Rietveld re finement of powder X-ray diffraction,microstructural and mechanical studies of magnesium matrix composites processed by high energy ball milling
T.Ramkumar,M.Selvakumar,R.Vasanthsankar,A.S.Sathishkumar,P.Narayanasamy,G.Girija
aDepartment of Mechanical Engineering,Dr.Mahalingam College of Engineering and Technology,Pollachi 642003,India
bDepartment of Automobile Engineering,Dr.Mahalingam College of Engineering and Technology,Pollachi 642003,India
cDepartment of Mechanical Engineering,Sree Sowdambika College of Engineering,Aruppukottai 626134,India
dDepartment of Mechanical Engineering,Kamaraj College of Engineering and Technology,Virudhunagar 626001,India
Abstract This research reports the processing of magnesium matrix composites reinforced with silicon carbide(SiC)and aluminium oxide(Al2O3)using powder metallurgy technique through high energy milling.Samples of Mg-SiC and Mg-Al2O3composites subjected to high energy ball milling for different vol%of secondary particles 20,30 and 40%of SiC and Al2O3are studied by X-Ray diffraction technique.The rietveld method as implemented in the Fullprof program is applied in order to determine the quantities of the resulting crystalline phases and amorphous phases at each stage of the mechanical treatment.Microstructural examination is carried out using Scanning Electron Microscope(SEM).In addition,crystal structural analysis using appropriate size and strain models is performed in order to handle the distinctive anistrophy that is observed in convinced crystallographic directions for the magnesium composite.The results are furnished in terms of crystalline domains size enlargement of the magnesium composites phases upon prolonged milling duration and discussed in the light of up to date views and theories on crystal growth of nanocrystaline materials.The hardness of the composite samples is calculated by Vickers’s Hardness tester.Further,dry sling wear test and corrosion test are performed for the fabricated composites.Composite with 30%secondary particles incorporated magnesium composites exhibits better wear and corrosion resistance than the other composites.
Keywords:Rietveld re finement;X-ray diffraction;Crystal structure;Micro structure;Wear and corrosion.∗Corresponding author.
1.Introduction
Magnesium based composites are widely used in automotive sectors because it is light and ductile in nature,even though the intrinsic properties has been not sufficient for the specific applications[1].Several researchers have accomplished the work using magnesium based composites reinforcing with W,TiC etc.,but still the properties have not met out the requirements.The performance of moving parts in automotive sector mainly depends on friction and corrosion resistance[2-4];however,poor wear,friction and corrosion resistance has a major problem to its practical applications.Various methods are there to fabricate the magnesium based composites such as liquid methodology,solid methodology and infiltration processes.Among these techniques,powder metallurgy(P/M)is very prominent technique to fabricate the composites,because of its homogeneous dispersion of the secondary particles and clear net shape of the product[5-7].

Fig.1.(a)and(b)View of the Mg-SiC and Mg-Al203lattice where two cells are visualized orthorhombic original cell with space group of C2/m.
Crystal structure fortitude has been extensively used in some fields such as physics,material science and medicine and it is been developed into a specialized technology.The exist X-ray and neutron diffraction is necessitated for crystal structure determination that reveals the crystal components and internal atomic or molecular structure of a crystal[8].Precise determination of the crystal cell parameters is a significant step in the steps of crystal structure determination.The microstructural characterizations of these materials are of essential importance as it may have an important effect upon the mechanical properties.Powder diffraction is now one of the most extensively used techniques available to materials scientists for studying the structure and microstructure of crystalline solids.In 1969,Rietveld[9]proposed a full spectrum fitting method of computer simulation to analyze neutron diffraction data,which not only uses diffraction integral intensity data,but also uses the information of diffraction spectrum for getting the relevant information of powder material structure.This method is named as Rietveld method that discloses the whole pattern fitting based on powder diffraction and crystal structure[10].Microstructure features can strongly adapt diffraction line profile,leading to broadened and occasionally shifted or asymmetric diffraction lines.These features include finite crystalline size,extended defects such as crystal imperfection or micro strains in lattice parameter.
