Pretreatment Serum MCP-1 Level Predicts Response to Risperidone in Schizophrenia
Yezhe LIN, Yanmin PENG, Cuizhen ZHU, Yousong SU, Yuan SHI, Zhiguang LIN, Jinghong CHEN ,3*, Donghong CUI,3*
Pretreatment Serum MCP-1 Level Predicts Response to Risperidone in Schizophrenia
Yezhe LIN1,2, Yanmin PENG1,2, Cuizhen ZHU1,2, Yousong SU1, Yuan SHI1,2, Zhiguang LIN1, Jinghong CHEN1,3*, Donghong CUI1,2,3*
MCP-1; risperidone; response; predictor
1. Background
Schizophrenia is a chronic debilitating disease with a prevalence of 1% worldwide.[1]The pathogenesis of schizophrenia still remains unclear. Currrently, the hypothesis of Th1/Th2 cell dysfunction presents mild inflammation in schizophrenia patients,[2]which is characterized by the elevation of pro-inflammatory cells with a drop in anti-inflammatory cells.[3]Studies have shown resemblance of the cytokine network in schizophrenia to a state of acute stress, in which proinflammatory cytokines, such as Interleukin-1β (IL-1β)and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), were elevated.[3-5]IL-1 and TNF-α were generated by T cells or monocyte/macrophages. They also activated the intracellular NF-κB signaling pathway,[6]whose general activation was commonly associated with autoimmune disease.[7]All of these results support the hypothesis regarding schizophrenia as an autoimmune disease. Additionally,cytokine monocyte chemokine protein 1 (MCP-1), also called C-C motif chemokine ligand 2 (CCL2), has now being drawing attention in research. MCP-1 is involved in the defect of Th2 cell polarity[8]and also affects the generation of interleukin-4 (IL-4), interferon-γ (IFN-γ), and interleukin-12 (IL-12).[9]The alterations of peripheral IL-4,IFN-γ, and IL-12 levels in schizophrenia patients indicates that MCP-1 might be associated with Th1/Th2 dysfunction in schizophrenia.[10]More interestingly, some studies showed the SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism)subtypes, rs4795893, rs1024611, rs4586 and rs2857657,of CCL2, the coding gene of MCP-1, were associated with treatment resistance of risperidone in the Han Chinese population.[11]
Previous studies demonstrated some association between cytokines IL-1β, TNF-α and MCP-1 and schizophrenia, however, few studies have focused on predicting response to antipsychotics by testing peripheral blood cytokines. Risperidone and olanzapine are both second generation antipsychotics, but they are greatly different in structure with different mechanisms.[12]They are one of the most widely used medications in the same class, therefore it is meaningful to study them. We performed a cross-sectional and a perspective natural observational cohort study on schizophrenia patients who were first-episode and drug-naive or un-medicated over the past 6 months.Here, we investigate cytokine levels at baseline to compare the cytokine levels in schizophrenia patients and Healthy controls (HCs), thereafter to explore cytokine levels at baseline in predicting response to antipsychotics.
2. Subjects and Methods
2.1 Study Design
Cross-sectional study design was applied to compare the difference in serum level of cytokines, IL-1β,TNF-α and MCP-1, between schizophrenia patients and HCs. We studied the role of those cytokines in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. We also performed a perspective natural observational study to follow schizophrenia patients with risperidone or olanzapine monotherapy up to 4 weeks afterwards, to explore the relationship between the baseline level of cytokines, IL-1β, TNF-α and MCP-1, and the response to risperidone and olanzapine.
2.2 Subjects
Patients were recruited from the inpatient units of Shanghai Mental Health Center, and HCs were volunteers recruited through advertisement. All subjects were recruited from October 2016 to May 2017. The present study was approved by the Shanghai Mental Health Center ethics committee. All participants or their legal guardians provided written informed consent to participate in this study.
