超敏肌钙蛋白I联合GRACE2.0评分对ACS患者近期死亡风险的预测价值
麦 超,简华刚
(1.川北医学院附属医院急诊科,四川南充 637000;2.重庆医科大学附属第二医院急救部 400010)
论著·临床研究
超敏肌钙蛋白I联合GRACE2.0评分对ACS患者近期死亡风险的预测价值
麦 超1,简华刚2△
(1.川北医学院附属医院急诊科,四川南充 637000;2.重庆医科大学附属第二医院急救部 400010)
目的评估入院时超敏肌钙蛋白I(hs-TnI) 联合全球急性冠状动脉事件注册(GRACE)2.0评分在急性冠状动脉综合征(ACS)患者近期死亡风险预测中的价值。方法回顾性地分析川北医学院附属医院2015年12月至2016年12月收治的347例ACS患者入院时的hs-TnI水平和GRACE2.0评分,随访观察hs-TnI和GRACE2.0评分高低对ACS患者近期(30 d)心血管疾病病死率的影响,并应用Kapian-Meier生存曲线分析hs-TnI和GRACE2.0评分对ACS患者近期心血管病死率的影响。结果死亡组hs-TnI平均值[(7.5±5.6)μg/L]明显高于存活组[(1.2±2.9)μg/L],P<0.01,ACS患者近期心血管病死率与hs-TnI呈明显正相关(P<0.01)。Kapian-Meier生存曲线分析hs-TnI对ACS患者近期心血管病死率影响,hs-TnI>0.014 μg/L者近期预后明显较差(Log rank 62.81,P<0.01);GRACE2.0评分积分与ACS患者30 d心血管病死率呈明显的正相关(P<0.01),随着CRACE危险评分的增加,极高危ACS患者近期生存率明显降低(Log rank 116.56,P<0.01)。而hs-TnI的生存曲线下面积(AUC)为0.079(95%CI:0.75~0.83,P<0.01),GRACE2.0评分AUC为0.81(95%CI:0.79~0.84,P<0.01)。二者比较,GRACE2.0风险评分预测价值较hs-TnI稍高。hs-TnI与GRACE风险评分联合可以提高预测ACS患者近期心血管病死率的价值[AUC=0.84(0.81~0.91)]。结论hs-TnI联合GRACE2.0评分在ACS患者近期心血管死亡风险具有重要预测价值。
肌钙蛋白I;全球急性冠状动脉事件注册2.0;急性冠状动脉综合征;死亡率
及时、准确地对急性冠状动脉综合征(acut coronary sundrome,ACS)患者进行风险评估,对提高医疗质量,减低死亡风险,具有重要参考价值[1-3]。全球急性冠状动脉事件注册(GRACE)、心肌梗死溶栓(TIMI)评分是最有价值,临床最常用的评估工具,被国内外权威指南推荐使用[3-5]。但是既往的GRACE和TIMI评估系统有一定缺点,因此,有最新版的GRACE2.0 应用于临床。目前的研究认为超敏肌钙蛋白I(hs-TnI)是诊断心肌损伤敏感性和特异性最好的指标,在ACS早期诊断和风险评估中较普通肌钙蛋白T及肌红蛋白、肌酸激酶(CK)等生化指标具有显著优势[6-9]。hs-TnI联合GRACE2.0评分是否能提高ACS患者近期死亡风险预测价值,目前尚不明确。本研究的目的拟通过回顾性临床研究来评估hs-TnI联合GRACE2.0评分在ACS死亡风险预测中的价值。
1 资料与方法
1.1一般资料 选择2015年12月至2016年12月川北医学院附属医院急诊收治入院的ACS患者,主要包括不稳定型心绞痛(UA)、非 ST 段抬高型心肌梗死(NSTEMI)、ST 段抬高型心肌梗死(STEMI)3类患者。诊断标准符合我国《2015版急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死诊断和治疗指南》[10]和《2015 ESC非持续性ST段抬高型急性冠状动脉综合征管理指南》[11]。排除合并急性呼吸窘迫综合征(ARDS)、重症感染、主动脉夹层、急性肺栓塞、严重机械性并发症、心肌炎、慢性阻塞性肺疾病急性加重(AECOPD)患者等。