一种安全的多帧遥感图像的外包融合去噪方案
黄冬梅 戴 亮 魏立斐 魏泉苗 吴国健
1(上海海洋大学信息学院 上海 201306) 2(国家海洋局东海分局 上海 200136) (dmhuang@shou.edu.cn)
2017-06-10;
2017-07-29
国家自然科学基金项目(61402282,61672339,41671431);上海市青年科技英才扬帆计划项目(14YF1410400);上海市科委地方高校能力建设项目(15590501900) This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61402282, 61672339,41671431), the Shanghai Yang-Fan Plan (14YF1410400), and the Local University Capacity Enhancement Project of Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality (15590501900).
魏立斐(Lfwei@shou.edu.cn)
一种安全的多帧遥感图像的外包融合去噪方案
黄冬梅1戴 亮1魏立斐1魏泉苗2吴国健1
1(上海海洋大学信息学院 上海 201306)2(国家海洋局东海分局 上海 200136) (dmhuang@shou.edu.cn)
遥感图像去噪是图像处理领域的热门研究课题.伴随着采集设备改进和技术提升, 同一场景下的多帧图像的融合去噪已经成为可能.然而海量遥感图像去噪在单机上暴露出处理速度慢、并发性差等问题,利用云计算平台进行海量数据的存储和处理是大势所趋.为保护外包计算的遥感图像的安全性,提出了一种针对多帧遥感图像的安全外包融合去噪方案.方案利用Paillier加密算法的密文加法同态性和Johnson-Lindenstrauss转换近似保留欧氏距离的特性,对平均图像进行基于动态滤波参数的融合去噪.选用从多幅Landsat 8遥感图像中截取多个512×512像素的图像作为实验对象,搭建了Spark单机环境来模拟云环境.实验数据表明:提出的外包方案可以有效地保证遥感图像的安全性;同时,融合去噪方案的效果明显优于已有的密文去噪方案和单帧密文去噪方案,且对不同图像、不同大小的噪声均有很好的去噪效果.
多帧图像;遥感;安全外包;融合去噪;Paillier同态加密;Johnson-Lindenstrauss转换
“空天地底”立体观测技术的高速发展,使得高精度、高频率、大覆盖、多模态遥感数据呈几何级数爆炸式增长,已成为公认的“大数据”[1-2].但遥感图像在获取、传输、接收、输出等过程中往往会受到噪声的污染[3],使得遥感图像出现边缘纹理等细节模糊,导致图像质量降低,增大了遥感图像后期处理与分析的难度[4].因此,遥感图像必须进行降噪预处理[5].
遥感图像不同于普通图像,存在多个波段、16位深的灰度值及高分辨率的遥感图像的文件尺寸很大,传统的图像去噪如非局部均值去噪方法[6]、基于偏微分方程的去噪方法[7-8]、基于小波的去噪方法[9]和基于稀疏表示的去噪方法[10]等,处理难度较大.伴随着遥感图像采集设备的改进和技术的提升,短时间内采集同一场景的多帧遥感图像提供了更丰富的空域信息,为遥感图像去噪提供了新的研究思路,但同时也增加了遥感图像去噪的难度.在短时间内采集的同一场景的多幅图像中含有噪声的强度大小相近,且噪声分布相似.多帧图像叠加平均方法利用多帧图像的时间域相关性,可以较好地削弱图像中的噪声,还原出更清晰的图像.多帧图像去噪如以块为单位的多帧图像去噪方法[11]、单/多帧图像相结合的去噪方法[12]、基于时域叠加平均和空域非局部均值的多帧图像去噪方法[13]、基于平均图像的多图非局部均值去噪方法[14]等.然而,上述遥感图像的单机处理模式暴露出处理速度慢、并发性差等问题,尤其对于多帧遥感图像数据量大,更无法满足海量遥感图像存储与处理的需求.
云计算是一个典型的分布式、并行计算模式,能提供海量存储空间和计算能力.但云平台并非完全可信[15],为了保护数据的安全与隐私,需要对数据先进行加密再存储在云平台.目前,在云环境下已经出现了密文搜索[16]、密文模式匹配[17-18]、密文信号处理[19-20]、密文矩阵计算[21-22]、密文最优化计算[23-24]等密文处理方案.然而,针对图像外包去噪研究刚刚起步,Hu等人提出了针对单帧普通图像的安全去噪方案[25].遥感图像作为国家重要的战略资源,对遥感图像进行加密,被认为是保护遥感图像中信息隐私的有效方式[26].现有的图像外包去噪方案[25],只考虑了单帧图像的空间域相关性,未考虑多帧图像的时间域相关性.多图非局部去噪[14]利用多帧图像的时间域相关性和空间域相关性,可在非局部去噪过程中找到更多、相似程度更高的像素点,更好地削弱图像中的噪声.
本文在已有工作的基础上,提出了遥感图像外包去噪的单帧去噪方案和融合去噪方案,并给出了实验对比结果:
1) 利用Paillier加密算法[27-28]的密文加法同态性和JL(Johnson-Lindenstrauss)转换[29-30]近似保留欧氏距离的特性,采用双密文策略,对密文遥感图像进行基于动态滤波参数的外包去噪.
2) 基于文献[14]中的融合去噪方案,提出了一种针对多帧遥感图像的安全外包融合去噪方案,对平均图像进行基于动态滤波参数的外包融合去噪.
3) 选用从多幅Landsat8遥感图像中截取多个512×512大小的图像作为实验对象,搭建了Spark单机环境来模拟云环境.实验数据表明:本文提出的外包方案可以有效地保证遥感图像的安全性;同时,本文的融合去噪方案明显优于已有的密文去噪方案[25]和单帧去噪方案,对不同大小的噪声均有很好的去噪效果.
