虾青素的来源、生物功效及吸收代谢研究进展
周庆新,刘婷婷,杨鲁
(1.日照职业技术学院海洋工程学院,山东日照276826;2.中国海洋大学食品科学与工程学院,山东青岛266003)
虾青素的来源、生物功效及吸收代谢研究进展
周庆新1,刘婷婷1,杨鲁2
(1.日照职业技术学院海洋工程学院,山东日照276826;2.中国海洋大学食品科学与工程学院,山东青岛266003)
对目前有关虾青素来源、存在形态、生物学功能和吸收代谢的研究进展进行系统综述。在此基础上,对天然来源虾青素作为功能因子使用时遇到的问题做思考和总结。以期为把握虾青素相关研究领域的前沿方向,探究虾青素营养功能与其作用机理,以及结构与功能之间关系的阐明起指导作用。同时,为解决虾青素营养特性保持和终端食品合理开发等产业实际问题提供参考。
虾青素;来源;生理功能;吸收;代谢
虾青素(Astaxanthin)作为非维生素A原脂溶性酮式类胡萝卜素,在海洋动植物、微型藻类以及酵母中广泛分布[1]。独特的化学结构赋予其有效淬灭活性氧的能力,是迄今为止人类发现的自然界中最强的抗氧化剂,受到各国科研工作者和消费者的广泛关注。虾青素在人体内无法合成,只能通过膳食摄取。美国食品和药物管理局(FDA)禁止化学合成虾青素作为膳食补充剂用于食品生产,但是批准其作为着色剂在动物及水产饲料和日化领域中使用,欧盟委员会批准天然虾青素作为食品着色剂在食品行业应用[2]。在自然界中,天然虾青素的最主要摄食来源是海洋食品和雨生红球藻[3],目前有关虾青素对人类健康的功效已被大量研究证实,且虾青素是被发现唯一能穿透血-脑、血-视网膜屏障的类胡萝卜素,对中枢神经系统和大脑功能可产生积极的影响[4]。因此,将天然虾青素作为膳食营养补充剂用于食品、保健品或药品,对改善人类健康具有切实意义。本文从虾青素的来源、形态分布、生理活性以及吸收代谢特性等方面进行了概述,并对相关数据作了整合分析,以期为虾青素资源的开发和应用提供有效参考。
1 虾青素的结构特性、来源及存在形态
1.1 虾青素的结构特性
虾青素又名虾黄质、龙虾壳色素,化学名称为3,3′-二羟基-4,4′-二酮基-β,β′-胡萝卜素,分子式C40H52O4,其化学结构是由4个异戊二烯单位以共轭双键形式连接,在两端有两个异戊二烯单位组成的六元环结构[2]。一方面,其间存在有两个手性碳原子,分别是3C和3′C,而每个手性碳原子可有两种构象(即R型或S型),故相应会产生3种光学异构体:一对外消旋型虾青素(左旋型3S,3′S和右旋型3R,3′R)和一个内消旋型虾青素(3S,3′R);另一方面,虾青素分子中多个碳碳双键形成的共轭长链结构致使其容易发生顺反异构,形成多种几何异构体[5]。通常顺式构型中顺式双键附近的氢原子之间或氢原子与甲基之间空间位阻较大。因此,自然界中游离态虾青素多以全反式虾青素(all-trans-astaxanthin)存在,该种异构体分支基团(甲基)不会竞争空间位置,使其表现出相对较好的结构稳定性[6]。但是全反式虾青素易受溶剂特性、光、热、氧、金属离子等因素的影响而发生几何异构化反应,转化形成多种顺式构型异构体[7-8]。目前文献报道[7]的虾青素顺式异构体形式主要有:9-顺-虾青素(9-cisastaxanthin)、13-顺-虾青素(13-cis-astaxanthin)、15-顺-虾青素(15-cis-astaxanthin)、13,15-双-顺-虾青素(13,15-di-cis-astaxanthin),各虾青素异构体的结构如图1所示。
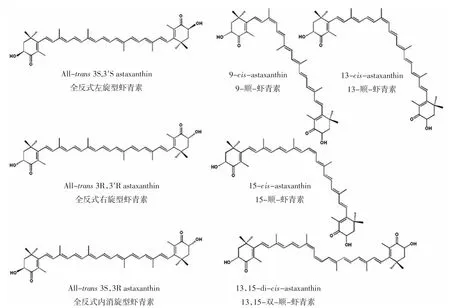
图1 虾青素几何异构体和光学异构体结构图Fig.1 The structure profile of astaxanthin geometrical isomers and stereoisomers
1.2 虾青素来源及存在形态
1.2.1 虾青素来源
目前商品化的虾青素产品主要来源于雨生红球藻、红法夫酵母和合成虾青素,另外还有部分富含虾青素的虾油产品。研究人员通过分析测定不同生物资源中虾青素的含量发现,雨生红球藻(Haematococcus pluvialis)是天然虾青素的良好来源[9],其中虾青素约占藻粉干重的4%~5%;红法夫酵母中虾青素约占干重的0.12%[10];其它几种常见水产资源中总虾青素的含量如图2所示,数据显示:南极磷虾体内总虾青素的含量约为120mg/kg,对虾和甜虾约为30mg/kg~60mg/kg,梭子蟹约在30mg/kg,三文鱼中约为15mg/kg~20mg/kg[11-12](均以干重计)。
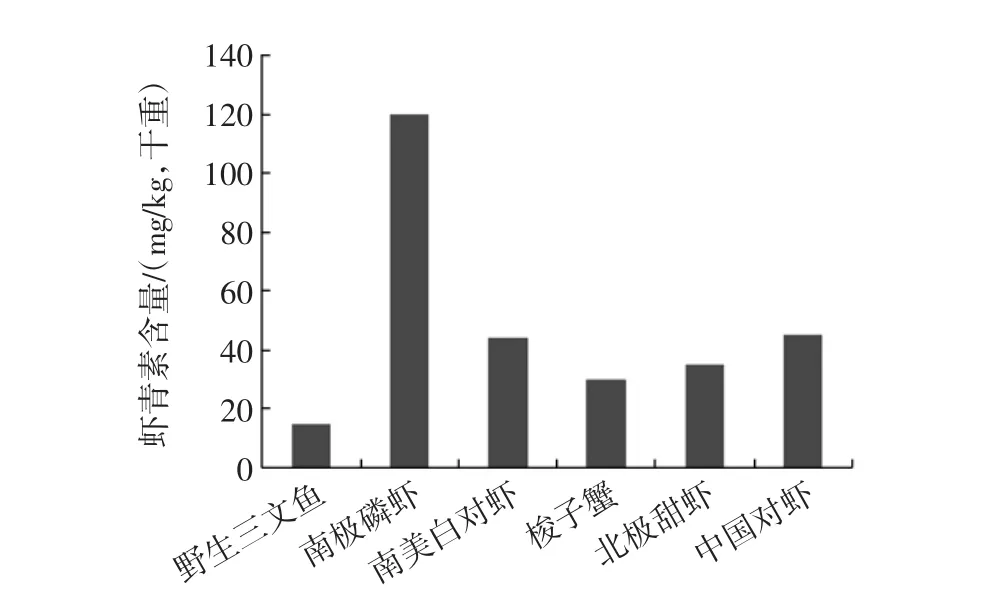
图1 蛋白质浓度标准曲线Fig.1 The standard curve of protein concentration
1.2.2 虾青素存在形态
