绿色农业
Kromp, B
Natural products in crop protection
Dayan, Franck E; Cantrell, Charles L; Duke, Stephen O
The green, blue and grey water footprint of crops and derived crop products
Mekonnen, MM; Hoekstra, AY
Bringing ecosystem services into economic decision-making: Land use in the United Kingdom
Bateman, Ian J; Harwood, Amii R;Mace, Georgina M; et al.
绿色农业的发展现状与未来展望
王德胜
我国微生物肥料研究现状及发展趋势
吴建峰,林先贵
绿色农业
·编者按·
党的十八大以来,党中央国务院高度重视绿色农业发展。习近平总书记多次强调,绿水青山就是金山银山。十九大报告指出,我们要建设的现代化是人与自然和谐共生的现代化。2017年9月,中共中央办公厅、国务院办公厅印发了《关于创新体制机制推进农业绿色发展的意见》,其目标任务是:把农业绿色发展摆在生态文明建设全局的突出位置,全面建立以绿色生态为导向的制度体系,基本形成与资源环境承载力相匹配、与生产生活生态相协调的农业发展格局,努力实现耕地数量不减少、耕地质量不降低、地下水不超采,化肥、农药使用量零增长,秸秆、畜禽粪污、农膜全利用,实现农业可持续发展、农民生活更加富裕、乡村更加美丽宜居。
当前,我国正在由中等收入国家向高收入国家迈进,显著的特点就是消费结构升级,由过去的吃得饱向吃得好、吃得健康转变。绿色农业是指通过增加、使用自然和可持续的养分投入、多样化作物轮作以及畜牧业和种植业一体化来恢复和提高土壤肥力的技术减少化肥使用,通过采用将生物防治和杂草管理相结合的实践,减少化学农药和除草剂使用。绿色农业不再狭隘地视农业只是提供食品、纤维、原材料等经济产品的产业,而是认为其具有多种价值和功能,是人类回归自然的必然之路,是反映人类与自然是否和谐的指示剂。推进农业绿色发展为我们提升现有农业资源的可承载性、扩展农业发展的空间指明了方向。
本专题得到王德胜教授(中国石油大学(华东))的大力支持。
·热点数据排行·
截至2017年11月20日,中国知网(CNKI)和Web of Science(WoS)的数据报告显示,以“绿色农业(green agriculture)”为词条可以检索到的期刊文献分别为条1668与2832条,本专题将相关数据按照:研究机构发文数、作者发文数、期刊发文数、被引用频次进行排行,结果如下。

研究机构发文数量排名(CNKI)
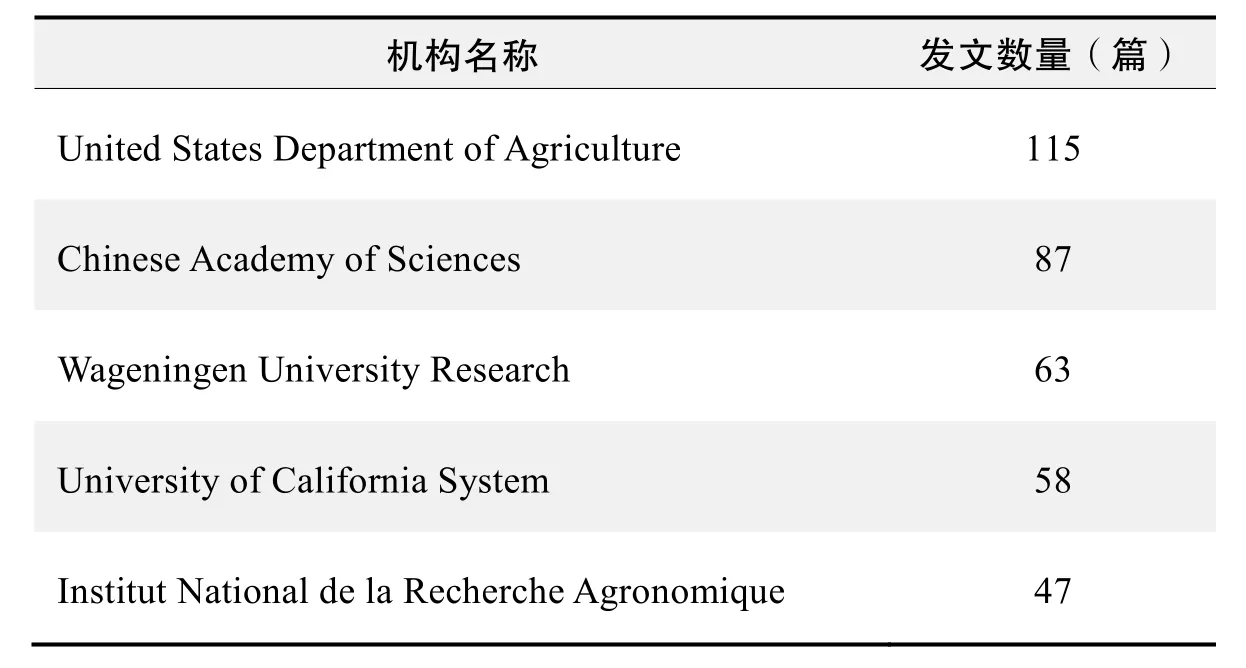
研究机构发文数量排名(WoS)
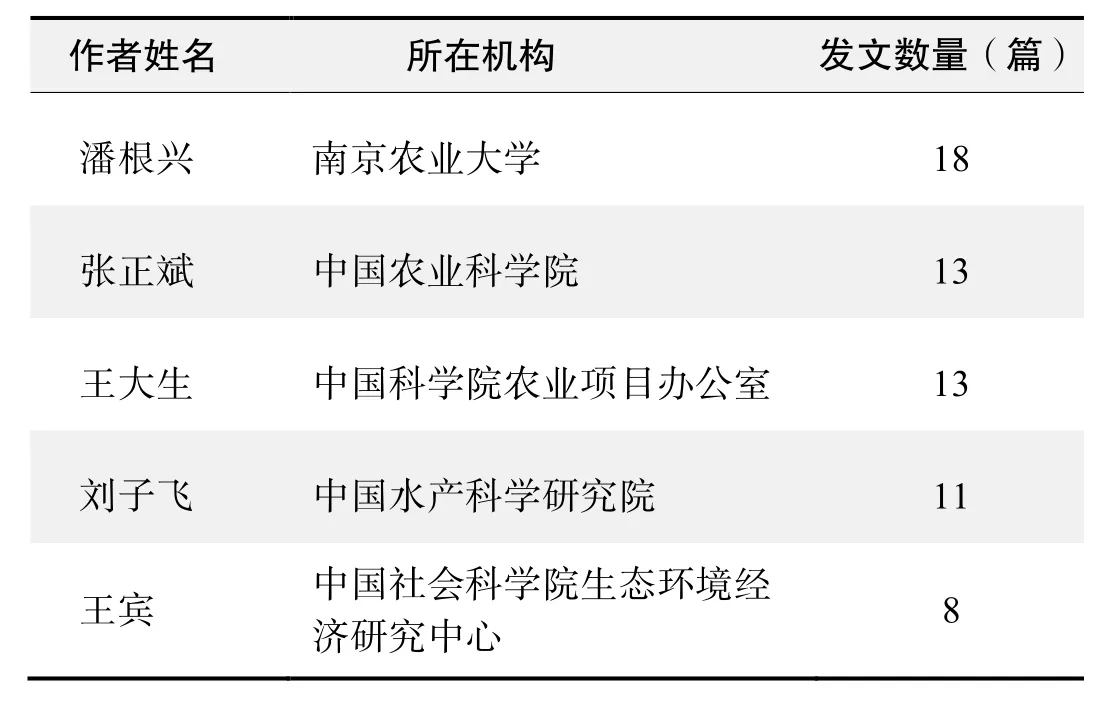
作者发文数量排名(CNKI)
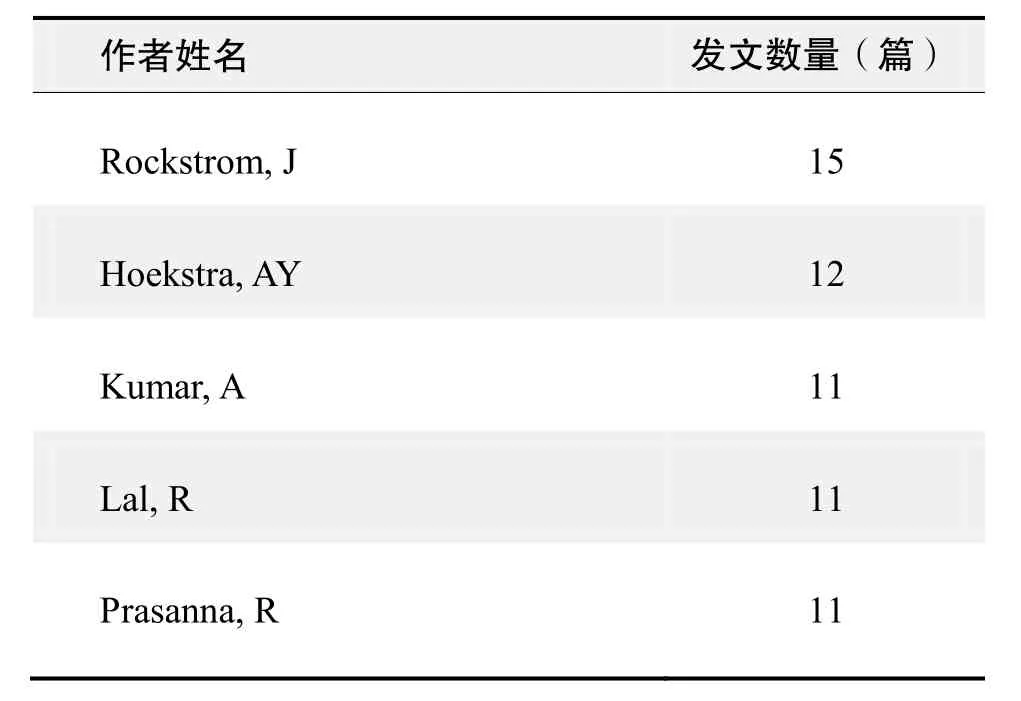
作者发文数量排名(WoS)

期刊发文数量排名(CNKI)
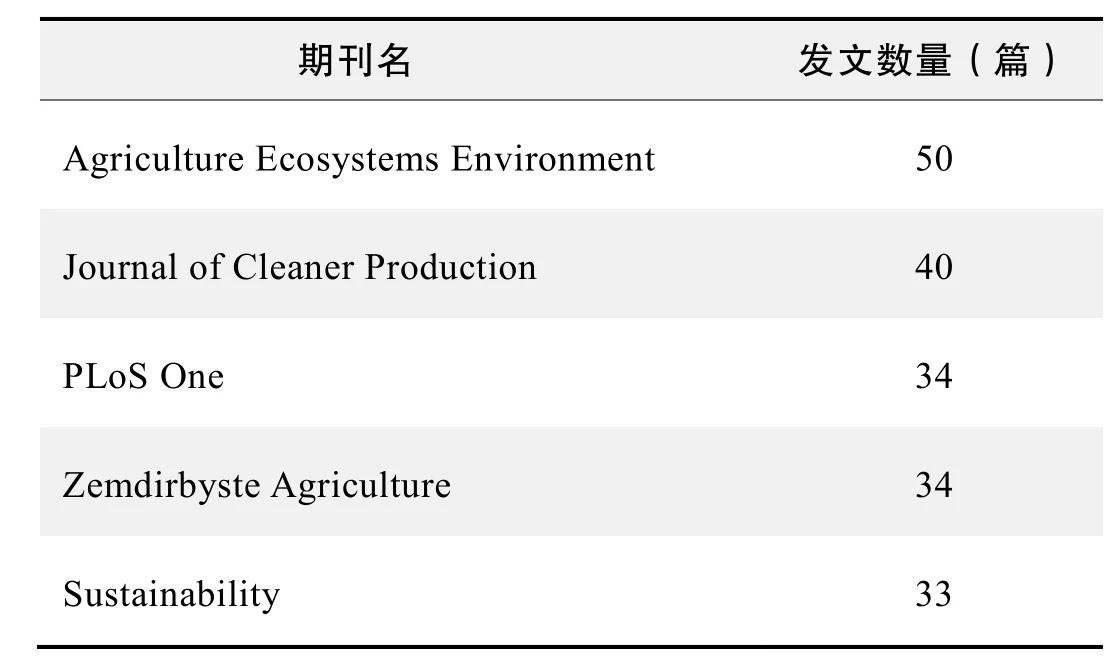
期刊发文数量排名(WoS)
根据中国知网(CNKI)数据报告,以“绿色农业(green agriculture)”为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。

国内数据库高被引论文排行
国内数据库高被引论文排行
根据Web of Science统计数据,以“绿色农业(green agriculture)”为词条为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。

国外数据库高被引论文排行
·经典文献推荐·
基于Web of Science检索结果,利用Histcite软件选取LCS(Local Citation Score,本地引用次数)TOP50文献作为节点进行分析,得到本领域推荐的经典文献如下。
来源出版物:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 180(50):20260-20264
Carabid beetles in sustainable agriculture:A review on pest control efficacy, cultivation impacts and enhancement
Kromp, B
Abstract:This review article an carabids in sustainable agro-ecosystems of the temperate Northern hemisphere presents a compilation of the available knowledge on the significance of carabids for natural pest control and the effects of cultivation methods (except pesticides) and landscape structural elements. Field carabids are species rich and abundant in arable sites, but are affected by intensive agricultural cultivation. For sampling, fenced pitfall trapping or pitfall trapping is recommended according to the type of study. Many of the assumed beneficial pest control activities of carabids are still based on laboratory feeding records. In the field, carabids have been demonstrated to reduce cereal and sugar beet aphid populations in their early colonization phase, mainly by foraging on aphids that have fallen from the vegetation.Egg predation on Dipteran eggs, e.g. the cabbage root fly,has been overestimated in earlier literature. Scattered data indicate carabidforaging on certain coleopteran pest larvae.In North America, some evidence has been found for control of pest lepidopterans. Larger carabids, e.g. Abax parallelepipedus, can effectively control slugs in greenhouses. Because of their spermophagous feeding habits, certain species of Harpalus and Amara could have some potential for biological weed control. As a result of their sensitive reaction to anthropogenic changes in habitat quality, carabids are considered of bioindicative value for cultivation impacts. Carabids seem to be negatively affected by deep ploughing and enhanced by reduced tillage systems. No negative effects have been found for mechanical weed control and flaming. Carabid recruitment is enhanced by proper organic fertilization and green manuring. Intensive nitrogen amendment might indirectly affect carabids by altering crop density and microclimate.Field carabid assemblages are not bound to a certain crop type, but shift in dominance according to the crop-specific rhythmicity of cultivation measures and changes in crop phenology and microclimate. Crop rotation effects could also be influenced by held-size dependent recolonization capability of carabids. They are enhanced by crop diversification in terms of monocrop heterogeneity and weediness as well as by intercropping and the presence of field boundaries, although corresponding increases in their pest reduction efficacy have not yet been evidenced.