1 系统描述
1.1系统模型
1.1.1 单帧图像模型
对于给定的任意一幅含有噪声的图像可以描述为:v={v(a)|a∈A},其中A表示该图像域.对于该图中的任意一个像素点a表示为
v(a)=u(a)+n(a),
(1)
其中,v(a)为像素点a的测定值,u(a)为像素点a的原始灰度值,n(a)为该图像在像素点a的噪声值.对于图像中任意一个像素点a,非局部均值去噪算法利用图像中所有相似像素点的灰度值加权平均得到该点的估计值,表示为
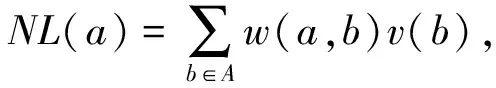
(2)
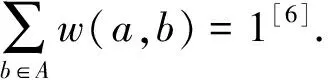
1.1.2 多帧图像模型
对于多帧图像,如图1所示,噪声图像nf1,nf2,…,nfn为短时间内采集到的同一场景的多帧图像,平均图像nf0为多帧图像叠加平均得到.a1,a2,…,an是时间域上对应空间位置的像素点,分别来自nf1,nf2,…,nfn.那么在平均图像nf0中像素点a0处融合去噪后的估计值为
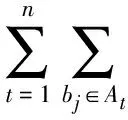
(3)


(4)
其中高斯公式
(5)
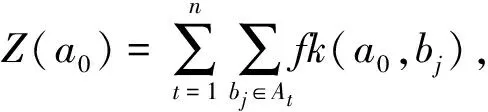
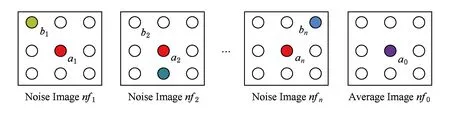
Fig. 1 Multi-images and average image图1 多帧图像及叠加平均

Fig. 2 Outsourced fusion denoising framework图2 外包融合去噪框架图
1.2安全模型
本文采用云平台是诚实且好奇(honest but curious)模型[26],即云平台会诚实地执行用户预设的计算,但是云平台可能会窥探数据内容.如图2所示,用户在上传到云平台前进行遥感图像的加密,然后云平台基于密文遥感图像进行多帧遥感图像的融合去噪,最后用户解密云平台返回的遥感图像,获得完成融合去噪后的遥感图像.
1.3算法描述
根据Gennaro等人提出的安全外包计算的形式化定义[31],本文给出遥感图像外包融合去噪方案的定义.方案包括4个算法:密钥生成(KeyGen)、问题生成(ProbGen)、问题计算(Compute)和问题解决(Solve).
1) 密钥生成.KeyGen(τ)→(skPerm,skJL,pkPail,skPail).输入一个随机的安全参数τ,输出随机置换密钥skPerm;输出JL转换的密钥skJL;输出Paillier加密的公私钥对pkPail和skPail.
2 安全外包融合去噪方案
本文的方案分成密钥生成(KeyGen)、问题生成(ProbGen)、问题计算(Compute)和问题解决(Solve)四个算法.
2.1密钥生成KeyGen
本文的遥感图像安全外包融合去噪方案所需要的密钥包括: 随机置换密钥skPerm;JL转换的密钥skJL=(P,ζ);Paillier加密的公钥pkPail=(N,g)和私钥skPail=(λ,g).
2.2问题生成ProbGen
二是角度。俗话说,果树丰产不丰产,开角是关键。拉枝是果树生产中的关键环节,枝势越强,拉枝角度越大。永久性主枝拉至80°~90°即可,临时辅养枝角度可加大至110°以上。
2.2.1 图像波段拆分
对于给定具有B个波段的遥感图像Ii(i=1,2,…,n),图像的长为im_h,宽度为im_w,按波段把这n幅遥感图像拆分成n×B个图像.
2.2.2 图像JL转换
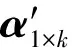
2.2.3 图像随机置换
为了让云平台计算出遥感图像中像素块之间的欧氏距离,需要将单波段图像Im1,Im2,…,Im n经过JL转换得到的图像EJL(Im1),EJL(Im2),…,EJL(Im n)发送到云平台,然而图像EJL(Im1),EJL(Im2),…,EJL(Im n)中保存了明文图像中的相邻像素的位置信息,虽然无法推断出该图像各个像素点准确的灰度值,但可以通过二值化攻击获得原始图像的大概轮廓.对图像EJL(Im1),EJL(Im2),…,EJL(Im n)进行二值化攻击,得到的结果如图3(a),(b)所示,攻击者依然能够获得海岸线、道路轮廓等地貌特征.


Fig. 3 Results of the Binarization attack before/after random permutation图3 随机置换前后二值化攻击效果图
2.2.4 图像Paillier加密
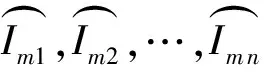
(gN)r5modN2.
(6)
2.3问题计算Compute
2.3.1 平均图像计算
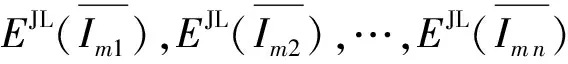
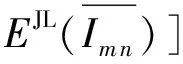
(7)

2.3.2 密文欧氏距离计算

dJL(a0,bj)=
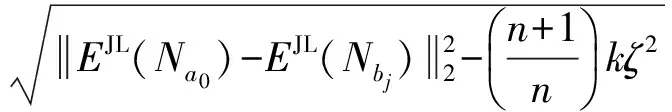
(8)
2.3.3 去噪权重计算
云平台需要对多帧遥感图像的单个波段的图像进行融合去噪,然而遥感图像中众多的相似度低的像素点增加了计算量,同时也会影响融合去噪算法的去噪效果.加权核函数对融合去噪性能和效率起着至关重要的作用.本文基于余弦型高斯核函数[33],提出了一种基于自适应滤波参数h2的融合去噪方法,其高斯函数为
fkJL(a0,bj)=
(9)
其中,h1为平滑参数,h2为滤波参数,且h2为集合{dJL(a0,bj)|bj∈At,1≤t≤n}中第M小的值,其中M为进行融合去噪而选取的相似度最大的像素点个数.
此时,权重
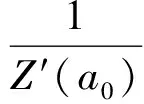
(10)
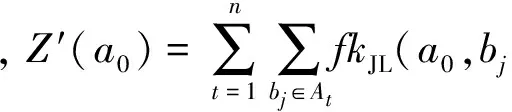
由于Paillier加密只能处理整数,w′(a0,bj)必须要转化为一个整数.权重取整转换为
(11)

2.3.4 融合去噪计算
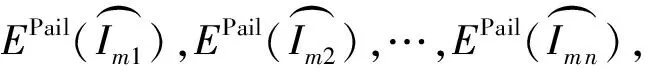
EPail[NL″(a0)]=
(12)
2.4问题解决Solve
2.4.1 图像Paillier解密
接收到云端返回的完成融合去噪的加密图像后,用户使用私钥skPail对收到的遥感图像进行Paillier解密并计算出该图像完成融合去噪后的结果.
