective function will lead the swarms moving to the position where the classification results are the best.It guarantees the DSMFs extracted by the optimal filter could reach the maximum classification accuracy.
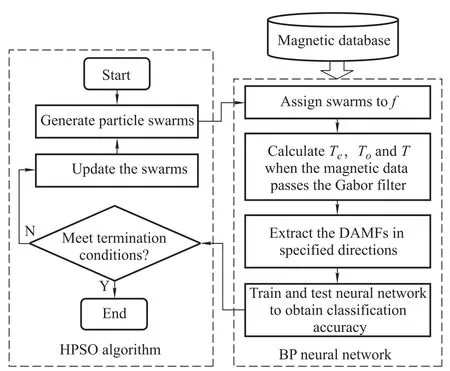
Fig.1 Schematic diagram of optimizing the filter’s parameters with HPSO algorithm
The intelligent optimization algorithm is applied in the proposed method,and no priori knowledge is needed,so the DSMF’s validity is ensured while the interference of human is reduced to the most extent.
3.3 Implementation of optimization of the Gabor filter
The magneticanomaly field mainly comes from the earth’s crust.Compared with the world’s main magnetic field,the magnetic anomaly field changes more obviously in local space.Hence,the world’s magnetic anomaly field model NGDC-720 is applied as the background magnetic field.
A magnetic area within the longitude range[34°E,39°E]and latitude range[47.812°N,53.812°N]is randomly selected to establish the local magnetic model.Then the Kriging interpolation method is applied to improve the accuracy of the map.After interpolation,the magnetic map’s accuracy is about 62.5 m,as is shown in Fig.2.
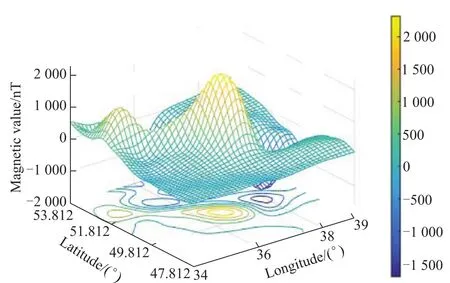
Fig.2 Local magnetic anomaly field model ofYcomponent
Considering the restrained factors such as the carrier’s motion and measuring errors of the equipment,the local magnetic anomaly field is divided into numbers of rectangular areas with a certain size.Denote them as candidate matching areas(CMAs).Extraction of DSMFs and calculation of correct matching probability are both based on the CMAs.
To provide guidance for BPNN and establish the direction navigability analysis model,categories of different directions in all CMAs should be distributed.
Correct matching probability calculates the ratio of the successful matching times and the total matching times[9],which is widely used to evaluate the matching performance of a CMA in geomagnetic navigation.It measures the credibility of the matching results in a CMA.Similarly,the direction correct matching probability can describe the matching credibility of a CMA’s direction.It can be achieved by simulation experiments.Assume the matching experiments are conductedNtimes in a specified directiondof a selected CMAi,and the center point of the matching sequence is different at each time.Denote the position error of the matching algorithm asEp(d,i),then the direction correct matching probabilityPr(d,i)is
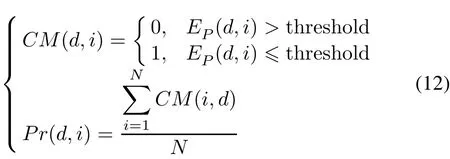
where the threshold is a constant(it is set to 125 m in this paper),it is used to judge whether a match is successful,andCM(d,i)calculates the total number of the effective matching.
On the basis of it,the category’s label can be assigned according toPr(d,i).Here,the direction whose correct matching probability is greater than 0.9 is considered suitable for matching,as is given in(13),a direction is labeled by category “0”or“1”.
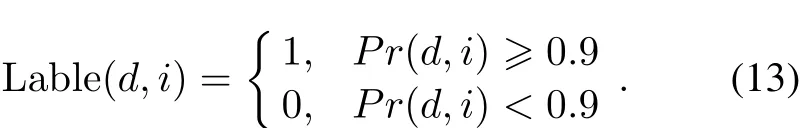
Therefore,every specified direction of all CMAs is labeled and each one has its DSMFs.All of them are independent when used to train the neural network.
In the following,the proposed optimization method based on the HPSO algorithm is illustrated.Here,a BPNN with two hidden layers is used to optimize the Gabor filter’s parameters.Usually,the optimized parameters obtained by a certain amount of samples in the database can be taken as the holistic optimal parameters.Thus 300 CMAs are randomly selected from the local magnetic anomaly field and their DSMFs and labels in six specified directions are calculated.Thus 1 800samples are obtained,of which two-thirds are used to train the BPNN and the other one-third to test the trained network.
ConsideringTe(x,y),To(x,y)andT(x,y)are all used to extract the DSMFs,there are 48 DSMFs in total.Therefore,input nodes of the BPNN is 48,and the output node is 1.And two hidden layers of 50×10 are chosen for the BPNN by experience.As for the HPSO algorithm,the search space offis within[10-3,100].The iteration number and the search precision are respectively set to 15 and 10-4,they are used to judge whether the termination conditions are met.In this section,the overall classification accuracy(OA)is taken as the objective function of the HPSO algorithm.Fig.3shows the fitness curve of the HPSO algorithm during the training process of BPNN when OA acts as the objective function.