关键词:carabids; review; sustainable agriculture; pest control; cultivation impacts; field boundaries
来源出版物:Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment,1999, 71(1-3):187-228
Natural products in crop protection
Dayan, Franck E; Cantrell, Charles L; Duke, Stephen O
Abstract:The tremendous increase in crop yields associated with the ‘green’ revolution has been possible in part by the discovery and utilization of chemicals for pest control. However, concerns over the potential impact of pesticides on human health and the environment has led to the introduction of new pesticide registration procedures,such as the Food Quality Protection Act in the United States. These new regulations have reduced the number of synthetic pesticides available in agriculture. Therefore, the current paradigm of relying almost exclusively on chemicals for pest control may need to be reconsidered.New pesticides, including natural product-based pesticides are being discovered and developed to replace the compounds lost due to the new registration requirements.This review covers the historical use of natural products in agricultural practices, the impact of natural products on the development of new pesticides, and the future prospects for natural products-based pest management.
关键词:natural pesticide; sustainable agriculture; natural herbicide; natural fungicide; natural insecticide; essential oils; biological control; triketone; corn gluten;momilactone; sorgoleone; bialaphos; spinosad; avermectins;milbemycins; ryania; sabadilla; chitin; harpin; strobilurins
来源出版物:Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2009,17(12):4022-4034
The green, blue and grey water footprint of crops and derived crop products
Mekonnen, MM; Hoekstra, AY
Abstract:This study quantifies the green, blue and grey water footprint of global crop production in a spatiallyexplicit way for the period 1996-2005. The assessment improves upon earlier research by taking a high- resolution approach, estimating the water footprint of 126 crops at a 5 by 5 arc minute grid. We have used a grid-based dynamic water balance model to calculate crop water use over time,with a time step of one day. The model takes into account the daily soil water balance and climatic conditions for each grid cell. In addition, the water pollution associated with the use of nitrogen fertilizer in crop production is estimated for each grid cell. The crop evapotranspiration of additional 20 minor crops is calculated with the CROPWAT model. In addition, we have calculated the water footprint of more than two hundred derived crop products, including various flours, beverages, fibres and biofuels. We have used the water footprint assessment framework as in the guideline of the Water Footprint Network. Considering the water footprints of primary crops, we see that the global average water footprint per ton of crop increases from sugar crops (roughly 200 m3ton-1),vegetables (300 m3ton-1), roots and tubers (400 m3ton-1),fruits (1000 m3ton-1), cereals (1600 m3ton-1), oil crops(2400 m3ton-1) to pulses (4000 m3ton-1). The water footprint varies, however, across different crops per crop category and per production region as well. Besides, if one considers the water footprint per kcal, the picture changes as well. When considered per ton of product, commodities with relatively large water footprints are:coffee, tea, cocoa,tobacco, spices, nuts, rubber and fibres. The analysis of water footprints of different biofuels shows that bioethanol has a lower water footprint (in m3GJ-1) than biodiesel, which supports earlier analyses. The crop used matters significantly as well:The global average water footprint of bio-ethanol based on sugar beet amounts to 51 m3GJ-1, while this is 121 m3GJ-1for maize. The global water footprint related to crop production in the period 1996-2005 was 7404 billion cubic meters per year(78% green, 12% blue, 10% grey). A large total water footprint was calculated for wheat (1087 Gm3yr-1),rice (992 Gm3yr-1) and maize (770 Gm3yr-1). Wheat and rice have the largest blue water footprints, together accounting for 45% of the global blue water footprint. At country level, the total water footprint was largest for India (1047 Gm3yr-1), China (967 Gm3yr-1) and the USA(826 Gm3yr-1). A relatively large total blue water footprint as a result of crop production is observed in the Indus river basin (117 Gm3yr-1) and the Ganges river basin(108 Gm3yr-1). The two basins together account for 25%of the blue water footprint related to global crop production.Globally, rain-fed agriculture has a water footprint of 5173 Gm3yr-1(91% green, 9% grey); irrigated agriculture has a water footprint of 2230 Gm3yr-1(48% green, 40%blue, 12% grey).
来源出版物:Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2011,15(5):1577-1600
Bringing ecosystem services into economic decision-making: Land use in the United Kingdom
Bateman, Ian J; Harwood, Amii R;Mace, Georgina M; et al.
Abstract:Landscapes generate a wide range of valuable ecosystem services, yet land-use decisions often ignore the value of these services. Using the example of the United Kingdom, we show the significance of land-use change not only for agricultural production but also for emissions and sequestration of greenhouse gases, open-access recreational visits, urban green space, and wild-species diversity. We use spatially explicit models in conjunction with valuation methods to estimate comparable economic values for these services, taking account of climate change impacts. We show that, although decisions that focus solely on agriculture reduce overall ecosystem service values,highly significant value increases can be obtained from targeted planning by incorporating all potential services and their values and that this approach also conserves wild-species diversity.
来源出版物:Science, 2013, 341(6141):45-50
·推荐综述·
绿色农业的发展现状与未来展望
王德胜
1 绿色农业概念的提出
2003年10月由中国绿色食品协会主持,在我国北京召开了“亚太地区绿色食品与有机农业市场通道建设国际研讨会”,这是一次有关我国农业发展的盛会,在会上中国绿色食品协会的专家首次提出了“绿色农业”的概念。为进一步开展国际间的合作,推动绿色农业理论和研究的发展。我国先后在中国科学院、中国工程院、中国社会科学院、中国农业科学院以及中国农业大学等单位成立了研究绿色农业基本理论的课题组,并投人大量的资金用于扶持该项目的建设,这标志我国正式进人到“绿色农业”的发展阶段。
2 绿色农业的内涵
有关“绿色食品”的概念出现在20世纪90年代初,紧接着“绿色农业”就成为大家议论的话题。
对于“绿色农业”的内涵我国许多专家、学者均做过积极的探索。知名专家刘连馥老师在其主编的论著《绿色农业初探》一书中,明确指出绿色农业是指充分运用当代的先进科学技术、装备和农业管理经验,以促进农产品安全、生态安全、资源安全和提高农业综合经济效益的协调统一为目标,以标准化农业生产为手段,推动人类社会和经济全面、协调、可持续发展的农业模式。但也有学者认为绿色农业仅是可持续农业发展中的一种;有的学者强调绿色农业就是要做大做强绿色食品产业。
总的来说,绿色农业涉及范围较广、领域较多,不仅仅是农业生产,还有工业、管理学等众多领域。但不可否认的是绿色农业将是当前和今后我国发展现代农业的主流,应该把农产品的食品安全、环境保护、资源可持续利用、人与自然协调发展之路作为首要目标。绿色农业的产品不仅要包括绿色食品、有机食品,还包括在绿色农业生产中的原料如纺织、橡胶、化工、包装材料等及绿色休闲产品如观光旅游度假休闲农业、生态景观农业、文化景观农业等,因此绿色农业的终端产品范围非常广阔。
3 我国绿色农业产业发展现状
自从2003年学者提出“绿色农业”概念之后,中国绿色农业的发展经历了从理论学习、借鉴国外的经验教训到自我创新等几个阶段,取得以下的成绩。尤其是近年来,绿色农业高速发展,产业链逐渐延长,形成了具有我国社会主义特色的模式,为保护生态环境、扩大就业、促进农民增收发挥了重要作用。
3.1 绿色农业发展具有一定的规模
从近年来我国绿色农业发展状况可见,我国绿色农业发展速度之快,产品总数、产量、销售额、出口额均呈逐年增长的态势,至2014年我国绿色食品已有14500个,其中有机食品2530个,绿色食品、有机食品产量分别达7520万t,300万t,销售额分别达1798亿元、81亿元,出口额分别达35亿美元、4.9亿美元。
3.2 绿色农业企业高速增长
绿色农业企业是绿色农业生产中的主力军,它统领全局,一只手连接着生产基地及农户,另一只手连接市场。近年来绿色农业企业发展势头良好。截止2014年底,绿色农业企业有8700家,其中国家级龙头企业已达239家,省级企业1194个,年增长率达20.7%。当年新增的绿色农业企业达580家。这些企业的产品约21153个。814家企业拥有并使用有机产品标志,其产品有3342个。全国建成了635个绿色食品标准化生产基地,种植规模达1066.67万hm2,达到有机农业标准的有17个,总面积达66.67万hm2。这些绿色食品基地带动农户2010万户,为农民增加收人10亿元。更重要的是这些企业通过多种方式与种植户对接,如“企业+专业合作组织+农户”或“企业+农户”等,除收购农产品之外,还为农民提供技术服务,为以后绿色农业的发展打下坚实的基础。
3.3 农民意识提高
农民是绿色农业生产中的细胞,是生产的基本单位。农民参与绿色农业,既提高了自己的收人,又为城市的居民提供绿色农产品。如2014年绿色农业生产共带动2100万个农户,直接增收10亿元以上。绿色农业建立了绿色农产品基地,在生产中,农民也学到了绿色农业技术,其自身的意识逐步提高,农业专业合作组织的出现就是典型的例子,这类组织是农户与企业的纽带,是农民自发形成的组织,结构虽然松散,但作用很大,使农民团结起来以应对市场的风险,将市场与农民紧紧地联系在一起。至2014年全国已有几千家农民专业合作社,约1000家通过了绿色食品的认证。
3.4 政策支持力度加大
我国政府制定了农业产业政策,提供公共服务,是当之无愧的绿色农业领导者。中央先后出台了许多利好的政策支持绿色农业的发展,如2008年6月1日起,对于生产、销售有机肥产品的企业与个人免征增值税;2009年拿出专项资金扶持绿色农用生物产品等。与此同时,我国政府加大对绿色农业发展的扶持力度,仅2014年建成的绿色农业生产基地及示范园区面积就达0.11亿多hm2。
4 我国绿色农业发展存在的不足
4.1 缺乏理论研究
20世纪90年代,我国农业专家学者开始“绿色农业”研究工作。纵观学术界发现均是自发的、分散的学术争鸣、理论探讨。21世纪开始,我国开始成立专业的绿色农业研究组织,但截止到目前,有关绿色农业的理论研究还很匮乏。至今国内已出版的有关“绿色农业”的专著或论文集仅有《绿色农业初探》《绿色农业生产技术指导原则》《绿色农业导论》《绿色农业与绿色生态江西研讨会论文集》等。绿色农业的发展缺乏成系统的理论支持,无法指导大规模的绿色农业生产。理论上绿色农业发展涉及的环节较多,要保质保量,达到经济效益和生态绿色的目标,需要工业、农业、经济和管理等多个领域的理论创新。但目前现有技术储备还难以完成指导绿色农业发展的整套规程,这严重制约绿色农业的发展。
4.2 标准不健全,疏于管理
绿色农业是一种标准化生产方式,由专业机构进行规范化管理。当前,我国绿色农业标准不健全,管理机构水平参差不齐,严重影响绿色农业的发展。按照我国的有关规定,参照GB/T24000—ISO14000、欧盟有机农业条例(2092/91)美国、日本等国家的有机农业标准,我国的绿色食品标准分为AA级和A级两个等级。同时也实施了《有机食品国家标准》,如绿色食品白菜类蔬菜标准(NY/T654—2002)、绿色食品茄果类蔬菜标准(NY/T655—2002)等。但总的看,我国绿色农业还较缺乏,没有形成自己的标准,更不必说标准体系。
另一方面,对于绿色食品的认证,表面上看制度健全,有相应的法规,有从中央至各省、市一级的较为完整的管理体系,但疏于监管的现象时有发生。比较突出的现象是绿色食品、无公害食品、有机食品的认证程序非常混乱,认证的机构很多,认证手段、方法及证书也均不一致。另外,许多并不具备绿色农业生产条件的企业也堂而皇之地披上了绿色农业的外衣,其产品也打上了绿色食品的标志,进行虚假的宣传,使消费者在市场上购买时分不清真假,而真正的绿色农业的产品反而败下阵来。
4.3 规模小,产品档次低,分布不均匀