在融合去噪过程中,使用w″(a0,bj)作为加权因子
w″(a0,bj)=Qw′(a0,bj)+ψ(a0,bj),
(13)
其中,ψ(a0,bj)为转化过程中的误差值,且|ψ(a0,bj)|<0.5.则NL″(a0)可以表示为
NL″(a0)=Q×NL′(a0)+
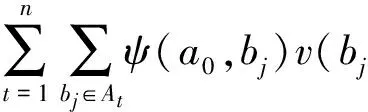
(14)
因此NL′(a0)可以表示为
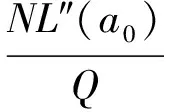
(15)
其中,R(a0)为转化过程中给融合去噪的结果带来的误差值,当Q足够大时,R(a0)<0.5,给融合去噪结果带来的影响非常小.因此:
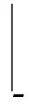
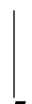
(16)
2.4.2 图像恢复
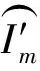
2.4.3 图像组合
对完成去噪后B个波段的遥感图像重新组合,即可得到完成融合去噪的遥感图像I′.
3 安全性分析
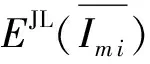
综上分析,本文的融合去噪方案具有良好的安全性,除了密文长度和遥感图像大小,攻击者无法获取到任何有用信息.
4 性能测试
实验数据选用从多幅Landsat 8遥感图像中截取多个512×512像素的图像,采用图像中空间分辨率为30 m的7个波段图像(波段名为Coastal,Blue,Green,Red,NIR,SWIR1,SWIR2)作为实验图像.实验环境为在计算机(处理器:i7-3770 3.4GHz、内存:8 GB 1 600 MHz、编程语言:Java)上搭建的Spark单机环境.
