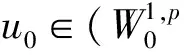RN上一类非线性Schrödinger-Kirchhoff型方程非平凡解的存在性和多重性
惠艳梅,郭祖记
(太原理工大学 数学学院,太原 030024)
1 主要结果
本文主要研究Schrödinger-Kirchhoff型问题
(P)

由于Kirchhoff型问题的重要性,近年来,很多学者研究了如下Kirchhoff型问题
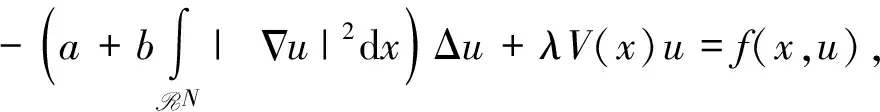
非平凡解的存在性[1-6]。最近文献[7]又研究了非线性项f具有次临界增长的Schrödinger-Kirchhoff型问题
(1)
非平凡解的存在性和多重性。本文受此启发,主要将问题(1)中p=2的情形推广到任意p的情况。从文中可以看出,这种推广并不是平凡的,需要克服许多困难,例如问题(P)的能量泛函满足(PS)条件的证明。

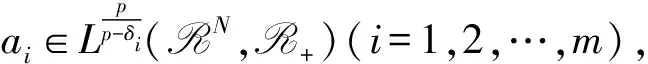
F2) 存在开集Ω⊂RN,常数ξ,η>0,k∈(1,p)使得对任意的(x,t)∈Ω×[-ξ,ξ],有
F(x,t)≥η|t|k.
F3) 对任意的(x,t)∈RN×R,有f(x,-t)=-f(x,t).
得到如下主要结论:
定理1 若条件V),F1),F2)成立,则问题(P)至少存在一个非平凡解。
定理2 若条件V),F1)-F3)成立,则问题(P)存在无穷多个非平凡解。
2 基本引理
对任意的1≤s≤+∞,|·|s表示通常的Lebesgue空间Ls(RN)上的范数。本文工作空间为
在E中引入范数
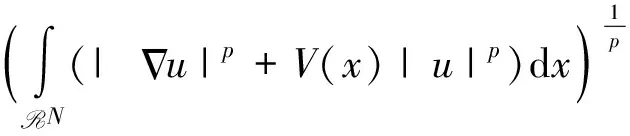
可以证明问题(P)所对应的能量泛函是
(2)
并且J∈C1(E,R).从而由式(2)定义的泛函J的临界点即为方程(P)在E中的解.本文中用C和Cp表示一些正常数。
下面的引理是证明本文主要结果的理论依据。

∑={A∈E
Kc={u∈E:J(u)=c,J'(u)=0},Jc={u∈E:J(u)≤c};
∑n={A∈E:γ(A)≥n};
其中亏格
γ(A)=inf{n∈N:∃φ∈C(A,RN
则有下面的结论。
引理2[9]J∈C1(E,N)是偶泛函,满足(PS)条件,对任意的n∈R,
1) 如果∑n≠Ø,cn∈R,那么cn是J的一个临界值。
2) 如果存在r∈N,使得cn=cn+1=…=cn+r=c∈R且c≠J(0),那么γ(Kc)≥r+1.
引理3 假设条件V),F1)成立,则J下方有界且满足(PS)条件。
证明:1) 证明J下方有界。由F1)及Hölder不等式可得