The inclusion criteria for schizophrenia patients were the following: (a) Meeting diagnostic criteria for schizophrenia according to the ICD-10[13]; (b)aged from 18 to 65, Han Chinese; (c) first-episode and drug-naive or un-medicated with neuroleptics except benzodiazepines over the past 6 months; (d)using olanzapine or risperidone monotherapy after recruitment. The exclusion criteria were the following:(a) presence of comorbid psychotic disorder, psychotic symptoms, psychoactive substance dependency or abuse,personality disorder, or mental retardation; (b) currently suffering from a severe medical condition, such as cancer autoimmune diseases, infection or neurological diseases;(c) metabolic or endocrine diseases, such as diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia; (d) in use of glucose, lipidlowering drugs, immunosuppressants, or special diet that affects the level of glucose and lipid; (e) currently pregnant or lactating.
HCs were matched with the patient group on age, gender, education years and BMI. The exclusion criteria were the following: (a) currently suffering from a severe medical condition; (b) currently suffering from a psychotic disorder; (c) family history of psychotic disorder; (d) pregnant or lactating women.
Demographic data, including name, age, education years, height and weight, and clinical correlates were collected at baseline and 4-weeks' follow-up. Positive and Negative Syndrome Scale (PANSS)[14]were employed to assess the psychopathological symptoms of patients.All interviewers were trained with professional PANSS scale and undergone assessment of consistency.
After strict screening, 64 patients were included in our study. 26 patients were involved in risperidone group, including 15 males and 11 females, whose mean(sd) age was 29.77(12.07). 38 patients were involved in olanzapine group, including 24 males and 14 females, whose mean(sd) age was 30.17(10.89).
2.3 Cytokine Assays
All peripheral blood samples were collected after an overnight fast between 06:00–07:00 a.m. 2 ml of blood was sampled into anticoagulant-free tubes before serum was isolated (centrifugation at 3000 rpm for 20 min at 4oC). The separated serum was stored at −80oC until being thawed for cytokine analysis.
Multiplex technology was applied to test several cytokines simultaneously.[15]Human Premixed Multi-ANAlyte kits for measuring cytokines and Tecan magnetic washing plate were purchased from Bio-Rad(Luminex, Austin, TX, USA).
2.4 Statistical Analyses
Statistical analyses were carried out using SPSS 20.0 for Windows (SPSS, Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Figures were made by software GraphPad Prism 6.0. The normal distribution of data was tested using the Kolmogorov-Smirnov one-sample test. All data were normally distributed and reported as mean(sd). Cytokine comparisons between groups were analyzed by independent sample t tests. Intra-group comparisons were tested by paired t test. Correlation was tested by Pearson and Spearman correlation analysis. Stepwise linear regression analysis was performed to control the confounders and evaluate the variables that might affect response. Significance was defined as p<0.05(two-tailed).
3. Results
3.1 Comparison of serum cytokines between schizophrenia and HC
After strict screening procedures, sixty-four patients with schizophrenia were included in our study,including 39 males and 25 females, with a mean(sd)age of 29.61(11.16) and mean(sd) BMI of 21.10(2.70).Fifty-three HCs were in the control group, including 35 males and 18 females, with a mean(sd) age of 32.25(10.46) and mean(sd) BMI of 21.41(1.74).
Significantly higher baseline level of MCP-1 was found in patients with schizophrenia than HCs. But levels of IL-1β, TNF-α were not different between the two groups (table 1).
3.2 Analysis of response to 4-weeks' olanzapine and risperidone monotherapy
Because there was no difference in duration of illness, gender, age, education years, baseline BMI,baseline PANSS scores, and cytokine levels between the olanzapine and risperidone groups (table 2), we examined the two groups of patients together and found significant reduction after treatment (table 3). According to a response criterion of a 30% reduction in symptoms[16](reduction rate = (baseline score - follow-up score) /(baseline score – 30) X 100%), we had total of 37 (57.8%)responders at the 4-week follow-up, including 22 (57.9%)responders in the olanzapine group and 15 (57.7%)responders in the risperidone group.
