炎症因子chemerin在有氧运动改善动脉粥样硬化大鼠血脂和主动脉硬化中的作用
林小晶, 鲁 林, 王晓慧
(上海体育学院运动科学学院,上海200438)
运动人体科学
炎症因子chemerin在有氧运动改善动脉粥样硬化大鼠血脂和主动脉硬化中的作用
林小晶, 鲁 林, 王晓慧
(上海体育学院运动科学学院,上海200438)
目的:研究炎症因子chemerin在有氧运动改善动脉粥样硬化大鼠血脂和主动脉硬化中的作用。方法:将30只雄性SD大鼠随机分为2组,AS造模组20只,采用一次性腹腔注射维生素D3(60万IU/kg)联合8周高脂饲料喂养的方法制备AS大鼠模型;正常对照组(Con)10只,腹腔一次性注射等量的生理盐水,并喂以8周普通饲料。建模成功的AS大鼠被随机分为AS组和运动+AS(EAS)组。EAS组大鼠在跑台上进行为期4周中等强度的有氧运动,每周运动6 d。油红O染色和HE染色检测AS程度,全自动生化分析仪检测大鼠血脂(血清TC、TG、LDL、HDL水平),ELISA检测血清chemerin水平,以及real time PCR和Western blot检测大鼠肝脏chemerin的mRNA和蛋白表达水平。结果:①与Con组相比,AS组大鼠出现血脂紊乱(血清TC、TG、LDL水平显著升高,HDL显著降低),以及主动脉粥样斑块,斑块处血管中膜的平滑肌细胞增生、排列紊乱,但AS组大鼠的空腹血糖无变化。②与AS组相比,EAS组大鼠的TC、TG、LDL水平显著降低、主动脉AS的大体和镜下病理改变均显著减轻;肾周脂肪量显著减少,以及空腹血糖无变化。③与Con组相比,AS组大鼠的血清chemerin、肝chemerin的mRNA和蛋白水平均显著升高。④与 AS组相比,EAS组大鼠的血清chemerin、肝chemerin的mRNA和蛋白水平均显著降低。结论: AS大鼠的血清chemerin、肝chemerin的mRNA和蛋白水平均显著升高;4周有氧运动改善AS大鼠的血脂、减少肾周脂肪量和减轻AS程度,这可能与其降低血清和肝的chemerin水平有关。
炎症因子;chemerin;大鼠;动脉粥样硬化;有氧运动;血脂
Author’s addressSchool of Kinesiology,Shanghai University of Sport,Shanghai 200438,China
随着人口老龄化以及多吃少动生活方式的盛行,肥胖及其相关疾病,如动脉粥样硬化(Atherosclerosis,AS)、糖尿病、冠心病等的发病率逐年上升,已成为危害人类健康的主要疾病。肥胖及其相关疾病被认为是系统性的慢性低度炎症[1]。肥胖时肝和脂肪组织中巨噬细胞的浸润以及血浆炎症因子CRP、TNF-"、IL-6和脂肪因子leptin的显著增加是慢性低度炎症最显著的特征[1-5]。除了上述经典的炎症和脂肪因子之外,chemerin在肥胖及其相关疾病中的作用日益引起人们关注,已成为肥胖及其相关疾病的研究热点。
chemerin是新发现的脂肪因子,亦被称为他扎罗汀诱导基因2和视黄酸受体反应因子2[6],在脂肪和肝组织中高表达。1997年首次在银屑病患者皮肤中发现,鉴别为他扎罗汀诱导基因2(TIG2),但直到2003年在人类炎症性液体中也检测到它时才命名为chemerin,被认为是一种孤儿G蛋白偶联受体趋化因子样受体1(CMKLR1,亦被称为ChemR23)的配体[7],到2007年才认识到它是一个脂肪因子和炎症因子。已证实chemerin与炎症标志物如CRP、TNF-"、IL-6等显著相关[8-9]。越来越多的研究证实,血浆chemerin的表达和活性在糖脂代谢紊乱疾病,如肥胖[10-11]、代谢综合征[11-12]、2型糖尿病[8,13-14],以及AS[15-18]中显著增加,且可能与疾病的发生、发展和严重程度密切相关。chemerin有可能成为治疗肥胖及其相关疾病的靶分子。值得一提的是,近年研究发现chemerin可促进巨噬细胞的胆固醇蓄积和巨噬细胞向泡沫细胞的转化,从而在AS的形成以及粥样斑块的大小中起重要作用[17]。
有氧运动减轻肥胖、改善肥胖相关疾病如AS、糖尿病已成为共识。有氧运动改善肥胖及其相关疾病的作用机制与其减轻这些疾病的炎症状态有关[19-20]。有氧运动改善AS大鼠的动脉硬化程度也与其抗炎作用有关,如减轻单核/巨噬细胞在主动脉壁的附着和浸润、降低主动脉壁炎症因子的水平[21],但目前还没有关于有氧运动改善AS是否与炎症因子chemerin有关的研究报道。可以明确的是,有氧运动能降低肥胖[22-24]和2型糖尿病[25]患者血清chemerin的水平,且chemerin的降低与肥胖和糖尿病患者的血脂、血糖的改善有关。本文拟在AS模型大鼠中研究4周有氧运动对chemerin的影响及其与血脂和主动脉AS程度改善的相关性,不仅有助于认识有氧运动改善AS的机制,还能为AS的治疗提供新的靶分子。
