冷冻电镜
Li, XM; Mooney, P; Zheng, S; et al.
Cryo-EM study of the chromatin fiber reveals a double helix twisted by tetranucleosomal units
Song, F; Chen, P; Sun, DP; et al.
Beam-induced motion correction for sub-megadalton cryo-EMparticles
Scheres, SHW
Cryo-EM structure of the Plasmodium falciparum 80S ribosome bound to the anti-protozoan drug emetine
Wong, W; Bai, XC; Brown, A; et al.
结构生物学研究方法的重大突破——电子直接探测相机在冷冻电镜中的应用
柳正,张景强
冷冻电镜
·编者按·
冷冻电子显微镜技术(cryo-electron microscopy,Cryo-EM)是指运用透射电子显微镜对低温样品进行观察和成像的显微技术,简称冷冻电镜技术。冷冻电镜技术由低温制样、低剂量电镜成像和计算机图像处理3部分组成。冷冻电镜是重要的结构生物学研究方法,与X射线晶体学和核磁共振一起构成了高分辨率结构生物学研究的基础,在获得生物大分子的结构并揭示其功能方面极为重要,在结构生物学领域引起了研究者的极大关注。
冷冻电镜理论在20世纪70年代提出,但直到21世纪初,冷冻电镜的分辨率水平依然没有得到突破。2013年,由于最新的直接电子探测器(Direct Electron Detector, DED)的应用,以及单颗粒三维重建算法的革新和不断改进,冷冻电镜技术取得了飞跃式的发展,通过该技术解析得到的生物大分子结构可以达到近原子分辨率(<4 Å)水平。
3位冷冻电镜领域的开拓者Richard Henderson、Joachim Frank和Jacques Dubochet分别在该领域的基本理论、重构算法和实验方面的早期研究中做出了重要贡献。他们也因为“在开发用于溶液中生物分子高分辨率结构测定的冷冻电镜技术方面的贡献”,被授予2017年诺贝尔化学奖。
本专题得到张景强教授(中山大学)、朱莉副教授(兰州大学)的大力支持。
·热点数据排行·
截至2017年11月9日,中国知网(CNKI)和Web of Science(WOS)的数据报告显示,以“冷冻电镜”等为词条可以检索到的期刊文献分别为153、4452条,本专题将相关数据按照:研究机构发文数、作者发文数、期刊发文数、被引用频次进行排行,结果如下。
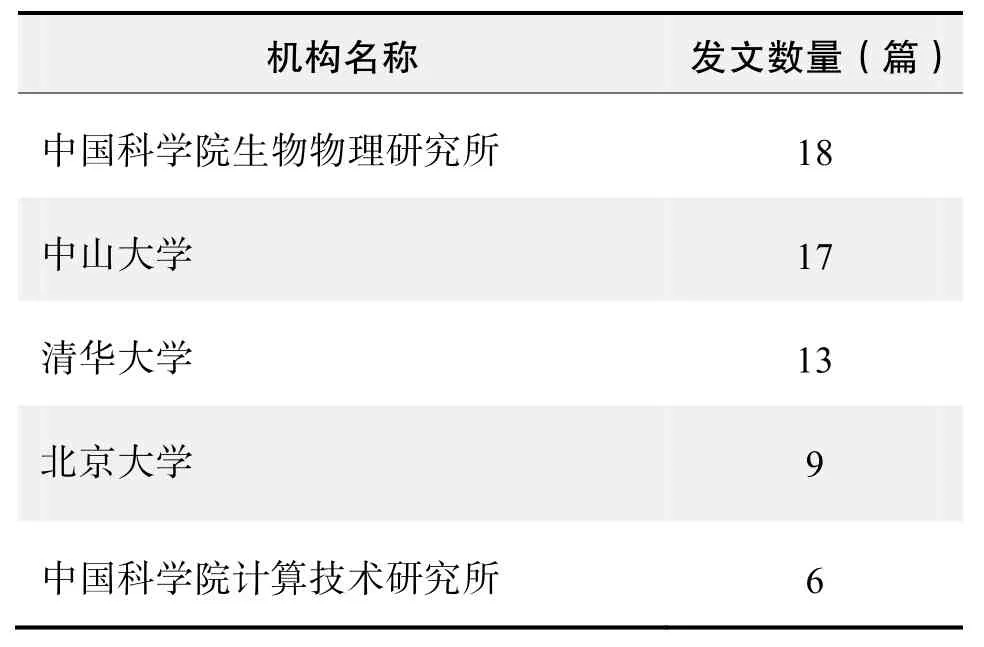
研究机构发文数量排名(CNKI)
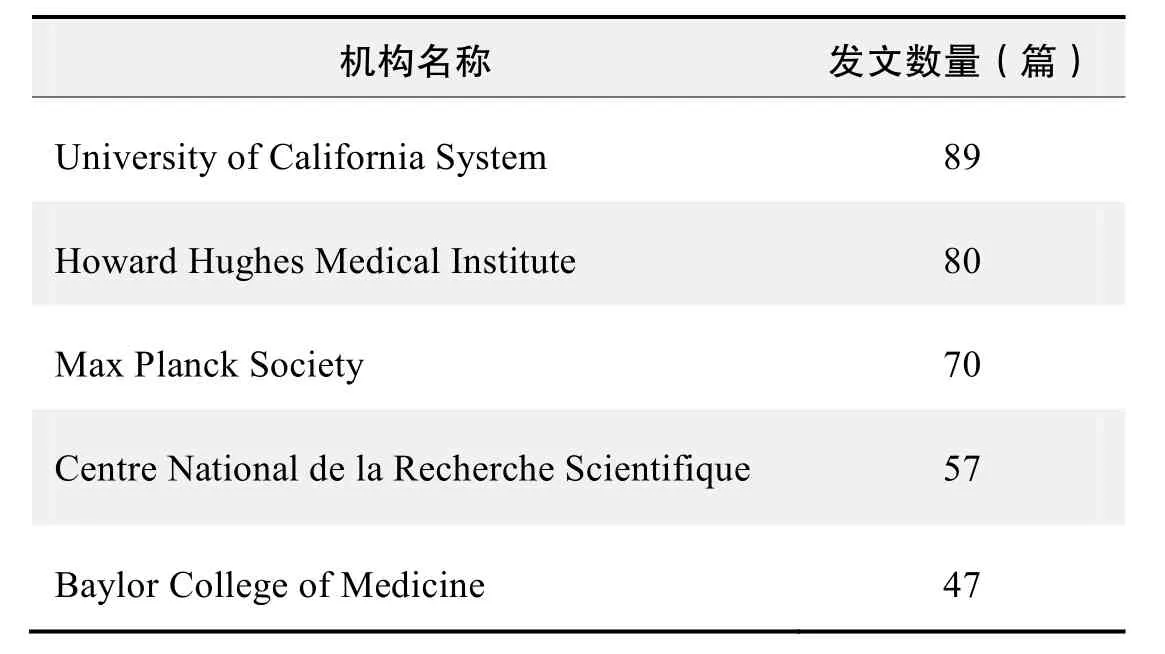
研究机构发文数量排名(WOS)

作者发文数量排名(CNKI)
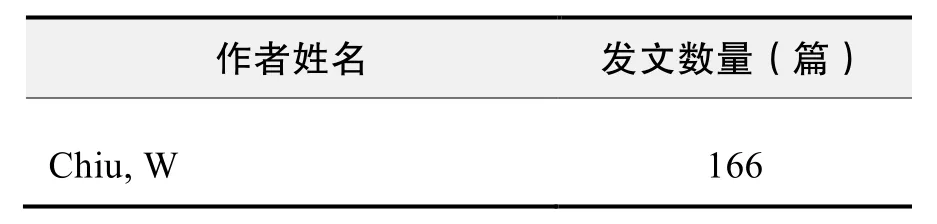
作者发文数量排名(WOS)
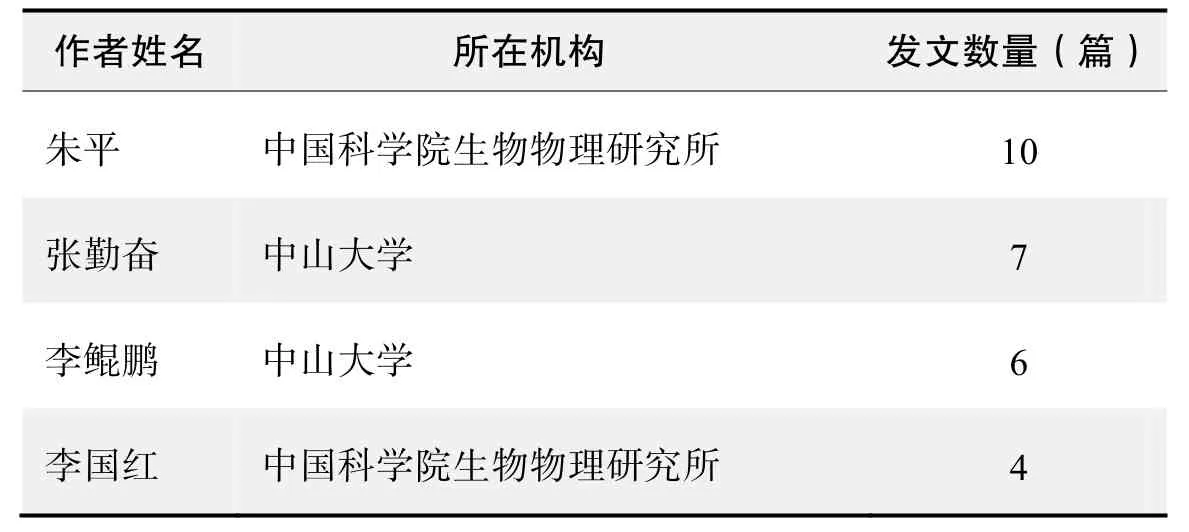
作者发文数量排名(CNKI)(续表)
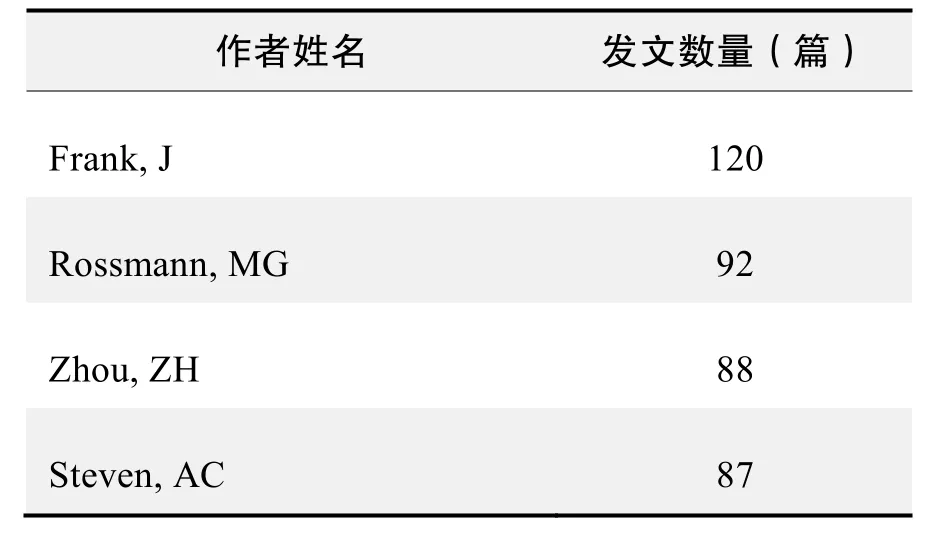
作者发文数量排名(WOS)(续表)
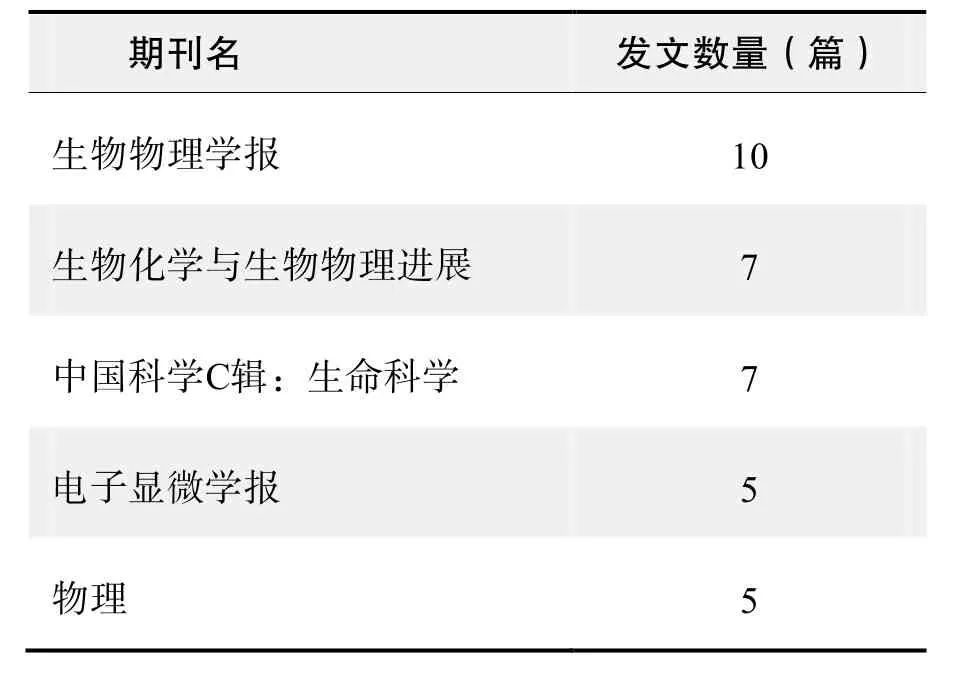
期刊发文数量排名(CNKI)
根据中国知网(CNKI)数据报告,以“冷冻电镜”等为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。

国内数据库高被引论文排行(续表)
根据Web of Science统计数据,以“冷冻电镜”等为词条可以检索到的高被引论文排行结果如下。
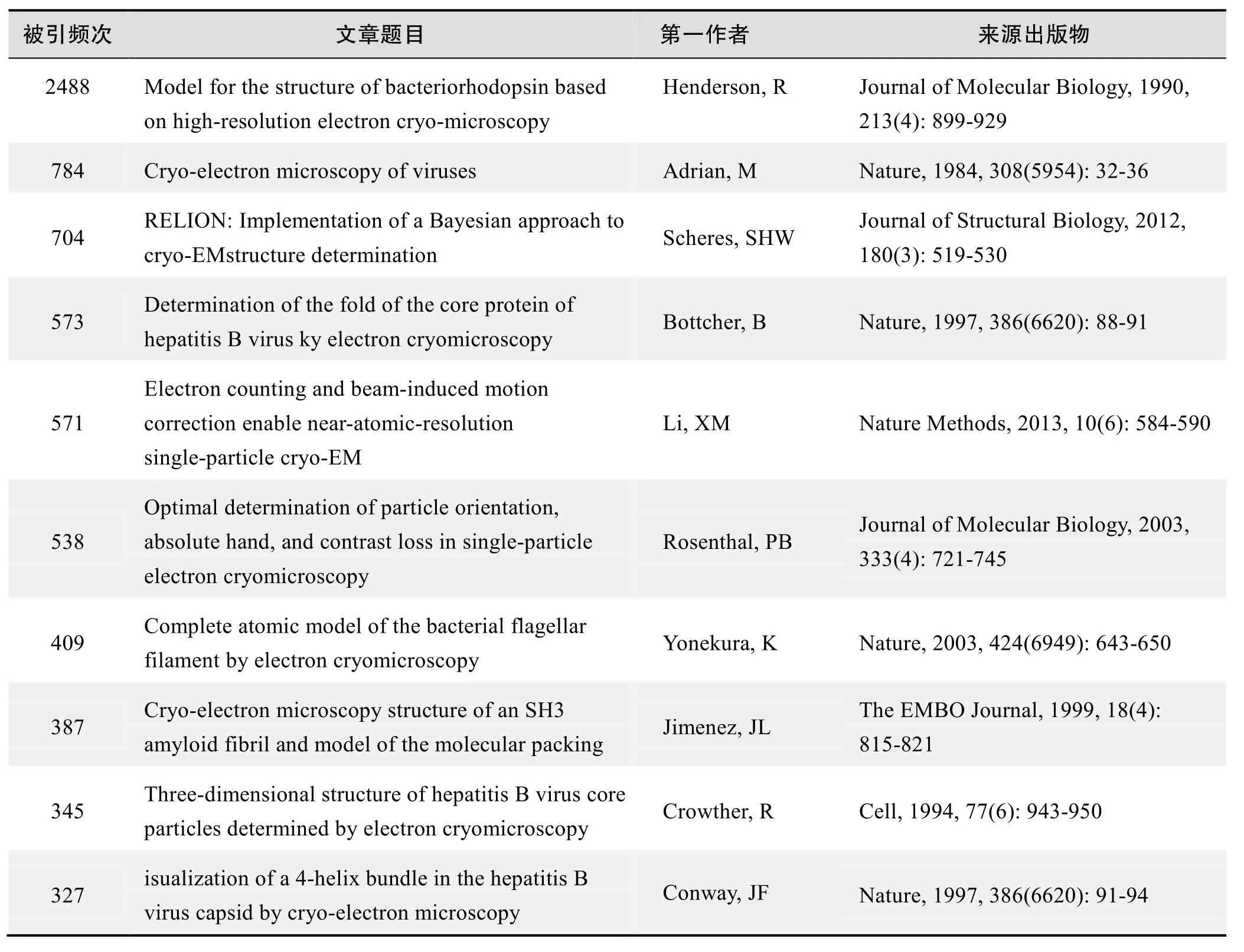
国外数据库高被引论文排行
·经典文献推荐·
基于Web of Science检索结果,利用Histcite软件选取LCS(Local Citation Score,本地引用次数)TOP 30文献作为节点进行分析,得到本领域推荐的经典文献如下。
electron microscopy; single-particle analysis;maximum likelihood; image processing; software development
来源出版物:Journal of Structural Biology, 2012, 180(3):519-530
Electron counting and beam-induced motion correction enable near-atomic-resolution single-particle cryo-EM
Li, XM; Mooney, P; Zheng, S; et al.
Abstract:In recent work with large high-symmetry viruses, single-particle electron cryomicroscopy (cryo-EM)has achieved the determination of near-atomic-resolution structures by allowing direct fitting of atomic models into experimental density maps. However, achieving this goal with smaller particles of lower symmetry remains challenging. Using a newly developed single electroncounting detector, we confirmed that electron beaminduced motion substantially degrades resolution, and we showed that the combination of rapid readout and nearly noiseless electron counting allow image blurring to be corrected to subpixel accuracy, restoring intrinsic image information to high resolution (Thon rings visible to ~3 Å).Using this approach, we determined a 3.3-Å-resolution structure of an ~700-kDa protein with D7 symmetry, theThermoplasma acidophilum20S proteasome, showing clear side-chain density. Our method greatly enhances image quality and data acquisition efficiency—key bottlenecks in applying near-atomic-resolution cryo-EM to a broad range of protein samples.
来源出版物:Nature Methods, 2013, 10(6): 584-590