绿色农业在我国出现的时间晚,发展的时间短,总体上看其规模和层次还处于初级阶段,在整个农业体系中占得比重还很小。一是绿色农业发展规模较少,辐射范围窄,影响能力小,截止2013年,我国现有绿色农业面积是1214.13万hm2,农作物播种面积为495万hm2,占总农作物播种面积的4.18%。其中产品达到绿色标准的数量很少。近年来,随着大家意识的加强,绿色农业发展较快,至2014年底,全国经过认证的无公害种植面积比重达14.6%(摘自国家统计局数据)。
二是绿色产品的质量和档次不高,深加工产品数量很少且分布不均衡。种植业产品较多,水产、畜牧等产品较少。据统计2014年初级产品数占61%,深加工产品占39%,从2014年绿色农业产品构成可以发现农林产品占大多数,其他的产品所占的比重较小。
4.4 科技投入明显不足,转化的结果较少,社会化服务体系不健全
科学技术是第一生产力。据测算,我国农业科技领域内科技的贡献率为57.1%,而美国超过78%,尽管较过去已有大幅的增长,但与发达国家相比,科技贡献率还有提升的空间。长期以来,对于科研单位来说农业科研活动往往停留在理论层次,与实践脱离,取得的成果多是束之高阁,缺乏推广应用方面的研究,如在蔬菜水果的栽培研究中往往只重视产量为的提高,过分依赖于高水高肥的投人,而轻视对节工降耗、低碳环保、绿色安全等栽培技术的研究。另外,我国有的农业科研工作者也想将其科研成果转化为生产力,但由于转化渠道不畅通,也制约了转化的结果。作为种植户来说也想得到最先进的种植技术,但苦于社会化服务体系的不健全,无法了解急需的技术,不能引导种植户进行绿色农业的生产。
5 我国绿色农业产业未来发展的建议
5.1 依靠科学技术
纵观人类发展的历史,不难发现每一次农业发展的进步最终决定力量均是科学技术的进步。我国绿色农业的发展离不开科学技术,离不开科研人员的努力,要把科技成果快速地转化为生产力,不仅是利用自己的成果,也要借鉴国外的优秀成果,对于不适合我国国情的成果进行适度的改造。从科研人员的角度来讲在项目申请前就应考虑到该项目的应用前景,是否属于绿色农业的范畴,是否达到绿色农业的标准。从农户的角度来讲在生产中要严格按照绿色农业的相关规定进行生产,认真学习相关的知识,不违规施用农药和化肥。
5.2 借鉴国外的先进经验
国外对于绿色农业高度重视,出台了相关的法律法规,使绿色农业生产有法可依,如美国出台了《有机食品生产法》《2002年农村安全及农村投资法》,规定对于绿色农业实施补贴。德国出台的法律较多,有《肥料使用法》《自然资源保护法》《垃圾处理法》《水资源保护法》等。日本颁布了《食物、农业、农村基本法》《可持续农业法》《堆肥平直管理法》和《食品废弃物循环法》等。上述的法律条文规范了绿色农业的生产和发展,对于国外绿色农业的健康发展功不可没。而我国仅制定了一些标准,未出台有关的法律。发达国家的经验表明绿色农业的发展离不开法律的支持,这一点值得我国学习。
5.3 扶持龙头企业,组建农民专业合作社
龙头企业引领着我国绿色农业的发展,但在其发展壮大的同时也受到体制和机制的困扰。作为政府应鼓励其发展,给予其更大的经营自主权,如对于种植业为主的企业,可以鼓励其与农民签订协议,承包农民的土地(原有的农民的土地承包经营权不变),建立原料生产加工基地,在资金投人、项目审批等方面给予照顾。在“扶持龙头企业”方面山西省的做法值得推广,省政府领导适时地提出了“一县一业,一村一品”的口号,涌现出多个龙头企业,仅上述这些企业进行的绿色食品、有机农产品的认证就达90多项,带动农户300万人。
在绿色农业生产中农户也深深地体会到过去那种一家一户式的生产方式无法适应标准化的生产,即使生产出合格的农产品也很难在市场经济的大潮中力拔头筹,结合规模化集约化的生产,农民专业合作社应运而生,这是农民自发地组织,但其的作用不可小视,但由于农民自身的文化程度低,对市场信息不了解,专业合作社的作用没有完全体现,这就要求我们的政府给予其领导,引领其走上正轨。
5.4 扩宽市场,提升绿色农产品价值
对于绿色农业的真正含义大多数消费者并不了解,使其市场占有率增长缓慢,由于现在新闻媒体很多,我们应当充分利用各种新闻传媒和舆论的力量,大力宣传绿色农业,使大家了解并认识它,同时让企业参加绿色农产品展示会,打造知名品牌,在同行业间政府也要加强管理,避免恶性竞争。适当提高绿色农产品的价格,调动种植户和企业的积极性,打击假冒产品,在适当的条件下建立绿色农产品专业批发市场完善农产品加工、销售等环节,尤其要利用互联网的平台引人电子商务等现代销售手段,拓宽销售渠道建立二维码追溯系统。有条件的要开拓国际市场。
(摘自《中国农业资源与区划》2016年2期)
·高被引论文摘要·
被引频次:174
我国微生物肥料研究现状及发展趋势
吴建峰,林先贵
为促进我国农业的可持续发展,适应有机、绿色农业的发展趋势,微生物肥料凭借其肥效高、无污染、成本低和节约能源等特点,将在未来农业中发挥重要的作用。本文概述了微生物肥料的特点及种类,分析了其开发利用现状,并从广义角度对“微生物肥料”的概念进行了相应讨论。
关键词:微生物肥料;发展趋势
来源出版物:土壤, 2002, 39(1):68-72
被引频次:106
我国农业污染现状、原因及对策研究
贾蕊,陆迁,何学松
摘要:集约化的农业生产模式在提高农产品产量的同时,也给我国带来了严重的农业污染。由于“小农经济”难以实现绿色生产等原因,农业污染已成为制约我国农业可持续发展的主要障碍。通过绿色扶持政策提高农民从事绿色生产的积极性等措施是控制农业污染问题的有效途径。
关键词:农业污染;现状;原因;对策
来源出版物:中国农业科技导报, 2006, 8(1):59-63
被引频次:101
微生物肥料效应及其应用展望
葛均青,于贤昌,王竹红,等
摘要:简述了微生物肥料种类、特点及其生理生态效应,指出应加强微生物肥料基础与应用研究,并展望微生物肥料发展前景。
关键词:微生物肥料;生理生态效应;绿色农业;环境保护
来源出版物:中国生态农业学报, 2003, 11(3):87-88
引频次:70
生物农药的研究应用现状及前景
桂永珠,池景良,胡永兰
摘要:随着工业发展进程的加快,工业污染的加剧,导致一些疾病发病率成倍增长,使人类的健康受到极大威胁。生物农药的发现和应用已有半个多世纪,主要用于防治农作物的病虫害。生物农药属低毒、无污染、无公害生物制剂,世界各国均很重视。积极提倡生态农业,扩大绿色食品的生产规模,生产无污染、优质食品,确保环境和健康安全,已成为人们共识。因此,在21世纪生物农药的研究和应用上必将有一个新的飞跃,前景是十分广阔的。
关键词:生物农药;农作物病虫害;绿色农业
来源出版物:微生物学杂志, 2001, 21(2):48-49
引频次:59
中国微生物肥料的研究现状及前景展望
刘鹏,刘训理
摘要:文章回顾了中国微生物肥料的发展历史,简述了微生物肥料的分类、主要功效、作用机制、在不同作物上的应用及发展过程中存在的问题。指出微生物肥料可有效改善土壤环境、提高土壤肥力、防治土传病害、增加作物产量和减少化肥使用量,是发展“绿色农业”“生态农业”的需要。目前,中国的微生物肥料仍存在着整体水平不高、技术创新不足、产品效果不稳定和市场管理混乱等问题,因此,需进一步加强基础性研究、完善生产工艺、加强监督管理,加大资金投入和协同创新,以促进微生物肥料的健康、快速发展。
关键词:微生物肥料;分类;功效;作用机制;应用现状
来源出版物:农学学报, 2013, 3(3):26-31
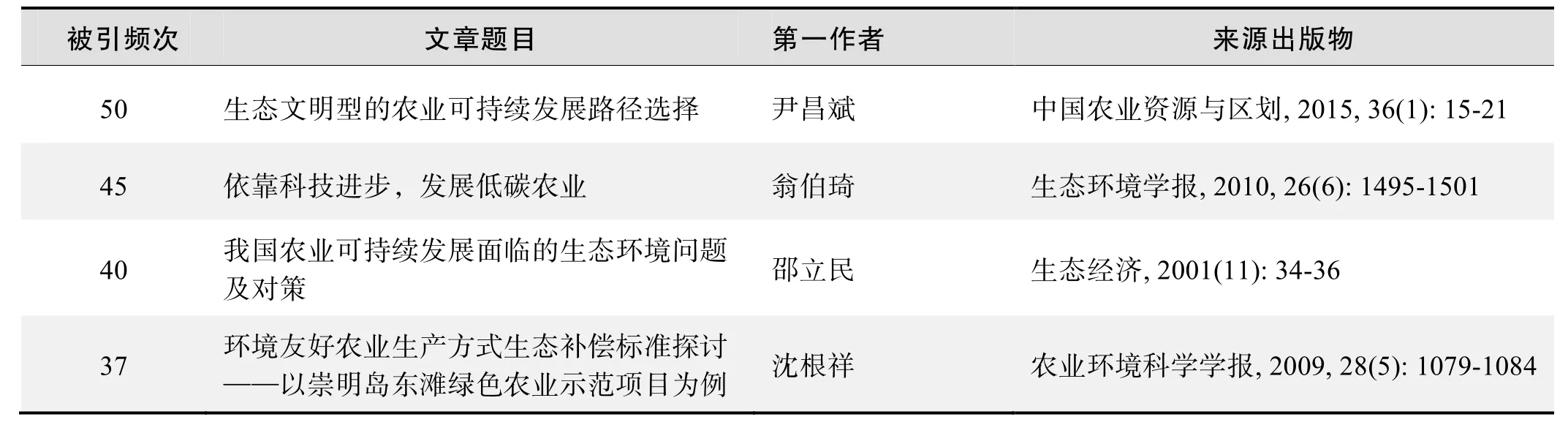
被引频次:50
生态文明型的农业可持续发展路径选择
尹昌斌,程磊磊,杨晓梅,等
摘要:该文系统地梳理了我国农业可持续发展面临着农产品数量与质量需求双重提升、农业资源压力越来越大、农业现代化进程中环境问题日益突出等挑战,基于“绿色、循环、低碳”的发展理念,阐述了生态文明型的现代农业主要表现为生产效益型的集约农业、资源节约型的循环农业、环境友好型的生态农业、产品安全型的绿色农业等4个特征,探讨了转变农业发展方式、构建生态文明型农业新型生产模式的路径选择,指出生态文明型的现代农业建设重点为加强农业资源保护、推进农业资源节约利用、构建循环型农业产业链、实施一批农业可持续发展工程等,并提出加强生态补偿等制度安排,对于探索生态文明型农业可持续发展道路,制定有针对性的推进策略具有十分重要的意义。
关键词:生态文明;可持续发展;现代农业;循环农业
来源出版物:中国农业资源与区划, 2015, 36(1):15-21
被引频次:45
依靠科技进步 发展低碳农业
翁伯琦,雷锦桂,胡习斌,等
摘要:在全球携手应对气候变暖、减少温室气体排放的背景下,发展低碳经济是解决气候变化与经济发展矛盾的有效途径。通过描述气候变化、固碳减排对粮食安全、土壤碳汇、森林固碳、资源循环利用等影响和促进作用,深入分析发展低碳经济与可持续发展的关系,探讨如何在农业领域内开发高效循环生产体系,从而实现农业生产过程的固碳减排目的。由此,提出发展低碳农业是实现低碳经济的目标之一,它是一个复合技术体系,涉及了绿色农业、循环农业、生态文明、可持续发展理念。必须通过科学技术的突破,改造、提升低碳农业技术,改变农业现有的“高能耗、高污染”的生产状况,实现低碳生产、生活方式的转变。最后提出发展现代的低碳农业产业经济的对策和思考。
关键词:低碳经济;温室气体;科技;循环农业;固碳减排
来源出版物:生态环境学报, 2010, 26(6):1495-1501
被引频次:40
我国农业可持续发展面临的生态环境问题及对策
邵立民,方天堃
摘要:本文就21世纪中国农业发展所面临的挑战与机遇、中国发展绿色农业的意义及条件等进行了分析,并在此基础上提出了相应的对策措施。
关键词:农业基础科学;可持续发展;综述;生态环境问题;对策
来源出版物:生态经济, 2001(11):34-36
被引频次:37
环境友好农业生产方式生态补偿标准探讨——以崇明岛东滩绿色农业示范项目为例
沈根祥,黄丽华,钱晓雍,等
摘要:以崇明岛东滩绿色农业示范项目为研究案例,在定量监测环境友好型肥料管理方式对化肥污染控制效果的基础上,运用相关经济学方法,从环境友好肥料管理方式所创造的生态效益价值和实际投入的额外成本两个角度出发,探讨了生态补偿标准的理论上限值和下限值,同时讨论了在实际制定补偿标准时需要考虑的其他因素和采取的补偿方式。结果表明,环境友好型肥料管理方式可有效削减氮素流失负荷和温室气体排放通量,削减率分别达到46.6%~61.8%和23.4%~46.7%;在梨园所创造的生态效益价值和实际额外投入成本分别为10135.6和3066.1元(RMB)·hm-2·a-1,在蔬菜田所创造的生态效益价值和实际额外投入成本分别为7640.1和3165.2元(RMB)·hm-2·a-1。因此,梨园和蔬菜田由于应用环境友好型肥料管理方式可获得的生态补偿理论值范围分别为3066.1~10135.6元(RMB)·hm-2·a-1和3165.2~7640.1元(RMB)·hm-2·a-1。
关键词:环境友好农业;生态补偿;生态效益;额外成本
来源出版物:农业环境科学学报, 2009, 28(5):1079-1084
被引频次:1439
Biofuels from microalgae-A review of technologies for production, processing, and extractions of biofuels and co-products
Brennan, Liam; Owende, Philip
Abstract:Sustainability is a key principle in natural resource management, and it involves operational efficiency, minimisation of environmental impact and socio-economic considerations. all of which are interdependent It has become increasingly obvious that continued reliance on fossil fuel energy resources is unsustainable, owing to both depleting world reserves and the green house gas emissions associated with their use Therefore, there are vigorous research initiatives aimed at developing alternative renewable and potentially carbon neutral solid, liquid and gaseous biofuels as alternative energy resources. However, alternate energy resources akin to first generation biofuels derived from terrestrial crops such as sugarcane, Sugar beet, maize and rapeseed place an enormous strain on world food markets,contribute to water shortages and precipitate the destruction of the world’s forests. Second generation biofuels derived from lignocellulosic agriculture and forest residues and from non-food crop feedstocks address some of the above problems; however there is concern over competing land use or required land use changes Therefore, based on current knowledge and technology projections, third generation biofuels specifically derived from microalgae are considered to be a technically viable alternative energy resource that is devoid of the major drawbacks associated with first and second generation biofuels. Microalgae are photosynthetic microorganisms with simple growing requirements (light, Sugars, CO2, N,P, and K) that can produce lipids, proteins and carbohydrates in large amounts Over short periods of time. These products can be processed into both biofuels and valuable co-products. This study reviewed the technologies underpinning microalgae-to-biofuels systems,focusing on the biomass production, harvesting, conversion technologies. and the extraction of useful co-products it also reviewed the synergistic coupling of microalgae propagation with carbon sequestration and wastewater treatment potential for mitigation of environmental impacts associated with energy conversion and utilisation. It was found that. whereas there are outstanding issues related to photosynthetic efficiencies and biomass output,microalgae-derived biofuels could progressively substitute a significant proportion of the fossil fuels required to meet the growing energy demand.
关键词:microalgae; biomass recovery; bioenergy;conversion; photobioreactor; CO2sequestration
来源出版物:Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews,2010, 14(2):557-577
被引频次:1066
Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture
Tilman, David; Balzer, Christian; Hill, Jason; et al.
Abstract:Global food demand is increasing rapidly, as are the environmental impacts of agricultural expansion. Here,we project global demand for crop production in 2050 and evaluate the environmental impacts of alternative ways that this demand might be met. We find that per capita demand for crops, when measured as caloric or protein content of all crops combined, has been a similarly increasing function of per capita real income since 1960. This relationship forecasts a 100%-110% increase in global crop demand from 2005 to 2050. Quantitative assessments show that the environmental impacts of meeting this demand depend on how global agriculture expands. If current trends of greater agricultural intensification in richer nations and greater land clearing (extensification) in poorer nations were to continue, similar to 1 billion ha of land would be cleared globally by 2050, with CO2-C equivalent greenhouse gas emissions reaching similar to 3 Gt y-1and N use similar to 250 Mt y-1by then. In contrast, if 2050 crop demand was met by moderate intensification focused on existing croplands of underyielding nations, adaptation and transfer of high-yielding technologies to these croplands,and global technological improvements, our analyses forecast land clearing of only similar to 0.2 billion ha,greenhouse gas emissions of similar to 1 Gt y-1, and global N use of similar to 225 Mt y-1. Efficient management practices could substantially lower nitrogen use. Attainment of high yields on existing croplands of underyielding nations is of great importance if global crop demand is to be met with minimal environmental impacts.