We defined PANSS reduction as scores at 4-weeks'follow-up minus scores at baseline. There was nosignificant difference in PANSS total score, PANSS positive score (PANSS-P) and PANSS general score(PANSS-G) between the olanzapine and risperidone groups. But we found PANSS negative score (PANSS-N)higher in the olanzapine group than in the risperidone group (t=2.03, p=0.047) (table 3).

Figure 1. The flowchart of the study
3.3 Pretreatment levels of cytokine and response to risperidone or olanzapine
In the analysis of correlation, we found that PANSS-G was negatively correlated with baseline level of MCP-1 in the risperidone group (r = -0.658; p=0.0003), but not with baseline levels of IL-1β and TNF-α in the same group.The correlation remained significant after using stepwise linear regression to control for the socio-demographic and clinical confounders, such as gender, age, education,BMI, and duration of illness (adjusted R2= 0.409, β= -0.658, p = 0.0003). In the olanzapine group, no significant correlation was found between cytokines and reduction of 3 PANSS factors (figure 1). There was no correlation between baseline level of 3 cytokines and PANSS total reduction in the two groups. But we found a tendency of correlation between baseline level of MCP-1 and PANSS total reduction in the risperidone group (r =-0.36, p= 0.075). Using socio-demographic and clinical confounders, such as gender, age, education, BMI, and duration of illness as independent variables, we also found the duration of illness could serve as a predictor for PANSS total reduction (adjusted R2= 0.077, β =-0.303, p = 0.015) and PANSS-G reduction (adjusted R2=0.087, β = -0.334, p= 0.040).
4. Discussion
4.1 Main findings