Cryo-EM study of the chromatin fiber reveals a double helix twisted by tetranucleosomal units
Song, F; Chen, P; Sun, DP; et al.
Abstract:The hierarchical packaging of eukaryotic chromatin plays a central role in transcriptional regulation and other DNA-related biological processes. Here, we report the 11-angstrom-resolution cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of 30-nanometer chromatin fibers reconstituted in the presence of linker histone H1 and with different nucleosome repeat lengths.The structures show a histone H1-dependent left-handed twist of the repeating tetranucleosomal structural units,within which the four nucleosomes zigzag back and forth with a straight linker DNA. The asymmetric binding and the location of histone H1 in chromatin play a role in the formation of the 30-nanometer fiber. Our results provide mechanistic insights into how nucleosomes compact into higher-order chromatin fibers.
来源出版物:Science, 2014, 344(6182): 376-380
Beam-induced motion correction for sub-megadalton cryo-EMparticles
Scheres, SHW
Abstract:In electron cryo-microscopy (cryo-EM), the electron beam that is used for imaging also causes the sample to move. This motion blurs the images and limits the resolution attainable by single-particle analysis. In a previous Research article we showed that correcting for this motion by processing movies from fast direct-electron detectors allowed structure determination to near-atomic resolution from 35000 ribosome particles. In this Research advance article, we show that an improved movie processing algorithm is applicable to a much wider range of specimens.The new algorithm estimates straight movement tracks by considering multiple particles that are close to each other in the field of view, and models the fall-off of high-resolution information content by radiation damage in a dosedependent manner. Application of the new algorithm to four data sets illustrates its potential for significantly improving cryo-EM structures, even for particles that are smaller than 200 kDa.
来源出版物:Elife, 2014, 3: e03665
Cryo-EM structure of the Plasmodium falciparum 80S ribosome bound to the anti-protozoan drug emetine
Wong, W; Bai, XC; Brown, A; et al.
Abstract:Malaria inflicts an enormous burden on global human health. The emergence of parasite resistance to front-line drugs has prompted a renewed focus on the repositioning of clinically approved drugs as potential anti-malarial therapies. Antibiotics that inhibit protein translation are promising candidates for repositioning. We have solved the cryo-EM structure of the cytoplasmic ribosome from the human malaria parasite, Plasmodium falciparum, in complex with emetine at 3.2 angstrom resolution. Emetine is an anti-protozoan drug used in the treatment of ameobiasis that also displays potent anti-malarial activity. Emetine interacts with the E-site of the ribosomal small subunit and shares a similar binding site with the antibiotic pactamycin, thereby delivering its therapeutic effect by blocking mRNA/tRNA translocation.As the first cryo-EM structure that visualizes an antibiotic bound to any ribosome at atomic resolution, this establishes cryo-EM as a powerful tool for screening and guiding the design of drugs that target parasite translation machinery.