Till the present,there have been many kinds of re finement software to be used for crystal structure re finement such as Fullprof,DBWS and GSAS.However,when we use the refinement software is used,there exist some outstanding issues including a great number of manual interventions,time consuming and low efficiency.The reasons for this limitation are well known.Most programs re fine the crystal by a local minimization method for instance,the least square method[11].Therefore,the main difficulty is the choice of an appropriate initial approximation.On the other hand,powder X-ray diffraction(PXRD)has actively deployed for the purposes of microstructural analysis during last decades and especially while studying nano-sized materials.An intrinsic feature of the XRD line profile analysis originating from its physical grounds,which gives the information for the bulk properties of a powder or polycrystalline solids.Rietveld re finement provides information as for the crystal-chemical changes,phase transition and quality of phases as well as for certain microstructural characteristics of the investigated crystalline matter like the coherently diffracting domain sizes and the micro strain distribution[12].
This paper,presents two case studies of Mg composites reinforcing SiC and Al2O3secondary particles with different crystallographic characteristics have been studied using Fullprof software/Rietveld Re finement.To treat anisotropic size effects,the XRD peak broadening is modeled with linear combinations of spherical harmonics,which allow the calculation of the crystalline average size along each reciprocal lattice vector.Further,the microstructural characteristics of the fabricated samples are evaluated using scanning electron microscope(SEM).In addition,tribological and corrosion behavior are also analyzed to seek the best composition of the secondary particles.

Fig.2.SEM micrograph of(a)Mg-SiC and(b)Mg-Al2O3.
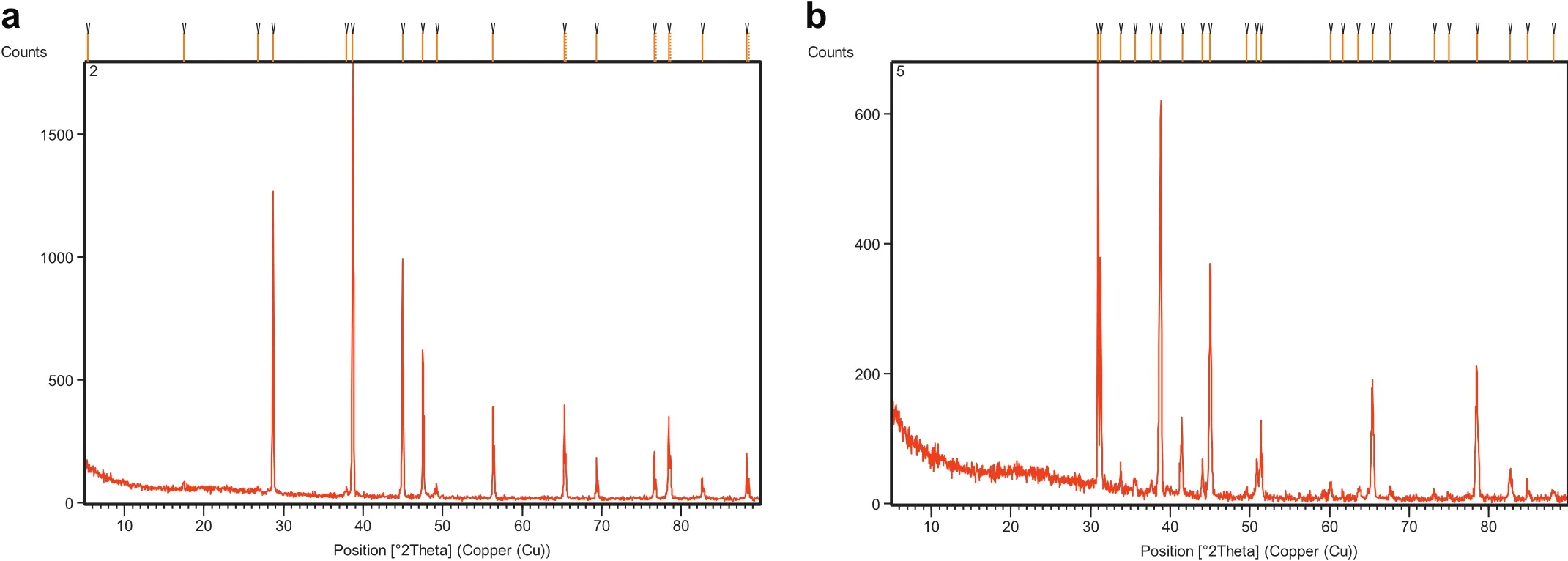
Fig.3.XRD pattern for(a)Mg-SiC and(b)Mg-Al2O3.