According to the main results of our present study, (1)pretreatment level of MCP-1 was higher in schizophrenia patients than HCs; (2) pretreatment MCP-1 level was negatively correlated with PANSS-G reduction in the risperidone group, indicating that pretreatment serum level of MCP-1 could serve as a biomarker predicting response to risperidone treatment. Additionally, our results showed (1) olanzapine was superior in response of negative symptoms than risperidone; (2) duration of illness could be a predictor indicating the response to olanzapine treatment.
Our result was consistent with a large-sample study that showed a higher MCP-1 level in chronic schizophrenia than HCs[17].But participants in their study were chronic schizophrenia patients with no washout ofmedications. In our study, all of our patients recruited had been un-medicated at least 6 months in order to exclude the effect of antipsychotics on cytokine levels.
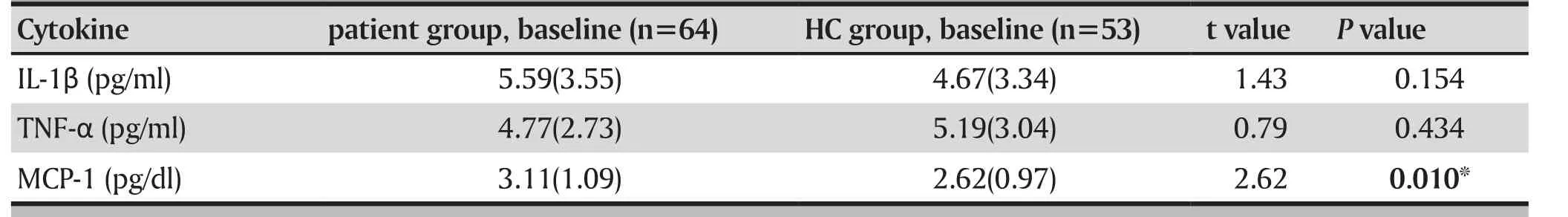
Table 1. Comparison between baseline level of cytokines in schizophrenia patients and healthy controls
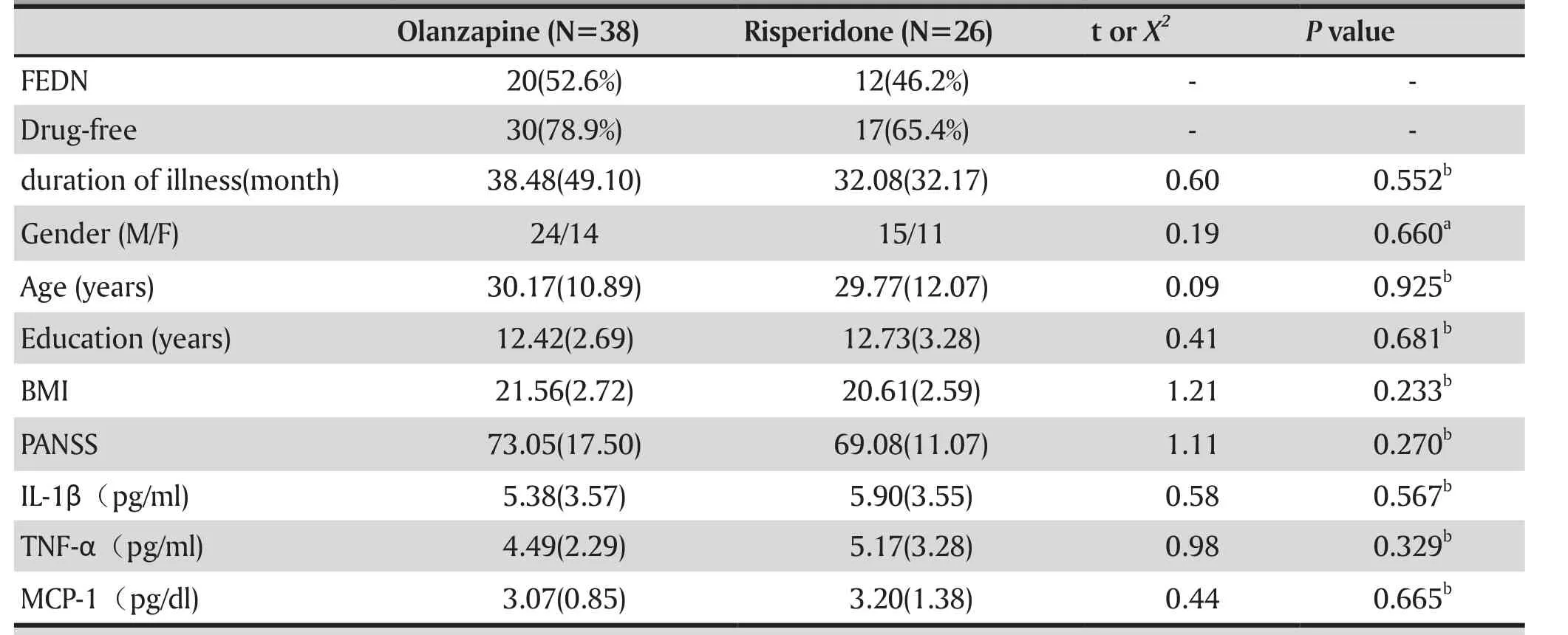
Table 2. Demographic, baseline PANSS scores and cytokine levels in the olanzapine and risperidone groups
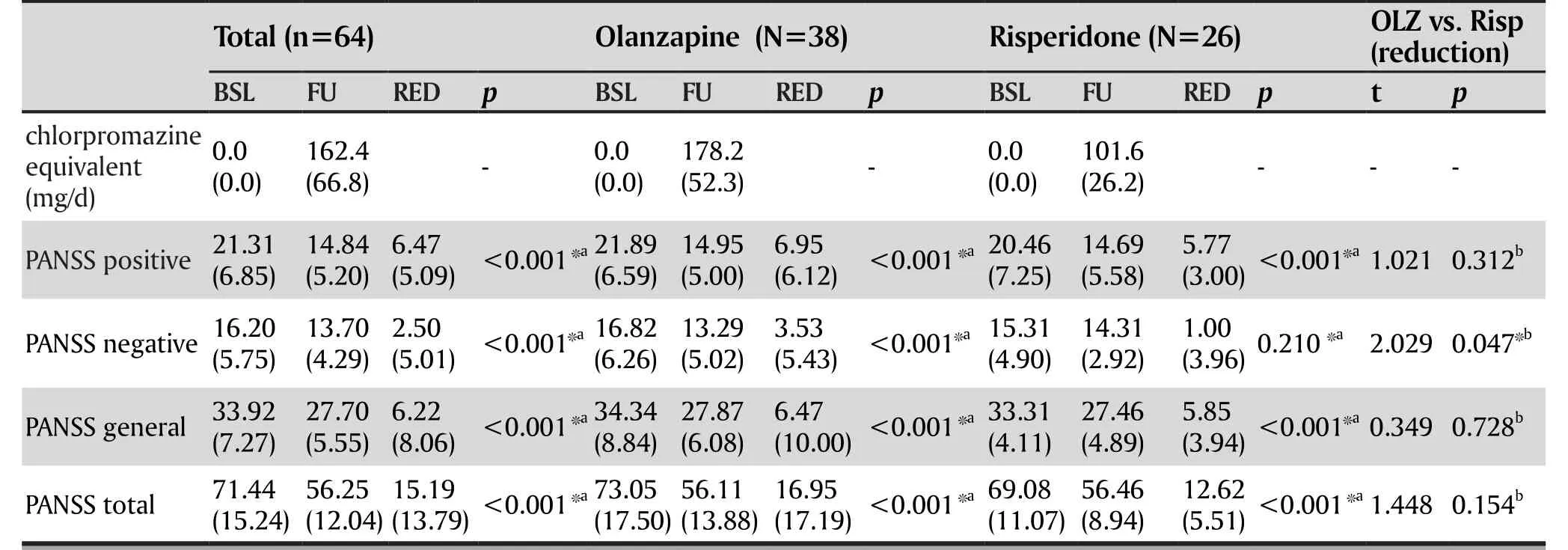
Table 3. Psychopathological evaluation following antipsychotic treatment
4.2 Limitations
The sample size is small, so further large-sample studies are needed to confirm our results. Therefore,we need to be cautious when explaining the results and generalizing the findings of this study.
4.3 Implications
To consider the factors of physical condition and the effect of medication on cytokines, all patients were matched in age, gender, BMI and education with HCs.Moreover, all patients were first-episode and drug-naive or un-medicated for over 6 months before they were recruited.