虾青素在自然界中的存在形态主要分为游离态和酯化态(单酯型和双酯型,结构如图3所示),且具有显著地物种差异性。研究显示在鲑鳟鱼和红法夫酵母中虾青素主要以游离态存在[13-14],而在藻、虾和蟹中主要以酯化态存在,游离态含量相对较少[15-17]。苗凤萍[17]报道,雨生红球藻中游离态虾青素、虾青素单酯和双酯分别约占5%、70%和25%。Gladis和Bjerkeng[16]对莫氏岩瓷蟹中的色素组分进行了研究,结果表明在总类胡萝卜素中,游离虾青素约占10%,虾青素单酯约占12%,虾青素双酯约占70%。几种常见水产资源中游离态虾青素和酯化态所占相对百分含量如图4所示。另外,与虾青素相链接的脂肪链多为长链脂肪酸,其中雨生红球藻来源虾青素酯结构中脂肪酸主要以十八碳酸和十六碳酸为主,在南美白对虾、南极磷虾以及梭子蟹中,虾青素酯的脂肪酸链多为C20∶5和C22∶6形式存在。在此值得注意的现象是:动物本身不能合成虾青素和虾青素酯[18],只能从食物中摄取,而虾青素在虾类水生生物体内主要以酯化型居多,在鱼类体内却多以游离态存在,说明动物体内虾青素的吸收、转化和蓄积具有很强的选择性,同时从仿生学的角度为研究改善虾青素在人体内的利用度提供新的思路。

图3 游离态虾青素、虾青素单酯和虾青素双酯的结构图Fig.3 Structures of astaxanthin,astaxanthin monoesters,and astaxanthin diesters
另一方面,自然界中的游离态虾青素多是以全反式虾青素(all-trans-astaxanthin)和13-顺-虾青素(13-cisastaxanthin)的几何构型存在,但不同生物体内虾青素光学构型却差异性显著。作者对国内外相关研究[10,17,19]进行了检索,对不同物种中虾青素的光学异构体构成进行了总结归纳(如图5所示),数据表明:雨生红球藻、三文鱼及南极磷虾体内的虾青素主要以3S,3’S构型存在,红法夫酵母中虾青素则全以3R,3’R构型存在,对虾和梭子蟹中3S,3’S和3S,3’R两种构型相对含量较高,合成虾青素则是3种构型虾青素的混合物(3S,3’S占25%、3R,3’R占25%,3S,3’R占50%)[9,10,16,20-21]。

图4 不同水产品中虾青素及虾青素酯的相对百分含量Fig.4 The relative percentage content of astaxanthin and astaxanthin esters in different aquatic products
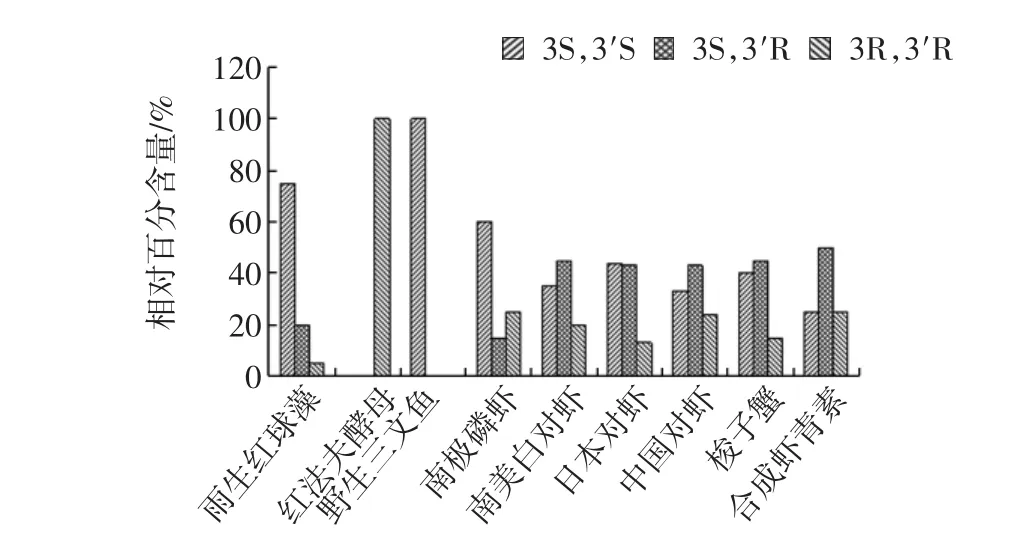
图5 不同样品中虾青素光学异构体相对百分含量Fig.5 The relative percentage content of Astaxanthin stereoisomers in different samples
2 虾青素的生物学功能及其吸收代谢研究
2.1 虾青素的生物学功能
虾青素分子结构中特殊的β-紫罗兰酮环和长链共轭烯烃结构赋予其有效淬灭活性氧的功能,它是迄今为止自然界中最强的天然抗氧化剂,其清除自由基能力是维生素E和其他类胡萝卜素(叶黄素、番茄红素和β-类胡萝卜素)的500倍之多[22],并且虾青素是目前发现唯一能穿透血-脑(Blood-Brain)、血-视网膜(Blood-Retina)屏障的类胡萝卜素[4],诸多结构和特性使虾青素表现出卓越的生物学功能。已有大量动物试验表明:虾青素具有抗肿瘤[23]、抗炎活性[24]、抗糖尿病[25]、减少氧化损伤[26]、加强机体免疫力[27]、改善运动机能[28]、预防心脑血管疾病[29]等功能。目前有关虾青素生物活性的研究报道归纳见表1。另外,国内外研究显示,不同虾青素异构体所表现出的生物学功能具有差异性,3S,3’S虾青素相较于3R,3’R和3S,3’R具有更好的生物学功能以及更强的抗氧化活性[9];Liu等[30]通过多种体外模拟试验证明:与全反式虾青素相比,9-顺-和13-顺-虾青素在多模拟体系中均表现出更高的抗氧化能力。
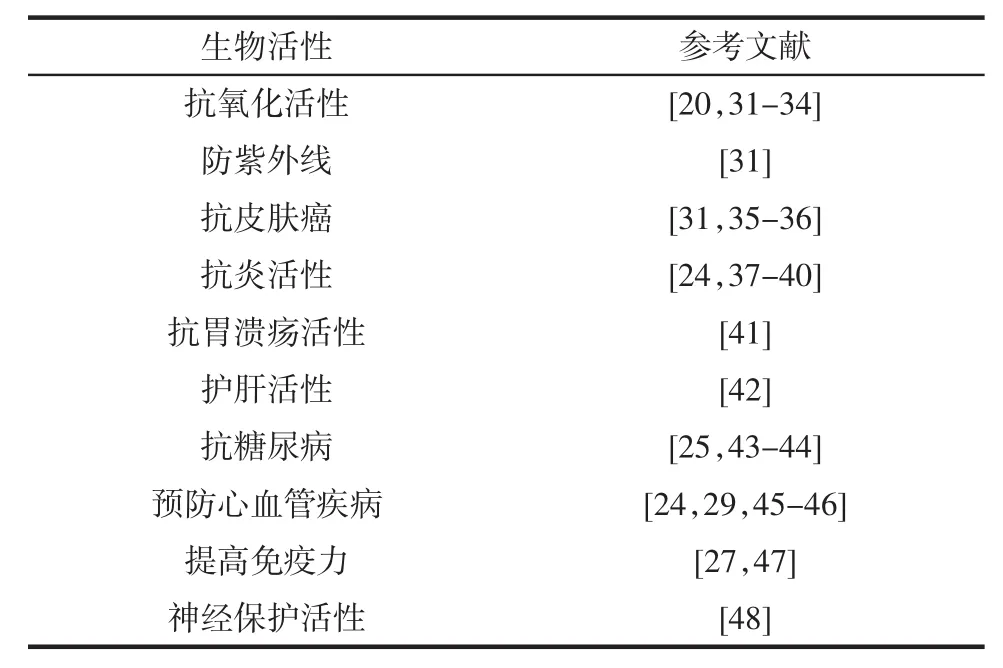
表1 体内或体外模型试验中虾青素的生物活性Table 1 Astaxanthin biological activities in vitro and in vivo models
2.2 虾青素的吸收代谢研究现状