Paillier加密的参数设置如下:p和q为256 b素数.JL转换中参数设置如下:高斯噪声参数ζ=0.5,维度k取值为9,12,15,18四种情况.融合去噪参数设置如下:滤波参数h1=384,像素块大小S×S=5×5,进行融合去噪的像素点个数M=512,权重转换参数Q=225.
加入N(0,5122)的高斯噪声后,遥感图像的峰值信噪比(peak signal to noise ratio,PSNR)为42.14 dB,均方误差(mean squared error,MSE)为262 277.00.分别运用4种方法:基于明文的非局部均值去噪方法[6]、Hu等人的密文方法[25]、本文方案的单幅图像去噪方法和多帧(n=3)图像融合去噪方法对上述含有噪声的遥感图像进行去噪对比.得到各个波段的PSNR值如表1所示,MSE值如表2所示.实验结果表明:本文的融合去噪方法优于密文去噪方法和单幅去噪方法,且在k较大时优于明文去噪方法.
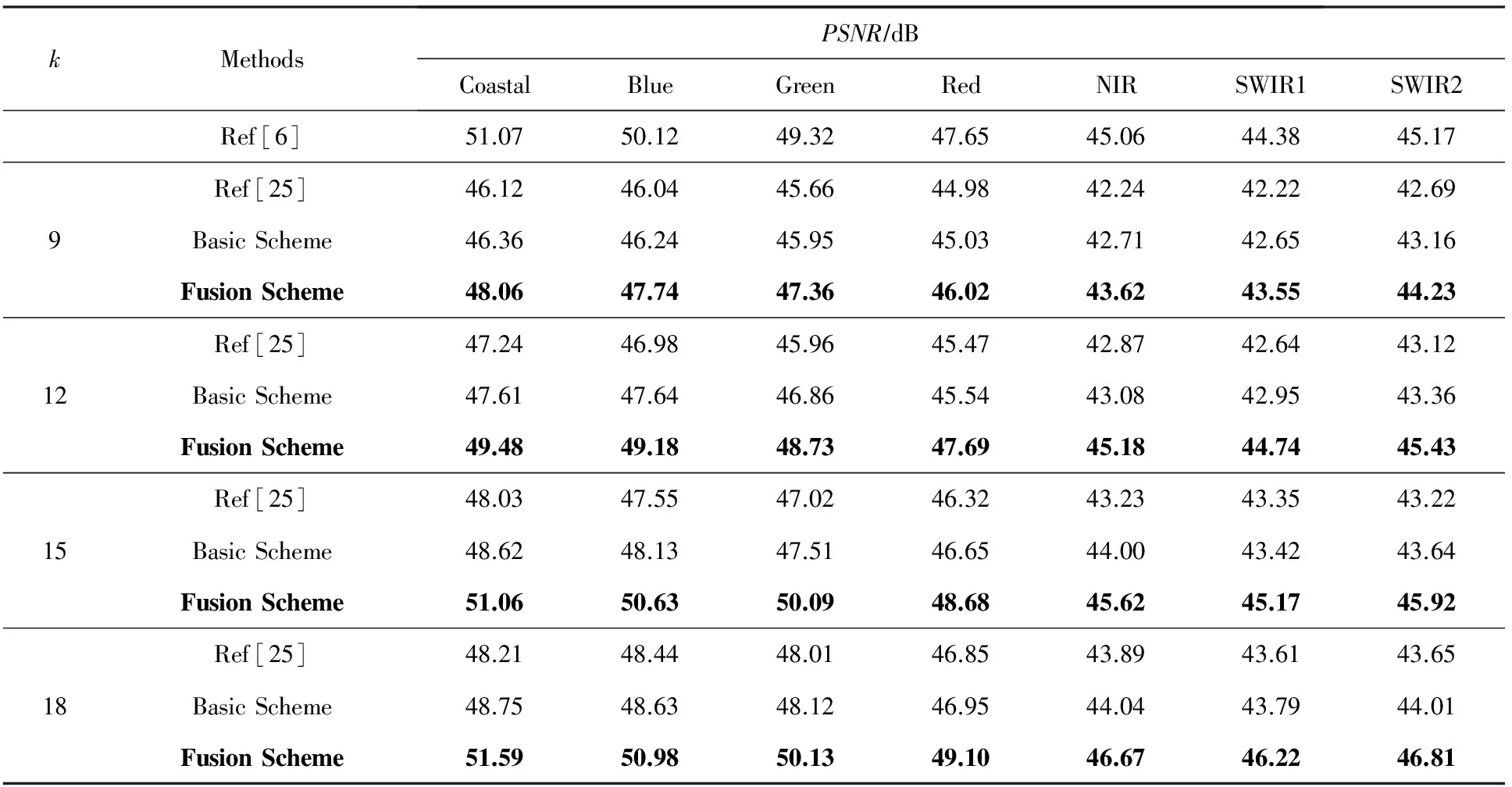
Table 1 PSNR Results of Remote Sensing Image Denoising
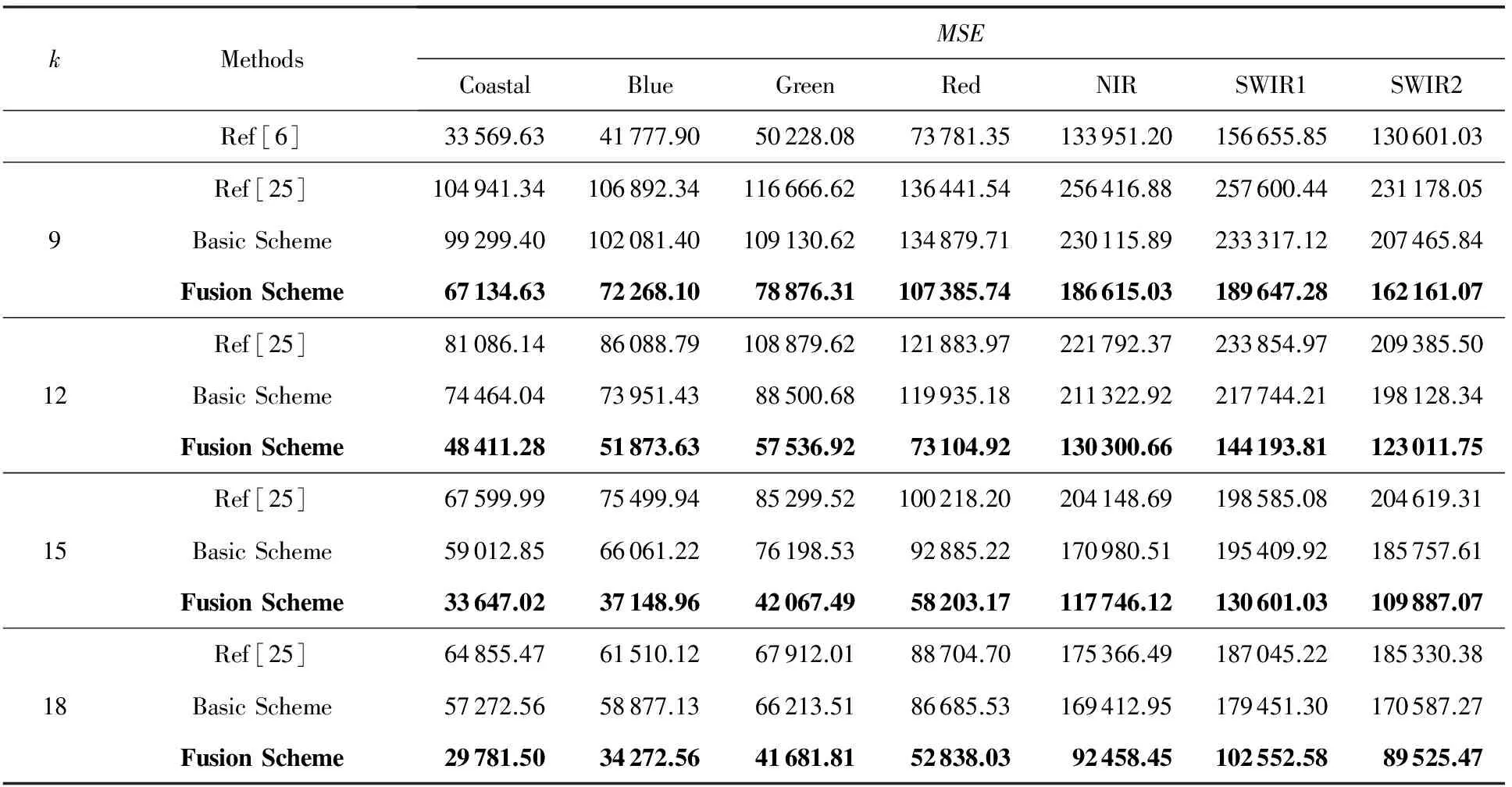
Table 2 MSE Results of Remote Sensing Image Denoising
使用本文的去噪框架,分别运用Hu等人的密文方法[25]、本文方案的单幅图像去噪方法和多帧(n=3)图像融合去噪方法,对不同波段的遥感图像进行去噪.图4给出了去噪效果PSNR与JL转换维度关系对比;图5给出了去噪效果MSE与JL转换维度关系对比;图6给出了去噪效率对比.实验结果表明:本文的融合去噪方法对于不同波段的遥感图像均有很好的去噪效果,且随着JL转换维度的增加,去噪效果越好;在遥感图像帧数n=3时,本文的融合去噪用时高于单幅图像去噪,但远低于密文去噪方法[25].