来源出版物:Elife, 2014, 3: e03080
·推荐综述·
结构生物学研究方法的重大突破——电子直接探测相机在冷冻电镜中的应用
柳正,张景强
引言
早在20世纪70年代,材料学研究中就使用电镜直接观察到了原子像。而生物材料由于含水、易受电子朿损伤及固有的低反差等问题,无法获得高分辨图像。后来,人们采用冷冻技术、低剂量成像及图像叠加等技术予以解决,从而在20世纪80年代出现了—种测定生物大分子三维结构的新方法——冷冻电镜技术。冷冻电镜技术由低温制样、低剂量电镜成像和计算机图像处理三部分组成。低温制样最先由Taylor和Glaeser成功应用,后经Dubochet的深入研究而完善,其基本流程是把载有样品(如缓冲液中病毒、蛋白质和DNA组装的颗粒等)的电镜载网快速投入经液氮/液氦冷却的液态乙烷中,在载网孔或支持膜上形成玻璃态的薄冰,样品颗粒(粒径大约十几到过百nm)分散包埋在其中而形成冷冻样品。电镜成像是指保持样品在液氮或液氦低温下,使用低电子剂量成像(通常使用20 e/Å2左右的低剂量)。计算机图像处理最先是指单颗粒图像分析,Frank及其同事做了大量的开创性工作,使其成为解析生物大分子三维结构的一个有力工具。单颗粒图像分析方法的要点是首先估计电子显微像中大量分散的样品颗粒(如核糖体、病毒颗粒和DNA颗粒等)的取向欧拉角和中心位置,并迭代精修,然后分类叠加平均,再根据测定的取向和位置参数,把二维像在傅里叶空间三维插值重构出其三维结构。随着研究的深入,证明应用单颗粒图像分析方法能够在原子分辨率尺度上解析生物大分子的结构。
虽然理论上可行,但由于冷冻电镜所获得的图像信噪比很低,在图像分析中很难准确地恢复高频信号及测定每个颗粒的取向和位置参数。因此,冷冻电镜单颗粒技术理论预期的能力在实践应用中很难达到。过去5年,也有一些高分辨率的结构被冷冻电镜单颗粒技术解析出来,但都局限于具有高对称性、刚性很好的大分子量球形病毒样品。近年来,电子显微镜开始装备了电子直接探测相机(electron direct detection device,DDD),已有研究组用这一装置对非对称性核糖体或者低对称性膜蛋白的结构进行研究,均获得了高分辨率的结果。本文将结合我们以往的冷冻电镜研究工作,介绍DDD相机的原理和技术优势,并结合冷冻电镜中的主要技术难题,展望DDD相机可能给冷冻电镜技术带来的突破性进展。
电镜中的成像载体
一般电镜中感光并记录图像的载体可以分为3类:荧光屏、感光胶片和CCD(charge-couple device)相机。荧光屏可实时显示所得的电子显微像,肉眼可直接观测但却无法永久保存。一般使用感光胶片或者CCD相机永久记录电子显微像。
胶片是一种对电子束敏感、颗粒度很小的溴化物乳胶底片,能很好地记录保存图像,但需要经常卸换底片(FEI的电镜通常一次只能装载56张底片),此过程会干扰电镜镜筒内的真空,并可能造成污染。另外,底片须在暗室内冲洗,扫描后才能进行图像处理和重构。我们曾使用感光胶片,应用髮夹灯丝200 kV的电镜,解析出亚纳米分辨率(9.8 Å)的戊型肝炎病毒(hepatitis E virus,HEV)的三维结构,在300 kV的场发射电镜下,解析了T7噬菌体衣壳的3.5 Å结构。
电镜CCD相机首先用闪烁器(scintillator)把入射电子信号转换成光信号,接着,用透镜或者光纤把光信号传送到像感应器,然后再转换为数字图像。入射电子每次进入闪烁器,都会在原位点发生偏离而形成扩散光云(cloud of light),常用点扩散函数(point spread function,PSF)来描述这一过程。点扩散函数随着入射电子数量的增加及深入而增大。因此,记录完整的一次曝光信号需要比较大的像素尺寸,如常见的CCD像素尺寸为15 μm。
与胶片相比,CCD相机的优点是无需卸换和冲洗,可以直接长时间连续地采集图像,与其他软件结合,还可以实现全自动高通量的数据收集。现在有不少实验室已经广泛使用CCD进行实时检测图像。我们也曾用CCD相机,在300 kV场发射电镜条件下,解析了昆虫质型多角体病毒(cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus,CPV)近原子分辨率(3.9 Å)的三维结构。
在CCD相机成像过程中,从成像电子入射直到最后的像被读出,要经历闪烁器中电子和光子的散射,以及光纤中的光子散射,还受到透镜耦合度的影响,这些都可能造成数据质量的下降。在高分辨率区域,CCD相机收集数据的检测量子效率(detective quantum efficiency,DQE,表示输入和输出图像的信噪比的比率)不如胶片,因此,在使用DDD相机之前,大多数的高分辨率病毒结构的电镜数据都是用感光胶片进行收集的。
DDD相机采用的是直接使用电子感光的方式。电子直接探测技术在其他领域(如高能粒子物理)早有应用,而由于电镜成像电子的能量很高,容易损伤传感器,限制了它在电镜领域的应用。经过几年的摸索,研究人员已经用DDD相机采集到的数据成功解析了多个非对称性或低对称性的高分辨率结构,如病毒、核糖体及其他蛋白等。得到的结构密度图能够直接进行氨基酸建模,可与解析生物大分子结构的传统方法(如X射线和NMR技术)相媲美。
DDD相机的原理与成像模式
DDD相机的基本原理是电子直接感光,不需要CCD相机那样的中间转换步骤。现代电子直接传感器主要源于在数码相机中发展的有源像素传感器(active pixel sensor,APS)互补金属氧化物半导体CMOS(complementary metal oxide semiconductor,CMOS)技术。在相机的芯片中,每个像素都有各自的信号放大器,各自进行电荷—电压的转换,从而提高了探测入射电子效率和像素读写的速度;再结合特殊线路布局,能够很好地承受电镜入射的高能电子。最早一代的DDD相机还采用背部比较厚的传感器,随着入射电子的增加与透入更深,PSF会增大;当前的DDD相机使用背部薄化(back-thinned)的传感器,避免了底层对电子的散射,仅仅在其上层硅质的介质中直接存贮入射的电子,然后进行信号转换,极大缩小了PSF。因此,这类传感器可以使用更小的像素尺寸(如K2 summit的为5 μm),从而可以在单位尺寸内应用更多像素。由于不需要中间的电子、光信号和图像的转换,免去了因此而产生的信号扭曲和失真。
调制传递函数(modulation transfer function,MTF)和检测量子效率(detective quantum efficiency,DQE)可以比较客观地描述DDD相机的性能特征。MTF是不同空间频率下相机信号的振幅函数,从数学上可以表征为PSF的傅立叶变换。而DQE是输入和输出图像的信噪比的比率。DDD相机与其它记录载体相比具有的特点是MTF和DQE在高频区域(高分辨率区)都很高,因而为电镜记录高分辨率的图像提供了保障。目前,DDD相机常用的成像模式可分为3种:整合模式(integrating mode)、计数模式(counting mode)和超分辨率模式(super-resolution mode)。用户可以根据自己的需要和所具备的计算设备的图像处理能力选择适合的模式。
整合模式与感光胶片和传统的CCD一样,DDD可以在曝光时间内把所有成像的入射电子一次性地收集与记录,并输出为图像。一次性的收集往往使得剂量都比较大,成像质量的提高来自DDD传感器自身较强的探测效率和内在较高的转换效率。
计数模式是对入射到探测器后的单个成像电子进行逐个记录,即把入射的电子模拟信号记录成离散的单个输出,这就要求传感器具有非常高的读出速率。一般读出速率400帧/s,如果相机的尺寸是4 K×
4 K,读出速率约为6 700 M·pixel/s,需要的计算机处理速率大概为100 Gb/s。
超分辨率模式是计数模式的进一步改进,记录的单个信号突破了物理像素的尺寸限制。其原理在于该模式下的传感器记录将PSF进一步缩小。可以把图像读出限制在信号产生的中心附近,这个范围往往都比一个像素的尺寸还小。因此,可以把信号局限在亚像素范围内。这种成像模式进一步地限制了噪声并提高了探测效率。DDD的共同优点是:可使用电影模式(movie mode)对同一区域进行多帧成像,再结合图像处理程序矫正研究对象在成像过程中产生的漂移(电子束相互作用引起的扰动,以及样品台的不稳定导致的移动等);但是,这样的数据采集方式,大大增加了数据量。一般来说,一次曝光存储25帧的话,对于4 K×
4 K的DDD,就需要1.6 G来存贮,对于一个预计重构到3点多埃的样品,如用自动采集软件收集数据,通常需要10 000张,这样一来获得的数据约为15 T。而超分辨模式更是把记录范围限制在信号产生的中心周围,从而将记录范围限制到了亚像素区域,这样可以在较低放大倍率下获得在整合模式或计数模式下同样的目标分辨率,从而在同样的成像区域内采集更多的数据,但在成像过程中,图像输出花费的时间比其它两种模式要多,在收集数据过程中,单位时间内采集的图像数比整合模式和计数模式要少。当前比较流行的三种DDD相机分别是K2 base/summit、FalconⅠ/Ⅱ和DE-12/20/64。在200 kV下,K2 base/summit和DE-12相机的DQE比FalconⅠ/Ⅱ高,而在300 kV,FalconⅡ的DQE在高频区比其他两款相机要好;另外,DE系列相机具有视场大的特点,价格也相对实惠。
DDD相机带来冷冻电镜的革新
对单颗粒技术的促进
对高对称性的样品来说,应用DDD收集数据,使获得高分辨率变得容易:1)同等分辨率下需要的颗粒数将大大降低,缩短了采集数据的时间。如轮状病毒,只要807个颗粒就达到了4.4 Å;2)达到同样分辨率的情况下,对图像处理的要求降低。如现在不需要考虑单个颗粒欠焦值、放大倍率和电子倾斜等多种参数的精修,就可以得到比较高的分辨率;3)采用同样的样品和策略,分辨率将进一步提升;4)对电镜的要求有所降低,如以往需要300 kV电镜才能达到4 Å的分辨率水平,现在用200 kV就可以达到。
DDD相机还将进一步降低以往电镜对研究生物大分子大小的限制(100~200 kD左右)。在传统的冷冻电镜技术中,由于低分子量的生物大分子对成像电子的散射很弱,图像输出信噪比很低,往往很难判断大分子颗粒的取向和位置相关参数,从而限制了其在小分子中的应用。对于某些小生物大分子,有时还需要借助负染色的方法来提高反差。DDD相机对较低分子量生物大分子成像时,可以保证产生足够的识别信号以进行图像的取向和位置参数的配准。最近已有160 kD的蛋白被解析到4.5 Å,450 kD的蛋白解析到3.2 Å。在膜蛋白结构的测定中,DDD也可以从去垢剂或者amphipols中的膜蛋白获得足够多的信号,从而满足图像处理的要求,重构得到高分辨率的结构。
对DDD相机采集的数据进行图像处理时,可对非均一性的样品实行有效的计算机纯化(purification in silico)。在很多执行生物功能的大分子样品中,基于功能因子的结合与否,构成了不同的构象状态或不同组成的复合物。目前的生物化学技术,如超速离心、柱层析等,不能将它们有效分离。从图像处理的角度,可用监督分类或者无监督分类将它们分离开来,尤其最近出现的最大似然估计(maximum likelihood)的无监督分类,给应用冷冻电镜进行结构研究带来了诸多方便,而信噪比的提高使得这些方法更加可靠。因此,冷冻电镜技术可以实时且在高分辨率下研究处理多种功能状态的分子,实现一次照相获得多个高分辨率结构。DDD相机带来的信噪比提高,还将会使得一些特殊的图像处理方法更加可靠。在研究具有区域对称性的样品时,如T7噬菌体,其具有二十面体的衣壳,还有不同对称性的尾部(参与构造的蛋白对称性各不相同),应用区域性重构的方法,可以避免其主要对称性对尾部的干扰而将其单独解析出来。