虾青素作为一种类胡萝卜素,在摄取后能否发挥生物活性的关键因素是其吸收利用或储存在人体中的比例,其利用率主要受分子结构、在食物中的物理结合方式、膳食中脂肪含量以及胃肠道中胰酶和胆盐的含量等因素影响[49]。目前有关虾青素在体内吸收代谢过程的研究相对较少,尤其是有关不同分子结构虾青素类化合物在生物体内的消化吸收过程鲜为报道。Ranga等[20,32]和Olson等[50]研究报道,通过在饮食中添加油脂,可有效提高虾青素的生物利用度,提示食品基质中的脂质种类和含量是影响虾青素在生物体内利用率的重要因素。Østerlie等[51]和Coral等[52]研究了人体口服摄入虾青素和虾青素酯后,虾青素在人体血清中的存在形态,研究结果表明:摄入游离态虾青素后其在血液中与脂蛋白结合;而摄入虾青素酯后,在血液中只检测到了游离态虾青素,无酯化态虾青素检出,并且其在血液中的响应值比摄入相同当量的游离虾青素低4~5倍,在此研究基础上推测,游离态虾青素可被人体直接吸收利用,而酯化态虾青素需要在消化道内先被水解成游离虾青素,然后以游离态形式被人体吸收,这一研究为虾青素酯在体内发挥与游离态虾青素相同的生物学效价提供了一定的证据,但是缺乏直观系统地研究数据来证明这一推测的准确性。Fukami等[53]利用化学法合成辛酸虾青素单酯和双酯,并利用大鼠模型对其药代动力学进行了研究,研究结果显示,推测中链虾青素酯的生物利用度优于长链虾青素酯。辛酸虾青素单酯在大鼠体内的生物利用率高于辛酸虾青素双酯,高于商品化雨生红球藻来源虾青素提取物(虾青素和虾青素酯的混合物),另外虾青素在肝脏中的最大代谢浓度是血清的3倍左右,据Fukami推断,中链脂肪酸链构成的虾青素酯具有较高的生物利用率。通过该研究结果可以看出,虾青素酯的脂肪酸链组成与其生物利用率具有相关性,但是目前有关虾青素酯结构-生物利用率之间的构效关系尚不明确,有待进一步研究证实。
3 结语
天然虾青素对于改善人体健康具有非常实际的意义,但其极不稳定,易受光、热、氧等外界因素作用而发生氧化降解,导致食品外观品质和营养性下降,且在体内的生物利用率较低,严重限制了其在食品行业中的应用。故食品中添加的虾青素须以一种相对稳定的高生物效价分子状态存在。另外,虾青素的稳定性和生物利用度除受分子结构影响外,还受食品体系等外在因素影响。然而,目前有关不同分子形态虾青素结构和食品体系对其稳定性和吸收代谢的影响及机制尚不明确。因此今后此类研究工作的开展显得尤为重要,其不仅对虾青素稳定性和生物利用度的影响因素、规律及机制的揭示具有重要的理论意义,同时可为筛选高稳定性和高生物利用度的虾青素分子形式,以及高生物利用度虾青素酯稳态化赋型食品的设计提供依据,最终为虾青素资源的高值化利用,及其科学营养膳食探寻新的策略和方案。
[1]HIGUERA-CIAPARA I,FELIX-VALENZUELA L,GOYCOOLEA F M.Astaxanthin:a review of its chemistry and applications[J].Critical reviews in food science and nutrition,2006,46(2):185-196
[2]AMBATI R R,PHANG S M,RAVI S,et al.Astaxanthin:Sources,extraction,stability,biological activities and its commercial applications—A review[J].Marine drugs,2014,12(1):128-152
[3]GUERIN M,HUNTLEY M E,OLAIZOLA M.Haematococcus astaxanthin:applications for human health and nutrition[J].TRENDS in Biotechnology,2003,21(5):210-216
[4]JYONOUCHI H,SUN S,IIJIMA K,et al.Antitumor activity of astaxanthin and its mode of action[J].Nutrition and cancer,2000,36(1):59-65
[5]胡金金,靳远祥,傅正伟.虾青素结构修饰的研究进展[J].食品科学,2008,28(12):531-534
[6]雷凤爱.雨生红球藻中虾青素的分离纯化及异构体的分析研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古农业大学,2009
[7]QIU D,WU Y C,ZHU W L,et al.Identification of Geometrical Isomers and Comparison of Different Isomeric Samples of Astaxanthin[J].Journal of Food Science,2012,77(9):934-940
