Variation of brachial artery,median nerve and axillary nerve of unilateral upper limb:a case report
HU Jun-da, XU Yan, CHEN Zeng-gan△
(1Department of Orthopeadics,Zhongshan Hospital,Fudan University,Shanghai 200032,China;2Department of Neurology,Huashan Hospital,Fudan University,Shanghai 200040,China)
Variation of brachial artery,median nerve and axillary nerve of unilateral upper limb:a case report
HU Jun-da1, XU Yan2, CHEN Zeng-gan1△
(1DepartmentofOrthopeadics,ZhongshanHospital,FudanUniversity,Shanghai200032,China;2DepartmentofNeurology,HuashanHospital,FudanUniversity,Shanghai200040,China)
The anatomical variation of the blood vessels and brachial plexus of the upper limb is very complicated.In general population,the brachial artery divides into the radial artery and ulnar artery in cubital fossa.The median nerve consists of lateral and medial roots,and the axillary nerve divides into anterior and posterior branches after passing through the quadrangular space.Although variations in the vascular or neural pattern of the upper limb in humans are fairly common,it is very rare to see complex neurovascular variations in one limb.The present study reports complicated variation of unilateral upper limb,which aims at emphasizing the rare formation of brachial plexus and vessel.
Clinical data When dissecting the upper limb of an embalmed adult cadaver (70 years old,male,Chinese) routinely,we observed the anatomical variations of brachial artery,median nerve and axillary nerve on the left side.We dissected and compared the upper limb on both sides.
Obvious variation was noted in the bifurcation of the left brachial artery in this case (Fig 1).The brachial artery was a continuation of the axillary artery and medial to the median nerve,when it walked into sulcus bicipitalis medialis.However,it divided into the radial artery and the ulnar artery at 15 cm proximal to cubital fossa.Diameter of the radial artery was 4.4 mm,and that of the ulnar artery was 4.7 mm.
In addition,we observed anomalies in the formation of the median nerve and the axillary nerve (Fig 2).The median nerve was sited lateral to the third part of the axillary artery,then passed into the arm anterior to the brachial artery.It consisted of three roots,one of which was given off from the medial cord and the other two from the lateral cord.The diameter of the medial root was 2.4 mm,and that of the lateral two roots were 2.5 mm and 2.4 mm from top to bottom respectively.
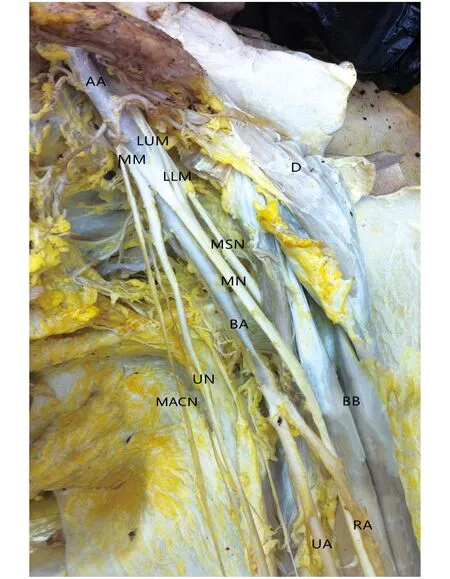
D:Deltoid muscle;AA:Axillary artery; MM:Medial root of the median nerve;LUM:Lateral upper root of the median nerve;LLM:Lateral lower root of the median nerve; MSN:Musculocutaneous nerve;MN:Median nerve;UN:Ulnar nerve; MACN:Medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve;BB:Biceps brachii;BA:Brachial artery;RA:Radial artery;UA:Ulnar artery.
Fig 1 The brachial artery was divided into the radial artery and the ulnar artery at high bifurcation
In the present case,the axillary nerve was observed to be divided into two branches before entering the quadrilateral foramen (Fig 2).Diameter of the anterior branch was 3.0 mm,and that of the posterior branch was 3.2 mm.No variations were noted in the formation and distribution of the right limb.

D:Deltoid muscle; AA:Axillary artery; MM:Medial root of the median nerve; LUM:Lateral upper root of the median nerve; LLM:Lateral lower root of the median nerve; MSN:Musculocutaneous nerve; MN:Median nerve; UN:Ulnar nerve; MACN:Medial antebrachial cutaneous nerve; BB:Biceps brachii; AAN:Anterior branch of axillary nerve; PAN:Posterior branch of axillary nerve; BA:Brachial artery.