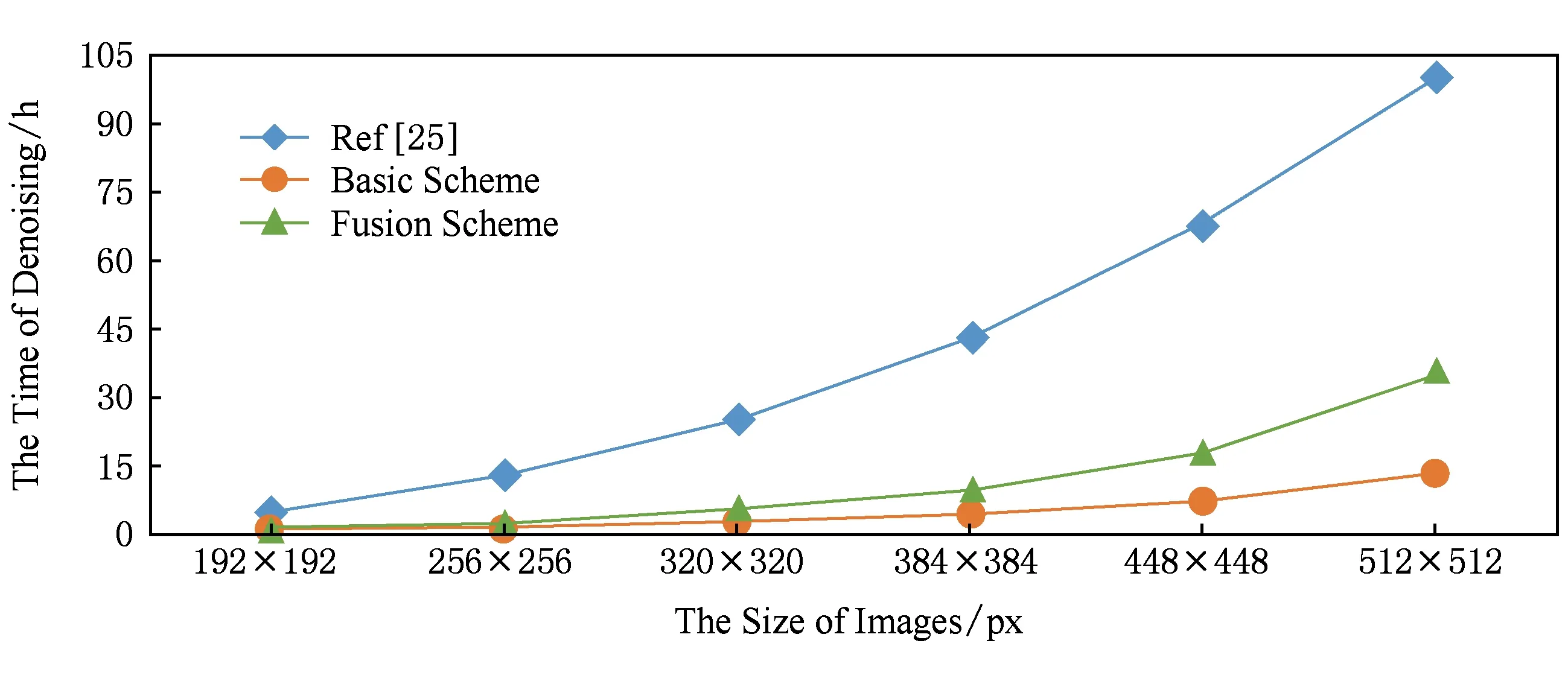
Fig. 6 The comparison on outsourced denoising efficiency图6 外包去噪效率对比图
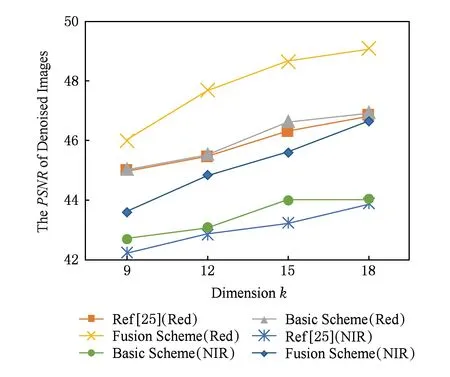
Fig. 4 The comparison on PSNR with different dimensions of JL transform图4 去噪效果PSNR与JL转换维度k关系对比图
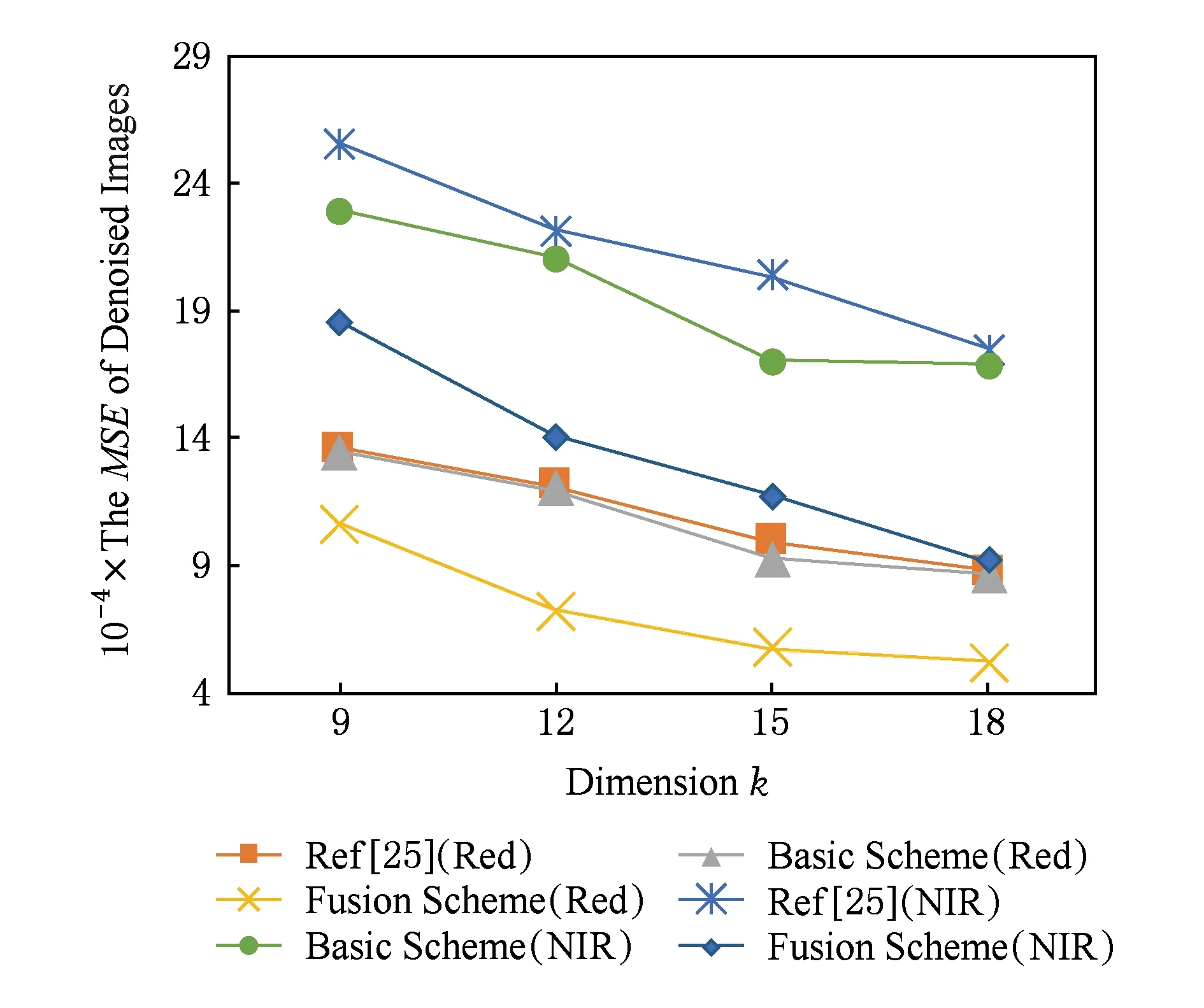
Fig. 5 The comparison on MSE with different dimensions of JL transform图5 去噪效果MSE与JL转换维度k关系对比图
本文融合去噪方法对于多幅图像的不同噪声去噪效果图如图7所示.图7(a1),(b1)为Landsat 8遥感图像1对应Red波段的图像,图7(c1),(d1),(e1),(f1)为Landsat 8遥感图像2和遥感图像3对应NIR波段的图像.第1列为原始图像;第2列为含有不同噪声的图像,图7(a2),(c2),(e2)为原始图像加了N(0,2562)的高斯噪声得到的其中一幅图像,图7(b2),(d2),(f2)为原始图像加了N(0,5122)的高斯噪声得到的其中一幅图像;第3列为基于含有噪声的明文图像进行非局部去噪得到的图像[6];第4列为基于含有噪声的密文图像运用本文的去噪方案基于单幅图像去噪得到的图像.第5列为基于含有噪声的密文图像运用本文的融合去噪方案得到的图像.实验结果表明:本文的融合去噪方法对于不同遥感图像中的不同大小的噪声都能有很好的去噪效果.