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验对象6周龄雄性SD大鼠30只,体重190~210 g,购于北京维通利华实验技术有限公司(合格证号:SCXK(京)2012—0001)。在上海体育学院SPF级动物实验室喂养大鼠,自由饮水饮食,温度控制在20~24℃,相对湿度为40% ~55% ,白天光照12 h,晚上关灯。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 AS模型大鼠的制备与分组 30只雄性SD大鼠被适应性喂养一周后,随机分为2组:AS造模组(20只)和正常对照组(Con,10只)。采用一次性腹腔注射维生素D3(60万IU/kg,购于上海通用药业股份有限公司)联合8周高脂饲料喂养(含3%胆固醇,0.5%胆酸钠,0.2%丙基硫氧嘧啶,5%白糖,10%猪油和81.3%普通饲料)的方法制备AS模型大鼠;Con组大鼠腹腔一次性注射等量的生理盐水后,喂以普通饲料。8周喂养后,Con组和AS造模组分别随机选择2只和4只,眼眶取血检测血脂水平,处死大鼠后剥离主动脉进行大体和病理学检查,以明确AS模型大鼠是否制备成功。确认成功后,AS造模大鼠被随机分为AS组和EAS(运动+AS)组,每组各8只。
1.2.2 运动干预 EAS组大鼠先进行3 d的跑台适应性训练,紧接着在跑台上进行为期4周的递增负荷中等强度有氧运动(表1)。

表1 有氧运动方案Table 1 Aerobic exercise protocol
1.2.3 空腹血糖和血清指标的检测 4周运动前后,大鼠禁食12 h后眼眶静脉丛采血,收集血清。最后一次跑台运动干预结束后36 h,水合氯醛麻醉处死大鼠,收集肝脏。罗氏血糖仪检测空腹血糖;全自动生化分析仪检测血清总胆固醇(total cholesterol,TC)、甘油三酯(triglyceride,TG)、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(low density lipoprotein cholesterol,LDL)和高密度脂蛋白胆固醇(high density lipoprotein cholesterol,HDL)的水平(试剂购自南京建成公司)。ELISA方法检测血清chemerin的水平(试剂盒购于美国Life Span Biosciences公司)。
1.2.4 主动脉AS程度的检测[26]大鼠麻醉后,沿主动脉弓至肾主动脉分支处剥离全长动脉。生理盐水清洗后,4%多聚甲醛固定,油红O染色。剪取有斑块的动脉进行石蜡包埋、切片和HE染色。
1.2.5 肝chemerin的mRNA检测 用TRIzol试剂(购自美国Invitrogen公司)抽提大鼠肝总的RNA,逆转录成 cDNA(逆转录试剂盒购自美国 Thermo公司),进行 real time PCR扩增(chemerin及内参GAPDH的引物序列见表2,上海生工生物工程公司合成,扩增试剂盒购自美国Roche公司),采用两步法45个循环,95℃变性15 s、60℃退火延伸60 s进行扩增。

表2 chemerin和GAPDH的引物序列Table 2 Primes sequences of chemerin and GAPDH
1.2.6 肝chemerin的蛋白水平检测 取50 mg肝脏,加入1 mL的含PMSF的RIPA裂解液(RIPA∶PMSF= 100∶1,购目上海碧云天公司),机械匀浆后超声裂解组织,4℃12 000 r/min离心30 min后取上清,用BCA法检测蛋白浓度。30 μg的待测样品进行聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳后转移到PVDF膜上,5%的脱脂奶粉4℃封闭过夜,加入chemerin(英国abcom公司,1∶500稀释)和β-actin(美国CST公司,1∶1 000稀释)的一抗,4℃孵育过夜,TBST洗3次后,加入相应的二抗(美国santa cruz公司,1∶5 000稀释),常温下孵育1 h,TBST洗3次后在显影仪(购自上海天能生物科技公司)上显影。
1.3 统计学分析采用SPSS17.0统计学软件包进行数据处理,结果采用平均数±标准差表示。体重和血糖、血脂采用重复测量的方差分析,其余指标采用单因素方差分析,P<0.05为显著性差异,P<0.01为非常显著性差异。
2 实验结果
2.1 AS模型大鼠成功建立AS模型大鼠出现了血脂异常,包括血清TC、TG、LDL水平显著升高,血清HDL水平显著降低(表3)。如图1(a)所示的主动脉大体标本,AS模型大鼠出现了红色的粥样斑块,而正常对照大鼠无粥样斑块;与正常对照大鼠相比,显微镜下见AS模型大鼠斑块处的主动脉管壁增厚,平滑肌细胞增生,细胞排列紊乱[图1(b)]。
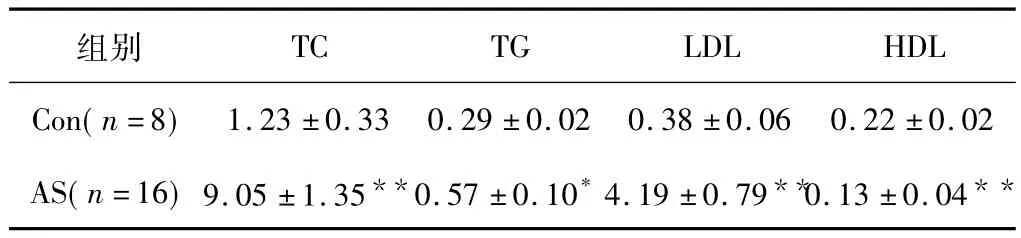