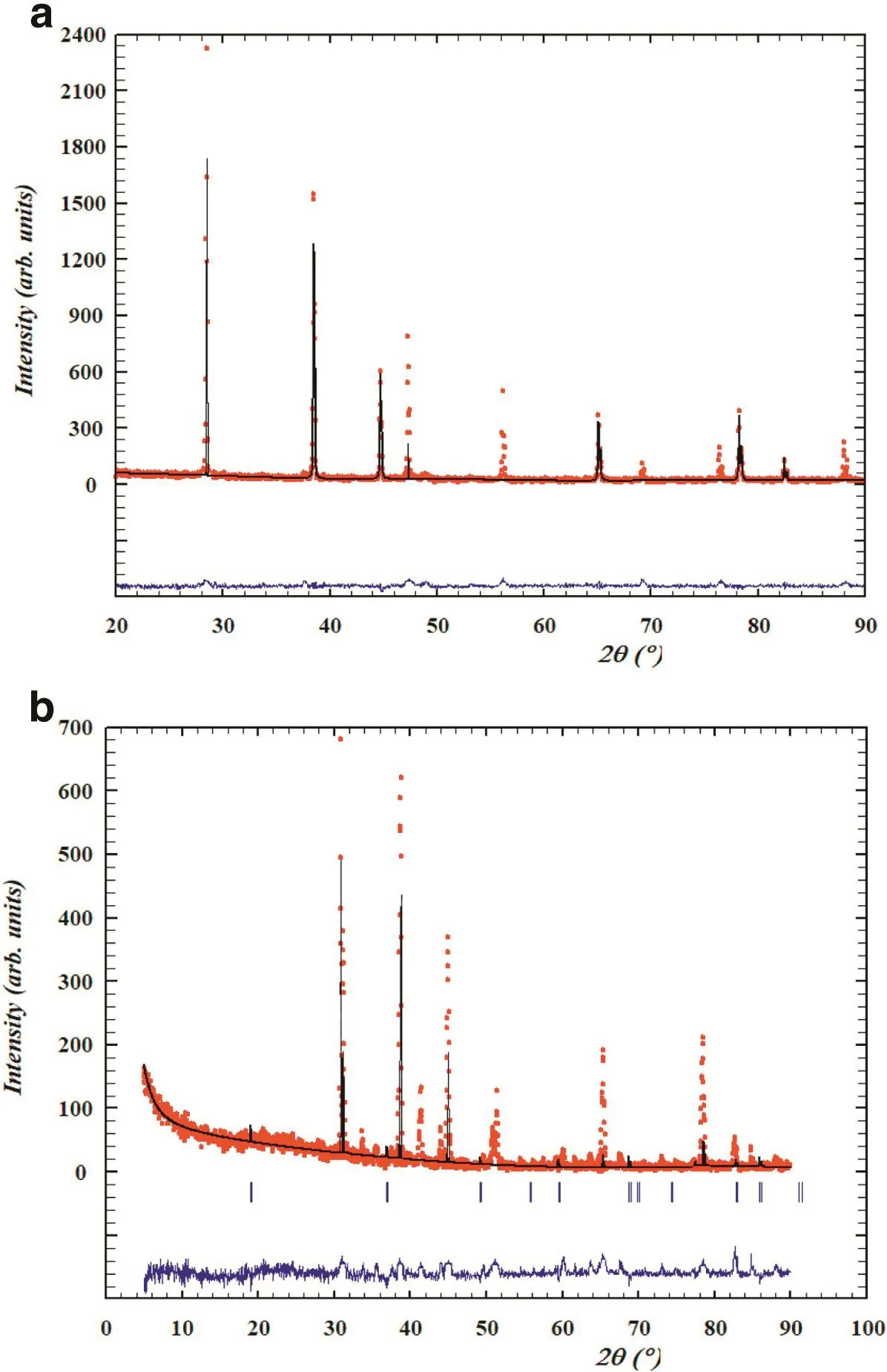
Fig.4.Experimental X-ray powder diffraction pattern(dotted curve)compared to the Rietveld-re fined profile(continuous line)for Mg-SiC and Mg-Al2O3using the space group of C2/m.