关键词:food security; land-use change; biodiversity;climate change; soil fertility
来源出版物:Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2011, 180(50):20260-20264
被引频次:674
Hyperspectral vegetation indices and novel algorithms for predicting green LAI of crop canopies: Modeling and validation in the context of precision agriculture
Haboudane, D; Miller, JR; Pattey, E; et al.
Abstract:A growing number of studies have focused on evaluating spectral indices in terms of their sensitivity to vegetation biophysical parameters, as well as to external factors affecting canopy reflectance. In this context, leaf and canopy radiative transfer models are Valuable for modeling and understanding the behavior of such indices.In the present work, PROSPECT and SAILH models have been used to Simulate a wide range of crop canopy reflectances in an attempt to study the sensitivity of a set of vegetation indices to green leaf area index (LAI), and to modify some of them in order to enhance their responsivity to LAI variations. The aim of the paper was to present a method for minimizing the effect of leaf chlorophyll content oil the prediction of green LAI, and to develop new algorithms that adequately predict the LAI of crop canopies.Analyses based on both simulated and real hyperspectral data were carried out to compare performances of existing vegetation indices (Normalized Difference Vegetation Index [NDVI], Renormalized Difference Vegetation Index[RDVI], Modified Simple Ratio [MSR], Soil-Adjusted Vegetation Index [SAVI], Soil and Atmospherically Resistant Vegetation Index [SARVI], MSAVI, Triangular Vegetation Index [TVI], and Modified Chlorophyll Absorption Ratio Index [MCARI]) and to design new ones(MTVI1, MCARI 1, MTV12, and MCAR12) that are both less sensitive to chlorophyll content variations and linearly related to green LAI. Thorough analyses showed that the above existing vegetation indices were either sensitive to chlorophyll concentration changes or affected by saturation at high LAI levels. Conversely, two of the spectral indices developed as a part of this study, a modified triangular vegetation index (MTV12) and a modified chlorophyll absorption ratio index (MCAR12), proved to be the best predictors of green LAI. Related predictive algorithms were tested on CASI (Compact Airborne Spectrographic Imager) hyperspectral images and, then, validated using ground truth measurements. The latter were collected simultaneously with image acquisition for different crop types (soybean, corn, and wheat), at different growth stages,and under various fertilization treatments. Prediction power analysis of proposed algorithms based on MCAR12 and MTV12 resulted in agreements between modeled and ground measurement of non-destructive LAI, with coefficients of determination (r2) being 0.98 for soybean,0.89 for corn, and 0.74 for wheat. The corresponding RMSE for LAI were estimated at 0.28, 0.46, and 0.85,respectively.
关键词:hyperspectral; spectral indices; green LAI;prediction algorithms; chlorophyll content; precision agriculture
来源出版物:Remote Sensing of Environment, 2004, 90(3):337-352
被引频次:583
Integrated narrow-band vegetation indices for prediction of crop chlorophyll content for application to precision agriculture
Haboudane, D; Miller, JR; Tremblay, N; et al.
Abstract:Recent studies have demonstrated the usefulness of optical indices from hyperspectral remote sensing in the assessment of vegetation biophysical variables both in forestry and agriculture. Those indices are, however, the combined response to variations of several vegetation and environmental properties, such as Leaf Area Index (LAI),leaf chlorophyll content, canopy shadows, and background soil reflectance. Of particular significance to precision agriculture is chlorophyll content, an indicator of photosynthesis activity, which is related to the nitrogen concentration in green vegetation and serves as a measure of the crop response to nitrogen application. This paper presents a combined modeling and indices-based approach to predicting the crop chlorophyll content from remote sensing data while minimizing LAI (vegetation parameter)influence and underlying soil (background) effects. This combined method has been developed first using simulated data and followed by evaluation in terms of quantitative predictive capability using real hyperspectral airborne data.Simulations consisted of leaf and canopy reflectance modeling with PROSPECT and SAILH radiative transfer models. In this modeling study, we developed an index that integrates advantages of indices minimizing soil background effects and indices that are sensitive to chlorophyll concentration. Simulated data have shown that the proposed index Transformed Chlorophyll Absorption in Reflectance Index/Optimized Soil-Adjusted Vegetation Index (TCARI/OSAVI) is both very sensitive to chlorophyll content variations and very resistant to the variations of LAI and solar zenith angle. It was therefore possible to generate a predictive equation to estimate leaf chlorophyll content from the combined optical index derived from above-canopy reflectance. This relationship was evaluated by application to hyperspectral CASI imagery collected over corn crops in three experimental farms from Ontario and Quebec, Canada. The results presented here are from the L’Acadie, Quebec, Agriculture and Agra-Food Canada research site. Images of predicted leaf chlorophyll content were generated. Evaluation showed chlorophyll variability over crop plots with various levels of nitrogen, and revealed an excellent agreement with ground truth, with a correlation ofr2=81 between estimated and field measured chlorophyll content data.
来源出版物:Remote Sensing of Environment, 2002,81(2-3):416-426
被引频次:424
Carabid beetles in sustainable agriculture: A review on pest control efficacy, cultivation impacts and enhancement
Kromp, B
Abstract:This review article an carabids in sustainable agro-ecosystems of the temperate Northern hemisphere presents a compilation of the available knowledge on the significance of carabids for natural pest control and the effects of cultivation methods (except pesticides) and landscape structural elements. Field carabids are species rich and abundant in arable sites, but are affected by intensive agricultural cultivation. For sampling, fenced pitfall trapping or pitfall trapping is recommended according to the type of study. Many of the assumed beneficial pest control activities of carabids are still based on laboratory feeding records. In the field, carabids have been demonstrated to reduce cereal and sugar beet aphid populations in their early colonization phase, mainly by foraging on aphids that have fallen from the vegetation.Egg predation on Dipteran eggs, e.g. the cabbage root fly,has been overestimated in earlier literature. Scattered data indicate carabidforaging on certain coleopteran pest larvae.In North America, some evidence has been found for control of pest lepidopterans. Larger carabids, e.g. Abax parallelepipedus, can effectively control slugs in greenhouses. Because of their spermophagous feeding habits, certain species of Harpalus and Amara could have some potential for biological weed control. As a result of their sensitive reaction to anthropogenic changes in habitat quality, carabids are considered of bioindicative value for cultivation impacts. Carabids seem to be negatively affected by deep ploughing and enhanced by reduced tillage systems. No negative effects have been found for mechanical weed control and flaming. Carabid recruitment is enhanced by proper organic fertilization and green manuring. Intensive nitrogen amendment might indirectly affect carabids by altering crop density and microclimate.Field carabid assemblages are not bound to a certain crop type, but shift in dominance according to the crop-specific rhythmicity of cultivation measures and changes in crop phenology and microclimate. Crop rotation effects could also be influenced by held-size dependent recolonization capability of carabids. They are enhanced by crop diversification in terms of monocrop heterogeneity and weediness as well as by intercropping and the presence of field boundaries, although corresponding increases in their pest reduction efficacy have not yet been evidenced.