表3 动脉粥样硬化模型大鼠的血脂水平 mmol/LTable 3 Serum lipids profile of the AS model rats

图1 动脉粥样硬化模型大鼠主动脉的大体(a)和镜下切片(b)改变Figure 1. Gross and pathological changes of aortas in AS model rats
2.2 有氧运动对AS大鼠的体重和肾周脂肪量的影响Con组大鼠的体重始终保持增长,AS和EAS组大鼠的体重负增长,但EAS与AS组相比,大鼠的体重无显著性变化(表4)。与Con组相比,AS组的相对肾周脂肪量(肾周脂肪重量/体重的比值)无显著性差异;但EAS组大鼠的相对肾周脂肪量比Con组和AS组显著降低(图2)。
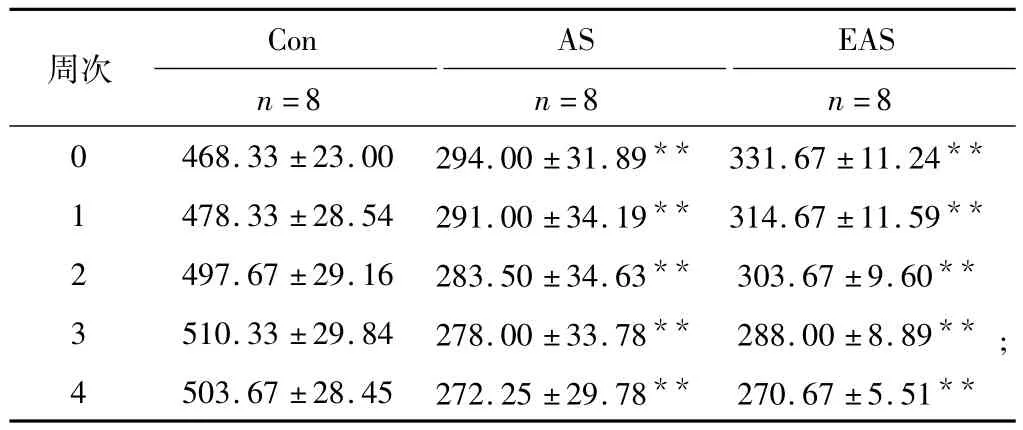
表4 4周有氧运动干预期间大鼠的体重变化 gTable 4 Difference of body weight between AS and EAS rats during 4 weeks exercise

图2 有氧运动降低动脉粥样硬化大鼠相对肾周脂肪的质量Figure 2. Aerobic exercise-induced decreases of perirena adipose/body weight ratio in AS rats
2.3 有氧运动对AS大鼠的空腹血糖和血清TG、TC、LDL和HDL的影响与Con组相比,AS造模大鼠(AS组和有氧运动干预前的EAS组)的空腹血糖均无显著性改变,在正常范围之内(图3)。有氧运动干预后的EAS组大鼠的空腹血糖与AS组无差别,且仍然在正常范围内。

图3 有氧运动不改变动脉粥样硬化大鼠的空腹血糖Figure 3. No change of fasting plasma glucose(FPG)between AS and EAS rats during 4 weeks exercise
4周有氧运动干预后,EAS组大鼠的血清TC、TG、LDL水平比AS组均显著降低,但仍高于Con组大鼠;而EAS组大鼠的血清HDL水平无显著变化(图4)。
2.4 有氧运动降低AS大鼠主动脉斑块的严重程度与AS组相比,EAS组大鼠主动脉的红色粥样硬化斑点较显著减少[图5(a)],且斑块处主动脉中膜的平滑肌细胞增生和排列紊乱显著改善[图5(b)]。
2.5 有氧运动降低AS大鼠的血清chemerin水平与Con组对比,AS组大鼠血清chemerin水平显著增加。4周有氧运动干预后,EAS组大鼠的血清chemerin水平显著降低,且降低至 Con组水平(图6)。
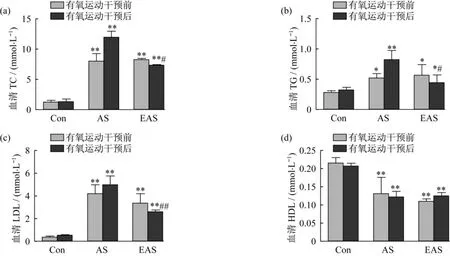
图4 有氧运动改善动脉粥样硬化大鼠的血脂水平Figure 4. Aerobic exercise-induced improvements of serum lipids in AS rats

图5 有氧运动减轻动脉粥样硬化大鼠主动脉斑块的严重程度Figure 5. Aerobic exercise-induced reduction of atherosclerosis severity of aorta in AS rats
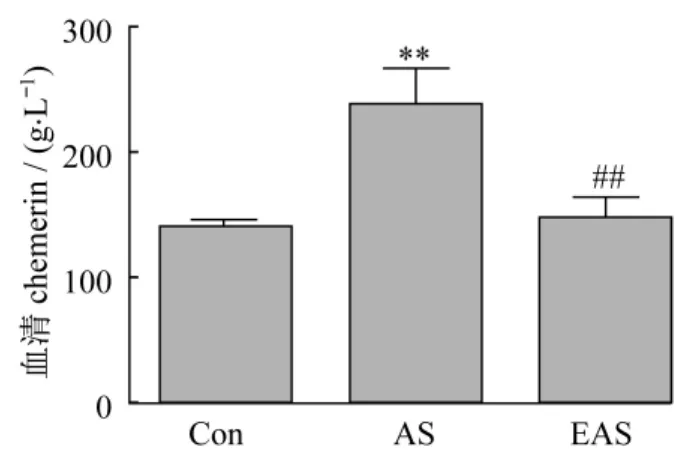
图6 有氧运动降低动脉粥样硬化大鼠的血清chemerin水平Figure 6. Aerobic exercise-induced retrieve of serum chemerin in AS rats
2.6 有氧运动降低AS大鼠肝chemerin的mRNA和蛋白水平与Con大鼠相比,AS组大鼠肝chemerin的mRNA[图7(a)]和蛋白[图7(b)]表达水平显著增加,而EAS组大鼠肝chemerin的mRNA和蛋白表达水平显著降低。

图7 有氧运动降低动脉粥样硬化大鼠肝chemerin的mRNA和蛋白表达水平Figure 7. Aerobic exercise-induced decreases of mRNA(A) and protein(B)levels of chemerin in the livers of AS rats
3 分析与讨论
作为一个趋化因子,chemerin促进多种表达其受体ChemR23的免疫细胞(巨噬细胞、未成熟的树突状细胞等)的募集和迁移[27],增强巨噬细胞与血管内皮的粘附,以及巨噬细胞在细胞间质的迁移[28],从而参与多种组织包括脂肪、肝、骨骼肌、胰岛和血管等的炎细胞浸润、黏附和迁移。除了促炎作用,chemerin在脂肪细胞的分化、脂肪分解和维持血糖稳态中也发挥重要作用[15,29]。ChemR23(chemerin的受体)基因敲除的小鼠较少发生严重的感染性疾病[29]的同时,脂肪的生成和糖耐量出现问题[30]、体重和肌肉重量减轻[31],这间接证明chemerin在调控炎症反应和糖脂代谢中起桥梁作用。chemerin能抑制脂肪的分解和肌肉等组织的糖摄取,导致胰岛素抵抗,在血糖和血脂的紊乱中发挥重要作用,且该作用可能与chemerin使调控糖、脂代谢的重要基因(如葡萄糖转运子4(GLUT4)、leptin和脂联素)的表达出现障碍有关[32]。