2.Experimental procedure
The elemental powders such as magnesium,silicon carbide and aluminium oxide are purchased from sigma Aldrich and Germany.The purity of the powders is checked and the test certificate is supplied by the supplier.Further,the secondary particles such as SiC and Al2O3are milled using planetary ball mill to reduce the size of the particles.The phase identification of the milled samples is established using XRD.The phase re finement and crystallography of the samples are determined using Fullprof software.Green compacts are prepared using Universal Testing Machine for a given load of 2.5 Gpa.Further,the samples are consolidated and coated with silica slurry and dried in the atmosphere for 12h.The samples were sintered in a vacuum furnace at an operating temperature of 480°C for a holding period of 1 h and the samples are subsequently cooled in the furnace till the room temperature was reached.The Vickers hardness is calculated for fabricated samples.Dry sliding wear test is conducted using pin on disc wear apparatus(DUCOM,Bangalore Type:TR-20LE-PHM-400)for various parameters such as applied load,sliding velocity and sliding distance.Corrosion behavior of the samples is resolute using electro-chemical workstation.
3.Results and discussion
3.1.Micro structural analysis
The powder X-ray diffraction recorded is in full agreement with that in Ref.[13].Mg-SiC and Mg-Al2O3is indexed with the C2/m space group.The super structure peaks in the range 2θ=0-80°indicate that the Si,C and Mg/Al,O and Mg atoms of the mixed layer are arranged following a“hydrogenated honeycomb”ordering scheme(see Fig.1).Rietveld re finement of Mg-SiC and Mg-Al2O3using the Fullprof pro-gram and the C2/m space group leads to re fined cell parameters with values a=4.0487˚A,b=4.0487˚A and c=4.0487˚A for Mg-SiC and a=3.8280˚A,b=3.8280˚A and c=3.8280˚A for Mg-Al2O3and it is shown in Fig.1(a)and(b).

Table 1 Re fined structural parameters for Mg-SiC and Mg-Al2O3composites.

Fig.5.Hardness profile of both Mg-SiC and Mg-Al2O3.
Fig.2 shows the SEM micrograph of Mg-SiC and Mg-Al2O3.From Fig.2,it reveals that the secondary particles has homogenously distributed in the matrix material.
3.2.Crystal structure refinemen
The crystal structure of magnesium composites has large hexagonal unit cell,contains 273 atoms in it and there are two equivalent sites for silicon and carbon/aluminium and oxygen.The researchers who have carried out the research carries have noticed the complexity of its crystal structure and the difficulties to obtain accurate crystal parameters by the conventional X-ray diffractometry,due to lower angular resolution[14-16].This makes the crystal structure of the magnesium composites,an intricate model for simulations of theoretical XRD patterns of samples.This is why during our investigations the fitting procedure has been carried out without re fining the atomic positions of the magnesium composites.The reason for this was that all attempts to re fine this phase crystal structure resulted in receiving physically unrealistic interatomic distances and angles for all the samples[17].Furthermore,the milling process would have been inevitably brought to numerous crystalline defects that would additionally complicate the re finement.In this research,re finement procedure is attempted for the Mg composite crystal structure for the milled samples of 40h.The crystal reliability is checked through the atoms dis. file created by Full Prof suite.

Fig.6.Wear rate of(a)and(b)Mg-SiC and(c)and(d)Mg-Al2O3for various loads.
Fig.3 shows the XRD results for Mg-SiC and Mg-Al2O3composites.The diffraction pattern revealed the successive crystallization of samples as observed and an increase in intensity and sharpness of peaks with the milling time.The reflection peaks are observed for SiC at 30-40°,which is ascribed to SiC and 35-40°ascribed to Al2O3.The crystalline size for most prominent peaks of composites has been calculated using Debye-Scherrer equation[18].

