基于EDEM的离心甩盘撒肥器性能分析与试验
刘彩玲,黎艳妮,宋建农,马 拓,王蒙蒙,王徐建,张 超
(中国农业大学工学院,北京 100083)
基于EDEM的离心甩盘撒肥器性能分析与试验
刘彩玲,黎艳妮,宋建农※,马 拓,王蒙蒙,王徐建,张 超
(中国农业大学工学院,北京 100083)
为提高颗粒肥料撒施均匀性,该文对离心甩盘式撒肥器进行甩盘转速、喂入量、喂入角和喂入位置角对抛撒均匀性单因素离散元仿真分析,完成多元回归正交旋转仿真试验和目标参数优化并进行台架试验,分析结果表明,喂入位置角与转速及喂入位置角与喂入角间交互作用对撒肥均匀性影响均高度显著;各因素影响主次顺序为甩盘转速、喂入角、喂入量、喂入位置角;当甩盘转速900 r/min、喂入量4 275 颗/s、喂入角110°、喂入位置角64°时均匀性变异系数为12.48%,仿真验证和实际试验验证结果与优化结果相吻合。机器前进速度为5.4 km/h时实际工况动态仿真得到工作幅宽内均匀性变异系数为11.43%,满足田间撒肥作业要求。研究结果可为颗粒肥撒施机设计提供参考。
农业机械;离散元法;数值分析;撒肥器;均匀性;试验
0 引 言
施用化肥是农作物增产最快、最有效的措施,合理施用化肥可提高肥料利用率,降低施肥量,从而提高经济效益,减少环境污染,实现农业可持续发展[1-2]。
目前国外大多采用圆盘式撒肥机进行撒肥作业,以美国John Deere、德国阿玛松、法国AMASAT变量撒播机为代表,但国外撒肥机械价格昂贵,配件供应不及时,撒肥均匀性有待提高[3-6]。国内近年来对撒肥机研究取得一些研究成果,如张睿等[7]设计了一种链条输送式变量肥料抛撒机,该机肥料到达落肥口时间较长,增加施肥作业时间;齐兴源等[8]设计了一种稻田气力变量施肥机,该机以空气流为动力输送和撒播肥料,能耗大,对气流稳定性要求较高,且管道输送存在排肥滞后现象;胡永光等[9]对茶园施肥机离心撒肥过程进行仿真优化,该机只适合窄行距茶园作业。总体看国内撒肥机的研究多处于试验研究阶段,实际应用中现有撒肥机均为圆盘式撒肥机构,且以水平圆盘式为主,撒施均匀性有待提高[10-11]。
针对目前肥料撒施不均匀问题,课题组提出一种离心甩盘撒肥机并取得初步成效[12]。为进一步提高撒肥器撒施性能,基于离散元仿真软件EDEM(enhances discrete element method)在国内外撒肥器研究中的有益应用[13-18],本文在分析肥料颗粒运动特性基础上对撒肥过程进行离散元仿真,探究各参数对撒施均匀性的影响规律,优化参数并进行台架试验,以期为颗粒肥撒肥机的设计提供参考。
1 撒肥器的结构及工作原理
离心甩盘撒肥器包括机架、肥箱、供肥槽轮、喂料斗、护罩、离心甩盘、直流电机,如图1a所示。
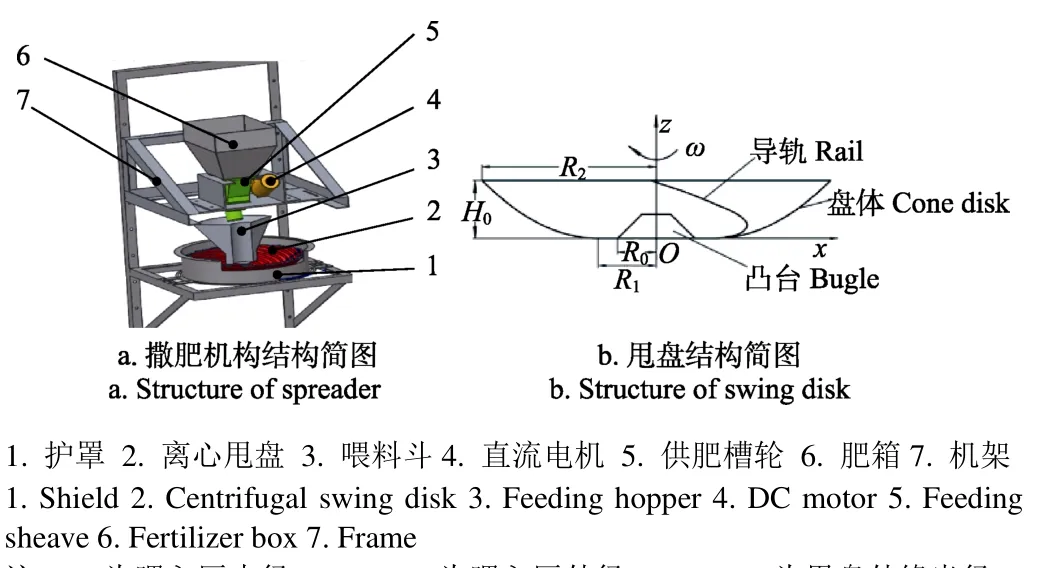
图1 离心甩盘式撒肥器结构示意图Fig.1 Structure of fertilizer spreader with centrifugal swing disk
关键部件离心甩盘由盘体、导轨和凸台组成,盘体为旋转抛物面,由一条水平线段和抛物线组成的母线绕固定轴旋转一周形成,如图1b所示,盘体母线方程为
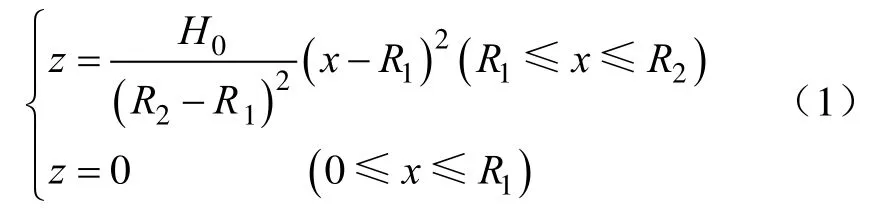
导轨轨迹线是以R1=60 mm为基圆半径的渐开螺旋线,断面为三角形,共 16条。喂入区是内径R0,外径R1的圆环面,内有径向导轨,其断面和渐开螺旋线导轨断面相同,数量一致。锥形凸台位于甩盘中央,甩盘外缘半径R2=180 mm,高度H0=60 mm,喂入区内径R0=40 mm,喂入区外径R1=60 mm,材料采用ABS工程塑料。喂料斗底部出肥口为圆环面,其内径40 mm,外径60 mm。
撒肥工作原理:肥料在供肥槽轮作用下进入喂料斗喂入区,在锥形离心甩盘高速旋转作用下沿渐开螺旋线导轨作加速运动,至锥盘边缘以一定速度抛出后做斜抛运动,最后落地完成撒肥作业过程。
2 颗粒肥的运动特性分析
假定肥料颗粒为一刚性质点,质量为m,忽略颗粒间相互作用和空气阻力。肥料沿导轨向上运动,在某点E时受力如图2a所示,建立空间坐标系如图2b所示。