关键词:carabids; review; sustainable agriculture; pest control; cultivation impacts; field boundaries
来源出版物:Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment,1999, 71(1-3):187-228
被引频次:400
Natural products in crop protection
Dayan, Franck E; Cantrell, Charles L; Duke, Stephen O
Abstract:The tremendous increase in crop yields associated with the ‘green’ revolution has been possible in part by the discovery and utilization of chemicals for pest control. However, concerns over the potential impact of pesticides on human health and the environment has led to the introduction of new pesticide registration procedures,such as the Food Quality Protection Act in the United States. These new regulations have reduced the number of synthetic pesticides available in agriculture. Therefore, the current paradigm of relying almost exclusively on chemicals for pest control may need to be reconsidered.New pesticides, including natural product-based pesticides are being discovered and developed to replace the compounds lost due to the new registration requirements.This review covers the historical use of natural products in agricultural practices, the impact of natural products on the development of new pesticides, and the future prospects for natural products-based pest management.
关键词:natural pesticide; sustainable agriculture; natural herbicide; natural fungicide; natural insecticide; essential oils; biological control; triketone; corn gluten;momilactone; sorgoleone; bialaphos; spinosad; avermectins;milbemycins; ryania; sabadilla; chitin; harpin; strobilurins
来源出版物:Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2009,17(12):4022-4034
被引频次:317
The green, blue and grey water footprint of crops and derived crop products
Mekonnen, MM.; Hoekstra, AY
Abstract:This study quantifies the green, blue and grey water footprint of global crop production in a spatiallyexplicit way for the period 1996-2005. The assessment improves upon earlier research by taking a high-resolution approach, estimating the water footprint of 126 crops at a 5 by 5 arc minute grid. We have used a grid-based dynamic water balance model to calculate crop water use over time,with a time step of one day. The model takes into account the daily soil water balance and climatic conditions for each grid cell. In addition, the water pollution associated with the use of nitrogen fertilizer in crop production is estimated for each grid cell. The crop evapotranspiration of additional 20 minor crops is calculated with the CROPWAT model. In addition, we have calculated the water footprint of more than two hundred derived crop products, including various flours, beverages, fibres and biofuels. We have used the water footprint assessment framework as in the guideline of the Water Footprint Network. Considering the water footprints of primary crops,we see that the global average water footprint per ton of crop increases from sugar crops (roughly 200 m3ton-1),vegetables (300 m3ton-1), roots and tubers (400 m3ton-1),fruits (1000 m3ton-1), cereals (1600 m3ton-1), oil crops(2400 m3ton-1) to pulses (4000 m3ton-1). The water footprint varies, however, across different crops per crop category and per production region as well. Besides, if one considers the water footprint per kcal, the picture changes as well. When considered per ton of product, commodities with relatively large water footprints are:coffee, tea, cocoa,tobacco, spices, nuts, rubber and fibres. The analysis of water footprints of different biofuels shows that bio-ethanol has a lower water footprint (in m3GJ-1) than biodiesel, which supports earlier analyses. The crop used matters significantly as well:the global average water footprint of bio-ethanol based on sugar beet amounts to 51 m3GJ-1, while this is 121 m3GJ-1for maize. The global water footprint related to crop production in the period 1996-2005 was 7404 billion cubic meters per year (78%green, 12% blue, 10% grey). A large total water footprint was calculated for wheat (1087 Gm3yr-1), rice (992 Gm3yr-1)and maize (770 Gm3yr-1). Wheat and rice have the largest blue water footprints, together accounting for 45% of the global blue water footprint. At country level, the total water footprint was largest for India (1047 Gm3yr-1), China(967 Gm3yr-1) and the USA (826 Gm3yr-1). A relatively large total blue water footprint as a result of crop production is observed in the Indus river basin (117 Gm3yr-1)and the Ganges river basin (108 Gm3yr-1). The two basins together account for 25% of the blue water footprint related to global crop production. Globally, rain-fed agriculture has a water footprint of 5173 Gm3yr-1(91%green, 9% grey); irrigated agriculture has a water footprint of 2230 Gm3yr-1(48% green, 40% blue, 12% grey).
来源出版物:Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2011,15(5):1577-1600
被引频次:362
Global inputs of biological nitrogen fixation in agricultural systems
Herridge, David F; Peoples, Mark B;Boddey, Robert M; et al.
Abstract:Biological dinitrogen (N2) fixation is a natural process of significant importance in world agriculture. The demand for accurate determinations of global inputs of biologically-fixed nitrogen (N) is strong and will continue to be fuelled by the need to understand and effectively manage the global N cycle. In this paper we review and update long-standing and more recent estimates of biological N2fixation for the different agricultural systems,including the extensive, uncultivated tropical savannas used for grazing. Our methodology was to combine data on the areas and yields of legumes and cereals from the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) database on world agricultural production (FAOSTAT) with published and unpublished data on N2fixation. As the FAO lists grain legumes only, and not forage, fodder and green manure legumes, other literature was accessed to obtain approximate estimates in these cases. Below-ground plant N was factored into the estimations. The most important N2-fixing agents in agricultural systems are the symbiotic associations between crop and forage/fodder legumes and rhizobia. Annual inputs of fixed N are calculated to be 2.95 Tg for the pulses and 18.5 Tg for the oilseed legumes.Soybean (Glycine max) is the dominant crop legume,representing 50% of the global crop legume area and 68%of global production. We calculate soybean to fix 16.4 Tg N annually, representing 77% of the N fixed by the crop legumes. Annual N2fixation by soybean in the U.S., Brazil and Argentina is calculated at 5.7, 4.6 and 3.4 Tg,respectively. Accurately estimating global N2fixation for the symbioses of the forage and fodder legumes is challenging because statistics on the areas and productivity of these legumes are almost impossible to obtain. The uncertainty increases as we move to the other agricultural-production systems-rice (Oryza sativa), sugar cane (Saccharum spp.), cereal and oilseed (non-legume)crop lands and extensive, grazed savannas. Nonetheless,the estimates of annual N2fixation inputs are 12-25 Tg(pasture and fodder legumes), 5 Tg (rice), 0.5 Tg (sugar cane), <4 Tg (non-legume crop lands) and <14 Tg(extensive savannas). Aggregating these individual estimates provides an overall estimate of 50-70 Tg N fixed biologically in agricultural systems. The uncertainty of this range would be reduced with the publication of more accurate statistics on areas and productivity of forage and fodder legumes and the publication of many more estimates of N2fixation, particularly in the cereal, oilseed and non-legume crop lands and extensive tropical savannas used for grazing.
关键词:associative; cyanobacteria.; dinitrogen (N2)fixation; endophytic; free-living; global; legumes; nitrogen(N); oilseed legumes; pulses; rhizobia; soybean
来源出版物:Plant and Soil, 2008, 311(1-2):1-18
被引频次:282
Green revolution: The way forward
Khush, GS
Abstract:The origin of agriculture led to the domestication of many plant species and to the exploitation of natural resources. It took almost 10000 years for food grain production to reach 1 billion tons, in 1960,and only 40 years to reach 2 billion tons, in 2000. This unprecedented increase, which has been named the‘green revolution’, resulted from the creation of genetically improved crop varieties, combined with the application of improved agronomic practices.
来源出版物:Nature Reviews Genetics, 2001, 2(10):815-822
被引频次:237
Bringing ecosystem services into economic decision-making: Land use in the United Kingdom
Bateman, Ian J; Harwood, Amii R;Mace, Georgina M; et al.
Abstract:Landscapes generate a wide range of valuable ecosystem services, yet land-use decisions often ignore the value of these services. Using the example of the United Kingdom, we show the significance of land-use change not only for agricultural production but also for emissions and sequestration of greenhouse gases, open-access recreational visits, urban green space, and wild-species diversity. We use spatially explicit models in conjunction with valuation methods to estimate comparable economic values for these services, taking account of climate change impacts. We show that, although decisions that focus solely on agriculture reduce overall ecosystem service values, highly significant value increases can be obtained from targeted planning by incorporating all potential services and their values and that this approach also conserves wild-species diversity.