The crystalline size of SiC and Al2O3corresponding to most prominent peak,micro strain,average size and dislocation density for orthorhombic phase of magnesium composites are found to be 56nm and 67nm,respectively.
Fig.4(a)and(b)shows the rietveld re finement plots of Mg-SiC and Mg-Al2O3composites,respectively.The re finement of diffraction data has been carried out using Full Prof software.The initial values of cell parameters,space group and atom coordinates are taken from matching reference patterns calculated through crystallography open database(COD).Fourier series with twelve re finable coefficients and the profile sharp re finement is described by pseuso-voigt function.The pseuso-voigt function is chosen for peak shapes because it is the linear combination of Lorentzian and Gaussian function,and can be used to resolve strain and size contributions to peak broadening.The good re finement model requires reproducing matched peak position as well as intensities.It can be clearly visualized in Fig.4(a)and(b)that the observed and calculated pattern in good agreement.The goodness of fit for peak shape and peak position,structure and back ground is calculated in terms of profile R-factors and shown in Table 1.The values of R-factors are less than 10%of existing pattern and re fined pattern confirmed the goodness of re finement as reported by various researchers[19-23].
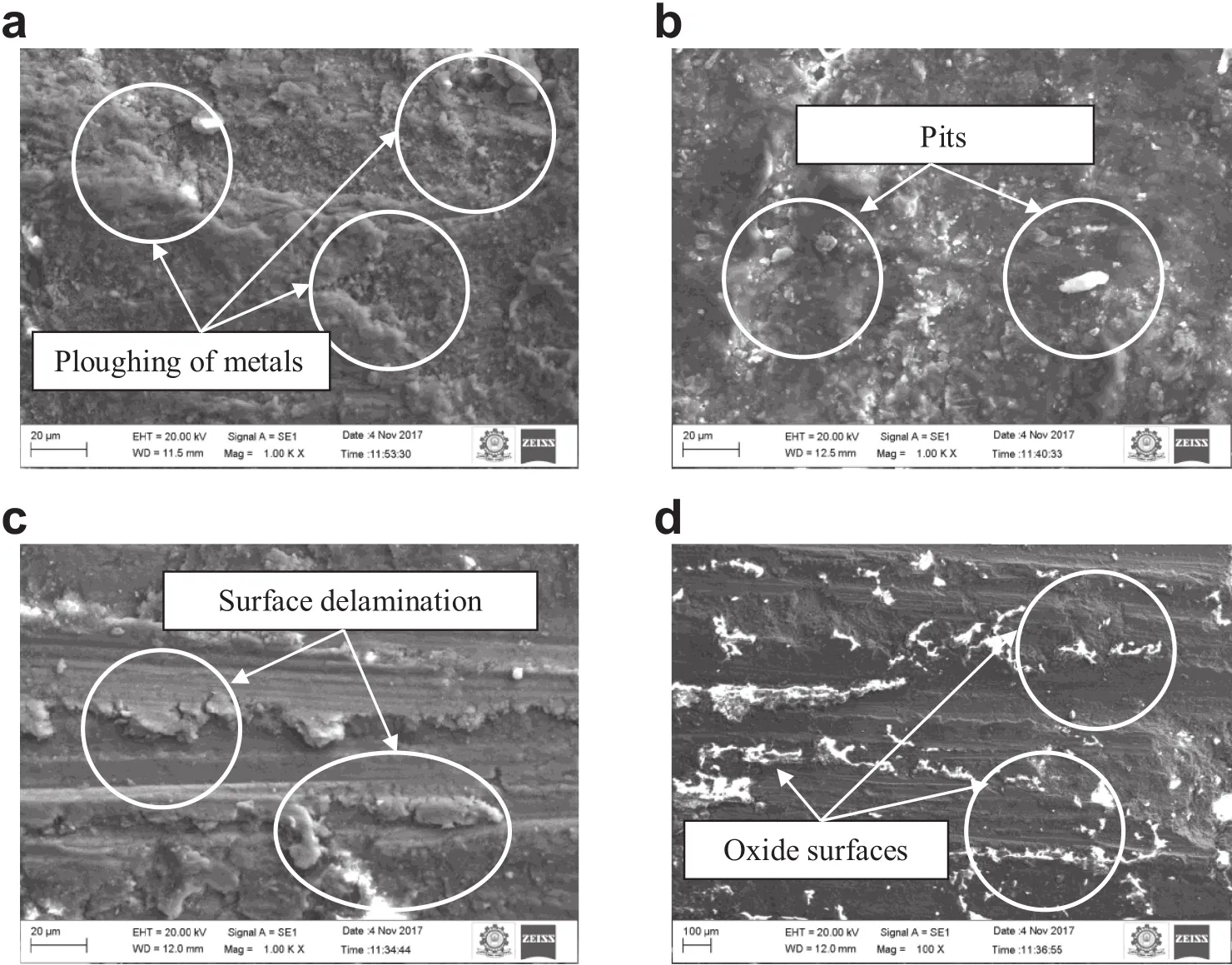
Fig.7.Worn surface of(a)and(b)Mg-SiC and(c)and(d)Mg-Al2 O3for various loads.