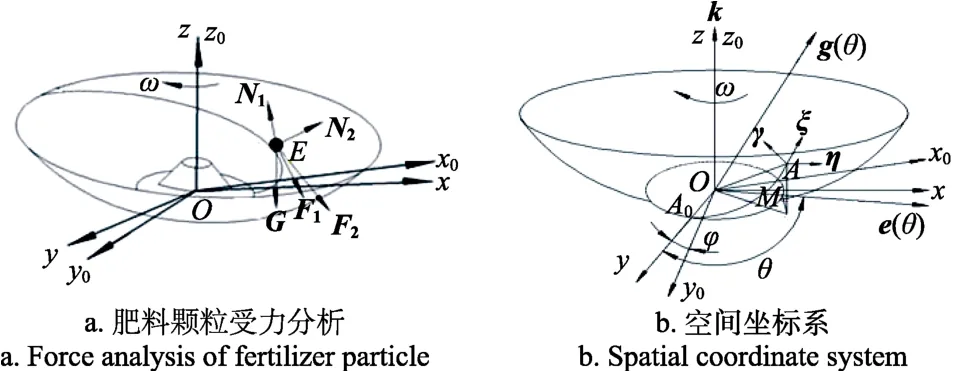
图2 肥料颗粒在甩盘上的受力分析Fig.2 Force analysis of fertilizer particle on swing disk
肥料颗粒从A0运动至A处,xOy坐标平面内基圆向径OM对应的转角为θ,(°);e(θ)、g(θ)、k分别为静坐标系中以O点建立的球坐标单位向量,其中k轴与动坐标系的z轴重合;ξ、η、γ分别为动坐标系中肥料颗粒在A点的切线、主法线、副法线方向单位向量。
肥料颗粒在P点时受合外力为F,则
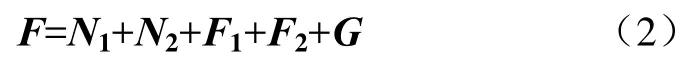
由牛顿第二运动定律可知

设肥料颗粒在P点时绝对加速度a,m/s2;牵连加速度加速度为ae,m/s2;科氏加速度为ac,m/s2;相对切向加速度为art,m/s2;相对法向加速度为arn,m/s2;则肥料颗粒的受力方程为
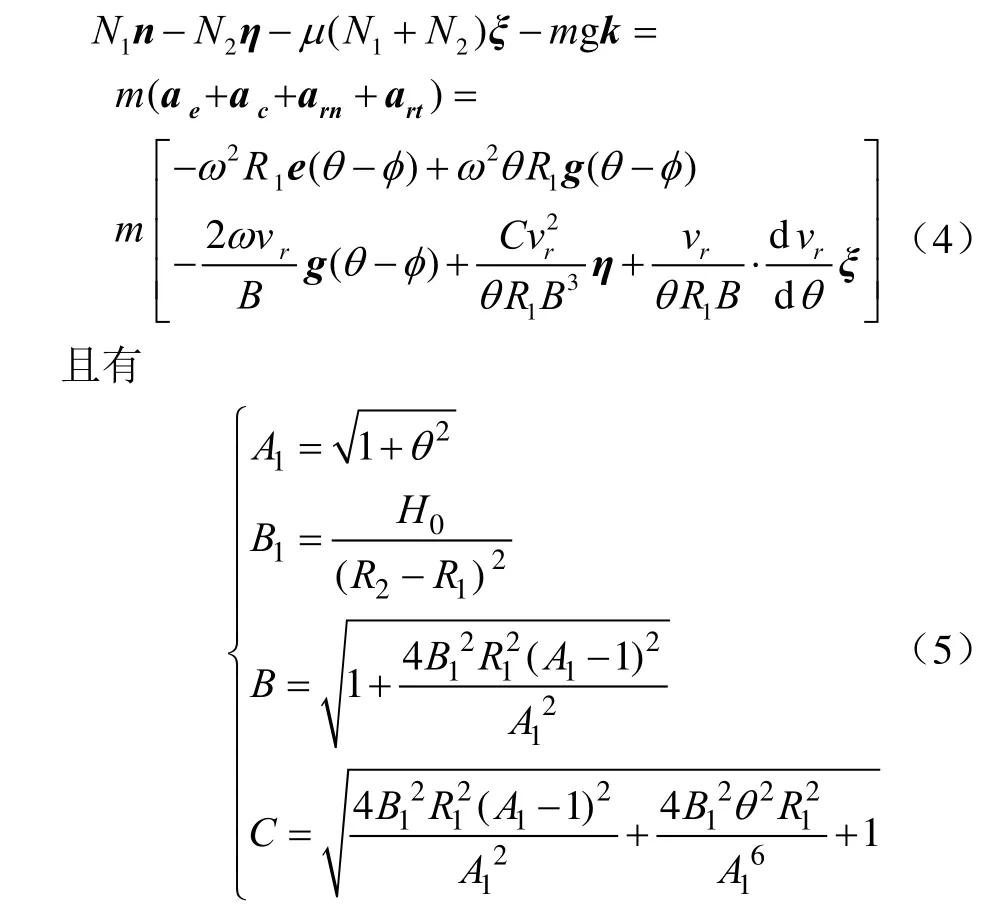
式中rv为肥料颗粒在E点的相对运动速度,m/s;μ为肥料颗粒与甩盘的摩擦系数;n为甩盘盘体母线法向方向的单位向量;g为重力加速度,m/s2。
为研究肥料颗粒抛出甩盘的速度,将动坐标系单位向量与肥料颗粒受力方程(4)作数积得其运动微分方程
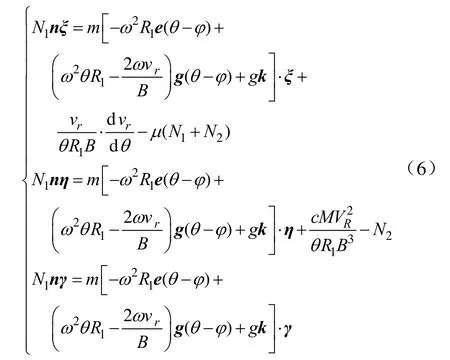
求解微分方程(6),得到肥料颗粒脱离甩盘时绝对速度av在x0y0z0静坐标系下各坐标轴上的分量为
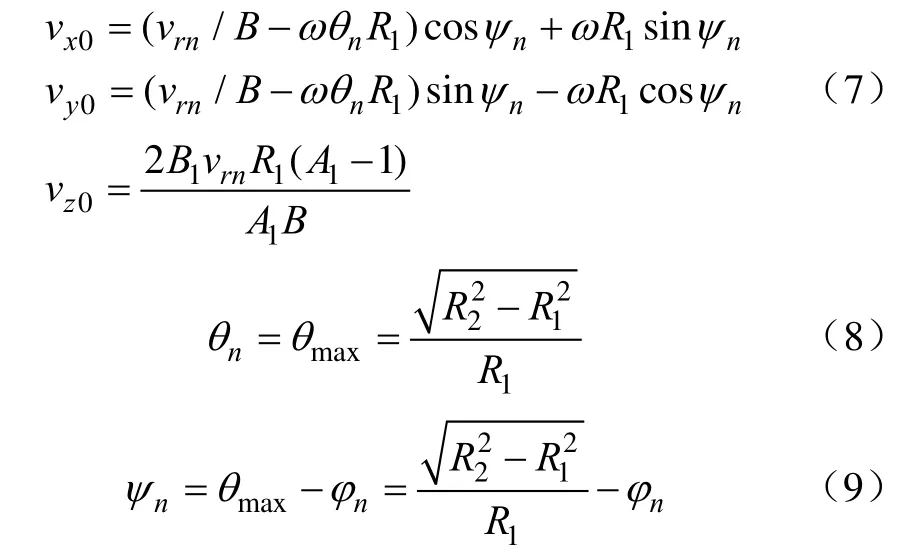
式中nθ取甩盘渐开螺旋线的最大展开角maxθ,(°);nφ为肥料颗粒离开甩盘位置时甩盘相对于机架的转动角度,(°);参见图2b;vrn为肥料颗粒脱离甩盘时的相对速度,m/s。由式(7)可以看出,肥料颗粒抛出甩盘时的速度取决于甩盘转速与甩盘结构。
3 EDEM离散元建模与仿真分析
3.1 三维仿真模型
去除图1a中与接触无关部件并将Creo软件绘制的撒肥器三维实体模型导入EDEM(图3)。设置土壤材料承接肥料颗粒,通过大量仿真统计不同喂入角下的施肥区域肥料分布质量,确保能够完全收集整个施肥区域肥料并考虑计算能力确定仿真区域3.92 m×2.40 m。
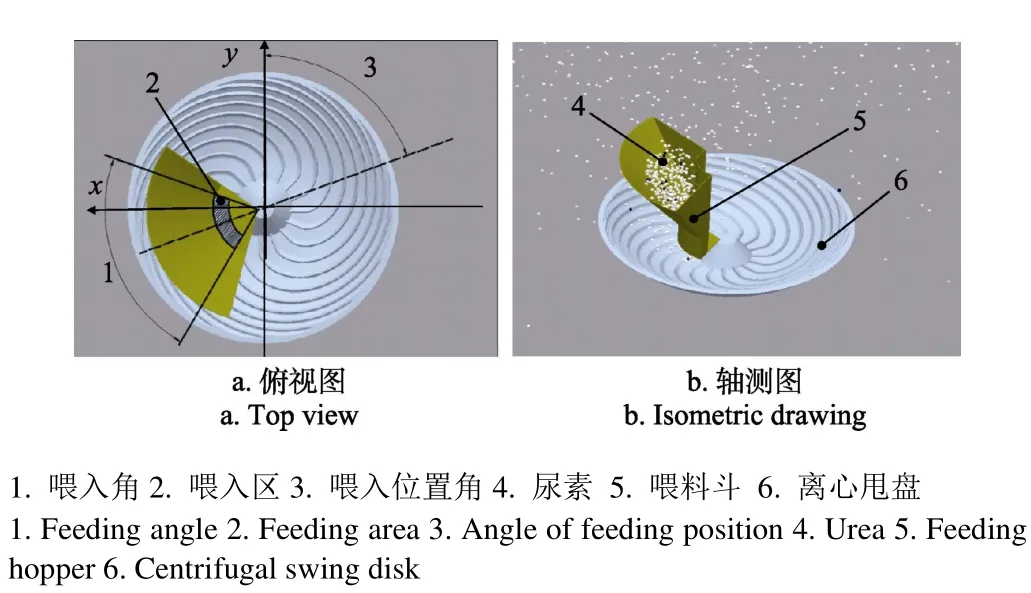
图3 离心甩盘式撒肥三维仿真模型Fig.3 3D simulation model of fertilizer spreader with centrifugal swing disk
3.2 仿真参数的确定
选用近似球体大颗粒尿素为研究对象,颗粒表面没有黏附力,选择Hertz-Mindlin 无滑动接触模型。甩盘采用ABS工程材料注模加工。为精确设定边界条件,利用自制试验平台对颗粒密度、颗粒与工程材料间弹性恢复系数和静摩擦系数进行试验测定[19-20],其余特性参数参考相关文献[9,16-18],确定仿真参数为:颗粒肥料直径4 mm,泊松比 0.4,弹性模量 28 MPa,密度 1 337 kg/m3;颗粒与颗粒间恢复系数、静摩擦因数、滚动摩擦因数分别为0.35、0.3、0.26,颗粒与工程材料间恢复系数、静摩擦因数、滚动摩擦因数分别为0.6、0.17、0.01。
3.3 仿真试验设计与试验指标
参照美国ASAE S341.2圆盘式撒肥机静态试验方法[21-22],使用二维矩阵法收集肥料并计算其均匀性。应用EDEM后处理Selection模块在纵向(Y方向)距离甩盘中心0.5 m处设置Grid Bin Group,每个网格大小140 mm ×200 mm(图4),3.92 m×2.40 m的收集矩形区域内共12行28列336个计算网格。将落入每列网格中肥料质量进行叠加,形成1×28的单行肥料收集矩阵,单行矩阵中肥料数值相当于撒肥装置以一定速度穿过单行网格后收集到的肥料。离心式撒肥机横向撒肥幅宽较大更易产生误差,常以横向幅宽方向撒肥变异系数作为撒肥均匀性试验指标[3,12,23]。
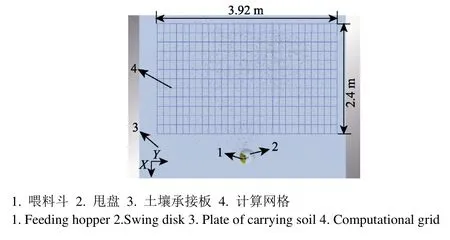