It is worth noting that pretreatment level of MCP-1 was significantly correlated with response to risperidone mono-treatment in schizophrenia patients.Higher levels of pretreatment MCP-1 indicated poorer response to risperidone treatment. For fortification purposes, we controlled confounders such as gender,age, BMI, duration of illness and education years, the only variable that remained with a predictive effect was MCP-1, whose higher level indicated less PANSS-G reduction in the risperidone group. A study on Han Chinese patients with schizophrenia found that SNP subtype of CCL2 gene, the coding gene of MCP-1,rs4795893, rs1024611, rs4586 and rs2857657 appeared more frequently in patients who were resistant to risperidone treatment.[11]This finding provided evidence supporting our present results. However,the underlying mechanism of how MCP-1 influences response to risperidone is still unclear. Some studies showed that cytokines were involved in the regulation of many neuronal functions thus representing the pathogenetic link to schizophrenia.[18]Other studies also found that receptors of MCP-1, CC chemokine receptor type 1 (CCR1) and CC chemokine receptor type 2 (CCR2), were expressed on the ventral midbrain of humans. CCL2 also played a role in development and differentiation of midbrain dopaminergic neurons.[19]Those studies indicate the potential role of MCP-1 in dopaminergic neuron growth. In a study of rats, long term intracranial injection of CCL2 activated dopamine release in the nigrostriatal area.[20]However, no finding has been reported on the effect of MCP-1 on the mesolimbic or mesocortical dopaminergic pathways.