来源出版物:Science, 2013, 341(6141):45-50
·推荐论文摘要·
福建省长汀县水土流失治理模式对绿色农业发展的启示
翁伯琦,徐晓俞,罗旭辉,等
摘要:长汀县是我国丘陵红壤区土壤侵蚀最严重的县份之一,水土流失严重制约着当地经济的发展。经过几十年的综合治理,长汀县水土流失得到有效控制,区域生态环境明显好转,乡村种植业、养殖业和加工业得到了发展,促进了农民增收,取得了良好的生态效益、经济效益和社会效益。通过对长汀县水土流失防控的阶段性经验的分析(如适合中度、强度侵蚀区的生态林草复合治理模式、适合所有侵蚀地的地表草被覆盖模式、山地果茶园复合循环模式、以产业提升为目的的农业综合开发治理模式及典型流域综合治理模式等)表明,水土治理必须依靠先进的科学技术,需要多方密切配合,治理过程需做到统筹协调。提出的未来水土流失治理和乡村绿色农业发展的对策,可为未来乡村绿色农业发展提供启示与借鉴,为探索农业可持续发展路子提供依据与参考。
关键词:水土流失;治理模式;治理成效;生态建设
来源出版物:山地学报, 2014, 32(2):141-149
LED光调控技术在芽苗菜生产中的应用
崔瑾,张晓燕,鲁燕舞
摘要:芽苗菜风味独特、品质柔嫩、营养价值高,但在生产中通常使用一些生长调节剂或微量元素溶液进行浸种或喷洒,易造成化学物质在芽苗菜内积累。光环境调控技术采用物理手段调控植物生长,符合绿色农业的要求。本文针对芽苗菜的研究现状、芽苗菜生产中存在的问题,综述发光二级管(LED)光调控技术在芽苗菜生产中的研究进展,展望LED光调控技术在芽苗菜生产中的应用前景。
关键词:芽苗菜;发光二极管(LED);光调控
来源出版物:科技导报, 2014, 32(10):32-35
国外发展绿色农业对陕西的启示
郝丽霞
摘要:绿色农业已成为世界农业发展的主要方向,也是陕西农业可持续性发展的必然选择。结合陕西绿色农业发展现状,借鉴国外绿色农业发展经验,提出了陕西绿色农业发展的战略,从规划绿色农业产业布局、构建绿色农业技术支撑体系、完善绿色农业标准化体系等方面促进陕西绿色农业的发展。
关键词:绿色农业;可持续发展;战略选择;陕西
来源出版物:山西农业科学, 2015, 43(2):225-228
作为一种生产方式的绿色农业
谭秋成
摘要:自1980年以来,中国农业增长和粮食产量提高主要依靠化肥、能源、机械动力等外部投入的增加,农业目前已处于常规石化农业时代。常规石化农业虽然短期内提高了农业产量,但破坏了土壤结构,污染了水源,并对生态系统和生物多样性造成威胁。传统农业解体主要是因为农业被纳入整个社会分工体系,农业内部封闭的循环被打破;农业内部种植业和畜牧业分离,培养地力的重要有机肥料牲畜粪便不再容易获得;农村劳动力纳入市场,劳动密集型的精耕细作农业的根基被瓦解。传统农业解体不仅表现在投入、技术和工具使用上的彻底变化,而且也表现在农民观念上对人与自然、人与土地关系的变化,正是后者的变化带来了掠夺性经营土地和破坏自然的风险。绿色农业耕作技术的中心内容是通过利用有机肥料、使用生物防治病虫害和杂草管理相结合的方式,保持和提高土壤肥力,节约和保护水资源,减少农业对生态环境破坏,恢复和重建生态资源基础。制约中国农业绿色转型的主要因素是:承包地产权残缺且不稳定,农民缺乏激励投资农业生产,施用有机肥改良土壤、提高肥力,缺乏学习如何改良土壤、如何合理施肥的动力,而且农民在化肥、农药等生产资料利用上也无法达到规模最优;农业科技过于集中于生物技术和化学技术上,对如何改良土壤、如何采用免耕法和覆盖作物耕作技术减少土壤侵蚀、如何节约利用水资源等方面的技术研发明显不足;农民对化肥农药等投入物的性质缺乏认知、对这些化学品可能给自然环境造成的影响不了解、而政府和社会为农业生产者提供的技术服务缺乏。
关键词:石化农业;传统农业;绿色农业;化肥施用
来源出版物:中国人口·资源与环境, 2015, 25(9):44-51
热裂解生物质炭产业化:秸秆禁烧与绿色农业新途径
潘根兴,李恋卿,刘晓雨,等
摘要:秸秆处理是当前中国农业与环境面临的重大挑战。分析了秸秆处理与禁烧存在的机制性困难,认为秸秆处理需要从市场经济规律寻求产业化解决途径,关键是能源利用下养分资源重回农业循环;介绍了生物质限氧热裂解新技术特点及其在秸秆处理中的优势,讨论了其产业主要产品——生物质炭的土壤和农业功效,分析了秸秆气炭联产多产品产业链的产业化前景,提出秸秆热裂解生物质炭产业化提供了既处理秸秆废弃物又促进农业增产优质安全的新技术选择,形成了以生物质炭土壤施用和生物质炭基肥料生产应用为中心的绿色农业新途径。建议国家进一步构建和完善秸秆禁烧大环境下秸秆处理补贴政策,加大秸秆收储配套服务,强化树立已经初现的秸秆生物质热裂解产业优势,通过绿色农业市场化发展带动解决秸秆问题,服务中国可持续农业。
关键词:北斗卫星导航系统;GPS;伪距单点定位;联合解算;可用性
来源出版物:武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2015, 40(4):529-533
生态文明型的农业可续发展路径选择
尹昌斌,程磊磊,杨晓梅,等
摘要:该文系统地梳理了我国农业可持续发展面临着农产品数量与质量需求双重提升、农业资源压力越来越大、农业现代化进程中环境问题日益突出等挑战,基于“绿色、循环、低碳”的发展理念,阐述了生态文明型的现代农业主要表现为生产效益型的集约农业、资源节约型的循环农业、环境友好型的生态农业、产品安全型的绿色农业等四个特征,探讨了转变农业发展方式、构建生态文明型农业新型生产模式的路径选择,指出生态文明型的现代农业建设重点为加强农业资源保护、推进农业资源节约利用、构建循环型农业产业链、实施一批农业可持续发展工程等,并提出加强生态补偿等制度安排,对于探索生态文明型农业可持续发展道路,制定有针对性的推进策略具有十分重要的意义。
关键词:生态文明;可持续发展;现代农业;循环农业
来源出版物:中国农业资源与区划, 2015, 36(1):15-21
中国绿色农业与食品产业的可持续发展战略
王光友
摘要:随着我国绿色农业的不断发展,给我国食品产业的可持续发展也提出了新的问题与挑战。本文通过对当前我国在绿色食品农业方面的发展情况进行分析,论述了在促进我国农业可持续发展的过程中大力推动绿色农业和绿色食品发展的重要意义和深远影响,对当前我国在绿色农业和绿色食品产业中存在的问题和不足进行分析,并且对绿色农业以及食品产业的可持续发展提出了几点建议,希望能够对相关的人员具有一定的参考价值。
关键词:绿色农业;食品产业;可持续发展
来源出版物:中国农业信息, 2015(3):129
中国设施蔬菜害虫天敌昆虫应用研究进展
张帆,李姝,肖达,等
摘要:设施蔬菜是现代农业生产中极为重要的组成部分,而且设施蔬菜的发展不仅使蔬菜生产的品种和产量得到快速增长,也为有机蔬菜的发展创造了有利条件。但是,设施蔬菜种植条件也给害虫提供了适宜生长、繁殖和危害的生态环境,严重影响了蔬菜的质量和产量,成为制约设施蔬菜产业进一步发展的关键因素。化学农药的长期使用带来了一系列的生态环境和食品安全问题,而治理化学农药污染不仅要求逐步减少其使用量,更需要寻求优化升级与替代传统防治方法的技术。天敌昆虫作为传统的生物防治产品,在控制设施蔬菜虫(螨)害,保证其产量和品质中起着不可替代的作用。随着人们环境保护意识的加强和绿色农业的发展,以天敌昆虫释放为主的生物防治技术在害虫综合治理(IPM)中发挥着越来越重要的作用。中国的天敌资源非常丰富,但目前在设施蔬菜生产中应用的种类相当有限。经过几十年的努力,中国在设施蔬菜害虫生物防治及应用领域开展了大量的研究工作,在天敌昆虫资源和应用基础、技术研发和配套技术及应用等方面取得了较大进展。本文概述了设施蔬菜害虫的主要发生种类及其危害特点、主要害虫天敌资源及其生物防治的技术途径等,重点介绍了蚜虫、粉虱、叶螨、蓟马等几种重大害虫的生物防治实例,并分析了中国天敌昆虫人工繁殖(人工饲料、规模化生产)的研究进展。此外,还综述了中国温室蔬菜害虫的天敌应用技术研究成果,从天敌昆虫保护利用、释放技术、控害效果评价、规模化生产等方面对设施蔬菜应用天敌昆虫进行生物防治中存在的问题进行了讨论,并展望了该领域的未来发展方向。
关键词:设施蔬菜;害虫;天敌昆虫;人工繁殖;生物防治
来源出版物:中国农业科学, 2015, 48(17):3463-3476
绿色农业的发展现状与未来展望
王德胜
摘要:绿色农业是一种现代农业发展的新模式,在我国起步较晚,但发展较快。文章简要介绍了绿色农业的概念与内涵,从产业发展规模、绿色农业企业、农民、国家政策等方面说明我国绿色农业的发展现状,如绿色农业具有一定发展规模、绿色农业企业高增速显著、农民绿色意识提高、政策对绿色农业支持力度加大等,并指出存在的不足,如缺乏理论研究、标准不健全、疏于管理、企业规模小、产品档次低,分布不均匀、科技投入明显不足、社会化服务体系不健全等,并提出依靠科学技术、借鉴国外经验、扶持龙头企业、组建农民专业合作社、提升绿色农产品价值等具体措施,以期为我国绿色农业的发展献言献策。
关键词:绿色农业;产业成长;借鉴意义;支持措施
来源出版物:中国农业资源与区划, 2016, 37(2):226-230
中国绿色农业指标体系建设指导原则和构架
张正斌,王大生,徐萍
摘要:本文论述了食品安全法的落实要建立在农产品质量安全法基础上,而农产品质量安全法的实施要建立在绿色农业(食品)安全法基础上。绿色农业应该成为未来现代农业发展的主流方向,绿色食品应该成为替代无公害食品和有机食品的主流食品。随着绿色农业(食品)国际联盟的建立,加快中国绿色农业和绿色食品的国际化发展成为当前和未来中国农业发展的重要任务。本文提出了加快中国绿色农业指标体系建设的指导原则和构架,为绿色农业(食品)基地的建设和评估提供理论依据,进一步提出了绿色农业(食品)标准体系制定的指导原则和构架,为各部门和各专业人员制定食品安全标准提供建设性指导意见,以加快我国食品安全标准的制定。
关键词:绿色农业;绿色食品;食品安全;指标体系;安全标准体系;生产技术标准体系
来源出版物:中国生态农业学报, 2011, 19(6):1461-1467
中国绿色农业发展历程、现状与预测
刘子飞
摘要:绿色农业是农业产业践行绿色发展理念和生态文明建设的具体生产方式,是适应居民收入提高消费升级阶段的绿色产业。以绿色农业典型政策和概念提出为节点,绿色农业发展历程可分为两期三阶段,即形成期(准备阶段)、成长期(迅速发展阶段和稳定发展阶段)。目前,绿色农业管理机制和认证体系仍需加强,绿色农业主要指标均呈快速增长态势。未来10年,绿色农业发展将比整体经济增长速度高2个百分点以上,发展潜力巨大。相关部门应加强健全管理机构、完善认证体系等绿色农业发展政策环境,企业、农场、农户等利益相关者应抓住绿色农业产业发展机遇期。
关键词:绿色农业;发展历程;指标预测
来源出版物:改革与战略, 2016(12):94-102
基于Tobit模型的低碳经济农业生产率增长影响因素实证研究
孔昕
摘要:改革开放以来,随着中国人口数量的快速增长,导致资源能源的匮乏,由此产生的环境问题也愈来愈严重,农业发展与农村经济的增长在人类社会的发展中有着举重若轻地地位,研究和推广一种农业低碳经济发展模式,对促进中国社会经济稳定协调发展具有深远的意义。文章在前人已有研究数据理论基础上,首先提出推进低碳农业的重要性,并基于我国发展低碳农业过程中存在的一些问题,采用Tobit模型进行量化研究分析低碳经济农业生产率增长影响因素,在实证分析部分分别对1994—2004年与2005—2014年等2个时间阶段影响低碳农业生产率增长的关键因素进行分析。在考虑农业碳排放特征的前提下,分析绿色农业生产率增长因素对低碳经济发展的影响程度及促进作用大小,并且判断未来中国农业经济在不同因素的影响程度下的增长形式,确定推进我国低碳经济的发展的最佳举措,以便将来在选择促进低碳经济发展的道路中提供战略性依据。
关键词:低碳农业Tobit模型;农业生产率;生态农业;发展方式
来源出版物:中国农业资源与区划, 2016, 37(10):140-145
蔬菜作物根结线虫病害防治研究进展
崔鑫,岳向国,李斌,等
摘要:根结线虫(Meloidogynespp.)是重要的蔬菜作物寄生线虫,分布于世界各地而且寄主范围广泛。目前根结线虫的危害程度已成为仅次于真菌的第二大植物病害。本文综述了蔬菜作物生产过程中农业防治、作物育种、生物防治和化学防治4种防治根结线虫的方法,探讨了各种防治方法的优势和局限性,并展望了现代有机绿色农业中根结线虫科学防治的研究方向和趋势。
关键词:根结线虫;生物防治;化学防治;设施蔬菜;综述
来源出版物:中国蔬菜, 2017, 1(10):31-38
我国北方农牧交错区土地生态安全评价——以白城市为例
张茹,戴文婷,刘兆顺,等
摘要:白城市位于北方农牧交错区,生态环境脆弱。为了解其土地生态安全状况,基于压力-状态-响应(pressure-stateresponse,简称PSR)模型,共选取21个指标构建了土地生态安全评价指标体系,对2007—2012年白城市及其所辖5个县区土地生态安全变化情况进行评价分析。结果表明:1)各县(市、区)土地生态压力-状态-响应情况不同,镇赉县、大安县及洮北区土地生态压力安全值较高,对安全综合值贡献率在38%以上;洮南市土地生态状态安全值较高,贡献率在36%以上;通榆县土地生态压力—状态—响应安全值分布比较均衡,贡献比为35∶34∶31。2)2007—2012年,白城市土地生态安全综合值由0.7122提高至0.7804,土地生态环境有所改善,但土地安全等级仍处于敏感级,生态环境比较脆弱。3)白城市土地生态安全状况的改善有赖于实施有效的人口政策,控制人口规模;引进人才,鼓励农民发展新型绿色农业,减轻土地污染压力;提高环境保护意识,加大环保投资力度,促进土地生态恢复。
关键词:农牧交错区;土地生态;安全评价;PSR模型;白城市
来源出版物:水土保持研究, 2017, 24(2):259-266
粮食安全背景下农业生态安全与绿色发展——以湖北省为例
汪成,高红贵
摘要:首先阐述了粮食安全与农业生态的内在联系。然后采用熵权法对湖北省2005—2014年的农业生态安全状况进行了评价。同时对影响农业生态安全的主要因素进行了分析。结果表明:湖北省农业生态安全评价得分值偏低,但整体呈上升的趋势。最后对如何保障农业生态安全,支持农业绿色发展提出了相关的对策建议。
关键词:粮食安全;绿色农业;农业生态安全
来源出版物:生态经济, 2017, 33(4):107-109
中国绿色农业生态补偿政策:理论及研究述评
王宾
摘要:中国农业要实现转型升级,绿色发展是必由之路。准确界定绿色农业生态补偿政策对于农业健康发展至关重要,文章在论述绿色农业生态补偿政策相关理论基础上,梳理了国内外有关绿色农业生态补偿政策的文献,指出了现有研究存在的不足,并提出了未来研究的趋势。
关键词:绿色农业;生态补偿;研究述评
来源出版物:生态经济, 2017, 33(3):19-23
基于脂质纳米载体农药包埋体系的研究进展
贺军波,史浩,张维农,等
摘要:农药在确保世界粮食生产中发挥着重要作用,但农药的大量使用也造成了严重的食品安全和环境污染问题,因此,绿色农业促进了基于纳米技术的新农药理念——纳米农药的发展。综述了以可再生、可生物降解、环境友好的脂质为载体包埋农药分子进而形成纳米农药的研究进展,主要从纳米脂质体、固体脂质纳米粒、纳米结构脂质载体和脂质-农药键合体4个方面综述了纳米农药的研究现状,并分析了当前存在的问题和未来的研究方向,旨在为深入开展以脂质为载体的农药纳米包埋和递送体系的研究提供参考。
关键词:脂质载体;纳米农药;包埋;缓释
来源出版物:农药, 2017(10):4-8
The future of urban agriculture and biodiversity-ecosystem services:Challenges and next steps
Lin, Brenda B; Philpott, Stacy M; Jha, Shalene; et al.
