汉诺威大楼,布拉德福德,英国
建筑设计:克劳斯-舍恩贝里建筑事务所
Architect: Kraus Schönberg Architects
汉诺威大楼,布拉德福德,英国
建筑设计:克劳斯-舍恩贝里建筑事务所
Architect: Kraus Schönberg Architects
Hanover House Bradford, United Kingdom, 2008
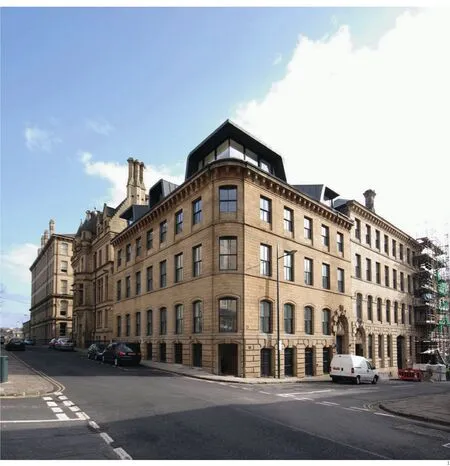

1 外景/Exterior view
项目信息/Credits and Data
客户/Client: 加布集团/Garbe Group
结构工程/Structural Engineer: EDA
项目管理/Project Management: Maber
总建筑面积/Gross Floor Area: 1300m2
造价/Cost: £1,600,000
摄影/Photos: 克劳斯-舍恩贝里建筑事务所/Kraus Schönberg Architects
英国二级保护建筑汉诺威大楼的改造是对一座维多利亚时期库房的翻新及屋顶的扩建。
汉诺威大楼位于布拉德福德的小德国区,那是一个历史价值很高、美轮美奂的保护区。这个地区独到的特色源自风格统一的19世纪建筑。
所用的砂岩和立面的装饰将街区统一起来——尽管与许多其他同时代的半工业区一样,小德国区的建筑大小和形式各不相同。因此,屋顶的景观也是丰富多样的。
这就为新屋顶的设计带来了灵感,并对周围的建筑形式、大小和朝向作出新的阐释。
屋顶轮廓的雕刻特征并非只是一场建筑幻想,而是与周边建筑的屋顶景观相映成趣,并构成了生活的空间。
为了建造一个高效的结构,这个屋顶被设计成一个自承重体系,避免给现有的楼板增加荷载。我们用人造木板作为可持续的高性能材料,以外墙为支撑创造出一个反复折叠的屋面。
屋顶折射出主体的结构、日照方向和各种景象。
进深15m的楼层平面需要精心设计的方案,以避免出现梁架过大的低效屋顶结构。所以屋面是顺着折板反复折叠的,这样就形成了一个以外墙为支撑的自承重结构。在高处,屋顶的承重点深入建筑内部,将结构的跨度从15m缩短到10m。倾斜的阳台侧墙将这些点上的反作用力传到外墙上。任何形成的侧向力都被传导在起拉结作用的楼板上。
屋面由交错层压人造木板制成。140mm厚的木板传热系数很好,构成了保温良好的屋顶。
所选的屋顶挂板用现代材料对街区传统的石板瓦屋顶进行了新的阐释。新屋顶采用无烟煤预锈化立缝锌挂板,外观与原屋顶相似。这个复杂的屋顶造型包括各种屋脊和天沟、斜墙、折面、曲面和辐射状转角。这就需要一种能够满足这些条件的施工技术。立缝锌屋顶是克服这一难题的最佳方案。
其空间概念已融入施工和结构,并构成了一个整体。□(尚晋 译)
The development of the grade II listed Hanover House involves the refurbishment and roof extension of a Victorian warehouse building.
Hanover House is located in Bradford's Little Germany, a conservation area of great historical interest and beauty. The unique character of the area is created by the uniformity of buildings dating from the 19th century.
The used sandstone material and the ornamental treatment of the facades unify the blocks - although, as with many other semiindustrial areas from the period, the buildings in Little Germany vary in size and form. Accordingly,the roofscape is one of great diversity.
This informs the design of the new roof, which reinterprets the surrounding forms, sizes and orientations.
The sculptural aspect of the roof silhouette is no mere architectural fancy, but ref l ects the roofscape of the surrounding buildings and has been used to form the living spaces.
Aiming to create a highly efficient structure, the roof has been designed as a self-supporting system to avoid additional loading onto the existing floors.We used engineered timber as a sustainable highperformance material, creating a roof surface which folds up and down and bears on the external walls.
The roof form reflects the construction of the primary structure, daylight direction and views.
The deep floor plan of 15m required an engineered solution to avoid an inefficient roof structure with oversized beams. Therefore the roof surface folds up and down to a folded plate creating a self supporting structure, which bears on the external walls. At high level the load bearing points of the roof are taken further into the building in order to shorten the span of the structure from 15m to 10m. The inclined balcony side walls transfer the reaction forces at these points into the external wall.Any resulting lateral forces are transferred into the floor plate which acts as a tie.
The roof surface is made of cross laminated engineered timber boards. The 140mm thick board has a good value and adds up to a highly insulated roof.
The chosen roof cladding re-interprets the traditional slate tiled roofs of the neighbourhood with a modern material. Similar in appearance the new roof is clad in anthracite pre-patinated standing seam zinc. The complex roof geometry with various ridges and valleys, inclined walls, folds, bends and radiused corners required a construction technique to accommodate these conditions. The standing seam zinc roof was an optimal solution for this challenge.
The spatial concept has merged with the construction and structure and has formed one entity. □