血清chemerin水平在肥胖及相关疾病如代谢综合征[11-12]、2型糖尿病[8,13-14]、AS[15-18]和冠心病[33]患者中显著增加,并与糖脂代谢的紊乱密切相关。肥胖患者减重手术后,伴随着显著的体重降低和糖脂代谢的改善,血浆 chemerin水平也显著降低[34],这证实了chemerin在肥胖患者糖脂代谢紊乱中的作用。chemerin在AS中的作用也得到较多文献的支持。如人体实验证实,在AS患者的血管外周脂肪、血管平滑肌细胞和泡沫细胞中检测到chemerin,且chemerin水平与AS的严重程度显著相关[35];冠状动脉粥样硬化心脏病(冠心病)患者的血清 chemerin水平显著升高[36],冠心病患者心包外膜的脂肪组织、冠状动脉斑块的泡沫细胞的chemerin基因高表达[37]。动物实验也证实,AS大鼠主动脉的chemerin基因表达水平显著增加[17]。在细胞水平上,chemerin能明显增加人巨噬细胞对胆固醇的摄取[38],以及促进THP-1源性巨噬细胞的胆固醇蓄积和巨噬细胞向泡沫细胞的转化[39]。上述人体和动物实验、在体和体外的研究均表明,高表达的chemerin促进AS的炎症反应,且与AS的严重程度有关。由于肝是血清chemerin的主要来源之一,故本文除了检测血清 chemerin水平,还检测了肝chemerin的mRNA和蛋白表达水平,证实了AS大鼠血清和肝的chemerin水平均显著升高,且与上述报道的结果一致。
周期性、中小运动强度的有氧运动有益于防治肥胖及其相关疾病,该作用至少部分与有氧运动的抗炎作用有关[40-42]。伴随着有氧运动改善糖脂代谢、提高胰岛素敏感性的同时,肥胖和糖尿病患者的炎症因子chemerin水平显著降低。如4个月[22,43]、甚至一次的有氧运动对肥胖患者[24]、1 a规律的中等强度行走对2型糖尿病患者[44]都有显著降低血浆chemerin水平的作用。本研究发现,AS大鼠的血脂异常(血清TC、TG和LDL升高,HDL降低都是AS的主要危险因素)和主动脉出现粥样硬化斑块的同时,血清和肝chemerin水平增加,而4周有氧运动改善AS大鼠的血脂、减少肾周脂肪和减轻AS程度的同时,血清和肝chemerin水平也降低,提示血清和肝chemerin的降低可能与有氧运动改善血脂、减少肾周脂肪和减轻主动脉AS程度有关。本文加深了对chemerin的认识,即在文献证实chemerin与有氧运动改善肥胖和2型糖尿病患者糖脂代谢有关的基础上,发现chemerin也与有氧运动改善AS的血脂、体脂和主动脉AS程度有关。
4 结束语
AS大鼠的血清chemerin、肝chemerin的mRNA和蛋白水平均显著升高。4周有氧运动改善AS大鼠的血脂、减少肾周脂肪量和减轻AS程度,这可能与其降低血清和肝的chemerin水平有关。
[1] Lumeng C N,SaltielA R.Inflammatory linksbetween obesity and metabolic disease[J].J Clin Invest,2011,121 (6):2111-2117
[2] McArdle M A,Finucane O M,Connaughton R M,et al.Mechanisms of obesity-induced inflammation and insulin resistance:Insights into the emerging role of nutritional strategies[J].Front Endocrinol(Lausanne),2013,4:52-54
[3] McClave S A,Frazier T H,Hurt R T,et al.Obesity,inflammation,and pharmaconutrition in critical illness[J].Nutrition,2014,30(4):492-494
[4] Forsythe L K,Wallace J M,Livingstone M B.Obesity and inflammation:The effects of weight loss[J].Nutr Res Rev,2008,21(2):117-133
[5] Wu M,Gu X,Li X,et al.C-Reactive protein and inflammatory cytokines during percutaneous coronary intervention[J].J Vasc Res,2016,53(1-2):39-48