(3)
由于1<δi 2) 证明J满足(PS)条件。令{un}是E中的(PS)序列,即当n→+∞时,J(un)→c,J'(un)→0.由式(3)可知,{un}有界,于是对于{un}的某个子列,仍记为{un},存在u0∈E,使得 (4) ‖un‖≤M,‖u0‖≤M. (5) 由J'(un)→0及式(4)可得 (6) 由条件F1)知,对任意ε>0的,取ρ>0可得 (7) 由条件F1),式(6),式(7),Hölder不等式及Sobolev嵌入定理可得 (8) 由式(4)知,存在{un}的某个子列,仍记为{un}以及非负可测函数U∈Lp(Bρ),使得当|x|≤ρ时,有|un|p,|u0|p≤U在Bρ(0)上几乎处处成立。由条件F1)有 (9) 由式(9)及Lebesgue控制收敛定理可知 (10) 从而由式(4),式(8),式(10)及Hölder不等式有 (11) 由式(4)知 V(x)|u0|p-2u0(un-u0))dx=o(1),n→+∞ . (12) 对任意的ξ,η∈RN,由不等式[10] (13) 知存在正常数Cp使得 (14) 且 (15) 从而由式(6),式(11),式(12),式(14)及式(15)可知 所以, (16) 由1 定理2的证明由引理3得到J∈C1(E,R)下方有界且满足(PS)条件。由F3)及式(2)知,J(0)=0且J是偶泛函。现在证明对任意的n∈N,存在ε>0使得 γ(J-ε)≥n. (17) 对任意的n∈N,取n个互不相交的开集Ωi使得 对每个i∈{1,2,…,n},取u=∑ni=1λiui. (18) 则有 (19) 且 (20) 因为有限维范数空间En中所有的范数都等价,因此存在常数C>0使得对任意的u∈En,有 C‖u‖≤|u|k. (21) 由条件F2),式(19)-式(21),对任意的u∈Sn,可知 (22) 由式(22)可知,对充分小的t>0,存在ε>0,δ>0,使得对任意的u∈Sn,有 J(δu)<-ε. (23) 令 (24) [1] CHENG B,WU X.Existence results of positive solutions of Kirchhoff type problems [J].Nonlinear Analysis:Theory,Methods and Applications,2009,71(10):4883-4892. [2] WU X.Existence of nontrivial solutions and high energy solutions for Schrödinger-Kirchhoff-type equations in RN[J].Nonlinear Anal Real World Appl,2011,12(2):1278-1287. [3] HE X M,ZOU W M.Existence and concentration behavior of positive solutions for a Kirchhoff equation in R3[J].Journal of Differential Equations,2012,252(2):1813-1834. [4] LIU W,HE X.Multiplicity of high energy solutions for superlinear Kirchhoff equations[J].Journal of Applied Mathematics & Computing,2012,39(1/2):473-487. [5] SUN J,WU T.Ground state solutions for an indefinite Kirchhoff type problem with steep potential well[J].J Differential Equations,2014,256(4):1771-1792. [6] WU Y,LIU S.Existence and multiplicity of solutions for asymptotically linear Schrödinger-Kirchhoff equations[J].Nonlinear Analysis Real World Applications,2015(26):191-198. [7] CHEN H,LIU H,XU L.Existence and multiplicity of solutions for nonlinear Schrödinger-Kirchhoff-type equations[J].Korean J Math Soc,2016,53(1):201-215. [8] MAWHIN J,WILLEM M.Critical point theory and Hamiltonian systems[J].Appl Math Sci,1989,74(2):339-359. [9] SALVARORE A.Homoclinic orbits for a special class of nonautonomous Hamiltonian systems[J].Nonlinear Analysis Theory Method & Applications,1997,30(8):4849-4857. [10] JULIO F,CORRA S A,FIGUEIREDO G M.On an elliptic equation of p-Kirchhoff type via variational methods[J].Bulletin of the Australian Mathematical Society,2006,74(2):263-277. [11] RABINOWITZ P.Minimax methods in critical point theory with applications to differential equations[C]∥AMS.CBMS Regional Conference Series in Mathernatics.Providence:AMS,1986,65:100.





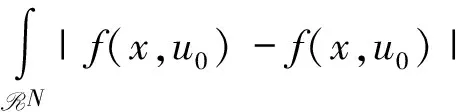
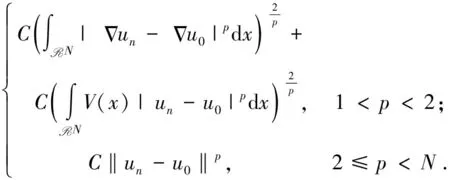


3 主要结果的证明