Abstract:Urban landscapes are spatially constrained, and vegetative land uses that provide beneficial ecosystem services are difficult to maintain. Urban Agricultural (UA)systems appear in many forms-from community farms and rooftop gardens to edible landscaping and urban orchards-and can be productive features of cities and provide important environmental services. As highly managed plant communities, UA can exhibit high levels of biodiversity, often exceeding that of other green space areas within the city. Additionally, it is likely that variation in vegetation cover, diversity, and structure influence not only the biodiversity in UA, but also the quantity and quality of ecosystem services supported by such systems.The Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (B&ES) of UA can have potentially large societal and environmental benefits for cities, such as enhanced food security, air quality, and water regulation. Yet few studies have synthesized knowledge regarding UA vegetation management impacts on the quantity, quality, and stability of B&ES provided. This article presents the first survey of the existing research on the characteristics of UA management and their potential to support ecosystem service delivery. Specifically, we examine:(1) biodiversity patterns in UA, (2) ecosystem services provided by UA,and (3) the challenges of promoting UA systems that support B&ES. Overall, our review reveals that varied vegetative structure, increased native plant diversity, and reduction of urban impervious surface are key features of UA systems that contribute significantly to urban biodiversity and provide important ecosystem services such as pollination, pest control, and climate resilience. We conclude with a discussion of critical gaps in current research and strategies to better understand and support UA and ecosystem services.
关键词:food security; urban planning; vegetation complexity; agricultural management; gardens; green space
来源出版物:Basic and Applied Ecology, 2015, 16(3):189-201
Environment friendly green composites based on soy protein isolate: A review
Koshy, Rekha Rose; Mary, Siji K; Thomas, Sabu; et al.
Abstract:As a result of the growing environmental awareness (e.g., increased pollution, increasing demand for biodegradable materials, material need for CO2neutrality and low greenhouse gas emissions, new environmental laws and regulations), manufacturers and scientists are keen to study novel environmental friendly materials. Soy Protein Isolate (SPI), a protein with reproducible resource,good biocompatibility, biodegradability and processability has a significant potential in the food industry, agriculture,bioscience and biotechnology. The aim of this review is to offer a comprehensive view of the recent state of art of eco-materials based on Soy Protein Isolate (SPI) with special reference to organic and inorganic fillers in the macro, micro and nano scale. Moreover, some applications of SPI-based materials, especially in the field of food preservation and packaging technology, are also discussed.
关键词:soy protein isolate; biopolymer; biocomposites;bionanocomposites; food preservation; packaging
来源出版物:Food Hydrocolloids, 2015, 50:174-192
Green and blue water footprint reduction in irrigated agriculture: Effect of irrigation techniques, irrigation strategies and mulching
Chukalla, AD; Krol, MS; Hoekstra, AY
Abstract:Consumptive water footprint (WF) reduction in irrigated crop production is essential given the increasing competition for freshwater. This study explores the effect of three management practices on the soil water balance and plant growth, specifically on evapotranspiration (ET)and yield (Y) and thus the consumptive WF of crops (ET /Y). The management practices are four irrigation techniques (furrow, sprinkler, drip and subsurface drip(SSD), four irrigation strategies (full (FI), deficit (DI),supplementary (SI) and no irrigation), and three mulching practices (no mulching, organic (OML) and synthetic(SML) mulching). Various cases were considered:arid,semi-arid, sub-humid and humid environments in Israel,Spain, Italy and the UK, respectively; wet, normal and dry years; three soil types (sand, sandy loam and silty clay loam); and three crops (maize, potato and tomato). The AquaCrop model and the global WF accounting standard were used to relate the management practices to effects on ET, Y and WF. For each management practice, the associated green, blue and total consumptive WF were compared to the reference case (furrow irrigation, full irrigation, no mulching). The average reduction in the consumptive WF is 8%-10% if we change from the reference to drip or SSD, 13% when changing to OML,17%-18% when moving to drip or SSD in combination with OML, and 28% for drip or SSD in combination with SML. All before-mentioned reductions increase by one or a few per cent when moving from full to deficit irrigation.Reduction in overall consumptive WF always goes together with an increasing ratio of green to blue WF. The WF of growing a crop for a particular environment is smallest under DI, followed by FI, SI and rain-fed. Growing crops with sprinkler irrigation has the largest consumptive WF,followed by furrow, drip and SSD. Furrow irrigation has a smaller consumptive WF compared with sprinkler, even though the classical measure of “irrigation efficiency” for furrow is lower.
来源出版物:Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 2015,19(2):4877-4897
Breeding annual grain legumes for sustainable agriculture: New methods to approach complex traits and target new cultivar ideotypes
Duc, Gerard; Agrama, Hesham; Bao, Shiying; et al.
Abstract:Although yield and total biomass produced by annual legumes remain major objectives for breeders, other issues such as environment-friendly, resource use efficiency including symbiotic performance, resilient production in the context of climate change, adaptation to sustainable cropping systems (reducing leaching, greenhouse gas emissions and pesticide residues), adaptation to diverse uses (seeds for feed, food, non-food, forage or green manure) and finally new ecological services such as pollinator protection, imply the need for definition of new ideotypes and development of innovative genotypes to enhance their commercialization. Taken as a whole, this means more complex and integrated objectives for breeders.Several illustrations will be given of breeding such complex traits for different annual legume species. Genetic diversity for root development and for the ability to establish efficient symbioses with rhizobia and mycorrhiza can contribute to better resource management (N, P, water).Shoot architectures and phenologies can contribute to yield and biotic constraint protection (parasitic weeds, diseases or insects) reducing pesticide use. Variable maturity periods and tolerance to biotic and abiotic stresses are key features for the introduction of annual legumes to low input cropping systems and for enlarging cultivated area.Adaptation to intercropping requires adapted genotypes.Improved health and nutritional value for humans are key objectives for developing new markets. Modifying product composition often requires the development of specific cultivars and sometimes the need to break negative genetic correlations with yield. A holistic approach in legume breeding is important for defining objectives with farmers,processors and consumers. The cultivar structures are likely to be more complex, combining genotypes, plant species and associated symbionts. New tools to build and evaluate them are important if legumes are to deliver their exciting potential in terms of agricultural productivity and sustainability as well as for feed and food.
关键词:breeding; forage; ideotype; ecosystem service;food; grain legumes
来源出版物:Critical Reviews in Plant Sciences, 2015,34(1-3):381-411
Fourteen years of evidence for positive effects of conservation agriculture and organic farming on soil life
Henneron, Ludovic; Bernard, Laetitia;Hedde, Mickael; et al.
Abstract:Conventional agriculture strongly alters soil quality due to industrial practices that often have negative effects on soil life. Alternative systems such as conservation agriculture and organic farming could restore better conditions for soil organisms. Improving soil life should in turn improve soil quality and farming sustainability. Here, we have compared for the first time the long-term effects of conservation agriculture, organic farming, and conventional agriculture on major soil organisms such as microbes, nematofauna, and macrofauna.We have also analyzed functional groups. Soils were sampled at the 14-year-old experimental site of La Cage,near Versailles, France. The microbial community was analyzed using molecular biology techniques. Nematofauna and macrofauna were analyzed and classified into functional groups. Our results show that both conservation and organic systems increased the abundance and biomass of all soil organisms, except predaceous nematodes. For example, macrofauna increased from 100% to 2500%,nematodes from 100% to 700%, and microorganisms from 30% to 70%. Conservation agriculture showed a higher overall improvement than organic farming. Conservation agriculture increased the number of many organisms such as bacteria, fungi, anecic earthworms, and phytophagous and rhizophagous arthropods. Organic farming improved mainly the bacterial pathway of the soil food web and endogeic and anecic earthworms. Overall, our study shows that long-term, no-tillage, and cover crops are better for soil biota than periodic legume green manures, pesticides,and mineral fertilizers.
关键词:soil biodiversity; functional groups; soil food web;soil functioning; soil quality; land management; agricultural sustainability; agro-ecosystems; agro-ecology
来源出版物:Agronomy for Sustainable Development 2015, 35(1):169-181
Urban vegetable for food security in cities:A review
McKenzie, Fiona C; Williams, John
Abstract:Global food production faces great challenges in the future. With a future world population of 9.6 billion by 2050, rising urbanization, decreasing arable land, and weather extremes due to climate change, global agriculture is under pressure. While today over 50% of the world population live in cities, by 2030, the number will rise to 70%. In addition, global emissions have to be kept in mind.Currently, agriculture accounts for around 20%-30% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Shifting food production to locations with high demands reduces emissions and mitigates climate change. Urban horticulture increases global food production by exploiting new locations for cultivation. However, higher land prices and urban pollution constrain urban horticulture. In this paper, we review different urban cultivation systems throughout the world. Our main findings from ecological, economical,and social aspects are:(1) Urban horticulture activities are increasing globally with at least 100 million people involved worldwide. With potential yields of up to 50 kg per m2per year and more, vegetable production is the most significant component of urban food production which contributes to global food security. (2) Organoponic and other low-input systems will continue to play an important role for a sustainable and secure food production in the future. (3) Despite the resource efficiency of indoor farming systems, they are still very expensive. (4)Integrating urban horticulture into educational and social programs improves nutrition and food security. Overlaying these, new technologies in horticultural research need to be adopted for urban horticulture to increase future efficiency and productivity. To enhance sustainability,urban horticulture has to be integrated into the urban planning process and supported through policies. However,future food production should not be “local at any price”,but rather committed to increase sustainability.
关键词:climate change; sustainable food; sky farming;urban population; vertical farming; urban agriculture; urban gardening
来源出版物:Agronomy for Sustainable Development,2015, 35(2):483-498
Green growth: The economic impacts of large-scale renewable energy development in China
Dai, Hancheng; Xie, Xuxuan; Xie, Yang; et al.
Abstract:This study assesses the economic impacts and environmental co-benefits of large-scale development of renewable energy (RE) in China toward 2050 using a dynamic computable general equilibrium (CGE) model with distinguished improvements in the power sector. Two scenarios are constructed:a reference scenario assuming conventional development of RE and an REmax scenario assuming large-scale RE development by tapping China’s RE potential. The results show that large-scale RE development would not incur a significant macroeconomic cost. On the contrary, it would have significant green growth effects that benefit the growth of upstream industries, reshape the energy structure, and bring substantial environmental co-benefits. If the share of RE reaches 56% in the total primary energy in 2050, then non-fossil power sectors will become a mainstay industry with value added accounting for 3.4% of the GDP, a share comparable to other sectors such as agriculture (2.5%),iron and steel (3.3%), and construction (2.1%). In RE max scenario, the large scale RE development will stimulate the output worth of $1.18 trillion from other RE related upstream industries and create 4.12 million jobs in 2050. In addition to economic benefits, it could substantially reduce the emissions of CO2and air pollutants such as NOx, SO2.
关键词:renewable energy; economic impact; green growth;general equilibrium model (CGE); China
来源出版物:Applied Energy, 2016, 162:435-449
Global agricultural intensification during climate change: A role for genomics
Abberton, Michael; Batley, Jacqueline;Bentley, Alison; et al.
Abstract:Agriculture is now facing the perfect storm of climate change, increasing costs of fertilizer and rising food demands from a larger and wealthier human population. These factors point to a global food deficit unless the efficiency and resilience of crop production is increased. The intensification of agriculture has focused on improving production under optimized conditions, with significant agronomic inputs. Furthermore, the intensive cultivation of a limited number of crops has drastically narrowed the number of plant species humans rely on. A new agricultural paradigm is required, reducing dependence on high inputs and increasing crop diversity, yield stability and environmental resilience. Genomics offers unprecedented opportunities to increase crop yield, quality and stability of production through advanced breeding strategies, enhancing the resilience of major crops to climate variability, and increasing the productivity and range of minor crops to diversify the food supply. Here we review the state of the art of genomic-assisted breeding for the most important staples that feed the world, and how to use and adapt such genomic tools to accelerate development of both major and minor crops with desired traits that enhance adaptation to,or mitigate the effects of climate change.
