黑种草子提取物调节血管内皮细胞功能及血管新生作用
王红蕊,闫 蓉,高 俐,李正涛,杨 淬,,杜冠华
(1.云南民族大学民族医药学院,民族药资源化学国家民委教育部重点实验室,云南 昆明 650500;2. 中国医学科学院药物研究所,药物靶点研究与新药筛选北京市重点实验室,北京 100050)
黑种草子提取物调节血管内皮细胞功能及血管新生作用
王红蕊1,闫 蓉2,高 俐1,李正涛1,杨 淬1,2,杜冠华2
(1.云南民族大学民族医药学院,民族药资源化学国家民委教育部重点实验室,云南 昆明 650500;2. 中国医学科学院药物研究所,药物靶点研究与新药筛选北京市重点实验室,北京 100050)
目的研究民族药黑种草子提取物调节血管内皮细胞功能和血管新生的作用及其机制。方法将不同浓度的黑种草子提取物作用于原代培养的大鼠胸主动脉内皮细胞(rat aortic endothelial cells, RAECs),观察其对RAECs体外成管、增殖和迁移的作用,同时以Western blot法检测RAECs中TGF-β1、Smad3、PDGFR、Cx43的表达水平,以及Akt和内皮型一氧化氮合成酶(endothelial nitric oxide synthase, eNOS)蛋白磷酸化水平,并检测RAECs产生一氧化氮(nitric oxide, NO)的情况。结果黑种草子提取物可浓度依赖性地促进RAECs的体外成管、增殖和迁移,明显上调RAECs中TGF-β1、Smad3、PDGFR以及Cx43蛋白的表达,促进Akt和eNOS的磷酸化水平,并可明显促进RAECs中 NO的生成。结论民族药黑种草子提取物可能通过激活Akt-eNOS通路,改善血管内皮细胞功能,通过激活TGF-β1-Smad3通路促进体外血管新生,并可提高PDGFR和Cx43蛋白的表达,从而促进新生血管的成熟与稳定。民族药黑种草子可能成为缺血性疾病的新型治疗药物。
民族药;黑种草子;血管新生;内皮细胞;缺血性疾病;内皮功能
血管新生是血管中的内皮细胞以出芽的模式形成新血管的过程[1]。血管新生是一个多因素参与的复杂病理生理过程,在机体的多种病理过程(如创伤愈合、胚胎发育、慢性炎症、缺血性疾病、恶性肿瘤、动脉粥样硬化等),特别是在组织修复和再生的过程中发挥着重要作用[2-3]。血管生成过程涉及多种复杂的至关重要的细胞行为,如内皮细胞的增殖和迁移,细胞外基质的降解蛋白质等[4]。寻找具有调节血管新生作用的药物[5],对于多种疾病的预防和治疗具有重要意义。
黑种草子(SemenNigellae)为毛茛科植物腺毛黑种草(NigellalanduliferaFrevnetSint.)的干燥成熟种子,广泛生长在地中海南部、中东、东欧和亚洲西部地区。在我国主要产于新疆及云南傣族聚居区。它可以在食物中当作香料使用,同时也被作为药物在许多国家使用,主要用于哮喘、咳嗽、支气管炎、头痛、风湿等疾病的治疗。近年来研究表明,黑种草子含有的化学成分包括生物碱、黄酮类、酚类、皂苷类以及挥发油、蛋白质、油脂类化合物[6],其提取物的药理作用主要表现为抗菌、抗肿瘤、抗氧化、抗血小板聚集、降脂、降糖、保肝等多种活性。但黑种草子调节血管新生的功能和机制尚未见报道。本文采用体外培养内皮细胞,研究了黑种草子提取物调节血管新生的作用及机制。
1 材料
1.1动物SD大鼠,♂,体质量(180±20)g,约16周龄,购自云南省昆明医科大学。
1.2药物与试剂干燥黑种草子,购自云南昆明市场;无水乙醇购自拓源生物有限公司;RPMI 1640培养基(批号:SH30809.01)购自Hyclone;优级胎牛血清(批号:FSP500)购自S.America;EDTA-胰蛋白酶消化液(批号:CB000-C022)购自ExCell Bio;青-链霉素(批号:SL6040)购自Solarbio;组织蛋白抽提试剂盒(批号:CW0891M)、HRP标记山羊抗大鼠IgG(H+L)(批号:CW0104)、HRP标记山羊抗兔 IgG(H+L)(批号:CW0103S)、ECL化学发光显色剂(批号:CW0049M),均购自北京康为世纪生物科技有限公司; Anti-eNOS 