对冷冻电子断层技术的促进
与单颗粒技术采集大量散落的单个颗粒相比,电子断层成像只对单个对象(病毒、细菌、复合物和细胞等)从多个角度进行二维成像,然后将多个二维图像整合成三维结构。这种方法在研究非定形、不对称和不具全同性的生物样品的三维结构和功能中,有着不可替代的作用。
但是,电子断层成像需对同一样品区域多次曝光,增加了曝光的电子剂量,可能会造成电子朿损伤。由于生物样品对电子辐射比较敏感,能承受的总电子剂量有限。如果将多次曝光累加的总电子剂量控制在稍高于单颗粒技术成像的电子剂量,在单张图像上的剂量就会很低,则图像的信噪比也很低。现在有研究者采用相位板或在图像处理时进行图像降噪以提高反差。显而易见,DDD相机的引入是很好的解决方法。首先,可在低剂量的情况下获得高信噪比;其次,能够在高频区域保存可以提取的高分辨率信息。如再结合其他已有的方法和技术,如多帧成像、配准叠加算法等,可以更进一步提高信噪比,使后续的图像处理变得更加可靠,分辨率也因为图像质量的提高和算法的可靠性而提高。结合已有的sub-volume平均,在某些样品上实现高分辨率或许值得期待。
对二维高分辨成像的促进
细胞超微结构的电镜研究是细胞生物学的重要基础,它着重对细胞内环境或者特定功能状态下的生物大分子或标记了的生物大分子复合物进行研究,以便从中获得重要的信息——细胞亚结构的病理变化、生理变化,以及生物大分子在细胞内的迁移和变化情况等。这类研究最关心的是如何保持样品处于活的状态和获得高分辨,以便观察到更小结构及其变化,而高分辨二维成像技术可满足这些要求。以往,普通超薄切片技术采用固定、脱水、包埋等一系列化学处理,使用化学染色帮助提高图像中的反差,但这些化学处理会损伤观察对象,在电镜下形成假象,且分辨率只达到几个nm水平。近年来,冷冻超薄切片技术的出现,使生物材料快速冰冻法固定和在-185~-15℃环境下进行超薄切片成为可能。应用这一方法,能制备水合样品,使生物结构保持或接近活体状态,防止可溶性物质的抽取、流失和移位,保持了生物大分子的活性,并大大缩短了样品的制备时间。
有了好样品,还要使用冷冻电镜技术提高分辨率。如果使用DDD相机电影模式的多帧成像并结合相应的图像处理方法,一来可以在低剂量的照相条件下保持样品的完整性,二来可以除去颗粒移动引起的图像模糊。在图像处理的过程中,还可进行配准和叠加平均以提高图像的反差,可以在高频区看到更多的细节,从而提高图像的分辨率。如区域性配准算法,可选择多帧配准算法和多参照相对位置配准,从而大大提高对图像的分辨能力,进而获得高分辨率(<1 nm)的结构,这将对细胞生物学研究产生很大的促进作用。
结论
冷冻电镜可以解析生物大分子的高分辨率结构,这一理论已提出了近20年,但在使用中,由于各种局限而未能发挥预期能力。这些局限主要有高通量收集数据、所研究的生物分子的异质性、电子辐射损伤、样品漂移和显微像信噪比低等。随着DDD相机的成熟使用,这些局限性可以在不同程度上被直接消除,或通过与其他方法(如图像处理新算法)结合来加以消除。因此,结合DDD相机,应用冷冻电镜技术可以比以往更容易解析到高分辨率的结构,冷冻电镜的高分辨率研究可以从高对称性拓宽到无对称性样品,进一步降低研究对象的分子量下限,顺利解析难以结晶的蛋白(如在生物体内非常重要的膜蛋白等)结构。最近,著名结构生物学家Rossmann也指出,由于成熟的DDD相机的应用,冷冻电镜技术将会成为结构生物学研究的主要工具。因而,我们完全有理由相信,这一结构解析的方法将在生物学中发挥更大的作用。
致谢 在本文写作过程中,谌东华博士阅读文稿并提供了宝贵意见,特此感谢!
冷冻电子断层成像可以在纳米级尺度上研究那些结构不具有均一性的分子、病毒、细胞器以及它们之间组成的复合体的三维结构。在过去的10年中,电子显微镜硬件、冷冻制样设备和技术,以及自动化断层数据收集方法的进步使得本研究领域得到快速发展。本文对冷冻电子断层成像的方法,包括基本原理、样品制备、断层数据采集和图像处理、三维重构以及重建信息的理解和展示、近年来在生物样品领域的一些典型应用以及前景作一简单介绍。
关键词:冷冻电镜;电子断层成像
来源出版物:生物物理学报, 2010 (7): 570-578
被引频次:7
结构生物学的新进展
张景强,卢炘英,张勤奋
摘要:文章概括地介绍了结构生物学在整个生命科学中的地位,结构生物学的研究内容和结构生物学的3种主要的研究方法:X射线单晶衍射方法、核磁共振(NMR)方法和电子显微方法,介绍了这3种方法在近年来所取得的新成果。重点介绍了冷冻电子显微技术结合计算机三维重构技术研究病毒三维结构的方法、特点以及所取得的成果。并简单介绍了物理学家在结构生物学研究中的作用。
关键词:结构生物学;三维结构;冷冻电镜;计算机重构方法
来源出版物:物理, 2001, 30(7): 407-412
被引频次:6
第一类肽链释放因子结构与功能研究的新进展
陈洁,柴宝峰,梁爱华
摘要:蛋白质生物合成过程的终止是由于第一类肽链释放因子识别终止密码子,并导致肽酰-tRNA酯键水解,释放出新合成的多肽链。近期,通过冷冻电镜、结晶学、核磁共振、分子动力学和生物化学等方面的研究,使第一类肽链释放因子的结构与功能逐渐清晰。对近期的研究进行了分析和整理。
关键词:第一类肽链释放因子;冷冻电镜;晶体结构;核磁共振;分子动力学
来源出版物:生物化学与生物物理进展, 2009, 36(7):817-822
被引频次:5
用含水冷冻电镜技术测定的水稻矮缩病毒的三维结构
卢光莹,蔡德友,陈声祥,等
摘要:用含水冷冻电镜技术和计算机数据处理方法分别测定了水稻矮缩病毒(RDV)完整颗粒和只含内壳层的颗粒的三维结构,其分辨率分别为2.6 nm和3.3 nm。从完整颗粒的结构中可以清晰地看到它的外壳层和内壳层的双层结构及其内部的RNA或非结构蛋白质的电子密度。完整颗粒和内壳层的直径分别为69.8 nm和54.0 nm,外壳层和内壳层的厚度分别为6.9 nm和2.5 nm。外壳层表面的三角形剖分数T=13。外壳层由260个衣粒(三体)组成,因此共有780个蛋白质亚基。外壳层和内壳层上均有许多通道。内外壳层之间以及外壳层的衣粒之间是以一种十分新颖的联锁方式相互连接的。
关键词:863计划项目;美国W. M. keck基金;国家研究资源中心;国家普通医学科学研究所
来源出版物:高技术通讯, 1995(1): 1-4
被引频次:5
单颗粒电子显微学的研究进展
蔡刚
摘要:单颗粒电子显微学是一种新型的结构生物学技术和方法,一方面,其解析生物大分子复合体结构的分辨率日益提高,可以达到近原子分辨率,提供大蛋白分子或复合体的精细结构;另一方面,还可以解析生物大分子在不同功能状态下的结构及变化,对于揭示生物大分子复合体结构的作用机理具有重要作用。本文就单颗粒电子显微学的研究进展作一综述。
关键词:单颗粒电子显微学;生物大分子复合体;自然生理条件;冷冻电镜;近原子分辨率;动态过程
来源出版物:生物物理学报, 2010, 26(7): 560-569
被引频次:3
冷冻电镜单颗粒重构中的病毒三维显示
李晶,李鲲鹏,柳正,等
摘要:利用冷冻电镜显微技术和单颗粒三维重建方法获得BmCPV(家蚕质多角体);CSBV(中蜂囊状幼虫病病毒);C6/36DNV(C6/36浓核病毒)的三维结构体数据,用空间低通滤波对体数据矢量场进行处理并进行三维显示,较之原来的显示,提高了信噪比,增强了显示稳定性与显示质量。病毒每个表面细节和轴上突起更加清晰可见。
关键词:冷冻电子显微技术;三维重构;低通滤波;三维显示;病毒
来源出版物:北京邮电大学学报, 2005, 28(s1): 96-98
被引频次:3
结构生物学研究方法的重大突破——电子直接探测相机在冷冻电镜中的应用
柳正,张景强
摘要:近年来,科学家应用冷冻电镜技术(cryo-EM)解析出了低对称性生物大分子的高分辨率(3~5 Å)三维结构,并用其密度图直接进行了分子建模。与传统的X-射线和NMR方法相比,冷冻电镜技术具有适用于分子量较大的生物分子、样品不需结晶且用量很少等优势。尤其是电子直接探测相机(electron direct detection device,DDD)在冷冻电镜技术中的应用,使高分辨率的结构研究变得更加简单、应用更为广泛,是一个重大突破。文章介绍DDD相机的原理和技术优势,及其在解决冷冻电镜技术困难中的一些应用,进而展望了DDD相机可能给冷冻电镜技术应用带来的突破性进展。
关键词:冷冻电镜;电子直接探测相机;低对称生物大分子;高分辨率
来源出版物:生物物理学报, 2014, 30(6): 405-415
被引频次:2
含水纳米材料冷冻电镜直接成像研究
李茵茵,李鲲鹏,李向辉,等
摘要:对细菌、聚合物胶束、载药脂质体和脂质体立方晶等含水纳米材料进行冷冻电镜直接成像研究。结果表明,与负染色技术相比,文中利用冷冻电镜技术观察到了保存更完整的细菌膜结构和细菌的部分内部结构、精细的多层聚合物胶束结构、包裹在脂质体内的纳米药物以及脂质体立方晶的晶格结构。与负染色技术相比,冷冻电镜技术能避免染色假象、真空变形等缺陷,更真实地反映了有关纳米材料的原有结构特点。
关键词:冷冻电镜;聚合物胶束;脂质体
来源出版物:电子显微学报, 2012, 31(4): 346-349.
被引频次:2
基于小波变换和高斯差分冷冻电镜生物大分子图像的自动分割
巫小蓉,吴效明
摘要:冷冻电镜生物大分子图像分割是进行冷冻电镜生物大分子颗粒识别的基础。文章分析了冷冻电镜生物大分子图像的主要特点,提出了基于小波变换和高斯差分的冷冻电镜生物大分子图像自动分割方法。该方法利用小波变换得到原图像的低分辨率图像,抑制了噪声,提高了图像的对比度;同时采用高斯差分算子解决了图像亮度不均匀的问题,并对高斯差分图像采用基于灰度梯度信息融合的分割方法。实验结果表明,该算法能有效的减少噪声对边缘提取的影响,分割效果良好,是一种全新的冷冻电镜生物大分子图像自动分割算法。
关键词:颗粒识别;小波变换;高斯差分;最大类间方差;冷冻电镜生物大分子图像分割
来源出版物:中国组织工程研究, 2009, 13(48): 9479-9482
被引频次:2
基于MDL的病毒冷冻电镜图像边缘检测
杨磊,吴效明,巫晓蓉
摘要:信息技术在生物分子病毒微观研究上有着越来越多的应用。本文介绍了应用MDL小波软阈值去噪结合盲目反卷积来实现病毒原图像的恢复,以达到对比度提高的效果。首先简单介绍了小波软阈值去噪和盲目反卷积原理。然后结合这两种算法,有效的恢复了冷冻电镜病毒图像。实验表明用该算法得到的病毒恢复图像来做边缘检测,在同一些经典图像复原算法比较中,衬度上有明显的改善。
关键词:小波软阈值去噪;盲目反卷积;冷冻电镜;图像恢复;边缘检测
来源出版物:中国医学物理学杂志, 2006, 23(6): 408-411
被引频次:2488
Model for the structure of bacteriorhodopsin based on high-resolution electron cryo-microscopy
Henderson, R; Baldwin, JM; Ceska, TA; et al.
