舌鳞癌患者外周血Th17细胞及其细胞因子变化的临床意义*
李燕波,何志良,苏丹妮,王承阳,贺成功,曹 雷
(河北省承德市中心医院:1.口腔科;2.手术室 067000)
舌鳞癌患者外周血Th17细胞及其细胞因子变化的临床意义*
李燕波1,何志良1,苏丹妮2,王承阳1,贺成功1,曹 雷1
(河北省承德市中心医院:1.口腔科;2.手术室 067000)
目的 探讨舌鳞癌患者外周血辅助性T细胞17(Th17)及其细胞因子变化的临床意义。方法 以该院2013年1月至2016年1月收治的66例舌鳞癌患者为研究对象,同期行健康体检的42例志愿者为对照。采集所有研究对象外周血,流式细胞术检测外周血Th17细胞比例,ELISA法检测白细胞介素(IL)-17、转化生长因子-β(TGF-β)和IL-6因子水平。结果 观察组和对照组外周血Th17细胞比例、IL-17、TGF-β、IL-6分别为(1.46±0.41)%、(0.31±0.12)%,(123.36±21.20)pg/mL、(20.76±8.95)pg/mL,(215.80±21.52)pg/mL、(26.90±10.41)pg/mL,(17.32±8.02)pg/mL、(5.85±1.49)pg/mL,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。Th17细胞比例、IL-17、TGF-β和IL-6水平随着舌鳞癌临床分期的增加而升高(P<0.01)。TGF-β与IL-17水平呈正相关(r=0.626,P=0.021),IL-6水平与Th17细胞比例和IL-17均呈正相关(r=0.626、0.597,P=0.021、0.034)。结论 Th17细胞和IL-17表达的增加在舌鳞癌的发生、发展中发挥着重要作用,Th17细胞和IL-17因子可成为抗肿瘤治疗的重要靶点。
舌;癌,鳞状细胞;Th17细胞;细胞因子;临床意义
舌鳞癌是最常见的头颈部恶性肿瘤之一,其治疗手段以放化疗和手术为主,5年生存率较低。研究表明,舌鳞癌患者常合并严重的免疫缺陷,提高舌鳞癌患者机体免疫系统能力和抗肿瘤的免疫治疗成为研究的热点[1]。辅助性T细胞17(Th17)及其相关细胞因子白细胞介素(IL)-17、转化生长因子-β(TGF-β)和IL-6在炎症、肿瘤和自身免疫性疾病中发挥着重要作用。本文即研究舌鳞癌患者外周血Th17细胞及其细胞因子变化的临床意义。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 以本院2013年1月至2016年1月收治的66例舌鳞癌患者为研究对象(观察组),均经病理组织学检查,由两名病理科医师确诊,组织学类型均为口腔鳞癌。观察组患者均未接受过手术、放化疗及生物治疗,排除合并感染、风湿或自身免疫性疾病,其他恶性肿瘤或转移、严重心肝肾功能不全者。以本院同期行健康体检的42例志愿者为对照组。观察组男38例,女28例,平均年龄(52.18±8.65)岁;对照组男23例,女19例,平均年龄(51.70±8.25)岁。两组性别、年龄差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05),具有可比性。观察组临床分期依据国际抗癌协会联盟(UICC)[2]制定的标准,Ⅰ期11例,Ⅱ期16例,Ⅲ期20例,Ⅳ期19例。本研究经医院伦理委员会批准,所有患者均签署知情同意书。
1.2 仪器试剂 流式细胞仪(美国BD公司FACS Calibur),别藻蓝素(APC)标记的抗人CD3单抗、异硫氰酸荧光素(FITC)标记的抗人CD8单抗、PE标记的抗人IL-17A单抗(美国eBioscience公司),淋巴细胞分离液、固定破膜剂等(美国Sigma公司)。人IL-17、TGF-β和IL-6酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA,美国BD公司)。
1.3 方法 所有研究对象均予抽取空腹静脉血5 mL,离心取上清按ELISA试剂盒说明书检测IL-17、TGF-β和IL-6水平;提取离心血淋巴细胞层进行刺激、胞外、胞内染色,然后上机检测Th17细胞比例。

2 结 果