抗体(批号:TA314271)、Anti-p-eNOS(Ser-1177)抗体(批号:TA333266),购自OriGene; Anti-TGF-β1抗体(批号:ab125310)、Anti-Akt抗体(批号:C67E7)、Anti-p-Akt(Ser-473)抗体(批号:AA329-1),均购自Abcam;Anti-Smad3(批号:#9523)、Anti-Cx43(批号:TA311737)、Anti-PDGFR(批号:#3169)抗体,均购自Cell Signaling公司;Matrigel(批号:356234)购自美国BD公司;台盼蓝(批号:T8070)购自索莱宝;NO试剂盒(批号:A012)购自南京建成生物工程研究所。
1.3仪器旋转蒸发仪(N-1100S,Ankeyq),高速离心机(5417R, Eppendrof),超声波清洗器(AS10200A,天津奥特赛恩斯),CO2培养箱(3517-2, SHELLAB),蛋白印迹体系(Bio-Rad),化学发光成像仪(ChemiDOCXS+,Bio-Rad),E-Plate L8 细胞培养板(ACEA),xCELLigence RTCA S16细胞分析仪(ACEA),酶标仪(MultiskanGo,Thermo),HW-1000超级恒温水浴(成都泰盟科技有限公司)。
2 方法
2.1黑种草子提取物的制备称取200 g黑种草子于2 000 mL圆底烧瓶中,加入 60%的乙醇1 200 mL,浸泡4~6 h后,约80℃加热回流提取4 h,滤出提取液,反复3~5次,合并回收溶剂,冷却后,超声震荡5~10 min,室温12 000 r·min-1离心20 min后,过滤得到滤液,用旋转蒸发仪浓缩,制得浸膏,备用。
2.2原代培养大鼠胸主动脉内皮细胞(rataorticendothelialcells,RAECs) 用10%的水合氯醛(3 mL·kg-1)腹腔注射SD大鼠,待麻醉后,在无菌条件下开胸取胸主动脉,将大鼠胸主动脉上的脂肪、结缔组织剔除干净,随后用剪刀剪成若干片,每片约3 mm×3 mm的大小,内皮面向下轻轻贴入25 cm培养瓶中。培养瓶置于37℃、5% CO2培养箱中培养2~4 h后,再向培养瓶中缓慢加入含10%胎牛血清(fetal bovine serum, FBS)、1%青-链霉素(penicillin-streptomycin, PS)的RPMI 1640培养基,待细胞长满后,用0.25%胰酶消化后传代用于实验。
2.3内皮细胞体外成管取 4℃冰箱过夜保存的基质(Matrigel),以每孔50 μL铺到96孔板中,于 37℃、5% CO2培养箱放置30 min使其凝固。加入100 μL血管内皮细胞悬液(4×107·L-1),然后加入药物,使其终浓度为500、100、20 mg·L-1,混匀,于37℃、5% CO2培养箱中培养,显微镜下观察微管形成情况。每孔选择上、下、左、右及中间共5个不同部位,计算微管形成数量,并进行统计学分析。
2.4细胞增殖向E-Plate L8细胞培养板中每孔加入50 μL培养基,放入细胞分子仪检测台上(置于培养箱中)开始检测基线。 然后, 收集对数期细胞并调制细胞浓度,将细胞悬液加入E-Plate检测板中,每孔50 μL约为104个细胞。将E-Plate L8细胞培养板置于超净台内,室温放置30 min后放到检测台上,进行实时动态的细胞增殖检测。等细胞完全贴壁后,再向E-Plate检测板中分别加入等体积的含有不同浓度黑种草子提取物的培养基,继续进行实时动态的细胞增殖检测。

Fig 1 Effects of Semen Nigellae. extract on the tube formation(±s, n=3)
A:Tube formations were detected. VEGF(10 μg·L-1) was used as the positive control;B: The area covered by the tube formation network was quantified.*P<0.05vscontrol group;C:Proliferation of RAECs in the presence or absence of the extract ofSemenNigellae.