[8]HOLTIN K,KUEHNLE M,REHBEIN J,et al.Determination of astaxanthin and astaxanthin esters in the microalgae Haematococcus pluvialis by LC-(APCI)-MS and characterization of predominant carotenoid isomers by NMR spectroscopy[J].Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry,2009,395(6):1613-1622
[9]LORENZ R T,CYSEWSKI G R.Commercial potential for Haematococcus microalgae as a natural source of astaxanthin[J].Trends Biotechnol,2000,18(4):160-167
[10]TETENS I.EFSA NDA Panel(EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies),2014 Scientific Opinion on the safety of astaxanthin-rich ingredients(AstaREAL A1010 and AstaREAL L10)as novel food ingredients[R].London:Europen Food Safety Authority,2014
[11]杨澍.南美白对虾中虾青素类化合物在贮藏及加工过程中变化规律的研究[D].青岛:中国海洋大学,2015
[12]CORRÊA N C F,DA SILVA MACEDO C,DE FC MORAES J,et al. Characteristics of the extract of Litopenaeus vannamei shrimp obtained from the cephalothorax using pressurized CO2[J].The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2012,66:176-180
[13]ANDREWES A G,STARR M P.(3R,3’R)-Astaxanthin from the yeast Phaffia rhodozyma[J].Phytochemistry,1976,15(6):1009-1011
[14]SHEEHAN E M,OCONNOR T P,SHEEHY P J A,et al.Stability of astaxanthin and canthaxanthin in raw and smoked Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar)during frozen storage[J].Food Chemistry,1998,63(3):313-317
[14]SHAHIDI F,SYNOWIECKI J.Isolation and characterization of nutrients and value-added products from snow crab(Chionoecetes opilio)and shrimp(Pandalus borealis)processing discards[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,1991,39(8):1527-1532
[16]CORAL-HINOSTROZA G N,BJERKENG B.Astaxanthin from the red crab langostilla(Pleuroncodes planipes):optical R/S isomers and fatty acid moieties of astaxanthin esters[J].Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B:Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2002,133(3):437-444
[17]苗凤萍.雨生红球藻(Haematococcus pluvialis)虾青素酯和脂肪酸的鉴定及差异表达基因的分析[D].武汉:中国科学院研究生院(武汉植物园),2007
[18]BURRI B J,CHANG J S T,NEIDLINGER T R.β-Cryptoxanthinand α-carotene-rich foods have greater apparent bioavailability than β-carotene-rich foods in Western diets[J].British Journal of Nutrition,2011,105(2):212-219