图4 EDEM中计算网格的布置图Fig.4 Layout diagram of computational grid in EDEM
横向均匀性变异系数Cv计算方法如下:
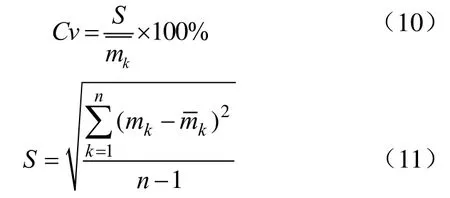
其中S为标准差,g;为收集域内每个网格收集肥料的平均值,g;mk为第k列收集网格肥料质量,g;n为收集网格的列数。
4 离散元仿真试验与优化
4.1 单因素优化仿真试验与结果分析
喂入角影响肥料颗粒在盘面上的分布,喂入量(颗粒工厂生成颗粒的速度,颗/s。)影响颗粒数量及颗粒间作用力,喂入位置角影响颗粒离开甩盘的位置、速度与运动轨迹,因此基于已有研究及前文分析[12,23-26],确定甩盘转速、喂入位置角、喂入量为试验因素,仿真持续时间为6 s。
4.1.1 甩盘转速对撒肥分布的影响
保持喂入角、喂入位置角、喂入量分别为60°、70°、2 000颗/s,甩盘转速从600到1000 r/min变化,增量为100 r/min。横向幅宽方向肥料分布规律如5b所示,肥料颗粒主要落在-1.8~1.8 m区域,随甩盘转速增大横向有效幅宽增大,肥料分布峰值降低,横向撒肥均匀性逐渐变好,施肥一致性逐渐提高。根据ASAE S341.2的定义[21],施肥横向有效幅宽为目标施肥量的1/2处对应的施肥宽度,如图5a所示。
4.1.2 喂入角对撒肥分布的影响
保持甩盘转速、喂入位置角、喂入量分别为700 r/min、70°、2 000 颗/s,喂入角从 20°到 100°变化,增量为 20°。横向幅宽方向肥料分布规律如图 5c所示,在 40°~100°时,随喂入角增大肥料分布峰值降低,分布图形逐渐向梯形转变,有效幅宽逐渐增加,肥料横向分布波动减小,施肥均匀性提高。20°时肥料总质量峰值与总和最小,其原因为喂入角过小使肥料喂入甩盘速度小于其落入喂料斗速度,因此在相同时间内肥料撒施量较小。为使喂入角不影响肥料喂入甩盘转速应使喂入角大于20°。
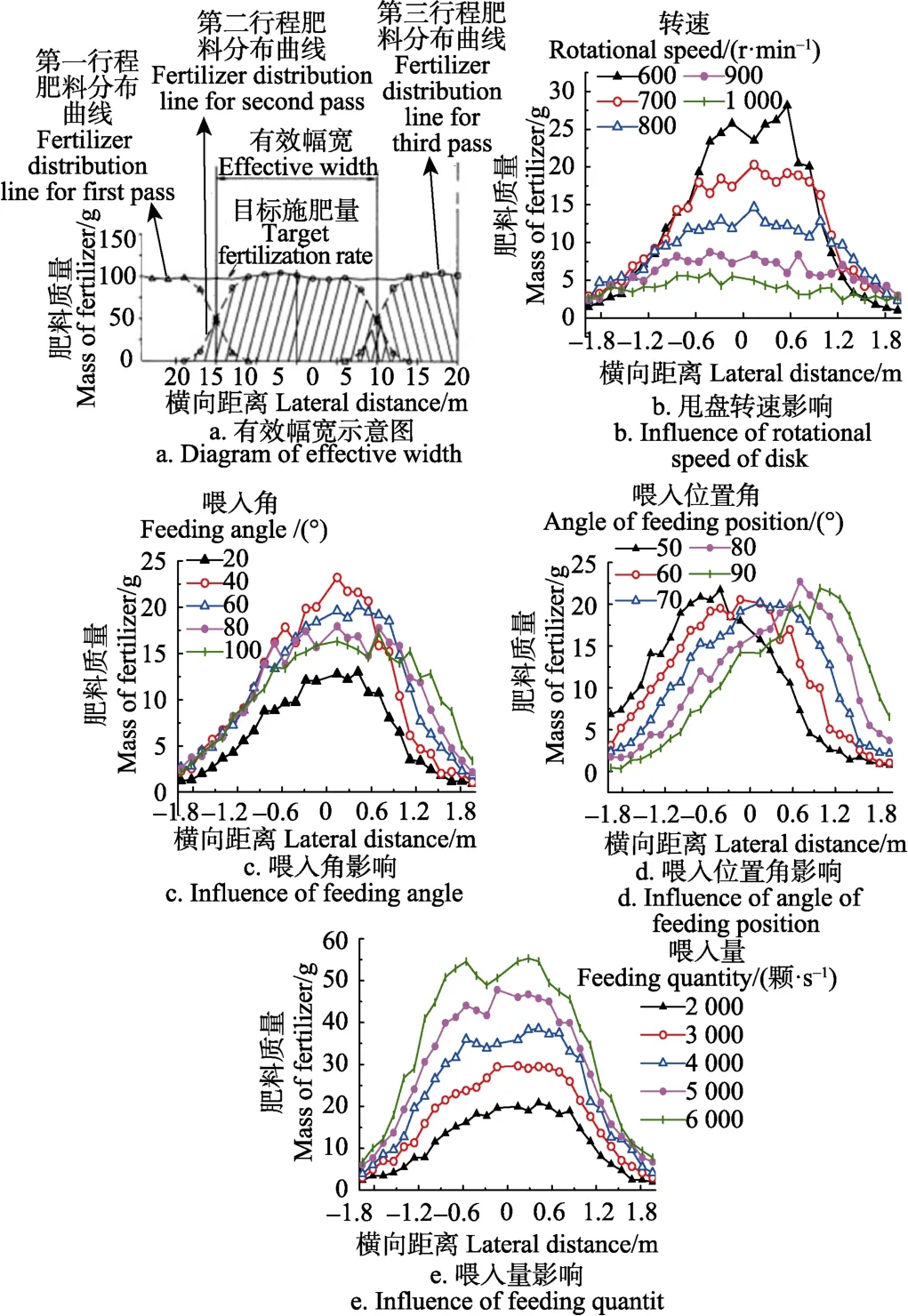
图5 甩盘转速、喂入角、喂入位置角和喂入量对肥料分布的影响Fig.5 Influence of rotational speed of disk, feeding angle, angle of feeding position and feeding quantity on fertilizer distribution
4.1.3 喂入位置角对撒肥分布的影响
保持甩盘转速、喂入角、喂入量分别为700 r/min、60°、2 000颗/s,喂入位置角从 50°到 90°变化,增量为10°。横向幅宽方向肥料分布规律如图5d所示,喂入位置角影响肥料撒施分布的对称性,从而影响施肥机田间往复或回转施肥时的均匀性[27]。随喂入位置角增大,肥料在横向幅宽方向分布的对称轴由负向逐渐向正向移动,喂入位置角为70°时对称轴在盘心的置,对称分布最佳。横向撒肥均匀性 50°~70°随喂入位置角增大逐渐变好,70°~90°规律相反,70°时变异系数最小。
4.1.4 喂入量对撒肥分布的影响
保持甩盘转速、喂入角、喂入位置角分别为700 r/min、60°、70°,喂入量从2 000~6 000颗/s变化,增量为1 000颗/s。横向幅宽方向肥料分布规律如图 5e所示,随喂入量变化,肥料分布质量曲线出现明显波动,影响肥料横向撒施均匀性,随喂入量增大,施肥均匀性提高。
单因素仿真试验表明,横向幅宽方向分布于中心位置肥量较多并上下波动,两侧撒施量逐渐减少,甩盘转速、喂入角、喂入量、喂入位置角影响横向分布均匀性。
4.2 正交回归旋转中心仿真试验
为研究离心甩盘撒肥器施肥均匀性,以均匀性变异系数Cv为试验指标进行二次正交回归旋转仿真试验。
4.2.1 二次正交回归旋转组合试验
以甩盘转速、喂入角、喂入量、喂入位置角为因素设计四元二次回归正交旋转组合试验,星号臂γ=2.0,因子区域中心试验点个数为6,因素编码见表1[28],试验方案及试验结果见表2。
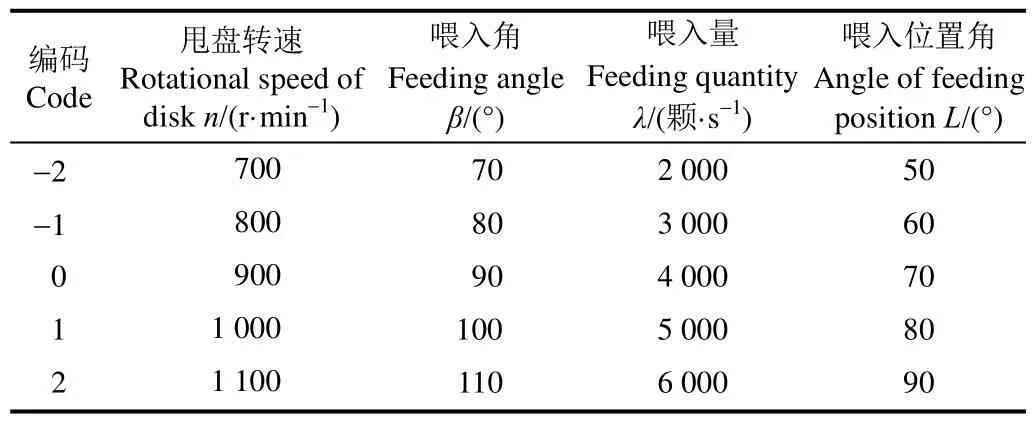
表1 因素水平编码Table 1 Coding of factors and levels