本研究共纳入ACS患者356例,失访者9例,失访率约为2.5%。最终本研究共纳入ACS患者347例,其中男189例,女158例,年龄36~89岁,平均(66±9)岁。UA 89 例,占25.6%; NSTEMI 138例,占39.8%;STEMI 120例,占34.6%。平均随访(28±6)d,患者近期由心血管疾病导致死亡33例,心血管疾病病死率为9.5%。采用再灌注治疗45例(PCI 39例,溶栓6例),总再灌注治疗率为13.0%;过往有心肌梗死21例(6.1%),高血压139例(40.1%),糖尿病93例(26.8%),吸烟史76例(21.9%)。
1.2方法 应用EpiData临床研究软件记录患者的原始病例资料,包括姓名、性别、年龄、电话等一般情况、既往病史(高血压、糖尿病、冠心病、高脂血症、肾病等)及相关个人史、入院时基本生命体征、入院检查结果(12导联心电图、hs-TnI)等。将GRACE2.0评分APP软件安装于手机中,计算每例患者的院内评分,评分0.7%~91%,主要包括年龄、心率、收缩压、肌酐、ST段变化、肌钙蛋白升高、入院时心脏骤停等项目,随访时间是从患者入院至住院第30天。主要观察终点为患者30 d心血管疾病病死率。
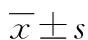
2 结 果
2.1入院时hs-TnI对ACS患者近期心血管疾病病死率的影响 本研究纳入的所有患者入院即刻检测hs-TnI平均值为(1.80±3.7)μg/L,死亡组hs-TnI平均值[(7.5±5.6)μg/L]明显高于存活组[(1.2±2.9)μg/L],差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。本研究死亡的33例患者中, ACS患者近期心血管疾病病死率与hs-TnI呈明显正相关(P<0.01)。进一步应用Kapian-Meier生存曲线分析hs-TnI对ACS患者近期心血管疾病病死率影响,hs-TnI>0.014 μg/L者近期预后明显较差(Log rank 62.81,P<0.01),见图1。
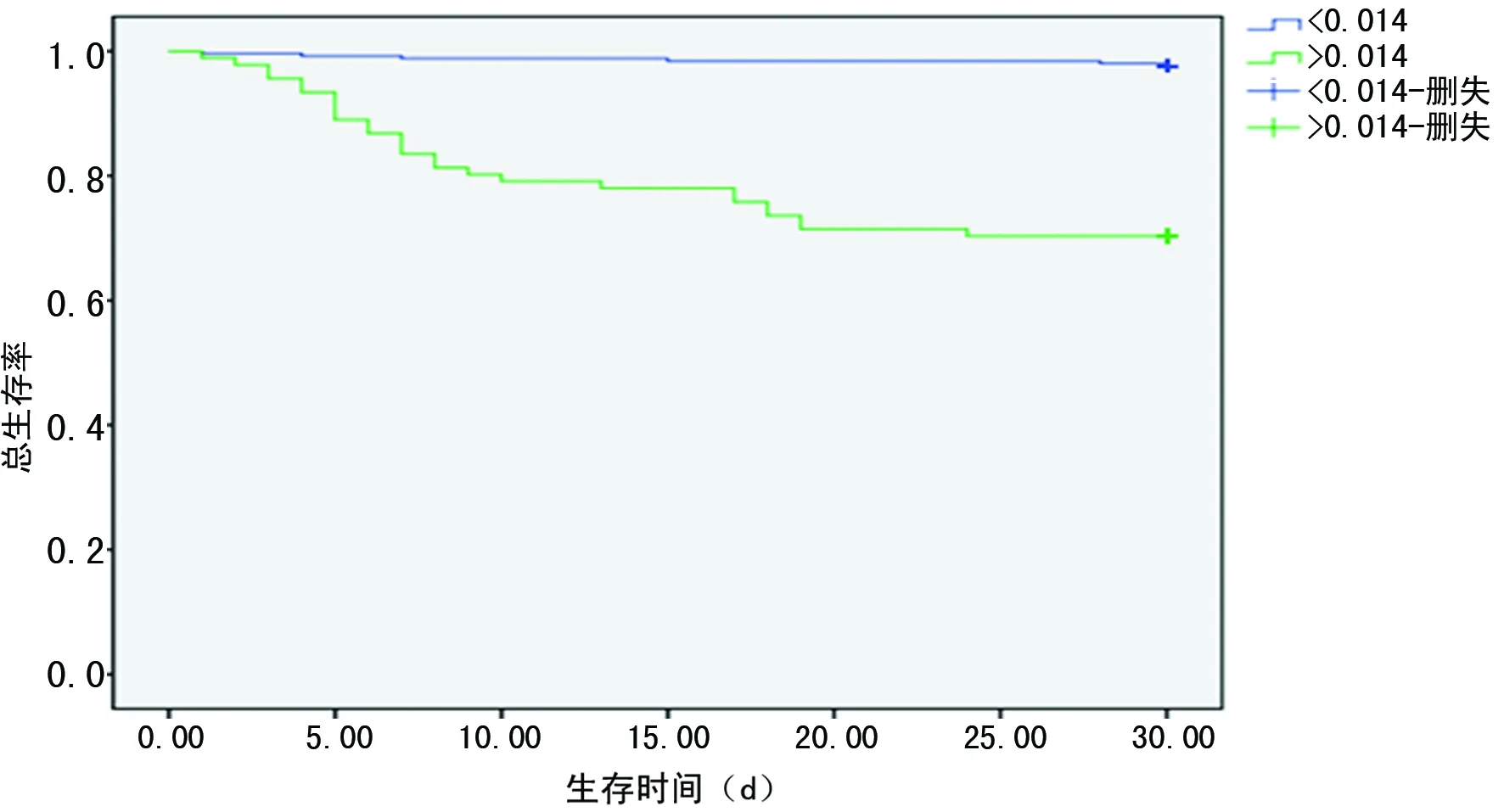
图1 Kapian-Meier生存曲线分析hs-TnI与ACS患者近期病死率的关系
2.2GRACE2.0评分对ACS患者30 d心血管病死率的影响 利用Kapian Meier生存曲线对GRACE2.0评分进行分析评估。将GRACE分为4级:近期病死率小于10%为1级,10%~20%为2级,>20%~40%为3级,>40%为4级,如图2所示, GRACE2.0评分与ACS患者30 d心血管病死率呈明显正相关,极高危ACS患者近期生存率明显降低(Log rank 116.56,P<0.01)。而hs-TnI的生存曲线下面积(AUC)为0.079(95%CI:0.75~0.83,P<0.01),GRACE2.0危险积分AUC为0.81(95%CI:0.79~0.84,P<0.01)。二者比较,GRACE2.0风险积分较hs-TnI预测价值稍高。hs-TnI与GRACE2.0风险评分联合可以提高预测ACS患者近期心血管疾病病死率的价值[AUC=0.84(0.81~0.91]。

图2 Kapian-Meier生存曲线分析GRACE2.0危险积分与ACS患者近期病死率的关系
2.3Cox回归多因素分析hs-TnI及GRACE2.0评分在ACS患者近期心血管疾病死亡风险评估中的价值 经过年龄、hs-TnI、病史,左室射血分数(LVEF)等多因素校正后,30 d心血管疾病病死率多变量Cox回归模型表明,GRACE2.0评分是ACS患者近期心血管疾病病死率的独立危险因素,见表2。Cox回归模型多因素分析表明:hs-TnI及GRACE2.0评分对ACS患者近期心血管疾病死亡风险具有重要预测价值。

表2 ACS患者30 d心血管病死率Cox回归模型
3 讨 论