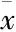
A:The migration of RAECs was determined by using a Transwell system. VEGF(10 μg·L-1) was used as the positive control;B:Numbers of the migrating RAECs.*P<0.05vscontrol group
2.5Transwell实验Transwell板中加入无血清的RPMI 1640培养基,于培养箱中平衡1 h,上室加入100 μL含有不同浓度的黑种草子提取物的无血清RPMI 1640培养基RAECs细胞悬液,下室加入含有0.6 mL 10% FBS、1%青链霉素的RPMI 1640培养基刺激迁移,置于5% CO2培养箱中37℃培养24 h,然后弃去培养液,用90%乙醇固定30 min,0.4%台盼蓝常温染色10 min后,显微镜下观察拍照。计算迁移细胞数量,并进行统计学分析。
2.6免疫蛋白印迹实验(Westernblot) 按照RIPA蛋白质抽提试剂盒提取细胞总蛋白,以上样缓冲液与蛋白样品4 ∶1的比例稀释混合后,120℃加热3 min,离心后上样,电泳后,200 V、400 mA转膜2.5 h,经封闭和洗膜后,加入用TBST稀释的一抗,4℃摇晃孵育过夜。再用TBST溶液洗膜3次,每次10 min,加入辣根过氧化物酶结合的二抗,常温摇晃孵育结合2~4 h后,在化学发光成像仪下显色。
2.7NO的测定按照NO测定试剂盒使用方法,测定各组样品的吸光度。根据下式计算NO含量:NO含量/μmol·L-1=(测定OD值-空白OD值)/(标准OD值-空白OD值) ×标准品浓度(100 μmol·L-1)×样品测试前稀释倍数。

Fig 3 Extract of Semen Nigellae. enhenced Akt and eNOScontents and levels of their phosphorylation(±s,n=3)
A,C:RAECs were incubated with the extractofSemenNigellae(500, 100, 20 mg·L-1) for 15 min. VEGF(10 μg·L-1) was used as the positive control. Levels of phosphorylated and total Akt and eNOS;B: Average densitometric quantification showed the ratio of phosphorylated Akt to total Akt protein levels;D: Average densitometric quantification showed the ratio of phosphorylated eNOS to total eNOS protein levels.*P<0.05vscontrol group

Fig 4 Extract of Semen Nigellae increased levels oftotal TGF-β1 and Smad3(±s,n=3)
A,C:RAECs were pretreated with the extract ofSemenNigellae(20, 100, 500 mg·L-1) for 24 h. VEGF(10 μg·L-1) was used as the positive control. The levels of total TGF-β1 and Smad3;B,D:Average densitometric quantification of TGF-β1 and Smad3 proteins levels in different concentrations. β-actin served as a loading control.*P<0.05vscontrol group
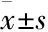
3 结果
3.1黑种草子提取物促体外成管和增殖作用不同浓度的黑种草子提取物作用于RAECs 3.5 h后,可浓度依赖性地促进RAECs体外成管;同样,也可促进RAECs的增殖(Fig 1)。
3.2黑种草子提取物对细胞迁移的影响不同浓度的黑种草子提取物作用于RAECs后,经台盼蓝染色10 min后,显微镜下拍照并计数。Fig 2结果显示,黑种草子提取物能够明显促进内皮细胞的迁移。

Fig 5 Extract of Semen Nigellae increased levels oftotal PDGFR and Cx43(±s,n=3)
A, C:RAECs were pretreated with the extract ofSemenNigellae(20, 100, 500 mg·L-1) for 24 h. VEGF(10 μg·L-1) was used as the positive control. The levels of total PDGFR and Cx43;B, D:Average densitometric quantification of PDGFR and Cx43 protein levels in different concentrations. β-actin served as a loading control.*P<0.05vscontrol group
3.3黑种草子提取物对细胞TGF-β1、Smad3、PDGFR、Cx43以及磷酸化Akt和eNOS表达的影响提取内皮细胞总蛋白后,Western blot法检测RAECs中TGF-β1、Smad3、PDGFR、Cx43蛋白表达水平,以及 Akt和内皮型一氧化氮合成酶(endothelial nitric oxide synthase,eNOS)磷酸化水平。Fig 3、4、5结果显示,黑种草子提取物可明显上调RAECs中TGF-β1、Smad3、PDGFR、Cx43蛋白的表达,并可明显促进Akt和eNOS的磷酸化水平。