Abstract:The light-driven proton pump-bacteriorhodopsin occurs naturally as two-dimensional crystals. A threedimensional density map of the structure, at near-atomic resolution, has been obtained by studying the crystals using electron cryo-microscopy to obtain electron diffraction patterns and high-resolution micrographs. New methods were developed for analysing micrographs from tilted specimens, incorporating methods previously developed for untilted specimens that enable large areas to be analysed and corrected for distortions. Data from 72 images, from both tilted and untilted specimens, were analysed to produce the phases of 2700 independent Fourier components of the structure. The amplitudes of these components were accurately measured from 150 diffraction patterns. Together, these data represent about half of the full three-dimensional transform to 3.5 Å. The map of the structure has a resolution of 3.5 Å in a direction parallel to the membrane plane but lower than this in the perpendicular direction. It shows many features in the density that are resolved from the main density of the seven α-helices. We interpret these features as the bulky aromatic side-chains of phenylalanine, tyrosine and tryptophan residues. There is also a very dense feature, which is the β-ionone ring of the retinal chromophore. Using these bulky side-chains as guide points and taking account of bulges in the helices that indicate smaller side-chains such as leucine, a complete atomic model for bacteriorhodopsin between amino acid residues 8 and 225 has been built.There are 21 amino acid residues, contributed by all seven helices, surrounding the retinal and 26 residues,contributed by five helices, forming the proton pathway or channel. Ten of the amino acid residues in the middle of the proton channel are also part of the retinal binding site.The model also provides a useful basis for consideration of the mechanism of proton pumping and allows a consistent interpretation of a great deal of other experimental data. In particular, the structure suggests that pKchanges in the Schiff base must act as the means by which light energy is converted into proton pumping pressure in the channel.Asp96 is on the pathway from the cytoplasm to the Schiff base and Asp85 is on the pathway from the Schiff base to the extracellular surface.
来源出版物:Journal of Molecular Biology, 1990, 213(4):899-929
被引频次:784
Cryo-electron microscopy of viruses
Adrian, M; Dubochet, J; Lepault, J; et al.
Abstract:Thin vitrified layers of unfixed, unstained and unsupported virus suspensions can be prepared for observation by cryo-electron microscopy in easily controlled conditions. The viral particles appear free from the kind of damage caused by dehydration, freezing or adsorption to a support that is encountered in preparing biological samples for conventional electron microscopy. Cryo-electron microscopy of vitrified specimens offers possibilities for high resolution observations that compare favourably with any other electron microscopical method.
来源出版物:Nature, 1984, 308(5954): 32-36
被引频次:704
RELION: Implementation of a Bayesian approach to cryo-EMstructure determination
Scheres, SHW
Abstract:RELION, for REgularized LIkelihood OptimizatioN, is an open-source computer program for the refinement of macromolecular structures by single-particle analysis of electron cryo-microscopy (cryo-EM) data.Whereas alternative approaches often rely on user expertise for the tuning of parameters, RELION uses a Bayesian approach to infer parameters of a statistical model from the data. This paper describes developments that reduce the computational costs of the underlying maximum a posteriori (MAP) algorithm, as well as statistical considerations that yield new insights into the accuracy with which the relative orientations of individual particles may be determined. A so-called gold-standard Fourier shell correlation (FSC) procedure to prevent overfitting is also described. The resulting implementation yields highquality reconstructions and reliable resolution estimates with minimal user intervention and at acceptable computational costs.
关键词:electron microscopy; single-particle analysis;maximum likelihood; image processing; software development
来源出版物:Journal of Structural Biology, 2012, 180(3):519-530
被引频次:573
Determination of the fold of the core protein of hepatitis B virus ky electron cryomicroscopy
Bottcher, B; Wynne, SA; Crowther, R
Abstract:Hepatitis B virus, a major human pathogen with an estimated 300 million carriers worldwide, can lead to cirrhosis and liver cancer in cases of chronic infection. The virus consists of an inner nucleocapsid or core, surrounded by a lipid envelope containing virally encoded surface proteins. The core protein, when expressed in bacteria,assembles into core shell particles, closely resembling the native core of the virus. Here we use electron cryomicroscopy to solve the structure of the core protein to 7.4 Å resolution. Images of about 6400 individual particles from 34 micrographs at different levels of defocus were combined, imposing icosahedral symmetry. The threedimensional map reveals the complete fold of the polypeptide chain, which is quite unlike previously solved viral capsid proteins and is largely α-helical. The dimer clustering of subunits produces spikes on the surface of the shell, which consist of radial bundles of four long α-helices. Our model implies that the sequence corresponding to the immunodominant region of the core protein lies at the tip of the spike and also explains other properties of the core protein.
来源出版物:Nature, 1997, 386(6620): 88-91
被引频次:571
Electron counting and beam-induced motion correction enable near-atomic-resolution single-particle cryo-EM
Li, XM; Mooney, P; Zheng, S; et al.
Abstract:In recent work with large high-symmetry viruses, single-particle electron cryomicroscopy (cryo-EM)has achieved the determination of near-atomic-resolution structures by allowing direct fitting of atomic models into experimental density maps. However, achieving this goal with smaller particles of lower symmetry remains challenging. Using a newly developed single electroncounting detector, we confirmed that electron beaminduced motion substantially degrades resolution, and we showed that the combination of rapid readout and nearly noiseless electron counting allow image blurring to be corrected to subpixel accuracy, restoring intrinsic image information to high resolution (Thon rings visible to ~3 Å).Using this approach, we determined a 3.3-Å-resolution structure of an ~700 kDa protein with D7 symmetry, theThermoplasma acidophilum20 S proteasome, showing clear side-chain density. Our method greatly enhances image quality and data acquisition efficiency—key bottlenecks in applying near-atomic-resolution cryo-EM to a broad range of protein samples.
来源出版物:Nature Methods, 2013, 10(6): 584-590
被引频次:538
Optimal determination of particle orientation,absolute hand, and contrast loss in single-particle electron cryomicroscopy
Rosenthal, PB; Henderson, R
Abstract:A computational procedure is described for assigning the absolute hand of the structure of a protein or assembly determined by single-particle electron microscopy.The procedure requires a pair of micrographs of the same particle field recorded at two tilt angles of a single tilt-axis specimen holder together with the three-dimensional map whose hand is being determined. For orientations determined from particles on one micrograph using the map, the agreement (average phase residual) between particle images on the second micrograph and map projections is determined for all possible choices of tilt angle and axis. Whether the agreement is better at the known tilt angle and axis of the microscope or its inverse indicates whether the map is of correct or incorrect hand.An increased discrimination of correct from incorrect hand(free hand difference), as well as accurate identification of the known values for the tilt angle and axis, can be used as targets for rapidly optimizing the search or refinement procedures used to determine particle orientations.Optimized refinement reduces the tendency for the model to match noise in a single image, thus improving the accuracy of the orientation determination and therefore the quality of the resulting map. The hand determination and refinement optimization procedure is applied to image pairs of the dihydrolipoyl acetyltransferase (E2) catalytic core of the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex fromBacillus stearothermophilustaken by low-dose electron cryomicroscopy. Structure factor amplitudes of a three-dimensional map of the E2 catalytic core obtained by averaging untilted images of 3667 icosahedral particles are compared to a scattering reference using a Guinier plot. A noisedependent structure factor weight is derived and used in conjunction with a temperature factor (B=-1 000 Å2) to restore high-resolution contrast without amplifying noise and to visualize molecular features to 8.7 Å resolution,according to a new objective criterion for resolution assessment proposed here.
关键词:electron cryomicroscopy; single particle reconstruction; absolute hand; pyruvate dehydrogenase; tilt pairs
来源出版物:Journal of Molecular Biology, 2003, 333(4):721-745
被引频次:409
Complete atomic model of the bacterial flagellar filament by electron cryomicroscopy
Yonekura, K; Maki-Yonekura, S; Namba, K; et al.
Abstract:The bacterial flagellar filament is a helical propeller for bacterial locomotion. It is a helical assembly of a single protein, flagellin, and its tubular structure is formed by 11 protofilaments in two distinct conformations,L- and R-type, for supercoiling. The X-ray crystal structure of a flagellin fragment lacking about 100 terminal residues revealed the protofilament structure, but the full filament structure is still essential for understanding the mechanism of supercoiling and polymerization. Here we report a complete atomic model of the R-type filament by electron cryomicroscopy. A density map obtained from image data up to 4 Å resolution shows the feature of α-helical backbone and some large side chains. The atomic model built on the map reveals intricate molecular packing and an-helical coiled coil formed by the terminal chains in the inner core of the filament, with its intersubunit hydrophobic interactions having an important role in stabilizing the filament.
来源出版物:Nature, 2003, 424(6949): 643-650
被引频次:387
Cryo-electron microscopy structure of an SH3 amyloid fibril and model of the molecular packing
Jimenez, JL; Guijarro, JL; Orlova, E; et al.
Abstract:Amyloid fibrils are assemblies of misfolded proteins and are associated with pathological conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and the spongiform encephalopathies. In the amyloid diseases, a diverse group of normally soluble proteins self-assemble to form insoluble fibrils. X-ray fibre diffraction studies have shown that the protofilament cores of fibrils formed from the various proteins all contain a cross-β-scaffold, with β-strands perpendicular and β-sheets parallel to the fibre axis. We have determined the threedimensional structure of an amyloid fibril, formed by the SH3 domain of phosphatidylinositol-3′-kinase, using cryo-electron microscopy and image processing at 25 Å resolution. The structure is a double helix of two protofilament pairs wound around a hollow core, with a helical crossover repeat of ∼600 Å and an axial subunit repeat of ∼27 Å.The native SH3 domain is too compact to fit into the fibril density, and must unfold to adopt a longer, thinner shape in the amyloid form. The 20×40-Å protofilaments can only accommodate one pair of flat β-sheets stacked against each other, with very little inter-strand twist. We propose a model for the polypeptide packing as a basis for understanding the structure of amyloid fibrils in general.
关键词:amyloid fibrils; cryo-electron microscopy; protein misfolding; SH3 domain; single particle analysis
来源出版物:The EMBO Journal, 1999, 18(4): 815-821
被引频次:345
Three-dimensional structure of hepatitis B virus core particles determined by electron cryomicroscopy
Crowther, RA; Kiselev, NA; Bottcher, B; et al.
Abstract:Human hepatitis B virus core protein expressed in E. coli assembles into two sizes of particle. We have determined their three-dimensional structures by electron cryomicroscopy and image processing. The large and small particles correspond to triangulation number T = 4 and T =3 dimer clustered packings, containing 240 and 180 protein subunits, respectively. The local packing of subunits is very similar in the two sizes of particle and shows holes or channels through the shell. The native viral core particle packages RNA and is active in reverse transciption to DNA. The holes we observe may provide access for the necessary small molecules. Shells assembled from the intact core protein contain additional material, probably RNA, which appears as an icosahedrally ordered inner shell in the three-dimensional map.