Magnesium composites crystalline is a Orthorhombic type structure that can be described as an hexagonal close packed structure of hydroxyl ions,with XY carbon packing and Al2O3occupying cubic interstices one plan out of two in Z positions(refer Fig.1).The XRD pattern of electro active suffers from a strong anisotropic diffraction peak broadening.
3.3.Hardness
Fig.5 shows the hardness of the fabricated samples.Fig.5 reveals the continuous improvement of hardness in addition to secondary particles in matrix.Further,the result shows that 30%(SiC and Al2O3)displays higher hardness.This can be attributed to the addition of ceramic particle that has been uniformly distributed in the matrix material.By adding the ceramic particle into the base material,the hardness has been significantly increased.Moreover,the hardness of the composites is nearly twice to that of the base material[24,25].It can be further deduced and the hardness of all the composites was significantly greater than the base material because of high volume fraction of the nano ceramic particles in the matrix.
3.4.Dry sliding wear properties
The dry sliding wear behavior of the prepared composites is evaluated using pin-on-disc wear testing machine.The disc is made up of EN 31 steel subjected to 60 HRC.The input parameters are selected based on the[26].The experiment is executed at an applied load of 10-30N with an increment of 5N and sliding velocity of 1m/s to 3m/s,with increment of 0.5m/s,respectively.The sliding distance and track diameter are kept constant for all the specimens.The experiment is conducted in room temperature.
Fig.6(a)-(b)and(c)-(d)shows the wear loss of all the fabricated samples.From the figure,it reveals that while increasing the load,the wear loss is also increases accordingly.During the initial phase of experiment the metal to metal contact is heavier because of the applied load and sliding velocity,which is observed in the graph as well as SEM micrographs(refer Fig.7(a)and(f)).While increasing the presence of ceramic content in the matrix,it is observed that a decrease in the wear loss,confirms the composite’s effect in wear property of the base material[27].If dispersion of ceramic in the matrix material gets increased,the base material will exhibit high strength at room temperature.Because of the fact that the hard asperities have been penetrated into the soft matrix material.
The SEM micrographs of the worn surface of the magnesium composites are shown in Fig.9.It has been clearly visualized by severe adhesive wear in the composite.Furthermore,it shows that ploughing of metals appears parallel to the sliding direction(refer Fig.9(a)).When the disc contacts the sample,the hard counter steel body abrades the fabricated specimen,so that the wear loss becomes high.The ploughing of metal is possible due to the direct metal contact between the specimen and steel counter disc;this is exerted by the hardened wear debris from the matrix material[27].The ceramic particle acts as a shielding that protects the matrix from the plastic deformation and foremost to the reduced micro ploughing and thus lower the wear rate of the composites.
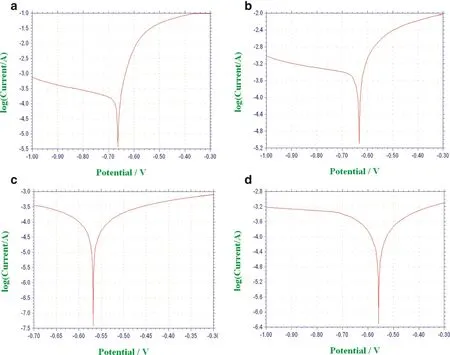
Fig.8.Tafel plot for(a)and(b)Mg-SiC and(c)and(d)Mg-Al2O3.