[19]BREITHAUPT D E.Identification and quantification of astaxanthin esters in shrimp (Pandalus borealis)and in a microalga(Haematococcus pluvialis)by liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry using negative ion atmospheric pressure chemical ionization[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2004,52(12):3870-3875
[20]RANGA R A,RAGHUNATH REDDY R L,BASKARAN V,et al. Characterization of microalgal carotenoids by mass spectrometry and their bioavailability and antioxidant properties elucidated in rat model[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2010,58(15): 8553-8559
[21]杨澍,张婷,徐杰,等.高效液相色谱手性拆分法分析生物体内的虾青素光学异构体[J].食品科学,2015,36(8):139-144
[22]NAGUIB Y M.Antioxidant activities of astaxanthin and related carotenoids[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2000,48 (4):1150-1154
[23]裴凌鹏.虾青素体内抗肿瘤及其免疫调节作用的实验研究[J].上海中医药杂志,2009,43(6):68-69
[24]CHEW W,MATHISON B D,KIMBLE L L,et al.Astaxanthin decreases inflammatory biomarkers associated with cardiovascular disease in human umbilical vein endothelial cells[J].American Journal of Advances in Food Science and Technology,2013,1:1-17
[25]UCHIYAMA K,NAITO Y,HASEGAWA G,et al.Astaxanthin protects β-cells against glucose toxicity in diabetic db/db mice[J].Redox Report,2002,7(5):290-293
[26]曹秀明,杨贵群,杨菲菲.虾青素对过氧化氢所致HepG2细胞线粒体氧化损伤及生存能力下降的保护作用 [J].中国海洋药物, 2010,5:26-32
[27]PARK J S,CHYUN J H,KIM Y K,et al.Astaxanthin decreased oxidative stress and inflammation and enhanced immune response in humans[J].Nutrition and Metabolism,2010,7:1-10
[28]IKEUCHI M,KOYAMA T,TAKAHASHI J,et al.Effects of astaxanthin supplementation on exercise-induced fatigue in mice[J].Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin,2006,29(10):2106-2110
[29]PASHKOW F J,WATUMULL D G,CAMPBELL C L.Astaxanthin:a novel potential treatment for oxidative stress and inflammation in cardiovascular disease[J].The American Journal of Cardiology, 2008,101(10):58-68