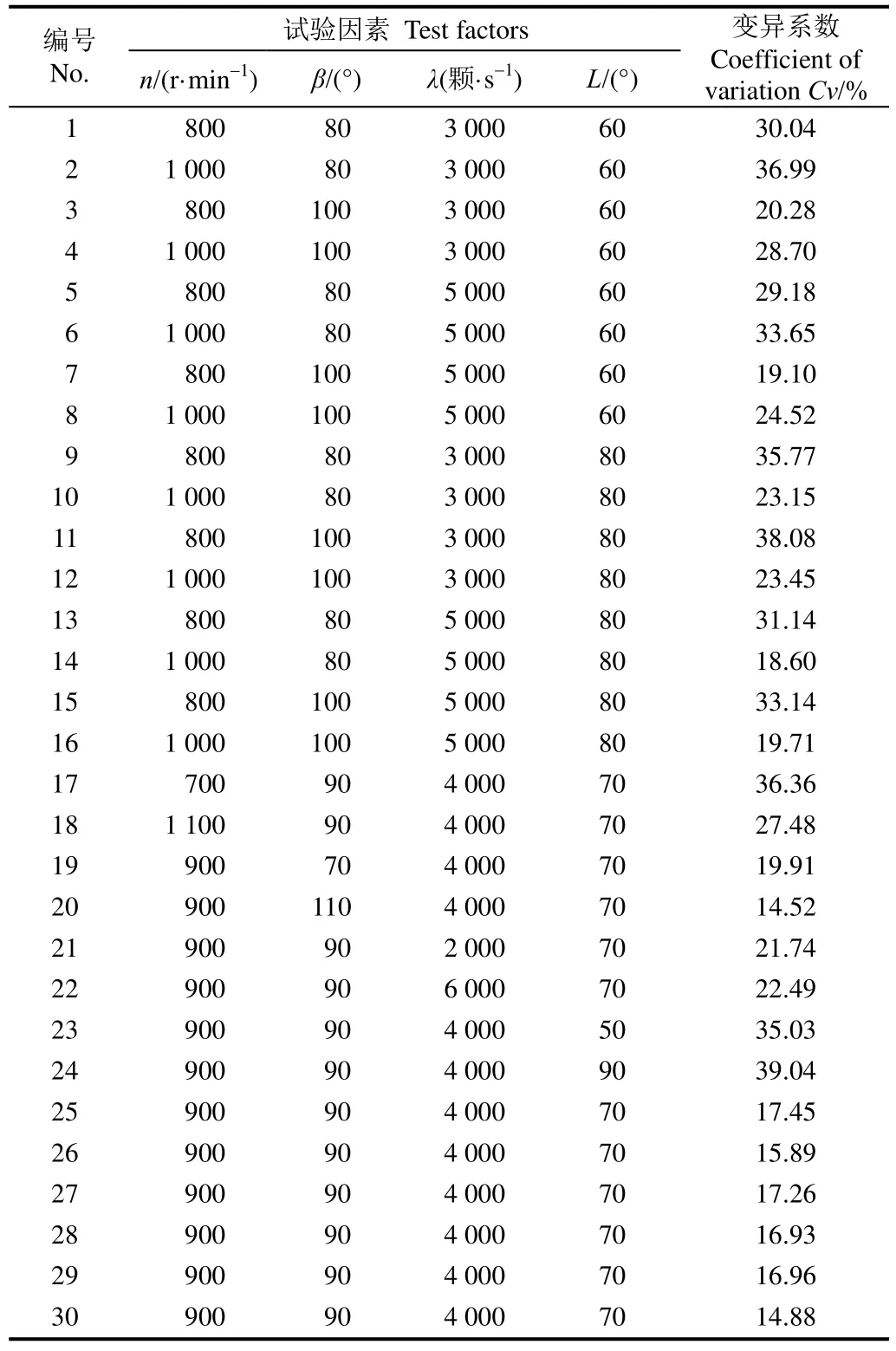
表2 二次正交回归旋转组合试验试验方案及结果Table 2 Test plan and data of quadratic regression rotatable orthogonal design
4.2.2 试验结果方差分析
采用Design-Expert 8.0.6对表2中试验结果进行多元回归拟合分析,得到横向均匀性变异系数方差分析如表3,二次回归模型高度显著[29](P<0.000 1),失拟项(P=0.081 9>0.05)不显著,回归方程不失拟。依据系数间不存在线性相关性,经逐步回归法剔除不显著因素得各因素与变异系数Cv回归响应面方程为
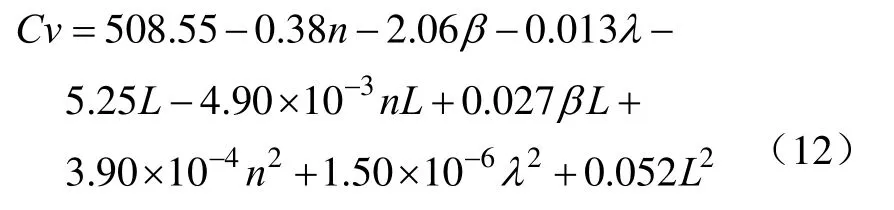
表3方差分析结果表明影响因子L2、n2、nL、βL、n、β、λ2、λ对均匀性变异系数Cv影响高度显著,因此甩盘转速、喂入角、喂入量对变异系数有重要影响,虽然喂入位置角不显著,但其平方项和交互作用项高度显著,因此不可忽略该因素对试验指标的影响,各因素对试验指标影响的显著性由大到小依次为甩盘转速、喂入角、喂入量和喂入位置角。甩盘转速与喂入位置角及喂入角与喂入位置角交互作用影响不可忽视。
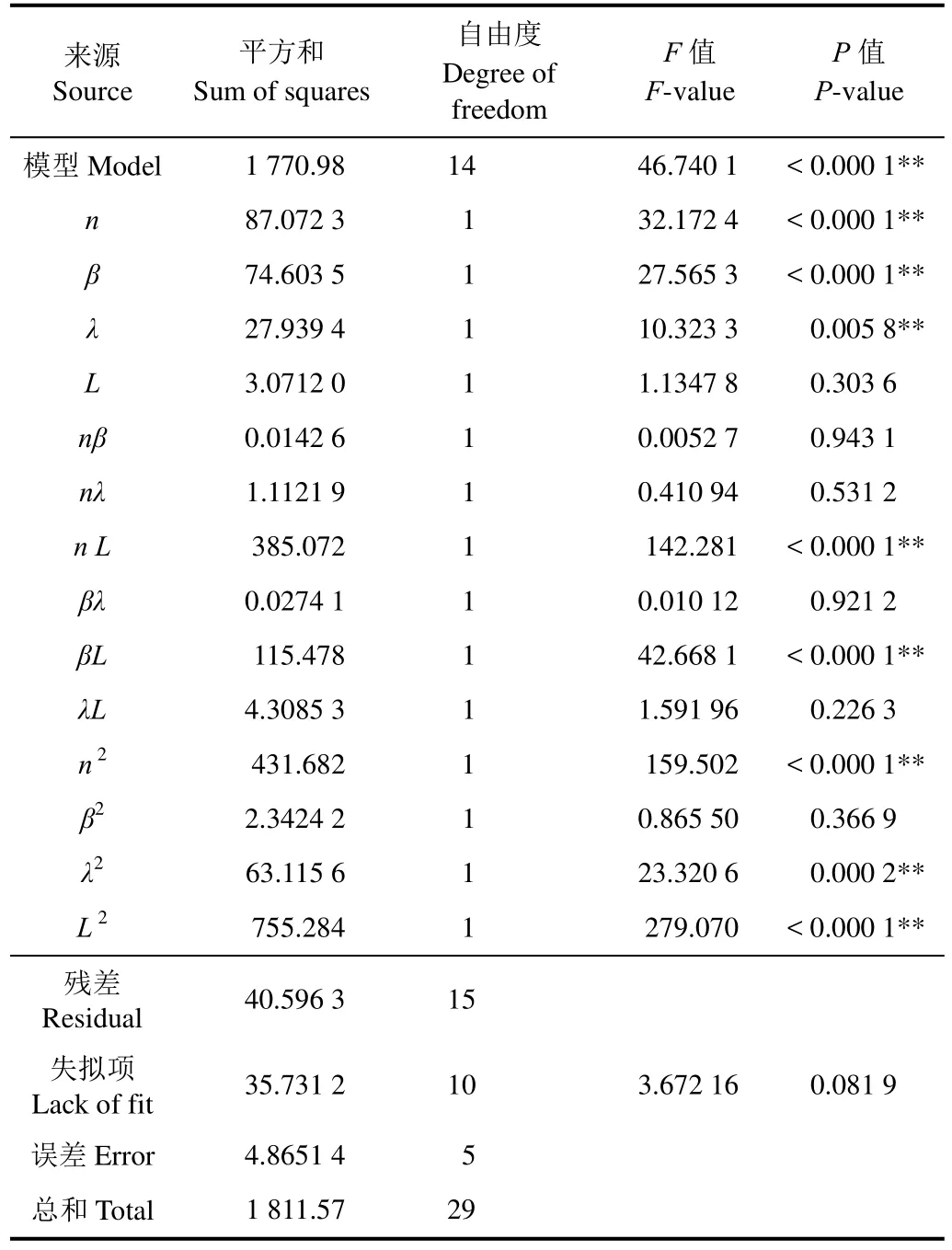
表3 变异系数方差分析Table 3 Variance analysis for variation coefficient
4.2.3 响应曲面分析
为直观分析试验指标和各个因素之间的关系,利用Design-Expert 8.0.6 软件得到交互作用显著因素间的响应曲面,如图6所示。
当喂入角为90°,喂入量为4 000颗/s时,甩盘转速与喂入位置角交互作用的响应曲面如图 6a,表明甩盘转速 700~900 r/min范围时随喂入位置角增大变异系数增大,900~1 100 r/min转速范围影响规律相反;喂入位置角50°至70°范围时随转速增大变异系数增大,70°至90°影响规律相反;甩盘转速900 r/min及喂入位置角为70°时有最小凹点,施肥均匀性较好。甩盘转速和喂入位置角共同决定肥料颗粒离开甩盘的位置和速度,从而影响肥料撒施与分布规律。
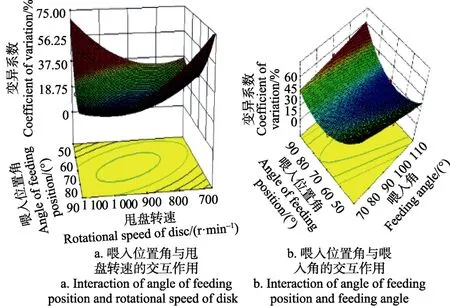
图6 变异系数的双因素响应曲面Fig.6 Response surface of two factors for coefficient of variation
甩盘转速为900 r/min,喂入量为4 000颗/s,喂入位置角与喂入角交互作用响应曲面如图 6b,表明一定喂入角时随喂入位置角增大变异系数先降后升,70°时颗粒离开甩盘速度方向与机具前进方向匹配较好,横向分布更均匀。50°~70°喂入位置角区域随喂入角增大变异系数减小,70°~90°喂入位置角区域变化规律相反。
4.3 试验结果的目标优化
为寻求各因素最优组合,以表 1中各因素范围为约束条件,以变异系数回归模型式(12)为目标函数,求解其最小值,得变异系数最低时优化解为甩盘转速899.84 r/min(取900 r/min)、喂入量4 274.63颗/s(取4 275 颗/s)、喂入角 110°、喂入位置角 64.2°(取 64°),此时变异系数为12.48%。将优化参数进行仿真验证,得横向变异系数为13.52%,与优化结果基本相吻合。
5 优化参数试验验证
选择与仿真条件一致的大颗粒尿素,试验地点为中国农业大学工学院地下室。按照 ASAE试验标准每隔两列计算网格摆放 10×12个盒子形成与仿真一致的3.92 m×2.40 m收集域(图7),每个盒子面积与计算网格面积相同(140 mm×200 mm)。测定肥料颗粒与纸盒碰撞恢复系数为 0.63,为使肥料不从纸盒中弹出,其底部铺80 g经孔径Ф2 mm检验筛筛分出的细土。在最优参数组合下进行 3次重复试验,得变异系数分别为 13.50%、12.44%、12.48%,均值为12.81%,与优化结果基本一致,验证仿真模型精度和边界参数可靠性,静态试验撒肥效果较好。

图7 试验现场Fig.7 Diagram of test site