Fig.3 Fitness curve of HPSO when OA is the objective function
It can be seen that after several iterations, the best fitness reaches 99.00%.It illustrates the DSMFs extracted with the guidance of the optimized parameter have reached a correct classification probability of 99.00%.Thus the proposed optimization method for the Gabor filter is feasible.Validity of the method will be verified in Section 4.
4.Direction navigability analysis based on DSMFs
In practice,evaluating whether a given direction is suitable for matching is more efficient and meaningful than calculating its precise correct classification probability.In this sense,the direction navigability analysis of geomagnetic navigation can be regarded as a pattern recognition problem.Considering its excellent non-linear mapping ability and generalization ability,the support vector machine(SVM)is used to build a model to evaluate the direction navigability.Fig.4 shows the framework.As is shown,a certain amount of samples with DSMFs and their corresponding labels are selected,two-thirds of which are for training and the remaining are for testing.First,the principal component analysis(PCA)method is used to reduce the dimension of the DSMFs of the training set,then the DSMFs are sent to train the SVM to build the model of direction navigability.In this phase,parameters of SVM are optimized by the HPSO algorithm as well.

Fig.4 Framework of building the navigability analysis model
Once the analysis model is established,when the DSMFs of a new CMA with unknown navigability are input to the model,it will predict whether the givendirection is suitable for matching.
The following experiments are designed to verify the proposed direction navigability analysis method and the optimization algorithm of the Gabor filter.
4.1 Direction navigability analysis when the Gabor filter is optimized by OA
In this section,OA is taken as the objective function of the HPSO algorithm to optimize the Gabor filter’s parameters.With this condition,the DSMFs are extracted.Then according to the method above,1 600 training samples and 1 000 testing samples are randomly selected to build the direction navigability analysis model by the SVM.The simulation parameters of the HPSO algorithm are as follows:the number of the particle swarms is 20,parameterscandgof SVM are both searched within 0 to 50,the iterative time is 50,c1=1.5,c2=1.7;more than 95%of the principal components are sent to train and test the SVM,and a 5-fold cross-validation method is used to verify the established model.Fig.5 shows the fitness of each iteration when finding the optimal parameters for the SVM.
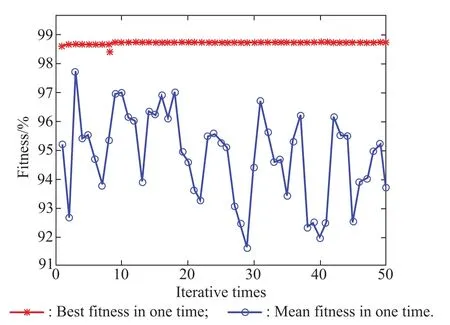
Fig.5 Fitness curve of parameters optimization of SVM
In the figure,the astroid line is the best fitness of all particles in each iteration and the circledot line is all particles’mean fitness of each step.After optimization,the optimal parameters of SVM(cbestandgbest)are obtained:cbest=6.69,gbest=50.Finally,the accuracy of the testing samples is calculated to be 98.75%.
Once the model is built,it can be used for navigability analysis.Randomly select 800 other samples from the database and use the established model to evaluate their navigability.Fig.6 is the classification results.

Fig.6 Classification results of SVM
In Fig.6,prediction label“1”(Pr(d,i)≥ 0.9)means the given direction is suitable for matching and a good matching performance can be obtained in this direction;while prediction label“0”(Pr(d,i)<0.9)means the direction is not suitable for matching.It proves that the trained SVM is reliable to evaluate the direction navigability in a given direction.In Table 2,the classification accuracies CA0,CA1,AA and OA of the 800 samples are listed out.
4.2 Direction navigability analysis when the Gabor filter is optimized by CA0
Usually,the direction whose prediction label is“1”is chosen for the matching algorithm to locate the carrier.However,if a direction is judged suitable for matching while in fact it is not,i.e.the model of direction navigability considers the prediction label of the direction is“1”while actually it is“0”,a large position error,or even false evaluation,will occur.This situation should be avoided as much as possible in the geomagnetic navigation.In this sense,though good classification results are obtained in Section 4.1,it is still very necessary to discuss the direction navigability when CA0is the objective function in parameter optimization of the Gabor filter.
In this section,the single classification accuracy of category “0”(CA0)is taken as the objective function of the HPSO algorithm to optimize the Gabor filter’s parameters.Other simulation parameters are the same as Section 4.1.Fig.7 shows the optimization process.