3.4黑种草子提取物对NO生成的影响按照NO测定试剂盒说明书,测定各组样品的吸光度,根据公式计算NO的含量。结果显示,黑种草子提取物可明显促进RAECs中 NO的生成(Fig 6)。

Fig 6 Effect of extract of Semen Nigellae onproduction of NO from RAECs(±s,n=3)
VEGF(10 μg·L-1) was used as the positive control.*P<0.05vscontrol group
4 讨论
心脑血管疾病是当前严重威胁人类生命健康的“第一杀手”。 肢体缺血性损伤、缺血性心肌梗死等缺血性疾病,已成为心脑血管疾病中一组严重危害人类生存质量的临床病症[7-8]。临床现阶段通过常规手术和药物治疗后[9],这一类缺血性疾病急性期的死亡率已有所下降,但是其所带来的如出血倾向、加重心衰等一系列药物副作用又给患者带来极大的困扰。近年来,随着治疗性血管新生观念的提出,促进血管新生已成为治疗缺血性疾病的研究热点[10]。血管新生对于肿瘤形成和转移、心血管以及免疫等系统疾病的防治极为重要,并存在复杂的分子调控机制。
黑种草子为我国传统民族药,具有多种保健及治疗功能。前期研究证明,黑种草子含有多种可能调节血管新生的活性化学成分。为了对黑种草子调控血管新生的作用进行探讨,本实验通过在体外原代培养RAECs,观察黑种草子提取物对RAECs形态结构、增殖及体外成管等的影响。同时,检测黑种草子提取物对血管新生相关病理生理过程涉及的分子通路的影响。
实验结果显示,黑种草子提取物可能通过激活内皮细胞内Akt-eNOS通路,改善血管内皮细胞功能,并可能激活TGF-β1-Smad3通路,促进体外血管新生,同时通过提高PDGFR和Cx43蛋白的表达,促进新生血管的成熟与稳定。民族药黑种草子可能成为缺血性疾病潜在的新型治疗药物,存在潜在的开发价值。
[1] 郭 浩,李 磊,侯金才,等. 中药促治疗性血管新生防治缺血性心脑血管疾病的研究进展[J].中国中药杂志,2015,40(1):24-8.
[1] Guo H,Li L,Hou J C,et al.Advance in prevention and treatment of ischemia cardio-cerebrovascular disease through increased therapeutic angiogenesis induced by traditional Chinese medicine[J].ChinJChinMatMed,2015,40(1):24-8.
[2] 尹玉洁,马柳一,位 庚,等. 桂芍通络对兔动脉粥样硬化早期外膜滋养血管新生及氧化应激水平的干预作用[J].中国药理学通报,2016,32(3):416-22.
[2] Yin Y J,Ma L Y,Wei G,et al.Influence of Guishaotongluo on angiogenesis of adventitial vasa vasorum and oxidative stress in early stage of atherosclerosis[J].ChinPharmacolBull,2016,32(3):416-22.
[3] 刘 暖,杨 雷,毛秉豫,等. 蛋白激酶D1在大鼠骨髓源性内皮祖细胞中的促血管新生作用[J].中国药理学通报,2015,31(9):1259-64.
[3] Liu N,Yang L,Mao B Y,et al.Angiogenesis of protein kinase D1 in bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells of rats[J].ChinPharmacolBull,2015,31(9):1259-64.
[4] 余曾洋,龚陈媛,张国庆,等. 氧诱导新生小鼠视网膜病变中血管新生和氧应激相关基因表达的变化[J]. 中国药理学通报,2014,30(10):1397-401.
[4] Yu Z Y,Gong C Y,Zhang G Q,et al.Altered expression of genes related with angiogenesis and oxidative stress during the development of oxygen-induced retinopathy in newborn mice[J].ChinPharmacolBull,2014,30(10):1397-401.
[5] 崔国祯,徐燕玲,孙安露,等. 丹参素衍生物对斑马鱼促血管新生作用的研究[J].中国药理学通报,2016,32(6):795-800.
[5] Cui G Z,Xu Y L,Sun A L,et al.Effect of Danshensu derivative on angiogenesis in zebrafish[J].ChinPharmacolBull,2016,32(6):795-800.
[6] 李雅丽,王增尚,刘 博,等. 黑种草子化学成分和药理研究进展[J].中国药学杂志,2016,51(14):1157-61.
[6] Li Y L,Wang Z S,Liu B,et al.Advance in research on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Nigella Seeds[J].ChinPharmJ,2016,51(14):1157-61.
[7] 林 超,刘兆国,钱 星,等. 自噬在心血管疾病中的作用研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2014,30(10):1347-9.
[7] Lin C,Liu Z G,Qian X,et al.Research progress on the role of autophagy in cardiovascular diseases[J].ChinPharmacolBull,2014,30(10):1347-9.
[8] 魏 英,余丽梅,王钰莹,等. 人参总皂苷促进血管新生改善急性心肌梗死大鼠心功能[J]. 中国药理学通报,2016,32(4):559-64.