[6] Nagpal S,Patel S,Jacobe H,et al.Tazarotene-induced gene 2(TIG2),a novel retinoid-responsive gene in skin[J].J Invest Dermatol,1997,109(1):91-95
[7] Wittamer V,Franssen J D,Vulcano M,et al.Specific recruitment of antigen-presenting cells by chemerin,a novel processed ligand from human inflammatory fluids[J].J Exp Med,2003,198(7):977-985
[8] Weigert J,NeumeierM,WanningerJ,etal.Systemic chemerin is related to inflammation rather than obesity in type 2 diabetes[J].Clin Endocrinol(Oxf),2010,72(3): 342-348
[9] Lehrke M,Becker A,Greif M,et al.Chemerin is associated with markersofinflammation and componentsofthe metabolic syndrome but does not predict coronary atherosclerosis[J].Eur JEndocrinol,2009,161(2):339-344
[10] Fulop P,Seres I,Lorincz H,et al.Association of chemerin with oxidative stress,inflammation and classical adipokines in non-diabetic obese patients[J].J Cell Mol Med,2014,18(7):1313-1320
[11] Li Y,Shi B,Li S.Association between serum chemerin concentrations and clinical indices in obesity or metabolic syndrome:A meta-analysis[J].PloS one,2014,9 (12):e113915
[12] Sledzinski T,Korczynska J,Hallmann A,et al.The increase of serum chemerin concentration is mainly associated with the increase of body mass index in obese,non-diabetic subjects[J].J Endocrinol Invest,2013,36(6):428-434
[13] Rourke J L,Dranse H J,Sinal C J.Towards an integrative approach to understanding the role of chemerin in human health and disease[J].Obes Rev,2013,14(3):245-262
[14] Yu S,Zhang Y,Li M Z,et al.Chemerin and apelin are positively correlated with inflammation in obese type 2 diabetic patients[J].Chin Med J(Engl),2012,125(19): 3440-3444
[15] Rhee E J.Chemerin:A novel link between inflammation and atherosclerosis?[J].Diabetes Metab J,2011,35(3):216-218
[16] Zhao D,Bi G,Feng J,et al.Association of serum chemerin levels with acute ischemic stroke and carotid artery atherosclerosis in a Chinese population[J].Med Sci Monit,2015,21:3121-3128
[17] 彭清,卢建刚,范忠才,等.动脉粥样硬化大鼠chemerin与炎症的相关性[J].中国动脉硬化杂志,2014,22(8): 789-794
[18] Herova M,Schmid M,Gemperle C,et al.Low dose aspirin is associated with plasma chemerin levels and may reduce adipose tissue inflammation[J].Atherosclerosis,2014,235 (2):256-262