ACS是冠状动脉内不稳定的粥样斑块破裂引起急性血栓形成所致的急性缺血综合征,发病急,病情变化快,临床表现复杂,病情严重程度相差很大,病死率高,是急诊常见的急危重症。对ACS患者进行危险分层对于急诊医师意义重大,可以帮助急诊医师辨别患者是否需要进行冠状动脉造影等特殊检查,是否需要专科医师(心内医师和介入医师)立即协助,有利于更准确了解病情和预后,有助于早期正确选择治疗策略,制订个体化的治疗方案等。GRACE评分是基于全球ACS事件注册研究的基础上发展而来,被认为是最有效的预测和评估ACS患者病情危险程度和预后的评分体系,它的变量通过常规的临床评估和实验室检查就可以得到,用手机在网上下载GRACE评分的APP就可以方便地在床旁使用,相对于其他的ACS危险评分系统,它的主要缺陷是太复杂,因此,简化版的GRACE2.0应运而生。有研究验证了GRACE2.0评分可以很好地区分高危和低危患者,预测住院期间病死率和心血管事件,对于远期病死率也有很好的预测能力,但是它也有一些缺陷,如没有考虑种族的差别,没有纳入对ACS患者有明显影响的很多指标如肌钙蛋白、反映斑块稳定的炎性标志物、冠状动脉造影结果等,导致其结果有一定的偏差[12]。血清hs-TnI是反映心肌损伤的一个敏感、可靠且实用的生化指标,被认为是目前临床敏感性和特异性最好的心肌损伤标志物,可以作为心肌梗死疾病的独立性诊断指标,hs-TnI的敏感性是传统肌钙蛋白检测的100倍,高敏感性能够探测更低浓度的血清肌钙蛋白水平,可以比通常的肌钙蛋白检测试剂更早地诊断出AMI,并可以对轻微心肌损伤作出诊断,hs-TnI水平的高低还可反映AMI患者缺血的严重程度,有助于对ACS患者进行危险因素分层,有利于对ACS患者进行早期诊断和及时救治[13-15],但是在合并心肌炎、肌炎、急性肺栓塞、慢性肾功能不全等疾病时对诊断的特异性有影响。
ACS的发生发展是一个复杂的病理生理过程,单一指标并不能完全准确地评估ACS的近期预后,国内外的许多研究发现多个指标联合使用可以明显提高ACS患者的预后评估[16-18]。本研究发现ACS患者近期心血管疾病病死率与hs-TnI呈明显正相关(P<0.01),应用Kapian-Meier生存曲线分析hs-TnI对ACS患者近期心血管疾病病死率影响,hs-TnI>0.014 μg/L者近期预后明显较差(Log rank 62.81,P<0.01)。GRACE2.0评分与ACS患者30 d心血管病死率呈明显的正相关,极高危ACS患者近期生存率明显降低(Log rank 116.56,P<0.01)。而hs-TnI的AUC为0.079(95%CI:0.75~0.83,P<0.01),GRACE2.0评分AUC为0.81(95%CI:0.79~0.84,P<0.01)。二者比较,GRACE2.0积分较hs-TnI预测价值稍高。hs-TnI与GRACE2.0风险评分联合可以提高预测ACS患者近期心血管病死率的价值[AUC=0.84(0.81~0.91)]。
综上所述,hs-TnI及GRACE2.0评分在ACS患者近期心血管死亡风险具有重要预测价值,在急诊临床工作中联合使用hs-TnI及GRACE2.0评分可以更好地评估 ACS患者的病情与预后,有助于指导急诊医师的临床决策。但是本研究为回顾性研究,样本量较小,随访时间短,二者的联合应用是否能形成一个新的评分系统尚需更大规模的、多中心的研究论证。
[1]Antman EM,Cohen M,Bernink PJ,et al.The TIMI risk score for unstable angina/non-ST elevation MI:a method for prognostication and therapeutic decision making[J].JAMA,2000,284(7):835.
[2]Boersma E,Pieper KS,Steyerberg EW,et al.Predictors of outcome in patients with acute coronary syndromes without persistent ST-segment elevation.Results from an international trial of 9 461 patients.The PURSUIT Investigators[J].Circulation,2000,101(22):2557-2567.