6 实际工况下的动态仿真试验
撒肥机动态性能研究试验量大且复杂,因此目前撒肥均匀性试验研究多基于静态试验法[8,9,12,23],少数动态试验[3,11]也只考虑单行程内肥料分布均匀性,与田间作业存在差距。本文依据撒肥机往返作业肥料抛撒重叠搭接实际作业情况进行最佳参数下动态仿真试验研究。文献[30]指出,离心式撒肥器撒施肥料横向分布不均匀,最大稠度区位于以D/2为半径的圆弧内(图8),与前述单因素试验分析规律一致,因此田间作业为满足撒施均匀性需有一定重叠量Δb,Δb为抛掷远度的25%左右。基于前述仿真模型和边界参数,前进速度分别为0. 5 m/s(1.8 km/h)和1.5 m/s(5.4 km/h),收集域3.92 m×5.20 m,采用回转作业方式进行多轨迹拟合叠加[4],得三维分布如图9a、9b,肥料总量分布如图9c,0.5 m/s和1.5 m/s时叠加后工作幅宽内均匀性变异系数分别为9.92%和11.43%,常用抛撒式施肥机要求横向施肥均匀度变异系数Cv≤20%,圆盘式撒肥机田间作业横向施肥均匀度变异系数Cv为10%~15%[22],因此能满足田间施肥实际需求。
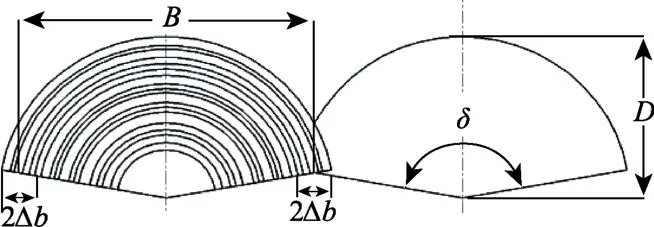
图8 肥料撒施的分布图Fig.8 Distribution map of fertilizer spreading
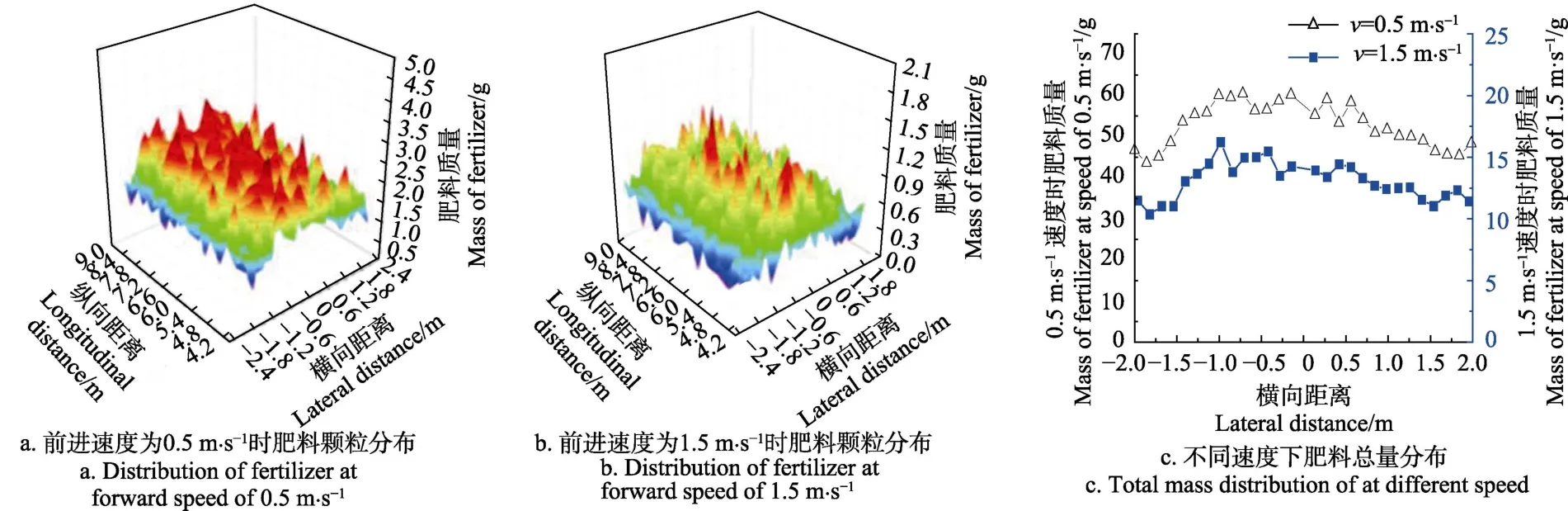
图9 不同前进速度时肥料颗粒的分布Fig.9 Distribution of fertilizer particles at different forward speed
7 结 论
1)为提高颗粒肥料撒肥均匀性,对设计的具有渐开螺旋线导轨的离心甩盘撒肥器进行了理论分析,结合单因素仿真试验研究了影响因素对撒肥均匀性的影响规律,确定了各因素的取值范围:甩盘转速为700~1 100 r/min,喂入角为 70°~110°,喂入量为 2 000颗/s~6 000颗/s,喂入位置角为50°~90°。
2)多元回归正交旋转试验二次回归方程与响应面分析表明,喂入位置角与甩盘转速及喂入位置角与喂入角间交互作用对撒肥均匀性影响均高度显著,各因素影响主次顺序为甩盘转速、喂入角、喂入量、喂入位置角。
3)对目标进行优化求解,甩盘转速900 r/min、喂入量4 275颗/s、喂入角110°、喂入位置角64°时均匀性变异系数12.48%,与仿真验证和实际验证试验结果基本一致。实际工况下多轨迹拟合与叠加动态仿真研究表明,前进速度为5.4 km/h时实际工作幅宽内均匀性变异系数为11.43%,满足田间撒肥作业要求。
[1] 付宇超,袁文胜,张文毅,等. 我国施肥机械化技术现状及问题分析[J]. 农机化研究,2017(1):251-255.Fu Yuchao, Yuan Wensheng, Zhang Wenyi, et al. Present situation and problem analysis of the technology offertilizer mechanization in China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2017(1): 251-255. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 陈远鹏,龙慧,刘志杰. 我国施肥技术与施肥机械的研究现状及对策[J]. 农机化研究,2015(4):255-260.Chen Yuanpeng, Long Hui, Liu Zhijie. Actuality and measures of fertilization technology and machinery in China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization, 2015(4):255-260. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 吕金庆,尚琴琴,杨颖,等. 