2.1 外周血Th17细胞比例和IL-17水平比较 观察组和对照组外周血Th17细胞比例分别为(1.46±0.41)%、(0.31±0.12)%,差异有统计学意义(t=3.314,P=0.014),见图1。Th17细胞比例随着舌鳞癌临床分期的增加而升高(P<0.01),见图2、表1。观察组和对照组外周血IL-17水平分别为(123.36±21.20)pg/mL、(20.76±8.95)pg/mL(t=4.983,P=0.006),IL-17水平随着舌鳞癌临床分期的增加而升高(P<0.01),见表1。
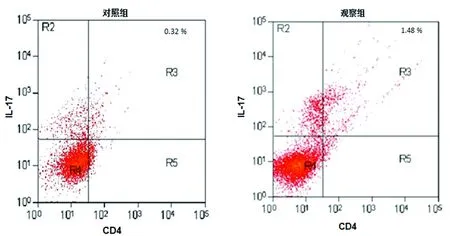
图1 观察组和对照组外周血Th17细胞比例
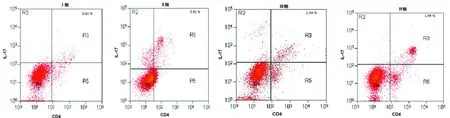
图2 不同分期舌鳞癌患者外周血Th17细胞比例

分期Th17(%)IL-17(pg/mL)TGF-β(pg/mL)IL-6(pg/mL)Ⅰ期0.62±0.2156.50±16.5262.98±18.019.81±3.25Ⅱ期0.91±0.33112.89±27.46170.40±26.9315.49±3.81Ⅲ期1.34±0.53125.90±25.21193.36±25.3116.98±7.28Ⅳ期1.98±0.67160.50±29.31339.40±35.2025.60±6.62F/H5.01311.64623.14112.053P0.0010.0000.0000.000
2.2 外周血TGF-β和IL-6水平比较 观察组和对照组外周血TGF-β水平分别为(215.80±21.52)pg/mL、(26.90±10.41)pg/mL(U=102.213,P=0.000);IL-6水平分别为(17.32±8.02)pg/mL、(5.85±1.49)pg/mL(t=10.589,P=0.000)。TGF-β、IL-6水平随着舌鳞癌临床分期的增加而升高(P<0.01),见表1。
2.3 Pearson相关分析结果 TGF-β水平与Th17细胞比例无明显相关性(r=0.431,P=0.103),TGF-β水平与IL-17水平呈正相关(r=0.626,P=0.021),IL-6水平与Th17细胞比例和IL-17均呈正相关(r=0.626、0.597,P=0.021、0.034)。
3 讨 论
Th17细胞参与恶性肿瘤、自身免疫性疾病与移植物抗宿主等疾病的发生、发展,已成为近年来免疫学研究领域的热点[3]。IL-17是Th17细胞发挥生物学作用的主要细胞因子,在炎症、肿瘤、自身免疫性疾病和移植排斥反应中发挥着重要作用[4]。
研究发现,多种肿瘤包括卵巢癌、胃癌、肝癌、肺癌和乳腺癌等均存在Th17细胞的浸润和IL-17表达的增加[5]。IL-17可促进多种促血管生成因子表达上调,如血管内皮生长因子(VEGF)、前列腺素E2等[6]。在肿瘤组织中,Th17细胞的浸润和IL-17表达的增加和微血管密度呈正相关,提示Th17细胞和IL-17可促进肿瘤血管的生成从而促进肿瘤的发生、发展[7]。在肝细胞癌组织中,Th17细胞是主要的浸润细胞,促进血管新生和肝癌的进展[8]。多发性骨髓瘤中,Th17细胞比例和IL-17的表达均升高,且具有促进骨髓瘤细胞生长,抑制机体免疫功能的作用[9]。以上结果均提示Th17细胞和IL-17因子的促肿瘤效应。本研究中,舌鳞癌患者外周血Th17细胞比例和IL-17水平均显著高于对照组,且随着舌鳞癌患者临床分期的增加,Th17细胞比例和IL-17水平随之升高,提示Th17细胞和IL-17表达的增加在促进舌鳞癌的发生、发展中起着重要作用。
研究表明,Th17细胞在肿瘤免疫中还具有保护效应,但其机制尚不完全清楚[10]。早期胃癌Th17细胞浸润程度较进展期胃癌高,Th17细胞可通过IFN-γ发挥抗肿瘤作用,还可通过募集Th1细胞发挥抗肿瘤效应[11-12]。以上提示Th17细胞和IL-17因子可能存在的抗肿瘤作用。因此,Th17细胞和IL-17因子促肿瘤和抗肿瘤的效应可能考虑与肿瘤微环境、肿瘤致病因素、类型和进展阶段等有关,其具体机制还需更多的研究以进一步探讨。