Fig.7 Fitness curve of HPSO when CA0is the objective function
As is shown,the classification accuracy of the testing samples reaches 100%,which means all testing samples with the guidance of CA0are correctly classified.It also proves the feasibility of the parameter optimization method of the Gabor filter.
Fig.8 shows the fitness of each iteration as the direction navigability analysis model is built.The astroid line is the best fitness of all particles in each iteration and the circledot line is all particles’mean fitness of each step.After optimization,the optimal parameters of SVM are:cbest=7.22,gbest=40.66.And the classification accuracy of the testing samples is 98.93%.

Fig.8 Fitness curve of parameters optimization of SVM
Randomly select 800 other samples from the database and use the established model to evaluate their navigability.Fig.9 gives SVM’s prediction results of the samples.Their corresponding classification accuracy CA0,CA1,AA and OA are listed in Table 2.
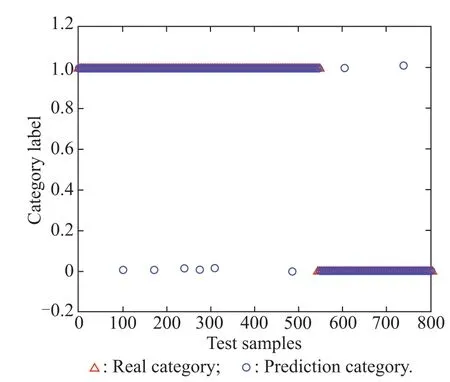
Fig.9 Classification results of SVM
Table 2 Classification accuracies in different conditions %
Objective function CA1CA0AA OA OA 99.09 98.81 98.95 99.00 CA099.09 99.21 99.15 99.13 None 91.96 47.43 69.69 77.88
4.3 Effectiveness evaluation of parameter optimization method of Gabor filter
Parameters of the Gabor filter influence the effectiveness of the DSMFs,which,in turn,affects the direction navigability analysis results.It has been proved that the proposed parameter optimization method of the Gabor filter is feasible,but the importance of the optimization is not discussed.Thus in this section,the Gabor filter’s parameterfis randomly set as 1 000.Then the DSMFs are extracted to build the direction navigability analysis model.Other simulation parameters are the same with Section 4.1.Fig.10 shows the fitness curve when the model is established.
Fig.10 Fitness curve of parameters optimization of SVM
It is shown the best classification accuracy of the testing samples is only 76.10%.While in Sections 4.1 and 4.2,when OA and CA0are used as the objective function to optimize the Gabor filter,the classification accuracy respectively reaches 99.00%and 100.00%.It proves the validity of optimized parameters of the Gabor filter,meaning the DSMFs will get a higher classification accuracy with its guidance.
Fig.11 is the classification results of the trained model for 800 new samples.
Fig.11 Classification results of SVM
Obviously,the results are very bad,especially a large number of samples whose category labels are“0”are classified as category “1”,i.e.the directions that are unsuitable for matching are considered suitable.This may result in serious consequence for geomagnetic navigation.The corresponding classification accuracy CA0,CA1,AA and OA are computed in Table 2.
In Table 2,if the Gabor filter’s parameters are not optimized,the classification accuracy of label“0”is only 47.43%,AA is 69.69%,OA is 77.88%,which are much lower than the ones with optimal parameters.Further analysis leads to the following conclusions:(i)Parameters of the Gabor filter have a significant influence on the DSMFs,which,in turn,affects the classification results of the direction navigability analysis.(ii)The direction navigability analysis model which takes CA0as the Gabor filter’s objective function can reduce the risk that the category “0”is incorrectly classified into category “1”.It meets the requirements of geomagnetic navigation better.
5.Conclusions
This paper mainly discusses the problems of extracting effective DSMFs and evaluating the direction navigability of the geomagnetic field based on the Gabor filter.Firstly,the parameters of the Gabor filter to be optimized are reduced by analyzing their mutual relationships.Then the classification accuracy is introduced as an objective function of the HPSO algorithm to find the optimal parameters.After that,the optimized Gabor filter is used to extract the DSMFs of the geomagnetic field.Together with the correct matching probability,the magnetic database for direction navigability analysis is established.Finally,an SVM is applied to build the navigability analysis model.Simulation experiments verify the effectiveness of the DSMFs and the direction navigability analysis method.It also suggests that the misclassification risk of direction navigability analysis can be reduced by taking CA0as the optimization objective.For further study,deep neural network can be taken into consideration to extract deeper features and simplify the procedure of navigability analysis.
[1]YAN M,ZHAO Y X,WU L G,et al.Navigability analysis of magnetic map with projecting pursuit-based selection method by using fire fl y algorithm.Neurocomputing,2015,159:288–297.
[2]ZHU Z L,YANG G L.Comprehensive evaluation method of geomagnetic map suitability analysis.Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology,2013,21(3):375–380.
[3]GUO C F,CAI H,VAN G H M.Feature extraction and geomagnetic matching.Journal of Navigation,2013,66(6):799–811.
[4]MART´INEZ J L,MANDOW A,REINA A,et al.Navigability analysis of natural terrains with fuzzy elevation maps from ground-based 3D range scans.Proc.of IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems,2013:1576–1581.
[5]VIPUL B A,RAVI K K,KIRUBAKARAN P S B.A Bayesian statistics approach for terrain based navigation and its terrain generation through second order Gauss-Markov process.International Journal of Engineering&Technical Research,2015,V4(4):367–379.
[6]BIAN H.Navigation for underwater vehicles using gray-scale histogram.Proc.of International Conference on Electronics and Information Engineering,2015:979420.
[7]ZHAO J H,WANG S P,WANG A X.Study on the selection of the geomagnetic adaptable matching area based on the geomagnetic co-occurrence matrix.Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2011,36(4):446–449.(in Chinese)
[8]WANG P,HU X P,WU M P.Matching suitability analysis for geomagnetic aided navigation based on an intelligent classiifcation method.Proc.of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers,Part G:Journal of Aerospace Engineering,2014,228(2):271–283.
[9]WANG P,HU X P,WU M P.A hierarchical decision-making scheme for directional matching suitability analysis in geomagnetic aided navigation.Proc.of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers Part G:Journal of Aerospace Engineering,2014,228(10):1815–1830.
[10]SONG X,LIU F,ZHANG Z,et al.2D Gabor filters-based steg analysis of content-adaptive JPEG steganography.Multimedia Tools&Applications,2016:1–29.
[11]DAUGMAN J G.Uncertainty relation for resolution in space,spatial frequency,and orientation optimized by two dimensional visual cortical filters.Journal of the Optical Society of America,1985,2(7):1160–1169.
[12]ARADHYA V N M,PAVITHRA M S.A comprehensive of transforms,Gabor filter and k-means clustering for text detection in images and video.Applied Computing&Informatics,2016,12(2):109–116.
[13]MAK K L,PENG P,YIU K C.Fabric defect detection using multi-level tuned-matched Gabor filters.Journal of Industrial and Management Optimization.2012,8(2):325–341.
[14]XIAO J,DUAN X S,QI X H,et al.Research on suitable matching area in geomagnetic navigation.Proc.of the 2nd International Conference on Advances in Mechanical Engineering and Industrial Informatics,2016:1513–1517.
[15]FAROKHIAN F,YANG C,DEMIREL H,et al.Automatic parameters selection of Gabor filters with the imperialism competitive algorithm with application to retinal vessel segmentation.Biocy bernetics&Biomedical Engineering,2017,37(1):246–254.
[16]LI J P,FU L Q.Parameter design of Gabor filter for feature extraction.Optics&Optoelectronic Technology,2010,8(3):79–83.(in Chinese)
Biographies