锥盘式撒肥装置的性能分析与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(11):16-24.Lü Jinqing, Shang Qinqin, Yang Ying, et al. Performance analysis and experiment on granular fertilizer spreader with swing disk[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Scoiety of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016,32 (11): 16-24. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] Klas. On the production of monodisperse particles with a spinning disk[J]. Precision Agricultural, 2014, 15(3): 304-320.
[5] Fulton J P, Shearer S A, Higgins S F, et al. A method to generate and use as-applied surfaces to evaluate variable-rate fertilizer applications[J]. Precision Agricultural, 2013, 14(2):184-120.
[6] Villette S, Cointault F, Piron E, et al. Centrifugal spreading:An analytical model for the motion of fertilizer particles on a spinning disk[J]. Biosystems Engineering, 2005, 92(2):157-164.
[7] 张睿,王秀,马伟,等. 变量施肥抛撒机撒肥机构研究[J].农机化研究,2013(11):153-155,163.Zhang Rui, Wang Xiu, Ma Wei, et al. Design and experiment on spreading mechanism of variable rate fertilizer spreader[J].Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2013(11):153-155, 163. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 齐兴源,周志艳,杨程,等. 稻田气力式变量施肥机关键部件的设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(6):20-26.Qi Xingyuan, Zhou Zhiyan, Yang Cheng, et al. Design and experiment of key parts of pneumatic variable-rate fertilizer applicator for rice production[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Scoiety of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE),2016, 32(6): 20-26. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 胡永光,杨叶成,肖宏儒,等. 