[30]LIU X,OSAWA T.Cis astaxanthin and especially 9-cis astaxanthin exhibits a higher antioxidant activity in vitro compared to the alltrans isomer[J].Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2007,357(1):187-193
[31]RANGA A R,SINDHUJA H N,DHARMESH S M,et al.Effective inhibition of skin cancer,tyrosinase,and antioxidative properties by astaxanthin and astaxanthin esters from the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2013,61(16):3842-3851
[32]RANGA A R,BASKARAN V,SARADA R,et al.In vivo bioavailability and antioxidant activity of carotenoids from microalgal biomass-A repeated dose study[J].Food Research International,2013,54(1):711-717
[33]SILA A,AYED-AJMI Y,SAYARI N,et al.Antioxidant and anti-proliferative activities of astaxanthin extracted from the shell waste of deep-water pink shrimp (Parapenaeus longirostris)[J].Journal of Natural Products,2013,3:82-89
[34]YANG Y,SEO J M,NGUYEN A,et al.Astaxanthin-rich extract from the green alga Haematococcus pluvialis lowers plasma lipid concentrations and enhances antioxidant defense in apolipoprotein E knockout mice[J].The Journal of Nutrition,2011,141(9):1611-1617
[35]MAOKA T,TOKUDA H,SUZUKI N,et al.Anti-oxidative,anti-tumor-promoting,and anti-carcinogensis activities of nitroastaxanthinand nitrolutein,the reaction products of astaxanthin and lutein with peroxynitrite[J].Marine Drugs,2012,10(6):1391-1399
[36]HUANGFU J,LIU J,SUN Z,et al.Antiaging effects of astaxanthinrich alga Haematococcus pluvialis on fruit flies under oxidative stress[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2013,61(32):7800-7804
[37]BHUVANESWARI S,YOGALAKSHMI B,SREEJA S,et al.Astaxanthin reduces hepatic endoplasmic reticulum stress and nuclear factor-κB-mediated inflammation in high fructose and high fat dietfed mice[J].Cell Stress and Chaperones,2014,19(2):183-191
[38]PARK J S,MATHISON B D,HAYEK M G,et al.Astaxanthin modulates age-associated mitochondrial dysfunction in healthy dogs[J]. Journal of Animal Science,2013,91(1):268-275
[39]GAL A F,ANDREI S,CERNEA C,et al.Effects of astaxanthin supplementation on chemically induced tumorigenesis in Wistar rats[J]. Acta Veterinaria Scandinavica,2012,54:1-6