TGF-β可增加内皮细胞对VEGF的敏感性,而前列腺素E2和IL-6可共同促进成纤维细胞之间的黏附分子表达,从而促进血管新生[13]。在结肠癌和乳腺癌的动物模型中,TGF-β可使IL-17表达增加,而IL-17可促进肿瘤细胞生长,同时起到抑制凋亡的作用[14]。IL-17可刺激黑色素瘤细胞及间质细胞生长,同时诱导产生IL-6,通过STAT3信号途径促进新生血管的生成[15]。本研究中,舌鳞癌患者外周血TGF-β和IL-6水平均显著高于对照组,随着舌鳞癌患者临床分期的增加,TGF-β和IL-6水平随之升高,且TGF-β水平与IL-17水平呈正相关,IL-6水平与Th17细胞比例和IL-17均呈正相关,提示在舌鳞癌中TGF-β和IL-6的升高一方面可诱导Th17细胞分化,另一方面在促进肿瘤血管新生和病程进展中发挥着重要作用。
综上所述,Th17细胞和IL-17表达的增加在舌鳞癌的发生、发展中发挥着重要作用。Th17细胞和IL-17因子可成为抗肿瘤治疗的重要靶点,但还需进一步的研究以证实。
[1]何志良,陈乔尔,王承阳,等.FasL及FasL ASODN在舌鳞癌细胞免疫逃逸中的作用[J].重庆医学,2015,44(1):27-31.
[2]Pan JJ,Ng WT,Zong JF,et al.Proposal for the 8th edition of the AJCC/UICC staging system for nasopharyngeal cancer in the era of intensity-modulated radiotherapy[J].Cancer,2016,122(4):546-558.
[3]Joerger M,Finn SP,Cuffe S,et al.The IL-17-Th1/Th17 pathway:an attractive target for lung cancer therapy? [J].Expert Opin Ther Targets,2016,11:1-18.
[4]Zhang N,Ma ZP,Wang J,et al.Human papillomavirus infection correlates with inflammatory Stat3 signaling activity and IL-17 expression in patients with breast cancer[J].Am J Transl Res,2016,8(7):3214-3226.
[5]Young MR.Th17 Cells in Protection from Tumor or Promotion of Tumor Progression[J].J Clin Cell Immunol,2016,7(3):431.
[6]Wu X,Yang T,Liu X,et al.IL-17 promotes tumor angiogenesis through Stat3 pathway mediated upregulation of VEGF in gastric cancer[J].Tumour Biol,2016,37(4):5493-5501.
[7]Maniati E,Hagemann T.IL-17 mediates resistance to anti-VEGF therapy[J].Nat Med,2013,19(9):1092-1094.
[8]Lin ZW,Wu LX,Xie Y,et al.The expression levels of transcription factors T-bet,GATA-3,RORγt and FOXP3 in peripheral blood lymphocyte (PBL) of patients with liver cancer and their significance[J].Int J Med Sci,2015,12(1):7-16.
[9]Feng P,Yan R,Dai X,et al.The alteration and clinical significance of Th1/Th2/Th17/Treg cells in patients with multiple myeloma[J].Inflammation,2015,38(2):705-709.