Hence,the wear resistance of the composites is better than that of the matrix.
3.5.Corrosion properties
The corrosion density(Icorr)and corrosion potential(Ecorr)is the superlative approach to investigate the feasibility of the composite against corrosion.In this analysis,corrosion studies are performed using the specimens of size 10×10×10mm in neutral chloride(3.5%Nacl)solution at 35°C.The specimens are placed in a te flon holder,with a 10mm diameter window exposed to the solution.The surface of the specimens is polished and degreased with acetone before use.Electrochemical studies are implemented out in a conservative three electrode cell assembly.The working electrode is Mg composite specimen surface.The saturated calomel electrode(SCE)and Cu are used as reference and counter electrodes,respectively[28].The reproducibility of data is censured by repeating the tests for two times.The surface integrity of the corroded samples is analyzed by Scanning Electron microscope(SEM).
Based on the examination of current density,(Mg-30%SiC and Al2O3)exhibits lower corrosion rate compared to the composites processed high energy milling.It is apparent that the high corrosion rate is perceived for the composite(Mg-30%SiC and Al2O3).Hardness is the one of the significant factors influencing the corrosion.There is a general trend that corrosion resistance increases as the hardness increases.High hardened processed composites(Mg-30%SiC and Al2O3)lead to the enhancement of corrosion resistance.The curves of the Mg-30%SiC and Al2O3composites are similar to magnesium,in a manner that the passivation of the latter lies at-0.5V.The surface integrity of the corroded samples is shown in Fig.8(a)-(d).There should not be any noteworthy attack by NaCl solution found on the magnesium matrix composites[29].Only a slight corrosion is observed on the surface as depicted in Fig.9(a)-(d).Large pits and small craters are scattered across the matrix,which confirms that the corroded zone is well defined by porosity.Few small pits and pores are observed in the corroded surfaces of 30%secondary particles reinforced composites as shown in Fig.9(b)and(d).This could be attributed to the greater corrosion resistance compared to the other composites[30-34].

Fig.9.Corrded surfaces for(a)and(b)Mg-SiC and(c)and(d)Mg-Al2O3.
The oxidation develops with time according to a parabolic law in nearly all composite interfaces.In this region,crack initiation is due to the thermally activated process and ions pass through the oxide film.Large stresses,either compressive or tensile,may often build up in oxide films and lead to breakaway on a fine scale,which prevent the development of extensive parabolic and the oxidation assumes an approximately linear rate or even faster.Fig.9(a)-(d)clearly reveals the intergranular corrosion and its association with the grain boundaries to undergo localized anodic attack[35].
4.Conclusion
A powder metallurgy route is developed to fabricate Mg-SiC and Mg-Al2O3composites with average crystalline size in nano meter range using high energy ball milling.The XRD and rietveld results incorrigible with the development of orthorhombic phase of magnesium composites.The values of rietveld profile parameter such as Rp,Rwp,Rexpand χ2are less than 10%in that way it indicates the goodness of rietveld analysis.The hardness result reveals that 30%of SiC and Al2O3afford higher hardness compared to the other composites.Increasing the secondary particles in the magnesium matrix has been tailored in the range of 30vol%reduces the wear and corrosion.
 Journal of Magnesium and Alloys2018年4期
Journal of Magnesium and Alloys2018年4期
- Journal of Magnesium and Alloys的其它文章
- Review on friction stir welding of magnesium alloys
- Effect of Si addition on microstructure and wear properties of Mg-Sn as-cast alloys
- Atomistic calculations of surface and interfacial energies of Mg17Al12-Mg system
- Effect of process parameters on depth of penetration and topography of AZ91 magnesium alloy in abrasive water jet cutting
- Corrosion protection of AZ91D magnesium alloy by acerium-molybdenum coating-The effect of citric acid as an additive
- The corrosion behavior and mechanical property of the Mg-7Y-xNd ternary alloys