Fig 2 Variation of median nerve and axillary nerve
Discussion The neural pattern of the brachial plexus was complex from its origin to its supply of the muscles and skin,which is the basis to make clear the normal nerves innervation and the muscle function.It also facilitates the localization diagnosis of the symptoms and signs resulting from a damage to the brachial plexus by clinicians.The neural and vascular pattern of the upper limb witnessed different variations.The knowledge on these variations is helpful to reduce trauma of surgery in this region.
Under normal circumstances,the brachial artery divides into the radial artery and ulnar artery near cubital fossa.Variations in the radial artery can occur in various types,among which high bifurcation of the brachial artery was reported to be one of the most common type,accounting for 20% of all the cases[1].In addition,Chakravarthi,etal[2]dissected 140 upper limb specimens of 70 cadavers and reported anatomical variations of the accessory brachial artery and its morphology,embryogenesis and clinical implications.Fu,etal[3]also reported one case of high bifurcation of brachial artery in Chinese.However,a low origin of the radial artery was found by Wysiadecki,etal[4].In this report,the brachial artery divided into the radial artery and the ulnar artery at 15 cm proximal to cubital fossa.
The median nerve is the union of lateral and medial roots originating from the lateral and medial cords of the brachial plexus respectively.In the present study,the median nerve was found consisting of three foots.Budhiraja,etal[5]and Bala,etal[6]also reported an additional root in the formation of the median nerve.In addition,Xia,etal[7]reported the variation of the median nerve and muscle cutaneous nerve in 2010.
The axillary nerve is one of the terminal branch of the posterior cord.It usually divides into anterior and posterior branches after turning backward and passing through the quadrangular space.The anterior terminal branch,which winds around the surgical neck of the humerus beneath the deltoid muscle,supplies the deltoid and the skin that covers its lower part.The posterior terminal branch gives off a branch to the teres minor muscle and a few branches to the deltoid.Many studies have described variations in the origin of the axillary nerve,such as direct branch of the upper trunk[8].
Although there are various forms of anatomical variation in the upper limb,it is rare to find so many variations in one limb.The variations in the formation,location,and course of the brachial plexus and blood vessels of the upper limb may be ascribed to an abnormal embryological development.Surgeons should be familiar with normal anatomy and acquire possible variations,in order to plan safe surgical procedures and avoid inadvertent damage.
brachial artery; median nerve; axillary nerve; complex variation
[1] PANAGOULI E,ANAGNOSTOPOULOU S,VENIERATOS D.Bilateral asymmetry of the highly bifurcated brachial artery variation[J].RomJMorpholEmbryol,2014,55(2):469-472.
[2] CHAKRAVARTHI KK,KS S,VENUMADHAV N,etal.Anatomical variations of brachial artery- its morphology,embryogenesis and clinical implications[J].JClinDiagnRes,2014,8(12):C17-C20.
[3] 付秀利,吴德昌,陈雪松,等.肱动脉高位分支1例[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,1997,15(2):107.
[4] WYSIADECKI G,POLGUJ M,HALADAJ R,etal.Low origin of the radial artery:a case study including a review of literature and proposal of an embryological explanation[J].AnatSciInt,2017,92(2):293-298.
[5] BUDHIRAJA V,RASTOGI R,ASTHANA AK.Variations in the formation of the median nerve and its clinical correlation[J].FoliaMorphol(Warsz),2012,71(1):28-30.
[6] BALA A,SINHA P,TAMANG BK,etal.Anatomical variation:median nerve formation——a case vignette[J].JClinDiagnRes,2014,8(6):D3-D4.
[7] 夏春波,蒋常文,秦小云,等.正中神经合并肌皮神经变异1例[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2010,28(2):126.
[8] SUBASINGHE SK,GOONEWARDENE S.A rare variation of the axillary nerve formed as direct branch of the upper trunk[J].JClinDiagnRes,2016,10(8):D1-D2.
R322
B
2016-11-03;编辑:段佳)
10.3969/j.issn.1672-8467.2017.04.028
2015年中山医院人才培养计划项目(2015ZSYXGG22)
△Corresponding author E-mail:chen.zenggan@zs-hospital.sh.cn
*This work was supported by the Personnel Training Program of Zhongshan Hospital in 2015 (2015ZSYXGG22).