最后,实验给出了用于多帧融合去噪的图像帧数n对图像去噪效果的影响.以图7中遥感图像1、遥感图像2和遥感图像3对应的Red波段图像为例,实验设定图像帧数n=1,2,3,4,5,噪声大小为N(0,5122)的高斯噪声,运用本文的融合去噪方法进行测试,测试结果如图8和图9所示.实验结果表明,在图像帧数不超过5的情况下,随着图像帧数的增加,多帧图像的去噪效果明显变好.

Fig. 7 The result of secure fusion denoising in remote sensing image图7 遥感图像安全融合去噪结果图
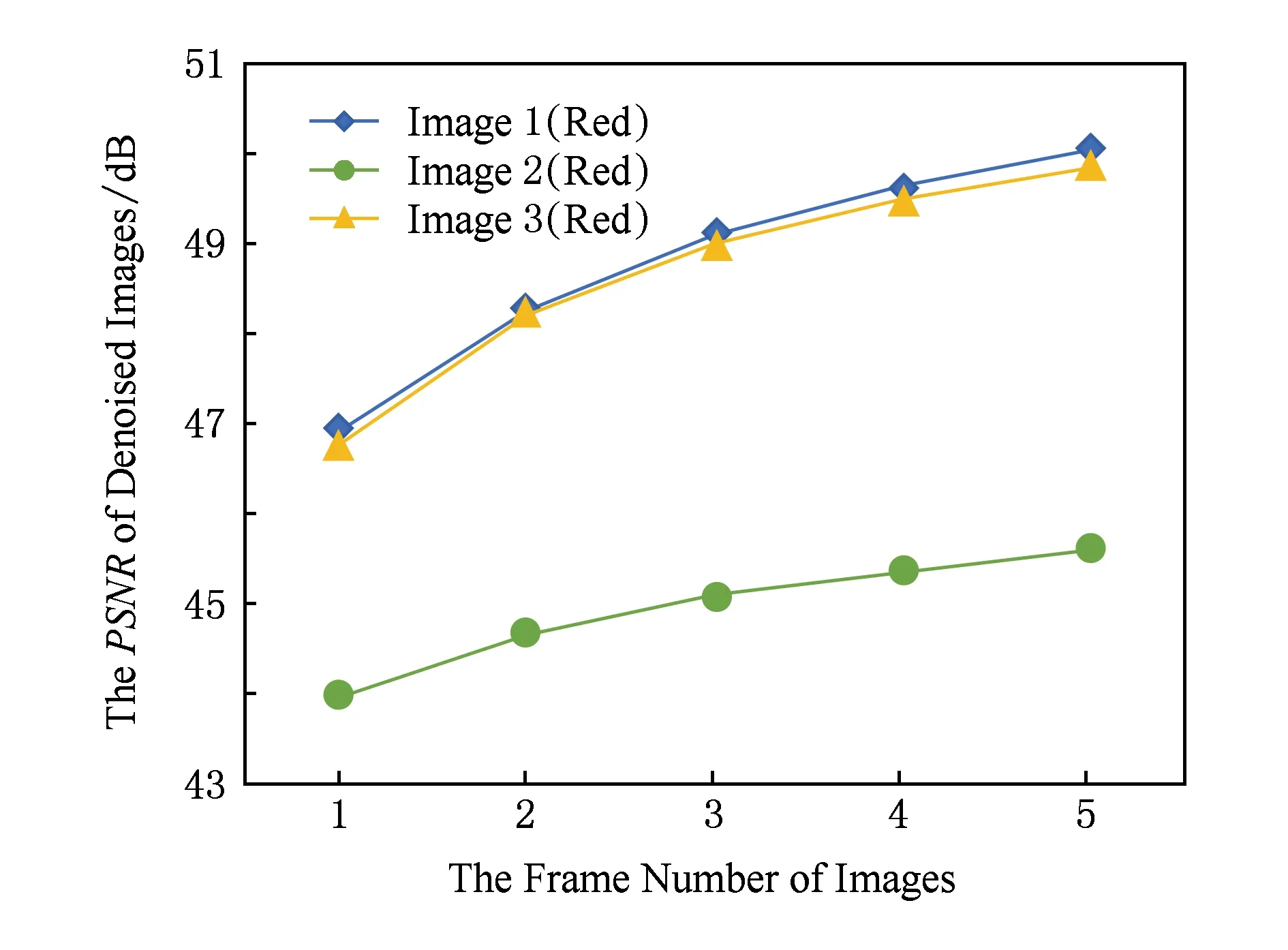
Fig. 8 The comparison on PSNR with different frame number of images图8 去噪效果PSNR与图像帧数关系对比图
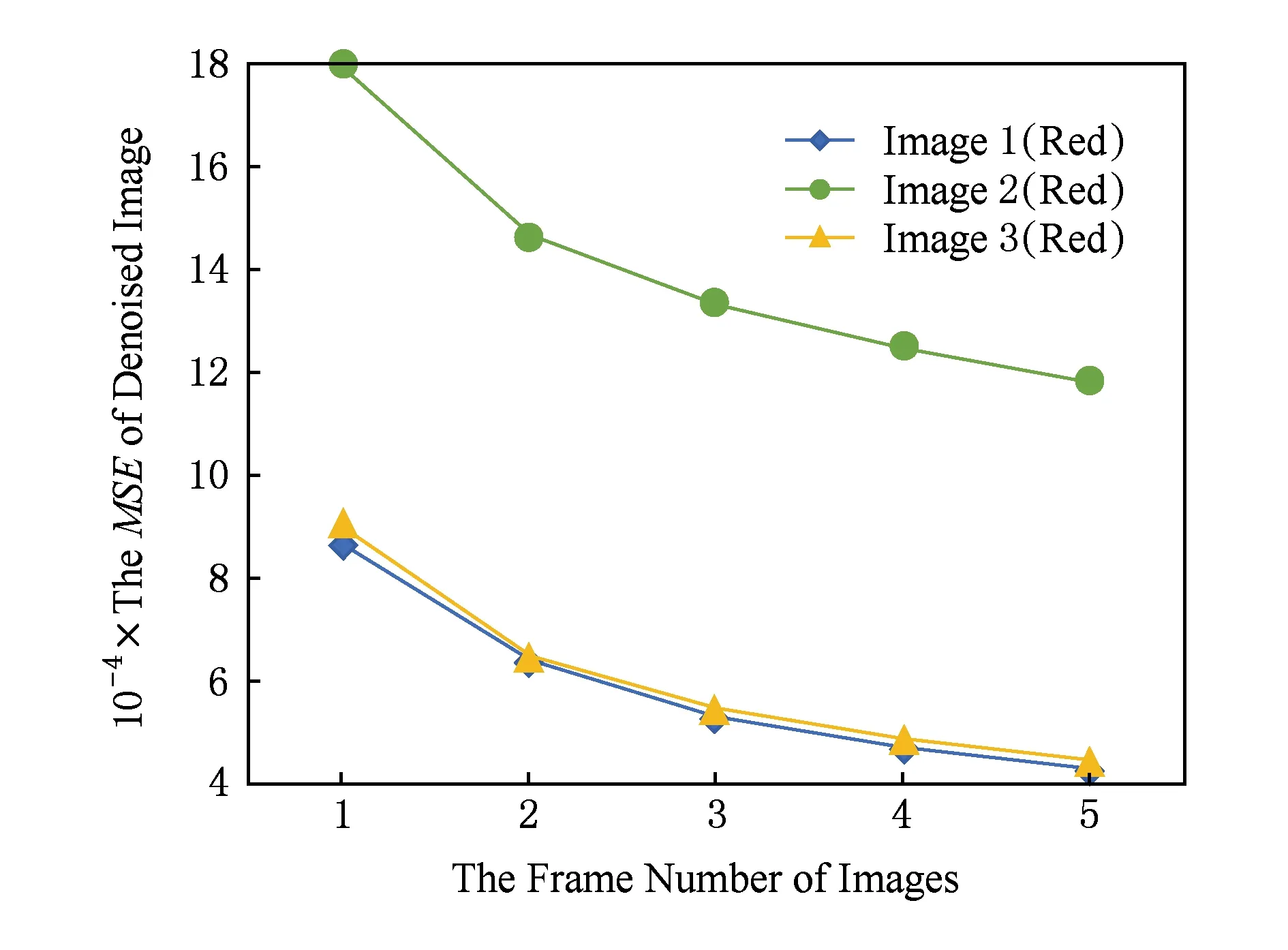
Fig. 9 The comparison on MSE with different frame number of images图9 去噪效果MSE与图像帧数关系对比图
5 结束语
随着云计算技术的进一步成熟,遥感图像外包处理的安全性已成为学术界和工业界的关注焦点.本文提出了一种多帧遥感图像安全外包融合去噪框架,采用双密文技术,实现对加密后的遥感图像进行基于动态滤波参数的融合去噪处理.实验结果表明,该安全外包方案可以有效地保证遥感图像的安全性,融合去噪效果明显优于已有的密文去噪方案和单帧密文去噪方案,对不同图像的不同大小的噪声均有很好的去噪效果,且随着多帧遥感图像帧数的增加,去噪效果明显变好.下一步的工作是在实际的云平台环境下实现遥感图像的安全外包去噪,并进一步利用同一地点不同时相的遥感图像进行融合去噪.
[1] He Guojin, Wang Lizhe, Ma Yan, et al. Processing of earth observation big data: Challenges and countermeasures[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2015, 60(5/6): 470-478 (in Chinese)
(何国金, 王力哲, 马艳, 等. 对地观测大数据处理: 挑战与思考[J]. 科学通报, 2015, 60(5/6): 470-478)
[2] Huang Dongmei, Geng Xia, Wei Lifei, et al. A secure query scheme on encrypted remote sensing images based on Henon mapping[J]. Journal of Software, 2016, 27(7):1729-1740 (in Chinese)
(黄冬梅, 耿霞, 魏立斐, 等. 基于Henon映射的加密遥感图像的安全检索方案[J]. 软件学报, 2016, 27(7): 1729-1740)
[3] Zhang Jiyao, Zhang Xie, Liu Xiao, et al. Investigation on adaptive denoising of remote sensing image[J]. Journal of Atmospheric and Environmental Optics, 2011, 6(5): 368-376 (in Chinese)
(张继尧, 张渫, 刘晓, 等. 遥感图像自适应去噪方法研究[J]. 大气与环境光学学报, 2011, 6(5): 368-376)
[4] Xia Qin, Xing Shuai, Ma Dongyang, et al. An improved K-SVD-based denoising method for remote sensing images[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2016, 20(3): 441-449 (in Chinese)
(夏琴, 邢帅, 马东洋, 等. 遥感卫星影像K-SVD稀疏表示去噪[J]. 遥感学报, 2016, 20(3): 441-449)
[5] Zhou Xiaojun, Tan Wei, Zhang Liao, et al. The research of remote sensing image denoising methods[J]. Industrial Instrumentation & Automation, 2015 (3): 69-72 (in Chinese)
(周小军, 谭薇, 张燎, 等. 遥感图像常用去噪方法[J]. 工业仪表与自动化装置, 2015 (3): 69-72)
[6] Buades A, Coll B, Morel J M. A review of image denoising algorithms, with a new one[J]. Multiscale Modeling & Simulation, 2005, 4(2): 490-530
[7] Perona P, Malik J. Scale-space and edge detection using anisotropic diffusion[J]. IEEE Trans on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 1990, 12(7): 629-639
[8] Lee S H, Seo J K. Noise removal with Gauss curvature-driven diffusion[J]. IEEE Trans on Image Processing, 2005, 14(7): 904-909
[9] Luisier F, Blu T. SURE-LET multichannel image denoising: Interscale orthonormal wavelet thresholding[J]. IEEE Trans on Image Processing, 2008, 17(4): 482-492
[10] Dou Nuo, Zhao Ruizhen, Cen Yigang, et al. Noisy image super-resolution reconstruction based on sparse representa-tion[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2015, 52(4): 943-951 (in Chinese)
(窦诺, 赵瑞珍, 岑翼刚, 等. 基于稀疏表示的含噪图像超分辨重建方法[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2015, 52(4): 943-951)
[11] Tico M, Vehvilainen M. Robust image fusion for image stabilization[C] //Proc of the 32nd IEEE Int Conf on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2007: 565-568
[12] Buades T, Lou Y, Morel J M, et al. A note on multi-image denoising[C] //Proc of the 2nd Int Workshop on Local and Non-Local Approximation in Image Processing. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2009: 1-15