3 外景/Exterior view

4 模型/Model
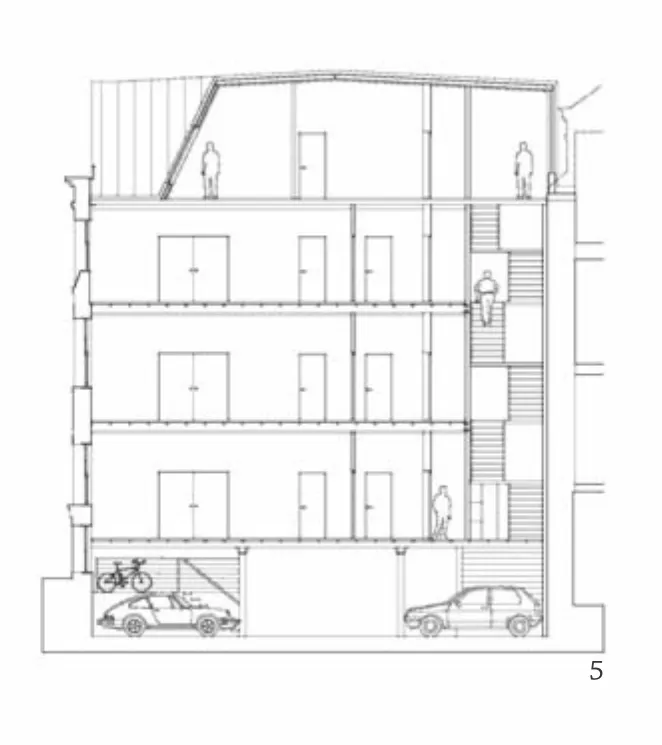
5 剖面/Section

6 四层平面/Floor 3 plan
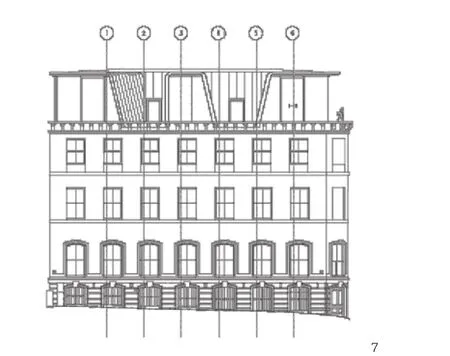
7 立面/Elevation
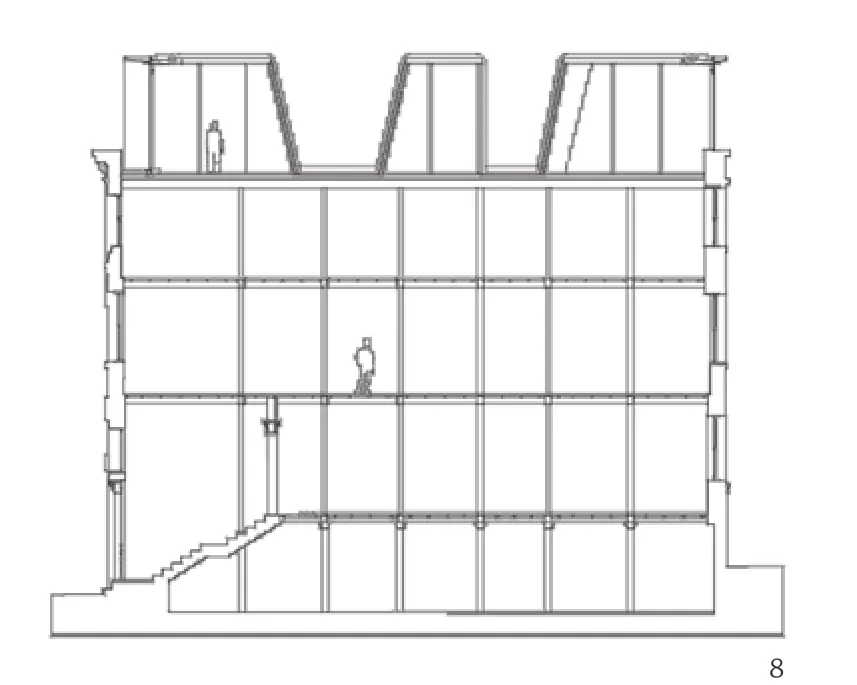
8 剖面/Section

9 外景/Exterior view

10 草图/Sketches

11 立面/Elevation


12-18 施工中/Under construction

19.20 草图/Sketches

21-23 施工中/Under construction

24 外景/Exterior view

25-27 内景/Interior views