[40]WIBRAND K,BERGE K,MESSAOUDI M,et al.Enhanced cognitive function and antidepressant-like effects after krill oil supplementation in rats[J].Lipids in Health and Disease,2013,12(6):1-13
[41]BENNEDSEN M,WANG X,WILLÉN R,et al.Treatment of H.pylori infected mice with antioxidant astaxanthin reduces gastric inflammation,bacterial load and modulates cytokine release by splenocytes [J].Immunology Letters,2000,70(3):185-189
[42]TURKEZ H,GEYIKOGLU F,YOUSEF M I.Beneficial effect of astaxanthin on 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced liver injury in rats[J].Toxicology and Industrial Health,2013,29(7):591-599
[43]CHAN K,PEN P J,YIN M.Anticoagulatory and antiinflammatory effects of astaxanthin in diabetic rats[J].Journal of Food Science, 2012,77(2):76-80
[44]DONG L Y,JIN J,LU G,et al.Astaxanthin attenuates the apoptosis of retinal ganglion cells in db/db mice by inhibition of oxidative stress [J].Marine Drugs,2013,11(3):960-974
[45]IIZUKA M,AYAORI M,UTO-KONDO H,et al.Astaxanthin enhances ATP-binding cassette transporter A1/G1 expressions and cholesterol efflux from macrophages[J].Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology,2012,58(2):96-104
[46]YOSHIDA H,YANAI H,ITO K,et al.Administration of natural astaxanthin increases serum HDL-cholesterol and adiponectin in subjects with mild hyperlipidemia[J].Atherosclerosis,2010,209(2):520-523
[47]PARK J S,MATHISON B D,HAYEK M G,et al.Astaxanthin stimulates cell-mediated and humoral immune responses in cats[J].Veterinary Immunology and Immunopathology,2011,144(3):455-461
[48]LU Y P,LIU S Y,SUN H,et al.Neuroprotective effect of astaxanthin on H2O2-induced neurotoxicity in vitro and on focal cerebral ischemia in vivo[J].Brain Research,2010,1360:40-48
[49]FAILLA M L,CHITCHUMRONCHOKCHAI C,FERRUZZI M G,et al.Unsaturated fatty acids promote bioaccessibility and basolateral secretion of carotenoids and α-tocopherol by Caco-2 cells[J].Food &Function,2014,5(6):1101-1112