来源出版物:Cell, 1994, 77(6): 943-950
被引频次:327
Visualization of a 4-helix bundle in the hepatitis B virus capsid by cryo-electron microscopy
Conway, JF; Cheng, N; Zlotnick, A; et al.
Abstract:Despite the development of vaccines, the hepatitis B virus remains a major cause of human liver disease. The virion consists of a lipoprotein envelope surrounding an icosahedral capsid composed of dimers of a 183-residue protein, ‘core antigen’ (HBcAg)2. Knowledge of its structure is important for the design of antiviral drugs, but it has yet to be determined. Residues 150-183 are known to form a protamine-like domain required for packaging RNA, and residues 1-149 form the ‘assembly domain’ that polymerizes into capsids and, unusually for a capsid protein, is highly α-helical. Density maps calculated from cryo-electron micrographs show that the assembly domain dimer is T-shaped: its stem constitutes the dimer interface and the tips of its arms make the polymerization contacts. By refining the procedures used to calculate the map, we have extended the resolution to 9 Å,revealing major elements of secondary structure. In particular, the stem, which protrudes as a spike on the capsid’s outer surface, is a 4-helix bundle, formed by the pairing of α-helical hairpins from both subunits.
来源出版物:Nature, 1997, 386(6620): 91-94
·推荐论文摘要·
冷冻电镜单颗粒技术解析生物大分子结构综述
张世超,欧阳燕,刘善辉,等
摘要:冷冻电镜单颗粒技术是从20世纪80年代发展起来的结构生物学新技术,特别是最近几年,由于高分辨成像设备的应用以及图像处理方法的改进,该领域取得了革命性的技术突破,分辨率达到原子水平,迅速发展成为结构生物学新的主流研究技术,尤其适合于研究生物大分子复合物的结构。简述了冷冻电镜单颗粒技术解析生物大分子结构的技术流程、最新技术进步以及未来发展方向。
关键词:冷冻电镜;单颗粒;三维重构;蛋白质结构
来源出版物:生物学杂志, 2017, 34(3): 74-77
联系邮箱:朱莉,zhuli@lzu.edu.cn
cryoSPARC软件:生物大分子冷冻电子显微镜三维重构技术的最新进展
苏晓东,高宁
摘要:2017年2月6日,Nature Methods杂志在线发表了加拿大多伦多大学和约克大学的电子工程与计算机科学系、生物化学系、医学生物物理系等多学科人员联合组成的研究小组开发的应用于冷冻电子显微镜(cryo-electron microscopy,cryo-EM)生物大分子结构解析的软件,cryoSPARC(cryo-EM single-particle ab initio reconstruction and classification),可以进行由低到高分辨率的快速、自动化的生物大分子结构解析。
来源出版物:中国科学:生命科学, 2017, 47(3): 345-346
联系邮箱:苏晓东,xdsu@pku.edu.cn
冷冻电镜技术的发展推动染色质高级结构的研究
朱平
摘要:染色质的结构及动态变化在基因转录及表观遗传调控中起了关键作用,但对于30 nm染色质纤维(通常认为是基因组DNA的二级结构)的高级结构组成以及细胞体内是否存在30 nm染色质的组织形式一直存在较大争议。近年来,冷冻电镜三维重构技术发展迅速,为研究30 nm染色质纤维高级结构提供了一个良好的工具,并起了较大的推动作用。该文介绍了本领域相关的一些研究进展。
关键词:染色质高级结构;冷冻电镜;表观遗传调控
来源出版物:中国细胞生物学学报, 2015, 37(11):1465-1471
联系邮箱:朱平,zhup@ibp.ac.cn
结构生物学研究方法的重大突破——电子直接探测相机在冷冻电镜中的应用
柳正,张景强
摘要:近年来,科学家应用冷冻电镜技术(cryo-EM)解析出了低对称性生物大分子的高分辨率(3~5 Å)三维结构,并用其密度图直接进行了分子建模。与传统的X-射线和NMR方法相比,冷冻电镜技术具有适用于分子量较大的生物分子、样品不需结晶且用量很少等优势。尤其是电子直接探测相机(electron direct detection device,DDD)在冷冻电镜技术中的应用,使高分辨率的结构研究变得更加简单、应用更为广泛,是一个重大突破。文章介绍DDD相机的原理和技术优势,及其在解决冷冻电镜技术困难中的一些应用,进而展望了DDD相机可能给冷冻电镜技术应用带来的突破性进展。
关键词:冷冻电镜;电子直接探测相机;低对称生物大分子;高分辨率
来源出版物:生物物理学报, 2014, 30(6): 405-415
联系邮箱:张景强,lsszhjq@mail.sysu.edu.cn
三维冷冻电镜成像技术成功运用于解析30nm染色质纤维的高分辨率结构
刘骏
摘要:经过多年来的不懈努力,中国科学院生物物理研究所的科学家,在破译“生命信息”的分子机理研究中,取得了重大成果。在这项突破性成果里,朱平研究员和李国红研究员领导的科研团队,利用先进的三维冷冻电子显微镜成像技术,首次解析了30 nm染色质纤维的高分辨率结构,并提出了一种全新的染色质纤维的双螺旋结构模型。
来源出版物:中国科学:生命科学, 2014(6): 636-636
联系邮箱:刘骏,Jun.Liu.1@uth.tmc.edu
26S蛋白酶体的结构生物学研究进展
王丰,施一公
摘要:26S蛋白酶体是真核细胞内负责蛋白质降解的主要分子机器,通过特异性降解目的蛋白质,几乎参与了生物体的绝大多数生命活动。26S蛋白酶体在结构上可分为19S调节颗粒和20S核心颗粒两部分。19S调节颗粒负责识别带有泛素链标记的蛋白质底物及对其进行去折叠,并最终将去折叠的蛋白质底物传送至20S核心颗粒中进行降解。由于26S蛋白酶体的结构组成复杂,分子量十分巨大,现有的X-ray技术和NMR技术对其完整结构的解析都无能为力,仅能解析出部分单个蛋白成员或分子量较低的亚复合物晶体结构。而冷冻电镜技术在相当一段时间内处于发展的初级阶段,导致其三维结构的研究进展曾经十分缓慢,严重阻碍了人们对其结构和功能的了解。近年来,随着在X-ray技术领域对大分子复合物结构解析的经验积累和冷冻电镜技术领域的技术革命,完整的26S蛋白酶体三维结构解析取得了飞速的发展。本文回顾了近几年在26S蛋白酶体结构生物学领域的重要进展,并展望了该领域未来的发展及面临的挑战。
关键词:26S蛋白酶体;结构生物学;冷冻电镜;X-ray晶体学
来源出版物:中国科学:生命科学, 2014, 44(10): 965-974
联系邮箱:施一公,shi-lab@tsinghua.edu.cn
电子显微学在结构生物学研究中的新进展
王大能,陈勇,隋森芳
摘要:电子显微学是结构生物学的重要分支,已经成为一种公认的研究生物大分子、超分子复合体及亚细胞结构的有力手段。本文先回顾了近期电子显微学在技术上的新进展,后概述了生物电子显微学的3个组成部分——电子晶体学,单颗粒技术,电子断层成像术的基本原理,技术方法与研究现状。最后,对电子显微学与其他结构生物学研究手段的结合以及电子显微学的未来发展做了简单的展望。
关键词:结构生物学;电子显微学;电子晶体学;单颗粒技术;电子断层成像术
来源出版物:电子显微学报, 2003, 22(5): 449-456
Phase-plate cryo-EM structure of a class B GPCR-G-protein complex
Liang, YL; Khoshouei, M ; Radjainia, M; et al.
Abstract:Class B G-protein-coupled receptors are major targets for the treatment of chronic diseases, such as osteoporosis, diabetes and obesity. Here we report the structure of a full-length class B receptor, the calcitonin receptor, in complex with peptide ligand and heterotrimeric Gαsβγ protein determined by Volta phase-plate singleparticle cryo-electron microscopy. The peptide agonist engages the receptor by binding to an extended hydrophobic pocket facilitated by the large outward movement of the extracellular ends of transmembrane helices 6 and 7.This conformation is accompanied by a 60° kink in helix 6 and a large outward movement of the intracellular end of this helix, opening the bundle to accommodate interactions with the α5-helix of Gαs. Also observed is an extended intracellular helix 8 that contributes to both receptor stability and functional G-protein coupling via an interaction with the Gβ subunit. This structure provides a new framework for understanding G-protein-coupled receptor function.
来源出版物:Nature, 2017, 546(7656): 118-123
联系邮箱:Wootten, D; denise.wootten@monash.edu
Using the Volta phase plate with defocus for cryo-EM single particle analysis
Danev, R; Tegunov, D; Baumeister, W
Abstract:Previously, we reported an in-focus data acquisition method for cryo-EM single-particle analysis with the Volta phase plate (Danev and Baumeister, 2016).Here, we extend the technique to include a small amount of defocus which enables contrast transfer function measurement and correction. This hybrid approach simplifies the experiment and increases the data acquisition speed. It also removes the resolution limit inherent to the in-focus method thus allowing 3D reconstructions with resolutions better than 3 angstrom.
来源出版物:Elife, 2017, 6: e23006
联系邮箱:Danev, R; danev@biochem.mpg.de
Cryo-EM structure of a native, fully glycosylated,cleaved HIV-1 envelope trimer
Lee, JH; Ozorowski, G; Ward, AB
Abstract:The envelope glycoprotein trimer (Env) on the surface of HIV-1 recognizes CD4+T cells and mediates viral entry. During this process, Env undergoes substantial conformational rearrangements, making it difficult to study in its native state. Soluble stabilized trimers have provided valuable insights into the Env structure, but they lack the hydrophobic membrane proximal external region (MPER,an important target of broadly neutralizing antibodies), the transmembrane domain, and the cytoplasmic tail. Here we present (i) a cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM)structure of a clade B virus Env, which lacks only the cytoplasmic tail and is stabilized by the broadly neutralizing antibody PGT151, at a resolution of 4.2 angstroms and (ii) a reconstruction of this form of Env in complex with PGT151 and MPER-targeting antibody 10E8 at a resolution of 8.8 angstroms. These structures provide new insights into the wild-type Env structure.
来源出版物:Science, 2016, 351(6277): 1043-10486
联系邮箱:Ward, AB; abward@scripps.edu
Breaking cryo-EM resolution barriers to facilitate drug discovery
Merk, A; Bartesaghi, A; Banerjee, S; et al.
Abstract:Recent advances in single-particle cryoelecton microscopy (cryo-EM) are enabling generation of numerous near-atomic resolution structures for wellordered protein complexes with sizes ≥∼200 kDa.Whether cryo-EM methods are equally useful for highresolution structural analysis of smaller, dynamic protein complexes such as those involved in cellular metabolism remains an important question. Here, we present 3.8 Å resolution cryo-EM structures of the cancer target isocitrate dehydrogenase (93 kDa) and identify the nature of conformational changes induced by binding of the allostericsmall-molecule inhibitor ML309. We also report 2.8-Å- and 1.8-Å-resolution structures of lactate dehydrogenase (145 kDa) and glutamate dehydrogenase(334 kDa), respectively. With these results, two perceived barriers in single-particle cryo-EM are overcome: (1)crossing 2 Å resolution and (2) obtaining structures of proteins with sizes < 100 kDa, demonstrating that cryo-EM can be used to investigate a broad spectrum of drug-target interactions and dynamic conformational states.