[8] Wei Y,Yu L M,Wang Y Y,et al.Total ginsenosides improve cardiac function via promoting angiogenesis in a rat model of acute myocardial infarction[J].ChinPharmacolBull,2016,32(4):559-64.
[9] 郎艳松,秘红英,刘红利,等. 通心络联合阿托伐他汀、阿司匹林对家兔动脉粥样硬化早期血管外膜滋养血管新生的干预作用[J].中国药理学通报,2015,31(1):71-6.
[9] Lang Y S,Mi H Y,Liu H L,et al.Interventional effects of Tongxinluo combined with atorvastatin and aspirin(ATS) on the angiogenesis of vasa vasorum in the early stage of atherosclerosis[J].ChinPharmacolBull,2015,31(1):71-6.
[10] 郭勇英,张军芳,贾存勤,等. 通心络联合外周血间充质干细胞移植对糖尿病足大鼠血管新生HIF-1/VEGF通路及miR-210表达的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2015,31(12):1749-54.
[10] Guo Y Y,Zhang J F,Jia C Q,et al.Treatment effect of Tongxinluo combined peripheral blood derived mesenchymal stem cells transplantation on angiogenesis of HIF-1/VEGF pathway and miR-210 in diabetic foot rats[J].ChinPharmacolBull,2015,31(12):1749-54.
RegulatingeffectsofSemenNigellaeextractonvascularendothelialcellsandangiogenesis
WANG Hong-rui1, YAN Rong2, GAO Li1, LI Zheng-tao1, YANG Cui1,2,DU Guan-hua2
(1.SchoolofEthnicMedicine,KeyLabofChemistryinEthnicMedicinalResources,StateEthnicAffairsCommission&MinistryofEducation,YunnanMinzuUniversity,Kunming650500,China;2.InstituteofMateriaMedica,ChineseAcademyofMedicalSciences&PekingUnionMedicalCollege,DrugTargets&ScreeningCenter-theKeyLabofBeijing,Beijing100050,China)
AimTo investigate the effects ofSemenNigellaeextract on regulating endothelial functions and angiogenesis and the underlying mechanisms.MethodsAfter the extract ofSemenNigellaewas obtained, the extract was administered to the primarily cultured rat aortic endothelial cells(RAECs). Then, the tube formation, proliferation and migration ability of RAECs were examined, and the expression of angiogenesis-related signaling pathways proteins, such as transforming growth factor-beta1(TGF-β1), Smad3, platelet derived growth factor receptor(PDGFR), Cx43, Akt and endothelial nitric oxide synthase(eNOS),were detected via Western blot analysis. Meanwhile, production of nitric oxide(NO) from RAECs was also measured after treatment with the extract ofSemenNigellae.ResultsThe extract ofSemenNigellaesignificantly promoted the tube formation, proliferation and migration of RAECs in a dose-dependent manner. The protein expressions of TGF-β1, Smad3, PDGFR, Cx43, Akt and eNOS, as well as phosphorylation levels of Akt and eNOS, in RAECs were also markedly elevated by the administration ofSemenNigellae. In addition, the production of NO was notably enhanced by the extract ofSemenNigellae.ConclusionsThe extract ofSemenNigellaemay improve endothelial functions and angiogenesis by activating Akt-eNOS and TGF-β1-Smad3 pathway. Meanwhile, it may also promote the maturation and stability of nascent vasculatures by activating the PDGFR and Cx43-related signaling pathways. Hence,SemenNigellaemay be a new therapeutic drug for ischemic diseases.
ethnomedicines;SemenNigellae; angiogenesis; endothelial cells; ischemic diseases; endothelial function
A
1001-1978(2017)11-1611-07
R-332;R284.1;R322.12;R329.24;R364.3;R364.12;R543.022
时间:2017-10-10 10:05 网络出版地址:http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/34.1086.R.20171010.1005.052.html
10.3969/j.issn.1001-1978.2017.11.026
2017-07-14,
2017-08-12
国家自然科学基金资助项目(No 81460553);第57批博士后科学基金项目(No 2015M570976)
王红蕊(1990-),女,硕士生,研究方向:民族药活性筛选,E-mail:1060653577@qq.com; 杜冠华(1958-),男,博士,研究员,研究方向:药物活性筛选,通讯作者,E-mail: dugh@imm.ac.cn; 杨 淬(1975-),男,博士,副教授,研究方向:民族药活性筛选,通讯作者,E-mail: yangynni@163.com