茶园施肥机离心撒肥过程仿真与参数优化[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(5):77-82.Hu Yongguang, Yang Yecheng, Xiao Hongru, et al.Simulation and parameter optimization of centrifugal fertilizer spreader for tea plants[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2016, 47(5):77-82. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 芦新春,陈书法,杨进,等. 宽幅高效离心式双圆盘撒肥机设计与试验[J]. 农机化研究,2015(8):100-103.Lu Xinchun, Chen Shufa, Yang Jin, et al. Design and experiment on double-disk spreader with wide breadth and highly efficiency[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanization Research, 2015(8): 100-103. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 陈书法,张石平,孙星钊,等. 水田高地隙自走式变量撒肥机设计与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2012,28(11):16-21.Chen Shufa, Zhang Shiping, Sun Xingzhao, et al. Design and experiment of self-propelled high-ground-clearance spreader for paddy variable-rate fertilization[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Scoiety of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2012, 28(11): 16-21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 张军奎. 水稻苗期施肥机的设计与试验研究[D]. 北京:中国农业大学,2012.Zhang Junkui. Design and Experiment Study on Topdressing Machine in Rice Seeding Stage[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] van Liedekerke P, Tijskens E, Dintwa E, et al. DEM simulations of the particle flow on a centrifugal fertilizer spreader[J]. Powder Technology, 2009, 190(3), 348-360.
[14] van Liedekerke P, Tijskens E, Dintwa E. et al. A discrete element model for simulation of a spinning disk fertilizer spreader I: Single particle simulation [J]. Powder Technology,2006, 170(2), 71-85.
[15] Cool S, Pieters J, Mertens K C, et al. A simulation of the influence of spinning on the ballistic flight of spherical fertiliser grains[J]. Computers and Electronics in Agriculture,2014(105): 121-131.