来源出版物:Cell, 2016, 165(7): 1698-1707
联系邮箱:Subramaniam, S; ss1@nih.gov
Cryo-EM structure of the yeast U4/U6.U5 tri-snRNP at 3.7 Å resolution
Nguyen, THD; Galej, WP; Bai, XC; et al.
Abstract:WU4/U6.U5 tri-snRNP represents a substantial part of the spliceosome before activation. A cryo-electron microscopy structure ofSaccharomyces cerevisiaeU4/U6.U5 tri-snRNP at 3.7 Å resolution led to an essentially complete atomic model comprising 30 proteins plus U4/U6 and U5 small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). The structure reveals striking interweaving interactions of the protein and RNA components, including extended polypeptides penetrating into subunit interfaces. The invariant ACAGAGA sequence of U6 snRNA, which base-pairs with the 5′-splice site during catalytic activation,forms a hairpin stabilized by Dib1 and Prp8 while the adjacent nucleotides interact with the exon binding loop 1 of U5 snRNA. Snu114 harbours GTP, but its putative catalytic histidine is held away from the γ-phosphate by hydrogen bonding to a tyrosine in the amino-terminal domain of Prp8. Mutation of this histidine to alanine has no detectable effect on yeast growth. The structure provides important new insights into the spliceosome activation process leading to the formation of the catalytic centre.
来源出版物:Nature, 2016, 530(7590): 298-302
联系邮箱:Nguyen, THD; knguyen@mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk
2.2 angstrom resolution cryo-EM structure of beta-galactosidase in complex with a cell-permeant inhibitor
Bartesaghi, A; Merk, A; Banerjee, S; et al.
Abstract:Cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) is rapidly emerging as a powerful tool for protein structure determination at high resolution. Here we report the structure of a complex between Escherichia coli betagalactosidase and the cell-permeant inhibitor phenylethyl beta-D-thiogalactopyranoside (PETG), determined by cryo-EM at an average resolution of similar to 2.2 angstroms (angstrom). Besides the PETG ligand, we identified densities in the map for similar to 800 water molecules and for magnesium and sodium ions. Although it is likely that continued advances in detector technology may further enhance resolution, our findings demonstrate that preparation of specimens of adequate quality and intrinsic protein flexibility, rather than imaging or image-processing technologies, now represent the major bottlenecks to routinely achieving resolutions close to 2 angstrom using single-particle cryo-EM.
来源出版物:Science, 2015, 348(6239): 1147-1151
联系邮箱:Subramaniam, S; ss1@nih.gov
Measuring the optimal exposure for single particle cryo-EMusing a 2.6 angstrom reconstruction of rotavirus VP6
Grant, T; Grigorieff, N
Abstract:Biological specimens suffer radiation damage when imaged in an electron microscope, ultimately limiting the attainable resolution. At a given resolution, an optimal exposure can be defined that maximizes the signal-to-noise ratio in the image. Using a 2.6 Å resolution single particle cryo-EM reconstruction of rotavirus VP6, determined from movies recorded with a total exposure of 100 electrons/Å2,we obtained accurate measurements of optimal exposure values over a wide range of resolutions. At low and intermediate resolutions, our measured values are considerably higher than obtained previously for crystalline specimens, indicating that both images and movies should be collected with higher exposures than are generally used. We demonstrate a method of using our optimal exposure values to filter movie frames, yielding images with improved contrast that lead to higher resolution reconstructions. This ‘high-exposure’ technique should benefit cryo-EM work on all types of samples,especially those of relatively low-molecular mass.
来源出版物:Elife, 2015, 4: e06980
联系邮箱:Grigorieff, N; niko@grigorieff.org
Structure of theE. coliribosome-EF-Tu complex at <3 Å resolution by Cs-corrected cryo-EM
Fischer, N; Neumann, P; Konevega, A; et al.
Abstract:Single particle electron cryomicroscopy(cryo-EM) has recently made significant progress in high-resolution structure determination of macromolecular complexes due to improvements in electron microscopic instrumentation and computational image analysis.However, cryo-EM structures can be highly non-uniform in local resolution and all structures available to date have been limited to resolutions above 3 Å. Here we present the cryo-EM structure of the 70S ribosome fromEscherichiacoliin complex with elongation factor Tu, aminoacyltRNA and the antibiotic kirromycin at 2.65-2.9 Å resolution using spherical aberration (Cs)-corrected cryo-EM. Overall,the cryo-EM reconstruction at 2.9 Å resolution is comparable to the best-resolved X-ray structure of theE. coli70S ribosome (2.8 Å), but provides more detailed information (2.65 Å) at the functionally important ribosomal core. The cryo-EM map elucidates for the first time the structure of all 35 rRNA modifications in the bacterial ribosome, explaining their roles in fine-tuning ribosome structure and function and modulating the action of antibiotics. We also obtained atomic models for flexible parts of the ribosome such as ribosomal proteins L9 and L31. The refined cryo-EM-based model presents the currently most complete high-resolution structure of theE. coliribosome, which demonstrates the power of cryo-EM in structure determination of large and dynamic macromolecular complexes.
来源出版物:Nature, 2015, 520(7548): 567-570
联系邮箱:Fischer, N; niels.fischer@mpibpc.mpg.de
Semi-automated selection of cryo-EM particles in RELION-1.3
Scheres, SHW
Abstract:The selection of particles suitable for highresolution cryo-EM structure determination from noisy micrographs may represent a tedious and time-consuming step. Here, a semi-automated particle selection procedure is presented that has been implemented within the opensource software RELION. At the heart of the procedure lies a fully CTF-corrected template-based picking algorithm,which is supplemented by a fast sorting algorithm and reference-free 2D class averaging to remove false positives. With only limited user-interaction, the proposed procedure yields results that are comparable to manual particle selection. Together with an improved graphical user interface, these developments further contribute to turning RELION from a stand-alone refinement program into a convenient image processing pipeline for the entire single-particle approach.
关键词:electron cryo-microscopy; single-particle analysis;automated particle picking
来源出版物:Journal of Structural Biology, 2015, 189(2):114-122
联系邮箱:Scheres, SHW; scheres@mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk
Structure of the TRPV1 ion channel determined by electron cryo-microscopy
Maofu, L; Erhu, C; David, J; et al.
Abstract:Transient receptor potential (TRP) channels are sensors for a wide range of cellular and environmental signals, but elucidating how these channels respond to physical and chemical stimuli has been hampered by a lack of detailed structural information. Here we exploit advances in electron cryo-microscopy to determine the structure of a mammalian TRP channel, TRPV1, at 3.4 Å resolution, breaking the side-chain resolution barrier for membrane proteins without crystallization. Like voltagegated channels, TRPV1 exhibits four-fold symmetry around a central ion pathway formed by transmembrane segments 5-6 (S5-S6) and the intervening pore loop,which is flanked by S1-S4 voltage-sensor-like domains.TRPV1 has a wide extracellular ‘mouth’ with a short selectivity filter. The conserved ‘TRP domain’ interacts with the S4-S5 linker, consistent with its contribution to allosteric modulation. Subunit organization is facilitated by interactions among cytoplasmic domains, including aminoterminal ankyrin repeats. These observations provide a structural blueprint for understanding unique aspects of TRP channel function.
关键词:electron cryo-microscopy; single-particle analysis;automated particle picking
来源出版物:Nature, 2013, 504(7478): 107-12.
联系邮箱:David, J; david.julius@ucsf.edu
2.9 Å resolution Cryo-EM 3D reconstruction of close-packed virus particles
Liu, Z; Guo, F; Wang, F; et al.
Abstract:Single-particle cryoelectron microscopy typically discards close-packed particle images as unusable data. Here, we report an image processing strategy and case study of obtaining near-atomic resolution 3D reconstructions from close-packed particles. Multiple independent de novo initial models were constructed to determine and cross-validate the particle parameters. The particles with consistent views were further refined including not only Euler angles and center positions but also defocus, astigmatism, beam tilt, and overall and anisotropic magnification. We demonstrated this strategy with a 2.9 Å resolution reconstruction of a 1.67 MDa virus-like particle of a circovirus, PCV2, recorded on 86 photographic films. The map resolution was further validated with a phase-randomization test and local resolution assessment, and the atomic model was validated with MolProbity and EMRinger. Close-packed virus particles were thus shown not only to be useful for high-resolution 3D reconstructions but also to allow data collection at significantly improved throughput for nearatomic resolution reconstructions.
来源出版物:Structure, 2016, 24(2): 319-328
联系邮箱:Wen, J; jiang12@purdue.edu
Cryo-EM shows the polymerase structures and a nonspooled genome within a dsRNA virus
Liu, H; Cheng, L
Abstract:Double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) viruses possess a segmented dsRNA genome and a number of RNA-dependent RNA polymerases (RdRps) enclosed in a capsid.Until now, the precise structures of genomes and RdRps within the capsids have been unknown. Here we report the structures of RdRps and associated RNAs within nontranscribing and transcribing cypoviruses (NCPV and TCPV, respectively), using a combination of cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) and a symmetry-mismatch reconstruction method. The RdRps and associated RNAs appear to exhibit a pseudo-D3 symmetric organization in both NCPV and TCPV. However, the molecular interactions between RdRps and the genomic RNA were found to differ in these states. Our work provides insight into the mechanisms of the replication and transcription in dsRNA viruses and paves a way for structural determination of lower-symmetry complexes enclosed in higher-symmetry structures.
来源出版物:Science, 2015, 349(6254): 1347-50.
联系邮箱:Liu, H; hrliu@hunnu.edu.cn
3.88 Å structure of cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus by cryo-electron microscopy
Yu, X; Jin, L; Zhou, ZH
Abstract:Cytoplasmic polyhedrosis virus (CPV) is unique within the Reoviridae family in having a turreted singlelayer capsid contained within polyhedrin inclusion bodies,yet being fully capable of cell entry and endogenous RNA transcription. Biochemical data have shown that the amino-terminal 79 residues of the CPV turret protein (TP)is sufficient to bring CPV or engineered proteins into the polyhedrin matrix for micro-encapsulation. Here we report the three-dimensional structure of CPV at 3.88 A resolution using single-particle cryo-electron microscopy. Our map clearly shows the turns and deep grooves of alpha-helices,the strand separation in beta-sheets, and densities for loops and many bulky side chains; thus permitting atomic model-building effort from cryo-electron microscopy maps. We observed a helix-to-beta-hairpin conformational change between the two conformational states of the capsid shell protein in the region directly interacting with genomic RNA. We have also discovered a messenger RNA release hole coupled with the mRNA capping machinery unique to CPV. Furthermore, we have identified the polyhedrinbinding domain, a structure that has potential in nanobiotechnology applications.
来源出版物:Nature, 2008, 453(7193): 415
联系邮箱:Zhou, ZH; Hong.Zhou@ucla.edu
Cryo-EM: Beyond the microscope
Earl, LA, Falconieri, V, Milne, JL; et al.