[13] Yang Jingyu, Gan Ziqiao, Wu Zhaoyang, et al. Estimation of signal-dependent noise level function in transform domain via a sparse recovery model[J]. IEEE Trans on Image Processing, 2015, 24(5): 1561-1572
[14] Wang Na. Multi-image denoising using nonlocal information[D].Xi’an: Xidian University, 2014 (in Chinese)
(王娜. 多图非局部去噪算法研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2014)
[15] Wu Jiyi, Shen Qianli, Zhang Jianlin, et al. Cloud computing: Cloud security to trusted cloud[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2011, 48(1): 229-233 (in Chinese)
(吴吉义, 沈千里, 章剑林, 等. 云计算: 从云安全到可信云[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2011, 48(1): 229-233)
[16] Wang Kaixuan, Li Yuxi, Zhou Fucai, et al. Multi-keyword fuzzy search over encrypted data[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2017, 54(2): 348-360 (in Chinese)
(王恺璇, 李宇溪, 周福才, 等. 面向多关键字的模糊密文搜索方法[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2017, 54(2): 348-360)
[17] Zhou Jun, Cao Zhenfu, Dong Xiaolei. PPOPM: More efficient privacy preserving outsourced pattern matching[C] //Proc of the 21st European Symp on Research in Computer Security. Berlin: Springer, 2016: 135-153
[18] Li Dongmei, Dong Xiaolei, Cao Zhenfu. Secure and privacy-preserving pattern matching in outsourced computing[J]. Security and Communication Networks, 2016, 9(16): 3444-3451
[19] Zhang Xinpeng. Lossy compression and iterative reconstruction for encrypted image[J]. IEEE Trans on Information Forensics and Security, 2011, 6(1): 53-58
[20] Zhang Xinpeng, Long Jing, Wang Zichi, et al. Lossless and reversible data hiding in encrypted images with public-key cryptography[J]. IEEE Trans on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2016, 26(9): 1622-1631
[21] Seitkulov Y N. New methods of secure outsourcing of scientific computations[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2013, 65(1): 469-482
[22] Hu Xing, Tang Chunming. Secure outsourced computation of the characteristic polynomial and eigenvalues of matrix[J]. Journal of Cloud Computing, 2015, 4(1): 1-6
[23] Hong Yuan, Vaidya J. An inference-proof approach to privacy-preserving horizontally partitioned linear programs[J]. Optimization Letters, 2014, 8(1): 267-277
[24] Ferdush J, Mehzabin T, Hashem M M A. Securely outsourcing of large scale linear fractional programming problem to public cloud[C] //Proc of the 5th Int Conf on Informatics, Electronics and Vision. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE, 2016: 373-378
[25] Hu Xianjun, Zhang Weiming, Li Ke, et al. Secure nonlocal denoising in outsourced images[J]. ACM Trans on Multimedia Computing, Communications, and Applications, 2016, 12(3): 40-63
[26] Cao Zhenfu, Dong Xiaolei, Zhou Jun, et al. Research advances on big data security and privacy preserving[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2016, 53(10): 2137-2151 (in Chinese)
(曹珍富, 董晓蕾, 周俊, 等. 大数据安全与隐私保护研究进展[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2016, 53(10): 2137-2151)
[27] Paillier P. Public-key cryptosystems based on composite degree residuosity classes[C] //Proc of the 18th Int Conf on the Theory and Applications of Cryptographic Techniques. Berlin: Springer, 1999: 223-238
[28] Bai Jian, Yang Yatao, Li Zichen. The homomorphism and efficiency analysis of Paillier cryptosystem[J]. Journal of Beijing Elrctronic Science and Technology Institute, 2012,20(4):1-5 (in Chinese)
(白健, 杨亚涛, 李子臣. Paillier公钥密码体制同态特性及效率分析[J]. 北京电子科技学院学报, 2012, 20(4): 1-5)