To the best of our knowledge, no previous study has focused on prediction of serum MCP-1 levels in response to risperidone. If our results could be confirmed in further studies with a larger sample, serum MCP-1 level would probably be a viable biomarker predicting response to risperidone in patients with schizophrenia. Meanwhile,MCP-1 could be a potential target in the mechanism of pathogenesis and treatment of schizophrenia, and is worth further exploration.
Acknowledgement
Special thanks to Doctor Guoqing Zhao, Zongfeng Zhang, Professor Guanning Lin, Attending doctor Caojun Ji, Fellow doctor Mengjuan Xing, Nurse Xiaonan Fan, Nurse Yujun Sun, Nurse Jialin Zhuang, Nurse Haitao Jiang, Xingshuo Li and Jinrui Rao at Shanghai Mental Health Center for providing help on the present study.
Funding statement
Funding for this study provided by: The National Key Research and Development Program
(2017YFC0909200); National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, 81171266, 81271481,81571326, 81500976); Ministry of Science and Technology Precision Medicine Project; Shanghai Key Laboratory of Psychotic Disorders (13dz2260500);Shanghai Municipal Planning Commission of Science and Research Fund (20154Y0194)

Figure 2. Relation between baseline levels of cytokine and PANSS-G reduction
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflict of interest related to this manuscript.
Informed consent
All participants or their legal guardians provided written informed consent to participate in this study.
Ethical approval
The present study wasapproved by the Shanghai Mental Health Center ethics committee.
Authors' contributions
Yezhe Lin, Yuan Shi, Zhiguang Lin, Yanmin Peng and Yousong Su were responsible for clinical data collection and lab experiments.
Yezhe Lin and Yanmin Peng managed the literature search and the statistical analyses.
Donghong Cui, Yezhe Lin, and Cuizhen Zhu were involved in formulating concepts and editing the manuscript.
Donghong Cui and Jinghong Chen were responsible for study design and revising.
All authors have contributed to and have approved the final manuscript.
1. Saha S, Chant D, Welham J, McGrath J. A systematic review of the prevalence of schizophrenia. PLoS Med. 2005; 2(5):e141. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pmed.0020141
2. Kirkpatrick B, Miller BJ. Inflammation and schizophrenia.Schizophr Bull. 2013; 39(6): 1174-1179. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/schbul/sbt141
3. Goldsmith DR, Rapaport MH, Miller BJ. A meta-analysis of blood cytokine network alterations in psychiatric patients:comparisons between schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depression. Mol Psychiatry. 2016; 21(12): 1696-1709. doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.3
4. Potvin S, Stip E, Sepehry AA, Gendron A, Bah R, Kouassi E. Inflammatory cytokine alterations in schizophrenia:a systematic quantitative review. Biol Psychiatry.2008; 63(8): 801-808. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2007.09.024
5. Miller BJ, Buckley P, Seabolt W, Mellor A, Kirkpatrick B.Meta-analysis of cytokine alterations in schizophrenia:clinical status and antipsychotic effects. Biol Psychiatry.2011; 70(7): 663-671. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2011.04.013
6. Akira S, Kishimoto T. NF-IL6 and NF-kappa B in cytokine gene regulation. Adv Immunol. 1997; 65: 1-646
7. Thomas R. The TRAF6-NF kappa B signaling pathway in autoimmunity: not just inflammation. Arthritis Res Ther.2005; 7(4): 170-173. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/ar1784
8. Gu L, Tseng S, Horner RM, Tam C, Loda M, Rollins BJ.Control of TH2 polarization by the chemokine monocyte chemoattractant protein-1. Nature. 2000; 404(6776): 407-411. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/35006097