关键词:climate change; food security; sustainability
来源出版物:Plant Biotechnology Journal, 2016, 14(4):1195-1098
Green concrete partially comprised of farming waste residues: A review
Mo, Kim Hung; Alengaram, U. Johnson;Jumaat, Mohd Zamin; et al.
Abstract:The growing demand of construction around the world has led to the increased usage of concrete. However,conventional concrete-making materials are not entirely environmental-friendly and this has enthused research on seeking greener alternative for concrete production. In the past, extensive research works had been carried out to utilize farming waste materials such as those from palm oil,coconut, sugarcane as well as the paddy industry and these findings indicate potential of utilizing such materials in concrete. The re-use of the farming waste materials in concrete could reduce the dependency on conventional concrete-making material as well as minimizing the negative impact on the environment besides ensuring waste conservation and reduction in waste disposal from these sectors. In this paper, a review on the utilization of emerging alternative farming waste materials in concrete such as from the farming of bamboo, corn, wheat, olive,sisal, seashells and more is carried out with the aim of examining the benefits and shortcomings of using these materials. This review shows the possible usage of farming waste materials in different form in concrete, such as partial cement and aggregate replacement, as well as fibre reinforcement. The main finding from the paper is that although usage of farming waste materials resulted in lowering of some concrete properties, appropriate treatment methods and selection of the waste materials would enable the production of concrete with improved performance. The summary and discussion provided in this paper should provide new information and knowledge on a greater variety of farming waste materials which are suitable to be used for the production of a greener and sustainable concrete.
关键词:farming waste; agriculture; aquaculture; concrete
来源出版物:Journal of Cleaner Production, 2016, 117:122-138
Soil sensing: A new paradigm for agriculture
Rossel, Raphael A. Viscarra; Bouma, Johan
Abstract:Last century, during the ‘Green Revolution’ the use of synthetic fertilizers contributed to increased agricultural production. However, their use did not reflect local soil and water conditions because recommendations were developed for larger agro-ecological zones. They only focused on increased productivity, neglecting any adverse environmental consequences. Largely, this legacy remains and recommendations are still made using top-down procedures based on limited data and generic, empirical relations between soil nutrient contents, fertilization rates and yields. Using soil sensors in agriculture can fundamentally change this approach by allowing innovative‘bottom-up’ approaches that characterize local soil and environmental conditions in space and time, improving the efficiency of production to maximize farm incomes and minimize environmental side effects. The sensed information can be used to build site-specific databases of relations between soil and plant condition and growth.Recent technological developments in sensing coupled with ongoing advances in information and communication technologies have given ground to a renewed interest in soil sensing and its use in different applications at different spatial scales. Soil sensing can facilitate the measurement and monitoring of the soil’s physical and biochemical attributes (e.g. nutrients, water) to better understand their dynamics, their interactions with the environment while considering their large spatial heterogeneity. The new sensing methods can also be used to effectively monitor soil organic carbon and be central to the adoption of best agronomic practices that also allow carbon sequestration and a reduction of greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions. Thus,sensing can help us to better articulate the potential of soil to meet the world’s needs for food, fiber, climate adaptation and environmental sustainability allowing the design and implementation of innovative management practices and policy aimed at sustainable development.
来源出版物:Agricultural Systems, 2016, 148:71-74
Energy, land-use and greenhouse gas emissions trajectories under a green growth paradigm
van Vuuren, Detlef P; Stehfest, Elke;Gernaat, David E. H. J; et al.
Abstract:This paper describes the possible developments in global energy use and production, land use, emissions and climate changes following the SSP1 storyline, a development consistent with the green growth (or sustainable development) paradigm (a more inclusive development respecting environmental boundaries). The results are based on the implementation using the IMAGE 3.0 integrated assessment model and are compared with a)other IMAGE implementations of the SSPs (SSP2 and SSP3) and b) the SSP1 implementation of other integrated assessment models. The results show that a combination of resource efficiency, preferences for sustainable production methods and investment in human development could lead to a strong transition towards a more renewable energy supply, less land use and lower anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions in 2100 than in 2010, even in the absence of explicit climate policies. At the same time, climate policy would still be needed to reduce emissions further, in order to reduce the projected increase of global mean temperature from 3 degrees C (SSP1 reference scenario) to 2 or 1.5 degrees C (in line with current policy targets). The SSP1 storyline could be a basis for further discussions on how climate policy can be combined with achieving other societal goals.
关键词:shared socio-economic pathways (SSPs);sustainable development; integrated assessment; climate change research; scenarios
来源出版物:Global Environmental Change-Human and Policy Dimensions, 2017, 42:237-250
Ten striking facts about agricultural input use in Sub-Saharan Africa
Sheahan, Megan; Barrett, Christopher B
Abstract:Conventional wisdom holds that Sub-Saharan African farmers use few modern inputs despite the fact that most poverty-reducing agricultural growth in the region is expected to come largely from expanded use of inputs that embody improved technologies, particularly improved seed,fertilizers and other agro-chemicals, machinery, and irrigation. Yet following several years of high food prices,concerted policy efforts to intensify fertilizer and hybrid seed use, and increased public and private investment in agriculture, how low is modern input use in Africa really?This article revisits Africa’s agricultural input landscape,exploiting the unique, recently collected, nationally representative, agriculturally intensive, and cross-country comparable Living Standard Measurement Study-Integrated Surveys on Agriculture (LSMS-ISA) covering six countries in the region (Ethiopia, Malawi, Niger, Nigeria, Tanzania,and Uganda). Using data from over 22000 households and 62000 agricultural plots, we offer ten potentially surprising facts about modern input use in Africa today.
关键词:improved seed; fertilizer; agro-chemical; machinery;irrigation; sub-Saharan Africa
来源出版物:Food Policy, 2017, 67:12-25
Cover crops support ecological intensification of arable cropping systems
Wittwer, Raphael A; Dorn, Brigitte; Jossi, Werner; et al.
Abstract:A major challenge for agriculture is to enhance productivity with minimum impact on the environment.Several studies indicate that cover crops could replace anthropogenic inputs and enhance crop productivity.However, so far, it is unclear if cover crop effects vary between different cropping systems, and direct comparisons among major arable production systems are rare. Here we compared the short-term effects of various cover crops on crop yield, nitrogen uptake, and weed infestation in four arable production systems (conventional cropping with intensive tillage and no-tillage; organic cropping with intensive tillage and reduced tillage). We hypothesized that cover cropping effects increase with decreasing management intensity. Our study demonstrated that cover crop effects on crop yield were highest in the organic system with reduced tillage (+24%), intermediate in the organic system with tillage (+13%) and in the conventional system with no tillage (+8%) and lowest in the conventional system with tillage (+2%). Our results indicate that cover crops are essential to maintaining a certain yield level when soil tillage intensity is reduced (e.g.under conservation agriculture), or when production is converted to organic agriculture. Thus, the inclusion of cover crops provides additional opportunities to increase the yield of lower intensity production systems and contribute to ecological intensification.
来源出版物:Scientific Reports, 2017, 7:41911
The impact of climate on farm inputs in developing countries agriculture
Mendelsohn, Robert; Wang, Jinxia
Abstract:The success of the green revolution has prompted some analysts to suggest it can be extended more broadly to all poor farmers. This paper argues that suitable natural endowments are an important precondition for high input farming. Examining production functions across China, we find that outcomes are very climate sensitive.It follows that we also find that input demand functions are climate sensitive. Efforts to intensify farming in undeveloped regions should focus on places with suitable soils and especially climate. The results also suggest that farmers will partially adapt to climate change by altering their input intensity.
关键词:adaptation; agriculture; climate change
来源出版物:Atmosphere, 2017, 30(2):77-86
Photovoltaic agriculture: New opportunity for photovoltaic applications in China
Xue, Jinlin
Abstract:Photovoltaic industry has been an important development direction of China’s strategic emerging industries since 2012, and more and more attentions have been paid to broaden the domestic demand to solve the problem of overcapacity of China’s PV industry.Photovoltaic agriculture, the combination of photovoltaic power generation and agricultural activities, is a natural response to supply the green and sustainable electricity for agriculture. There are several main application modes of photovoltaic agriculture such as photovoltaic agricultural greenhouse, photovoltaic breeding, photovoltaic wastewater purification, photovoltaic water pumping and new type rural solar power station. Photovoltaic agriculture can effectively alleviate the contradiction between more population and less land, powerfully promote the development of controlled environmental agriculture, evidently increase economic benefits of farmers, and significantly improve environment due to emissions reduction in China.In recent years, photovoltaic agriculture has a rapid development in China due to powerful support policies,flourishing controlled environmental agriculture, policyoriented rural electrification and promising electric machinery for greenhouse. Therefore, photovoltaic agriculture provides new opportunity for China’s photovoltaic industry, thus not only to solve the dilemma of overcapacity for China’s photovoltaic industry effectively,but also to accelerate the development of modern agriculture in China. However, the more theoretical researches and practical exploration must be conducted to optimize the combination of photovoltaic power generation and agricultural planting. And the unified standards must be established to standardize the design and scale of projects of photovoltaic agriculture. Also, photovoltaic enterprises need to produce widely applicable photovoltaic products for agricultural production and farmers’ life.
关键词:photovoltaics; agriculture; renewable energy;development; opportunity
来源出版物:Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews,2017, 73:1-9
Strategies for feeding the world more sustainably with organic agriculture
Muller, Adrian; Schader, Christian;Scialabba, Nadia El-Hage; et al.
Abstract:Organic agriculture is proposed as a promising approach to achieving sustainable food systems, but its feasibility is also contested. We use a food systems model that addresses agronomic characteristics of organic agriculture to analyze the role that organic agriculture could play in sustainable food systems. Here we show that a 100% conversion to organic agriculture needs more land than conventional agriculture but reduces N-surplus and pesticide use. However, in combination with reductions of food wastage and food-competing feed from arable land,with correspondingly reduced production and consumption of animal products, land use under organic agriculture remains below the reference scenario. Other indicators such as greenhouse gas emissions also improve, but adequate nitrogen supply is challenging. Besides focusing on production, sustainable food systems need to address waste, crop-grass-livestock interdependencies and human consumption. None of the corresponding strategies needs full implementation and their combined partial implementation delivers a more sustainable food future.
关键词:Nature Communications, 2017, 8:1290
Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture
Tilman, David; Balzer, Christian; Hill, Jason; et al.
Global food demand is increasing rapidly, as are the environmental impacts of agricultural expansion. Here,we project global demand for crop production in 2050 and evaluate the environmental impacts of alternative ways that this demand might be met. We find that per capita demand for crops, when measured as caloric or protein content of all crops combined, has been a similarly increasing function of per capita real income since 1960. This relationship forecasts a 100%-110% increase in global crop demand from 2005 to 2050. Quantitative assessments show that the environmental impacts of meeting this demand depend on how global agriculture expands. If current trends of greater agricultural intensification in richer nations and greater land clearing (extensification) in poorer nations were to continue, similar to 1 billion ha of land would be cleared globally by 2050, with CO2-C equivalent greenhouse gas emissions reaching similar to 3 Gt y-1and N use similar to 250 Mt y-1by then. In contrast,if 2050 crop demand was met by moderate intensification focused on existing croplands of underyielding nations,adaptation and transfer of high-yielding technologies to these croplands, and global technological improvements,our analyses forecast land clearing of only similar to 0.2 billion ha, greenhouse gas emissions of similar to 1 Gt y-1, and global N use of similar to 225 Mt y-1. Efficient management practices could substantially lower nitrogen use. Attainment of high yields on existing croplands of underyielding nations is of great importance if global crop demand is to be met with minimal environmental impacts.
food security; land-use change; biodiversity;climate change; soil fertility
文章题目第一作者来源出版物1 Global food demand and the sustainable intensification of agriculture Tilman, David Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2011, 180(50):20260-20264 2 Carabid beetles in sustainable agriculture:A review on pest Kromp, B Agriculture Ecosystems & Environment,control efficacy, cultivation impacts and enhancement 1999, 71(1-3):187-228 3Natural products in crop protection Dayan, Franck E Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry, 2009,17(12):4022-4034 4 The green, blue and grey water footprint of crops and Mekonnen, MM Hydrology and Earth System Sciences,derived crop products 2011, 15(5):1577-1600 5 Bringing ecosystem services into economic decision-Bateman, Ian J Science, 2013, 341(6141):45-50 making:Land use in the United Kingdom
中国石油大学(华东)】
卫夏雯