[29] Johnson W B, Lindenstrauss J. Extensions of Lipschitz mappings into a Hilbert space[J]. Contemporary Mathematics, 1984, 26(1): 189-206
[30] Indyk P, Motwani R. Approximate nearest neighbors: Towards removing the curse of dimensionality[C] //Proc of the 30th Annual ACM Symp on Theory of Computing. New York: ACM, 1998: 604-613
[31] Gennaro R, Gentry C, Parno B. Non-interactive verifiable computing: Outsourcing computation to untrusted workers[C] //Proc of Annual Cryptology Conf. Berlin: Springer, 2010: 465-482
[32] Deng R H, Ding Xuhua, Wu Yongdong, et al. Efficient block-based transparent encryption for H.264/SVC bitstreams[J]. Multimedia Systems, 2014, 20(2): 165-178
[33] Liu Xiaoming, Tian Yu, He Hui, et al. Improved non-local means algorithm for image denoising[J]. Computer Engineering, 2012, 38(4): 199-201 (in Chinese)
(刘晓明, 田雨, 何徽, 等. 一种改进的非局部均值图像去噪算法[J]. 计算机工程, 2012, 38(4): 199-201)
ASecureOutsourcedFusionDenoisingSchemeinMultipleEncryptedRemoteSensingImages
Huang Dongmei1, Dai Liang1, Wei Lifei1, Wei Quanmiao2, and Wu Guojian1
1(CollegeofInformation,ShanghaiOceanUniversity,Shanghai201306)2(EastChinaSeaBranch,StateOceanicAdministration,Shanghai200136)
Remote sensing image denoising is a hot research topic in the field of image processing. The improvement of remote sensing image acquisition equipment and technology has made it possible to collect multiple images from the same scene in a short period of time. However, the processing huge number of the remote sensing images on the ordinary computers has caused the low processing capability and poor concurrency. It is a trend to store and compute the big data outsourced to the cloud. To protect the security of outsourced remote sensing images, the article presents a secure outsourced fusion denoising scheme in multiple encrypted remote sensing images to implement the fusion denoising based on dynamic filtering parameters. In the schemes, the ciphertext from Johnson-Lindenstrauss transform is used to weight calculatation as well as the plaintext and the ciphertext from Paillier homomorphic encryption is used to fusion denoise by the linear calculation of ciphertext. The experiments use several 512×512 pixels remote sensing images based on the Spark alone-server environment to simulate the cloud platform. The experimental results show that the outsourcing schemes can effectively ensure the security of the remote sensing images and get better denoising quality with different sizes of noise than the existing schemes.
multiple images; remote sensing; secure outsourcing; fusion denoising; Paillier homomorphic encryption; Johnson-Lindenstrauss transform
TP309

HuangDongmei, born in 1964. Professor, PhD supervisor. Senior member of CCF. Her main research interests include big data, remote sensing and decision support system.

DaiLiang, born in 1993. Master candidate. Student member of CCF. His main research interests include remote sensing and information security (dailiang 19931020@163.com).

WeiLifei, born in 1982. PhD. Member of CCF. His main research interests include information security and cryptography.

WeiQuanmiao, born in 1964. Deputy director of the East China Sea Branch of State Oceanic Administration. His main research interests include database and ocean assistant decision-making system (qmwei@eastsea.gov.cn).

WuGuojian, born in 1993. Master candidate. Student member of CCF. His main research interests include remote sensing and information security (wuguojian 19930913@163.com).