[19] Nimmo M L,Viana,King.The effect of physical activity on mediators of inflammation[J].Diabetes Obes Metab,2013,15:51-60
[20] Hayashino Y,Jackson J L,Hirata T,et al.Effects of exercise on C-reactive protein,inflammatory cytokine and adipokine in patients with type 2 diabetes:A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J].Metabolism,2014,63(3): 431-440
[21] 林云,陈文鹤,肥胖症与动脉粥样硬化的关系研究进展[J].上海体育学院学报,2011,35(5):52-56
[22] Abbas Saremi1,Nader Shavandil,Mohammad Parastesh1,et al.Hassan Daneshmand2 M.Twelve-week aerobic training decreases chemerin level and improves cardiometabolic risk factors in overweight and obese men[J].Asian J Sports Med,2010,1(3):151-158
[23] Chakaroun R,Raschpichler M,Kloting N,et al.Effects of weight loss and exercise on chemerin serum concentrations and adipose tissue expression in human obesity[J].Metabolism,2012,61(5):706-714
[24] Lloyd J W,Evans K A,Zerfass K M,et al.Effect of an acute bout of aerobic exercise on chemerin levels in obese adults[J].Diabetes Metab Syndr,2016,10(1):37-42
[25] Herder C,Peltonen M,Koenig W,et al.Anti-inflammatory effect of lifestyle changes in the Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study[J].Diabetologia,2009,52(3):433-442
[26] 周永刚,蓝晓红,李祥,等.动脉粥样硬化大鼠实验模型的建立与评价[J].解放军药学学报,2011,27(5):399-403
[27] Parolini S,Santoro A,Marcenaro E,et al.The role of chemerin in the colocalization of N K and dendritic cell subsets into inflamed tissues[J].Blood,2007,109(9): 3625-3632
[28] Hart R,Greaves D R.Chemerin contributes to inflammation by promoting macrophage adhesion to VCAM -1 and fibronectin through clustering of VLA-4 and VLA-5[J].J Immunol,2010,185(6):3728-3739
[29] Ernst M C,Sinal C J.Chemerin:At the crossroads of inflammation and obesity[J].Trends Endocrinol Metab,2010,21(11):660-667
[30] Ernst M C,Haidl I D,Zuniga L A,et al.Disruption of the chemokine-like receptor-1(CMKLR1)gene is associated with reduced adiposity and glucoseintolerance[J].Endocrinology,2012,153(2):672-682