9. Omata N, Yasutomi M, Yamada A, Iwasaki H, Mayumi M,Ohshima Y. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 selectively inhibits the acquisition of CD40 ligand-dependent IL-12-producing capacity of monocyte-derived dendritic cells and modulates Th1 immune response. J Immunol. 2002; 169(9):4861-4866
10. Schwarz MJ, Muller N, Riedel M, Ackenheil M. The Th2-hypothesis of schizophrenia: a strategy to identify a subgroup of schizophrenia caused by immune mechanisms.Med Hypotheses. 2001; 56(4): 483-486.doi: https://doi.org/10.1054/mehy.2000.1203
11. Xiong Y, Wei Z, Huo R, Wu X, Shen L, Li Y, et al. A pharmacogenetic study of risperidone on chemokine(C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2) in Chinese Han schizophrenia patients. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2014; 51:153-158. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2014.01.017
12. Richelson E. Receptor pharmacology of neuroleptics:relation to clinical effects. J Clin Psychiatry. 1999; 60 Suppl:105-114
13. Organization WH. The ICD-10 Classification of Mental and Behavioural Disorders: Clinical Descriptions and Diagnostic Guidelines. 1992; Geneva: World Health Organization
14. Si TM, Yang JZ, Shu L, Wang XL, Kong QM, Zhou M, et al. [The Reliability, Validity of PANSS and its Implication]. Zhongguo Xin Li Wei Sheng Za Zhi. 2004; 18(1): 45-47. Chinese. doi:http://dx.chinadoi.cn/10.3321/j.issn:1000-6729.2004.01.016
15. Suzuki K, Matsuzaki H, Iwata K, Kameno Y, Shimmura C,Kawai S, et al.. Plasma cytokine profiles in subjects with high-functioning autism spectrum disorders. PLoS One.2011; 6(5): e20470. doi: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0020470
16. Peng JF, Wu DL, Gao BL, Ding SM, Liao CP, Wang P. [A related study of event-related potentials and the effects of treatment in patients with schizophrenia]. Lin Chuang Jing Shen Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2009; 19(3): 154-156
17. Drexhage RC, Padmos RC, de Wit H, Versnel MA, Hooijkaas H, van der Lely AJ, et al. Patients with schizophrenia show raised serum levels of the pro-inflammatory chemokine CCL2: association with the metabolic syndrome in patients?Schizophr Res. 2008; 102(1-3): 352-355. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.schres.2008.03.018
18. Mundo E, Altamura AC, Vismara S, Zanardini R, Bignotti S,Randazzo R, et al. MCP-1 gene (SCYA2) and schizophrenia:a case-control association study. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2005; 132B(1): 1-4. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.b.30100
19. Edman LC, Mira H, Arenas E. The beta-chemokines CCL2 and CCL7 are two novel differentiation factors for midbrain dopaminergic precursors and neurons. Exp Cell Res.2008; 314(10): 2123-2130. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2008.02.019
20. Guyon A, Skrzydelski D, De Giry I, Rovere C, Conductier G,Trocello JM, et al. Long term exposure to the chemokine CCL2 activates the nigrostriatal dopamine system: a novel mechanism for the control of dopamine release.Neuroscience. 2009; 162(4): 1072-1080. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2009.05.048
精神分裂症患者治疗前血清MCP-1水平预测利培酮疗效
林晔喆,彭延敏,朱翠珍,粟幼嵩,施源,林治光,陈京红,崔东红
精神分裂症, MCP-1,利培酮,疗效预测
Background:Schizophrenia is a chronic debilitating disease. The pathogenesis and treatment may be associated with inflammatory cytokines. There are few studies focusing on the prediction of cytokines in response to antipsychotics.
Aim:To investigate whether cytokines would predict response to antipsychotics.
Methods:Cross-sectional and natural observational cohort studies were applied to:(1) compare the baseline levels of serum IL-1β, TNF-α and MCP-1 between schizophrenia (n=64) and healthy controls (n=53); (2)To investigate the impact of baseline cytokines to psychopathology following olanzapine and risperidone monotherapy.