Abstract:The pace at which cryo-EM is being adopted as a mainstream tool in structural biology has continued unabated over the past year. Initial successes in obtaining near-atomic resolution structures with cryo-EM were enabled to a large extent by advances in microscope and detector technology. Here, we review some of the complementary technical improvements that are helping sustain the cryo-EM revolution. We highlight advances in image processing that permit high resolution structure determination even in the presence of structural and conformational heterogeneity. We also review selected examples where biochemical strategies for membrane protein stabilization facilitate cryo-EM structure determination,and discuss emerging approaches for further improving the preparation of reliable plunge-frozen specimens.
来源出版物:Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 2017,46: 71-78
联系邮箱:Subramaniam, S; ss1@nih.gov
Unravelling biological macromolecules with cryo-electron microscopy
Fernandez-Leiro, R; Scheres, SH
Abstract:Knowledge of the three-dimensional structures of proteins and other biological macromolecules often aids understanding of how they perform complicated tasks in the cell. Because many such tasks involve the cleavage or formation of chemical bonds, structural characterization at the atomic level is most useful. Developments in the electron microscopy of frozen hydrated samples (cryoelectron microscopy) are providing unprecedented opportunities for the structural characterization of biological macromolecules. This is resulting in a wave of information about processes in the cell that were impossible to characterize with existing techniques in structural biology.
来源出版物:Nature, 2016, 537(7620): 339
Achieving better-than-3-Å resolution by single-particle cryo-EM at 200 keV
Herzik, MA Jr; Wu, M; Lander, GC
Abstract:Nearly all single-particle cryo-EM structures resolved to better than 4-Å resolution have been determined using 300-keV transmission electron microscopes (TEMs). We demonstrate that it is possible to obtain reconstructions of macromolecular complexes of different sizes to better than 3-Å resolution using a 200 keV TEM.These structures are of sufficient quality to unambiguously assign amino acid rotameric conformations and identify ordered water molecules.
来源出版物:Nature Methods, 2017, 10.1038/nmeth.4461
Cryo-EM structures of human γ-secretase
Yang, G; Zhou, R; Shi, Y
Abstract:γ-secretase, a membrane-embedded aspartate protease, catalyzes peptide bond hydrolysis of a large variety of type I integral membrane proteins exemplified by amyloid precursor protein (APP). Cleavage of APP leads to formation of β-amyloid plaque, which is a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). Over 200 AD-associated mutations are mapped to presenilin 1 (PS1), the catalytic component of γ-secretase. In the past three years,several cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structures of human γ-secretase have been determined at near atomic resolutions. Here we summarize the methods involved and discuss structural features of γ-secretase and the associated functional insights.
来源出版物:Current Opinion in Structural Biology,2017, 46: 55
联系邮箱:Yang, G; guanghui_yang@163.com
Structure of phycobilisome from the red algaGriffithsia pacifica
Jun, Z; Jianfei, M; Desheng, L; et al.
Abstract:Life on Earth depends on photosynthesis for its conversion of solar energy to chemical energy.Photosynthetic organisms have developed a variety of light-harvesting systems to capture sunlight. The largest light-harvesting complex is the phycobilisome (PBS), the main light-harvesting antenna in cyanobacteria and red algae. It is composed of phycobiliproteins and linker proteins but the assembly mechanisms and energy transfer pathways of the PBS are not well understood. Here we report the structure of a 16.8-megadalton PBS from a red alga at 3.5 Å resolution obtained by single-particle cryoelectron microscopy. We modelled 862 protein subunits,including 4 linkers in the core, 16 rod-core linkers and 52 rod linkers, and located a total of 2048 chromophores.This structure reveals the mechanisms underlying specific interactions between linkers and phycobiliproteins, and the formation of linker skeletons. These results provide a firm structural basis for our understanding of complex assembly and the mechanisms of energy transfer within the PBS.
来源出版物:Nature, 2017, 10.1038/nature24278
Near-atomic resolution structure determination in over-focus with volta phase plate by Cs-corrected cryo-EM
Xiao, F; Lingyun, Z; Chuan, L; et al.
Abstract:Volta phase plate (VPP) is a recently developed transmission electron microscope (TEM) apparatus that can significantly enhance the image contrast of biological samples in cryoelectron microscopy, and therefore provide the possibility to solve structures of relatively small macromolecules at high-resolution. In this work, we performed theoretical analysis and found that using phase plate on objective lens spherical aberration (Cs)-corrected TEM may gain some interesting optical properties,including the over-focus imaging of macromolecules. We subsequently evaluated the imaging strategy of frozenhydrated apo-ferritin with VPP on a Cs-corrected TEM and obtained the structure of apo-ferritin at near-atomic resolution from both under- and over-focused dataset,illustrating the feasibility and new potential of combining VPP with Cs-corrected TEM for high-resolution cryo-EM.
关键词:cryo-EM; volta phase plate; Cs-corrector;over-focus; apo-ferritin; CTF; graphene grid
来源出版物:Structure, 2017, 25(10): 1623-1630
Structure of an intron lariat spliceosome fromSaccharomyces cerevisiae
Ruixue, W; Chuangye, Y; Rui, B; et al.
Abstract:The disassembly of the intron lariat spliceosome(ILS) marks the end of a splicing cycle. Here we report a cryoelectron microscopy structure of the ILS complex fromSaccharomyces cerevisiaeat an average resolution of 3.5 Å. The intron lariat remains bound in the spliceosome whereas the ligated exon is already dissociated. The step II splicing factors Prp17 and Prp18, along with Cwc21 and Cwc22 that stabilize the 5′ exon binding to loop I of U5 small nuclear RNA (snRNA), have been released from the active site assembly. The DEAH family ATPase/helicase Prp43 binds Syf1 at the periphery of the spliceosome, with its RNA-binding site close to the 3′ end of U6 snRNA. The C-terminal domain of Ntr1/Spp382 associates with the GTPase Snu114, and Ntr2 is anchored to Prp8 while interacting with the superhelical domain of Ntr1. These structural features suggest a plausible mechanism for the disassembly of the ILS complex.
关键词:pre-mRNA splicing; intron lariat spliceosome; ILS complex; cryo-EM; spliceosome disassembly; Prp43;DEAH-box ATPase/helicase; Ntr complex; Ntr1; Ntr2
来源出版物:Cell, 2017, 171(1): 120-132
Structure of the Nav1.4-β1 complex from electric eel
Zhen, Y; Qiang, Z; Lin, W; et al.
Abstract:Voltage-gated sodium (Nav) channels initiate and propagate action potentials. Here, we present the cryo-EM structure of EeNav1.4, the Navchannel from electric eel, in complex with the β1 subunit at 4.0 Å resolution. The immunoglobulin domain of β1 docks onto the extracellular L5Iand L6IVloops of EeNav1.4 via extensive polar interactions, and the single transmembrane helix interacts with the third voltage-sensing domain (VSDIII). The VSDs exhibit “up” conformations, while the intracellular gate of the pore domain is kept open by a digitonin-like molecule.Structural comparison with closed NavPaS shows that the outward transfer of gating charges is coupled to the iris-like pore domain dilation through intricate force transmissions involving multiple channel segments. The IFM fast inactivation motif on the III-IV linker is plugged into the corner enclosed by the outer S4-S5 and inner S6 segments in repeats III and IV, suggesting a potential allosteric blocking mechanism for fast inactivation.
关键词:voltage-gated sodium channels; Nav channels;Nav1.4; electromechanical coupling; fast inactivation;structural biology; cryo-EM; the beta-1 subunit
来源出版物:Cell, 2017, 170(3): 470-482
Particle segmentation algorithm for flexible single particle reconstruction
Qiang, Z; Niyun, Z; Hongwei, W; et al.
Abstract:As single particle cryo-electron microscopy has evolved to a new era of atomic resolution, sample heterogeneity still imposes a major limit to the resolution of many macromolecular complexes, especially those with continuous conformational flexibility. Here, we describe a particle segmentation algorithm towards solving structures of molecules composed of several parts that are relatively flexible with each other. In this algorithm, the different parts of a target molecule are segmented from raw images according to their alignment information obtained from a preliminary 3D reconstruction and are subjected to single particle processing in an iterative manner. This algorithm was tested on both simulated and experimental data and showed improvement of 3D reconstruction resolution of each segmented part of the molecule than that of the entire molecule.
关键词:single particle reconstruction; Cryo-EM; particle segmentation; local reconstruction
来源出版物:Biophysics Reports, 2017, 3(1): 43-55
联系邮箱:Qiang, Z; zhouqiang00@tsinghua.org.cn
Structural insights into Ca2+-activated long-range allosteric channel gating of RyR1
Risheng, W; Xue, W; Yan, Z; et al.
Abstract:Ryanodine receptors (RyRs) are a class of giant ion channels with molecular mass over 2.2 mega-Daltons.These channels mediate calcium signaling in a variety of cells. Since more than 80% of the RyR protein is folded into the cytoplasmic assembly and the remaining residues form the transmembrane domain, it has been hypothesized that the activation and regulation of RyR channels occur through an as yet uncharacterized long-range allosteric mechanism. Here we report the characterization of a Ca2+-activated open-state RyR1 structure by cryo-electron microscopy. The structure has an overall resolution of 4.9 Å and a resolution of 4.2 Å for the core region. In comparison with the previously determined apo/closedstate structure, we observed long-range allosteric gating of the channel upon Ca2+activation. In-depth structural analyses elucidated a novel channel-gating mechanism and a novel ion selectivity mechanism of RyR1. Our work not only provides structural insights into the molecular mechanisms of channel gating and regulation of RyRs, but also sheds light on structural basis for channel-gating and ion selectivity mechanisms for the six-transmembranehelix cation channel family.
来源出版物:Cell Research, 2016, 26(9): 977-994
RELION: Implementation of a Bayesian approach to cryo-EMstructure determination
Scheres, SHW
RELION, for REgularized LIkelihood OptimizatioN, is an open-source computer program for the refinement of macromolecular structures by single-particle analysis of electron cryo-microscopy (cryo-EM) data.Whereas alternative approaches often rely on user expertise for the tuning of parameters, RELION uses a Bayesian approach to infer parameters of a statistical model from the data. This paper describes developments that reduce the computational costs of the underlying maximum a posteriori(MAP) algorithm, as well as statistical considerations that yield new insights into the accuracy with which the relative orientations of individual particles may be determined. A so-called gold-standard Fourier shell correlation (FSC)procedure to prevent overfitting is also described. The resulting implementation yields high-quality reconstructions and reliable resolution estimates with minimal user intervention and at acceptable computational costs.
文章题目第一作者来源出版物1 RELION: Implementation of a Bayesian approach to Scheres, SHW Journal of Structural Biology, 2012,cryo-EMstructure determination 180(3): 519-530 2 Electron counting and beam-induced motion correction Li, XM Nature Methods, 2013, 10(6): 584-590 enable near-atomic-resolution single-particle cryo-EM 3 Cryo-EM study of the chromatin fiber reveals a double Song, F Science, 2014, 344(6182): 376-380 helix twisted by tetranucleosomal units 4 Beam-induced motion correction for sub-megadalton Scheres, SHW Elife, 2014, 3: e03665 cryo-EMparticles 5 Cryo-EM structure of the Plasmodium falciparum 80S Wong, W Elife, 2014, 3: e03080 ribosome bound to the anti-protozoan drug emetine
哥伦比亚大学生物化学与分子生物物理学系;中山大学生命科学学院】
(摘自《生物物理学报》2014年6期)
·高被引论文摘要·
被引频次:9
冷冻电子断层成像技术及其在生物研究领域的应用
黄晓星,宋晓伟,朱平
责任编辑:王微