[10]Majchrzak K,Nelson MH,Bailey SR,et al.Exploiting IL-17-producing CD4+and CD8+T cells to improve cancer immunotherapy in the clinic[J].Cancer Immunol Immunother,2016,65(3):247-259.
[11]Zhang W,Tian X,Mumtahana F,et al.The existence of Th22,pure Th17 and Th1 cells in CIN and Cervical Cancer along with their frequency variation in different stages of cervical cancer[J].BMC Cancer,2015,15:717.
[12]Guéry L,Hugues S.Th17 cell plasticity and functions in cancer immunity[J].Biomed Res Int,2015,2015:314620.
[13]Peng X,Luo Z,Kang Q,et al.FOXQ1 mediates the crosstalk between TGF-β and Wnt signaling pathways in the progression of colorectal cancer[J].Cancer Biol Ther,2015,16(7):1099-1109.
[14]Sun X,Zhang J,Hou Z.miR-146a is directly regulated by STAT3 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells and involved in anti-tumor immune suppression[J].Cell Cycle,2015,14(2):243-252.
[15]Hayata K,Iwahashi M,Ojima T,et al.Inhibition of IL-17A in tumor microenvironment augments cytotoxicity of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in tumor-bearing mice[J].PLoS One,2013,8(1):e53131.
《重庆医学》对临床研究论文医学伦理学要求
凡投本刊的涉及人的生物医学研究论文,作者应说明所在用的试验程序是否经过伦理审查委员会(单位性的、地区性的或国家性的)评估,注明批准号。涉及患者(受试者)的应签订知情同意书。
《重庆医学》编辑部
Clinical significance of peripheral blood Th17 cells and their cytokines in tongue squamous cell carcinoma*
LiYanbo1,HeZhiliang1,SuDanni2,WangChengyang1,HeChenggong1,CaoLei1
(1.DepartmentofStomatology;2.OperationRoom,ChengdeMunicipalCentralHospital,Chengde,Hebei067000,China)
Objective To investigate the clinical significance of peripheral blood Th17 cells and their cytokines in the patients with tongue squamous cell carcinoma.Methods Sixty-six cases of tongue squamous cell carcinoma in our hospital from January 2013 to January 2016 served as the research subjects and contemporaneous 42 volunteers undergoing healthy physical examination were selected as the control group.Peripheral blood was collected in all subjects.The proportion of peripheral blood Th17 cells was detected by flow cytometry.The IL-17,TGF-β and IL-6 cytokine levels were detected by ELISA.Results The proportion of peripheral blood Th17 cells,IL-17,TGF-β and IL-6 in the observation group and the control group were (1.46±0.41)%vs. (0.31±0.12)%,(123.36±21.20)pg/mLvs. (20.76±8.95)pg/mL,(215.80±21.52)pg/mLvs. (26.90±10.41)pg/mL,(17.32±8.02)pg/mLvs.(5.85±1.49)pg/mL respectively,the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).The proportion of peripheral blood Th17 cells,IL-17,TGF-β and IL-6 levels were increased with the increase of tongue squamous cell carcinoma clinical stage (P<0.01).The TGF-β level was positively correlated with the IL-17 level (r=0.626,P=0.021),the IL-6 level was positively correlated with the proportion of Th17 cells and IL-17 (r=0.626,0.597,P=0.021,0.034).Conclusion The increase of Th17 cells and IL-17 expression plays an important role in the development and progression of tongue squamous cell carcinoma,Th17 cells and IL-17 cytokine can become the important target spots of anti-tumor therapy.
tongue;carcinoma,squamous cell;Th17 cells;cytokines;clinical significance
��·临床研究
10.3969/j.issn.1671-8348.2017.20.008
2013年承德市科学技术研究与发展计划项目(2013201)。 作者简介:李燕波(1983-),主治医师,本科,主要从事口腔外科相关疾病诊疗研究。
R246
A
1671-8348(2017)20-2761-03
2017-02-03
2017-04-08)