[50]OLSON J A.Absorption,transport and metabolism of carotenoids in humans[J].Pure and Applied Chemistry,1994,66(5):1011-1016
[51]ØSTERLIE M,BJERKENG B,LIAAEN-JENSEN S.Plasma appearance and distribution of astaxanthin E/Z and R/S isomers in plasma lipoproteins of men after single dose administration of astaxanthin [J].The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry,2000,11(10):482-490
[52]CORAL-HINOSTROZA G N,YTRESTØYL T,RUYTER B,et al. Plasma appearance of unesterified astaxanthin geometrical E/Z and optical R/S isomers in men given single doses of a mixture of optical 3 and 3’R/S isomers of astaxanthin fatty acyl diesters[J].Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part C:Toxicology&Pharmacology,2004,139(1):99-110
[53]FUKAMI H,NAMIKAWA K,SUGIURA-TOMIMORI N,et al.Chemical synthesis of astaxanthin n-octanoic acid monoester and diester and evaluation of their oral absorbability[J].Journal of Oleo Science, 2006,55(12):653-656
Recent Progress in Sources,Biological Function,Absorption and Metabolism Characteristics of Astaxanthin
ZHOU Qing-xin1,LIU Ting-ting1,YANG Lu2
(1.College of Marine Engineering,Rizhao Polytechnic,Rizhao 276826,Shandong,China;2.College of Food Science and Engineering,Ocean University of China,Qingdao 266003,Shandong,China)
The sources,form distribution,biological function,absorption and metabolism characteristics of astaxanthin were reviewed.Based on these information,the problems in the process of using astaxanthin as functional factor was analysis and concluded.The current review has important significance for grasping the front direction of astaxanthin researching filed,function and mechanism investigation,and revealing relationship between structure and function.Meanwhile,the current review provides up-to-date information on nutrition maintenance of astaxanthin in processing,and rational development of functional food.
astaxanthin;sources;biological function;absorption;metabolism
2016-12-01
山东省自然科学基金博士基金项目(NO.ZR2016CB35)
周庆新(1986—),男(汉),博士,研究方向:水产化学、食品功效成分研究。
10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2017.16.046