[3]Granger CB,Goldberg RJ,Dabbous O,et al.Predictors of hospital mortality in the global registry of acute coronary events[J].Arch Intern Med,2004,13(2):2345-2353.
[4]Tang EW,Wong CK,Herbison P,et al.Global Registry of acute coronary Events(GRACE) hospital diseharge risk score accurately prediets long-term mortality post acute coronary syndrome[J].AM Heart J,2007,153(1):29-35.
[5]Hochholzer W,Reichlin T,Twerenbold R,et al.Incremental value of high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T for risk prediction in patients with suspected acute myocardial infarction [J].Clin Chem,2011,57(9):1318-1326.
[6]Haaf P,Drexler B,Reichlin T,et al.High-sensitivity cardiac troponin in the distinction of acute cardiac noncoronary artery disease [J].Circulation,2012,126(1):31-40.
[7]Khan DA,Sharif MS,Khan FA.Diagnostic performance of high-sensitivity troponin T,myelopeoxidase,and pregnancy-associated plasma protein A assays for triage of patients with acute myocardial infarction[J].Korean J Lab Med,2011,31(3):172-178.
[8]Reichlin T,Irfan A,Twerenbold R,et al.Utility of absolute and relative changes ai cardiac troponin concentrations in the early diagnosis of acute myocardial infarction[J].Circulation,2011,124(2):136-145.
[9]Hochholzer W,Reichlin T,Twerenbold R,et al.Incremental value of high-sensetivity cardiac troponin T for risk prediction in patients with suspected acute myocardial infarction[J].Clinchem,2011,57(9):1318-1326.
[10]中华医学会心血管病学分会,中华心血管病杂志编辑委员会.急性ST段抬高型心肌梗死诊断和治疗指南[J].中华心血管病杂志,2010,38(8):675-690.
[11]中华医学会心血管病学分会,中华心血管病杂志编辑委员会.不稳定性心绞痛和非ST段抬高心肌梗死诊断与治疗指南[J].中华心血管病杂志,2007,35(4):295-304.