Results:(1) Baseline MCP-1 level of patients with schizophrenia was significantly higher than healthy controls (t=2.62, p=0.010), while no significance was found in IL-1β (t=1.43, p=0.154) and TNF-α (t=0.79,p=0.434); (2) Pretreatment level of MCP-1 significantly correlated with PANSS-G reduction following 4 weeks' of risperidone monotherapy (r =-0.658; p<0.001) but not olanzapine monotherapy (r =-0.031;p=0.855); (3) Further stepwise multiple linear regression analysis indicated that higher MCP-1 level prior to treatment was a significant predictor of less PANSS-G reduction in schizophrenia patients following risperidone monotherapy (adjusted R2= 0.409, β = -0.658, p <0.001), but not in the olanzapine group.
Conclusion:MCP-1 may play a role in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. Pretreatment level of MCP-1 may serve as a biomarker indicating response to risperidone treatment.
[Shanghai Arch Psychiatry. 2017;29(5): 287-294.
http://dx.doi.org/10.11919/j.issn.1002-0829.217093]
1Shanghai Mental Health Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai, China
2Shanghai Key Laboratory of Psychotic Disorders, Shanghai, China
3Brain Science and Technology Research Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
*correspondence: Donghong Cui. E-mail: manyucc@126.com; Jinghong Chen. E-mail: chenjh_008@hotmail.com. Mailing address: No.3210 Humin Road,Shanghai, China. Postcode: 201108.
背景:精神分裂症是一种慢性致残性疾病,其发病及治疗可能与炎性细胞因子有关.目前细胞因子预测抗精神病药物疗效的研究尚少.
目的:研究细胞因子对抗精神病药物疗效的预测作用.方法:采用横断面与自然观察随访相结合的方法,(1)对比精神分裂症患者组(n=64)基线期和正常对照组(n=53)血清IL-1β、TNF-α和MCP-1水平;(2)探索基线期细胞因子水平对奥氮平或利培酮单药治疗效果的影响.
结果:(1)精神分裂症患者治疗前血清MCP-1水平明显高于健康对照组(t=2.62, p=0.010),IL-1β(t=1.43,p=0.154)、TNF-α(t=0.79, p=0.434)未见变化;(2)精神分裂症患者治疗前MCP-1水平与利培酮单药治疗4周后PANSS量表一般病理评分的减少量呈显著负相关(r =-0.658; p﹤0.001),但在奥氮平组中则未发现(r=-0.031; p=0.855);(3)纳入性别、年龄、受教育年限和BMI后等影响因素后,多元线性回归分析发现,基线血清MCP-1水平可作为利培酮单药治疗效果的独立预测因子(校正R2= 0.409, β= -0.658, p﹤0.001).
结论:MCP-1可能参与精神分裂症的发生,治疗前血清MCP-1水平可能是利培酮疗效预测的生物标记物.

Yezhe Lin has a Bachelor's degree of medicine (M.B.B.S). She graduated from the Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine in 2014. Afterwards, she studied as a graduate student at affiliated Mental Health Center of Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine until 2017. She began her residency at the Shanghai Mental Health Center in 2017 and is now working as a full-time resident doctor in the department of general psychiatry at Shanghai Mental Health Center. She is interested in transitional medicine and clinical studies, especially studies on the side effects of neuroleptics.
- 上海精神医学的其它文章
- Sample Size Calculations for Comparing Groups with Binary Outcomes
- Commentary on "Psychiatry and Cinema: What can We Learn from the Magical Screen?"
- Psychiatry and Cinema: What Can We Learn from the Magical Screen?
- Multidimensional Approaches for A Case of Severe Adult Obsessive - Compulsive Disorder
- A Cross-Sectional Study on the Characteristics of Tardive Dyskinesia in Patients with Chronic Schizophrenia
- Abnormal Concentration of GABA and Glutamate in The Prefrontal Cortex in Schizophrenia.-An in Vivo 1H-MRS Study