[16] 苑进,刘勤华,刘雪美,等. 配比变量施肥中多肥料掺混模拟与掺混腔结构优化[J]. 农业机械学报,2014,45(6):125-132.Yuan Jin, Liu Qinhua, Liu Xuemei, et al. Simulation of multi-fertilizers blending process and optimization of blending cavity structure in nutrient proportion of variable rate fertilization[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2014, 45(6): 125-132. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 周韦,王金峰,王金武,等. 基于EDEM的水田深施肥机构螺旋钢丝的数值模拟与分析[J]. 农机化研究,2015(1):27-30.Zhou Wei, Wang Jinfeng, Wang Jinwu, et al. Numerical simulation and analysis of a fertilizer can on fertilizer spreader based on EDEM[J]. Journal of Agricultural Mechanizaton, 2015(1): 27-30. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 张家华. 基于离散元法的变量施肥机排肥器排肥过程仿真分析[D]. 石河子:石河子大学,2015.Zhang Jiahua. Simulation Analysis of Variable Fertilizer Applicator Apparatus Fat Process Based on Diskrete Element Method[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] Liu Cailing, Wang Yali, Song Jiannong, et al. Experimental determination and numerical simulation of granular material restitution coefficient[J]. International Agricultural Engineering Journal, 2016, 25(4): 48-56.
[20] 刘彩玲,王亚丽,宋建农,等. 基于三维激光扫描的水稻种子离散元建模及试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(15):294-300.Liu Cailing, Wang Yali, Song Jiannong, et al. Experiment and diskret element model of rice seed based on 3D laser scanning[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Scoiety of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2016,32(15): 294-300. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] Procedure For Measuring Distribution Uniform and Calibrating Granular Broadcast Spreaders:ISO ASAE S341.2: 2006[S].
[22] Equipment for distributing fertilizers-Test methods-Part2:Fertilizer distributors in lines: ISO 5690: 1984[S].
[23] 董向前,宋建农,张军奎,等. 锥盘式颗粒肥撒施机构抛撒性能分析与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2013,29(19):33-40.Dong Xiangqian, Song Jiannong, Zhang Junkui, et al.Working performance and experiment on granular fertilizer spreader with cone disk[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Scoiety of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2013, 29(19): 33-40. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] Aphale A, Bolander N, Park J, et al. Granular fertiliser particle dynamics on and off a spinner spreader[J].Biosystems Engineering, 2003, 85(3): 319-329.
[25] Olieslagers R, Ramon H, Baerdemaeker J D. Calculation of fertilizer distribution patterns from a spinning disk spreader by means of a simulation model [J]. Journal of Agricultural Engineering Research, 1996, 63: 137-152.
[26] 蒋义然,王新旺,刘瑞静. 施肥幅宽对圆盘式变量撒肥机施肥一致性的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学,2012,40(23):11923-11925.Jiang Yiran, Wang Xinwang, Liu Ruijing. Effect of fertilization width on the fertilization consistency of spinning disk spreader[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2012, 40(23): 11923-11925. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[27] 吴辉. 圆盘式施肥机抛撒试验系统开发与撒肥规律研究[D]. 保定:河北农业大学,2007.Wu Hui. Development and Distribution Study on the Spreading Test System for a Spinner Spreader[D]. Baoding:Agricultural University of Hebei, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 任露泉. 回归设计及其优化[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2009.
[29] 徐向宏,何明珠.试验设计与Design-Expert、SPSS应用[M].北京:科学出版社,2010.
[30] 北京农业机械化学院. 农业机械学:上册[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社,1981.
Performance analysis and experiment on fertilizer spreader with centrifugal swing disk based on EDEM
Liu Cailing, Li Yanni, Song Jiannong※, Ma Tuo, Wang Mengmeng,Wang Xujian, Zhang Chao
(College of Engineering, China Agricultural University, Beijing100083,China)
Fertilizing operation is an important link in grain seeding, which plays an important role in ensuring the high yield.Fertilizer spreaders often are used in the operating process. At present, the spreading uniformity of most of the machines needs be improved. In order to improve the spreading performance, in this study, a centrifugal fertilizer spreader with a rotating swing disk with 16 involute spiral guide rails was studied and dynamic characteristic analysis of fertilizer particle was performed. A single factor simulation analysis on rotational speed of disk, feeding angle, feeding quantity and angle of feeding position was conducted using a disk rete element model based on theoretical analysis results. Influence of various factors on the spreading uniformity of the centrifugal swing disk was discussed. The working range of the parameters was derived. The rotational speed of disk ranged from 700 r/min to 1 100 r/min, feeding angle was from 70° to 110°, feeding quantity was from 2 000 particles to 6 000 particles per sencond, and angle of feeding position was from 50° to 90°. The urea with larger size was taken as the research material. The orthogonal regression rotation simulation experiment with four influencing factors was designed and the test indexes were coefficient of variation of fertilizer distribution on the lateral width direction. The simulation experiments on fertilizer spreading performance and target parameter optimization was done, and the static verification test was carried out. Multivariate nonlinear regression model was established and the affecting importance of factors on the uniformity and response surface analysis was finished. The experimental data were processed and optimized by Design-expert 8.0.6. The results showed that the interaction between angle of feeding position and rotational speed of disk,angle of feeding position and feeding angle had important influence on spreading uniformity. The order of importance was followed by rotational speed of disk, feeding angle, feeding quantity and angle of feeding position. The minimum uniformity coefficient of variation were 12.48% when rotational speed of disk, feeding quantity, feeding angle and angle of feeding position was 900 r/min, 4 275 per second, 110° and 64°, respectively. With the optimal parameters, the results of simulation and bench testing were mostly in agreement. The simulation research on fertilizer spreading performance of fertilizer spreader by EDEM was proved to be feasible. In order to verify operating effect under actual working conditions, the dynamic simulation research of multi-track fitting and superposition was carried out. The results showed that uniformity coefficient of variation were 9.92% and 11.43%, respectively when the forward speed of a machine was 0.5 m/s and 1.5 m/s. The fertilizer spreader can meet the technical requirements of field operations. The centrifugal fertilizer spreader with a rotating swing disk provides better working performance. The research results provide a theoretical reference for design and optimization of the granular fertilizer spreader with a spinning swing disk.
agricultural machinery; discrete element method; numerical analysis; spreader; uniformity; experiment
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.14.005
S224.2;TP391.9
A
1002-6819(2017)-14-0032-08
刘彩玲,黎艳妮,宋建农,马 拓,王蒙蒙,王徐建,张 超. 基于EDEM的离心甩盘撒肥器的性能分析与试验[J]. 农业工程学报,2017,33(14):32-39.
10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.14.005 http://www.tcsae.org
Liu Cailing, Li Yanni, Song Jiannong, Ma Tuo, Wang Mengmeng, Wang Xujian, Zhang Chao. Performance analysis and experiment on fertilizer spreader with centrifugal swing disk based on EDEM[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering (Transactions of the CSAE), 2017, 33(14): 32-39. (in Chinese with English abstract)
doi:10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2017.14.005 http://www.tcsae.org
2017-01-18
2017-05-24
国家重点研发计划课题—北方作物精量播种和精密化肥深施关键技术与装备(2016YFD0200607)
刘彩玲,女,河北秦皇岛人,副教授,博士,2012-2013年赴美国伊利诺伊大学香槟分校研修,主要从事现代农业机械与农业装备研究。北京 中国农业大学工学院,100083。Email:cailingliu@163.com。
※通信作者:宋建农,男,河北藁城人,教授,博士生导师,主要从事农业机械与农业装备研究。北京 中国农业大学工学院,100083。
Email:songjn@cau.edu.cn
中国农业工程学会高级会员:刘彩玲(E041200744S)