[12]Huang W,Fitzgerald G,Goldberg RJ,et al.Performance of the GRACE risk score 2.0 simplified algorithm for predicting 1-year death after hospitalization for an acute coronary syndrome in a contemporary multiracial cohort[J].Am J Cardiol,2016,118(8):1105-1110.
[13]Kavsak PA,Newman AM,Lustig V,et al.Long-term health outcomes associated with detectable troponin I concentrations[J].Clin Chem,2007,53(2):220-227.
[14]Melanson SE, Morrow DA, Jarolim P. Earlier detection of myocardial injury in a preliminary evaluation using a new troponin I assay with improved sensitivity[J]. Am J Clin Pathol,2007,128(2):282-286.
[15]Apple FS,Smith SW,Pearce LA,et al. Use of the centaur TnI-ultra assay for detection of myocardial infarction and adverse events in patients presenting with symptoms suggestive of acute coronary syndrome[J].Clin Chem,2008,54(4):723-728.
[16]Klingenberg R,Aghlmandi S,Rber L,et al.Improved risk stratification of patients with acute coronary syndromes using a combination of hsTnT,NT-proBNP and hsCRP with the GRACE score[J].Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care,2016:2048872616684678.
[17]Widera C,Pencina MJ,Bobadilla M,et al.Incremental prognostic value of biomarkers beyond the GRACE(Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events) score and high-sensitivity cardiac troponin T in non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome[J].Clin Chem,2013,59(10):1497.
[18]Gravning J,Smedsrud MK,Omland T,et al.Sensitive troponin assays and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide in acute coronary syndrome:prediction of significant coronary lesions and long-term prognosis[J].AM Heart J,2013,165(5):716-724.
Valueofhs-TnIcombinedwithGRACE2.0scoreinpredictingshorttermdeathriskinpatientswithACS
MaiChao1,JianHuagang1△
(1.DepartmentofEmergency,AffiliatedHospitalofNorthSichuanMedicalCollege,Nanchong,Sichuan637000,China;2.DepartmentofEmergency,SecondAffiliatedHospitalofChongqingMedicalUniversity,Chongqing400010,China)
ObjectiveTo evaluate the value of high sensitive troponin I (hs-TnI) combined with the Global Registry of Acute Coronary Events (GRACE) 2.0 score in the prediction of death risk in the patients with acute coronary syndrome(ACS).MethodsThe hs-TnI levels and GRACE2.0 scores at admission in 347 ACS patients treated in the hospital from December 2015 to December 2016 were retrospectively analyzed.The follow up was performed for observing the effect of hs-TnI level and GRACE2.0 score on the short term(30 d) mortality rate of cardiovascular diseases.And the Kapian-Meier survival curve analysis was also used to analyze the effects of hs-TnI level and GRACE2.0 score on the short term mortality rate of cardiovascular diseases.ResultsIn this study,the average value of hs-TnI level in the death group was (7.5±5.6)μg/L,which was significantly higher than (1.2±2.9)μg/L in the survival group (P<0.01).The short term cardiovascular morality rate in ACS patients was positively correlated with the hs-TnI level (P<0.01).The effect of hs-TnI level on short term cardiovascular morality rate in ACS patients was analyzed by the Kapian-Meier survival curve,the patients with hs-TnI >0.014 μg/L had significantly poor short term prognosis(Log rank 62.81,P<0.01);the GRACE2.0 score showed positive correlation with the 30 d cardiovascular morality in ACS patients(P<0.01),the short term survival rate in the patients with extremely high risk ACS was significantly decreased(Log rank 116.56,P<0.001).But the area under the survival curve(AUC) of hs-TnI was 0.079(95%CI:0.75-0.83,P<0.01),andAUCof GRACE2.0 score was 0.81(95%CI:0.79-0.84,P<0.01).In the comparison between them,the predictive value of GRACE2.0 risk score was slightly higher than that of hs-TnI.Therefore,the combination of hs-TnI and GRACE risk score could increase the value for predicting recent cardiovascular morality in ACS patients[AUC=0.84(0.81-0.91)].Conclusionhs-TnI combined with GRACE2.0 score has an important prediction value in short term cardiovascular death risk in ACS patients.
] troponin I;GRACE risk score 2.0;acute coronary syndrome;mortality
麦超(1975-),主治医师,硕士,主要从事急救医学研究。△
,E-mail:hgjian@sohu.com。
10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2017.36.024
R541.4
A
1671-8348(2017)36-5112-03
2017-08-23
2017-09-25)