XIAO Jingwas born in 1989.She is a Ph.D.candidate at the Department of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Engineering in Army Engineering University.She received her master’s degree from the Ordnance Engineering College in 2014.Her current research interests are geomagnetic navigation and integrated navigation.
E-mail:xiao jing801@163.com

DUAN Xiushengwas born in 1970.He is a Ph.D.and a professor at the Department of Electronic and Optical Engineering in Army Engineering University.He received his master’s degree from Electronic Engineering College in 1996 and his doctor’s degree from Ordnance Engineering College in 2009.His current research interests include navigation,guidance and control.
E-mail:sjzdxsh@163.com

QI Xiaohuiwas born in 1962.She is a Ph.D.and a professor at the Department of Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Engineering in Army Engineering University.Her research interests cover flight control theory and application for unmanned aerial vehicles.E-mail:qi-xh@163.com

WANG Jianchenwas born in 1987.He is an engineer in the Government Representative Of fi ce of the Northwestern Polytechnical University.He respectively received his master’s degree in 2011 and doctor’s degree in 2015 from Ordnance Engineering College.His research interests are flight control theory and navigation of unmanned aerial vehicles.
E-mail:lichen197@163.com
 Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics2018年2期
Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics2018年2期
- Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics的其它文章
- Health evaluation method for degrading systems subject to dependent competing risks
- Remaining useful life prediction for a nonlinear multi-degradation system with public noise
- Multi-focus image fusion based on block matching in 3D transform domain
- Hybrid artificial bee colony algorithm with variable neighborhood search and memory mechanism
- An optimization method:hummingbirds optimization algorithm
- Integrated modeling of spacecraft relative motion dynamics using dual quaternion