[31] Issa M E,Muruganandan S,Ernst M C,et al.Chemokinelike receptor 1 regulates skeletal muscle cell myogenesis[J].Am J Physiol Cell Physiol,2012,302(11):1621-1631
[32] Goralski K B,McCarthy T C,Hanniman E A,etal.Chemerin,a novel adipokine that regulates adipogenesis and adipocyte metabolism [J].The Journalofbiological chemistry,2007,282(38):28175-28188
[33] Leiherer A,Muendlein A,Kinz E,et al.High plasma chemerin is associated with renal dysfunction and predictive for cardiovascular events - Insights from phenotype and genotype characterization[J].Vascul Pharmacol,2016,77: 60-68
[34] Ress C,Tschoner A,Engl J,et al.Effect of bariatric surgery on circulating chemerin levels[J].Eur J Clin Invest,2010,40(3):277-280
[35] Kostopoulos C G,Spiroglou SG,Varakis J N,et al.Chemerin and CMKLR1 expression in human arteries and periadventitial fat a possible role for local chemerin in atherosclerosis[J].BMC Cardiovasc Disord,2014,14:56-58
[36] Yan Q,Zhang Y,Hong J,et al.The association of serum chemerin level with risk of coronary artery disease in Chinese adults[J].Endocrine,2012,41(2):281-288
[37] Gao X,Mi S,Zhang F,et al.Association of chemerin mRNA expression in human epicardial adipose tissue with coronary atherosclerosis[J].Cardiovasc diabetol,2011,10:87-88
[38] McCarthy T C,Zuniga L A,Zabel B A,et al.The novel adipokine chemerin significantly increases cholesterol uptake in human macrophages[J].The Faseb Journal,2008,22 (1):948-949
[39] 谢霆,刘陈桂,陈新忠,等.脂肪因子chemerin促进巨噬泡沫细胞形成[J].华中科技大学学报(医学版),2012,41(1):27-31
[40] Braam K I,van der Torre P,Takken T,et al.Physical exercise training interventions for children and young adults during and after treatment for childhood cancer[J].Cochrane Database Syst Rev,2016,3:CD008796
[41] Nimmo M A,Leggate M,Viana L,et al.The effect of physical activity on mediators of inflammation[J].Diabetes Obes Metab,2013,15(3):51-60
[42] Thompson D,Walhin J P,Batterham A M,et al.Effect of diet or diet plus physical activity versus usual care oninflammatory markers in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes:Theearlyactivity in diabetes(ACTID) randomized,controlled trial[J].J Am Heart Assoc,2014,3 (3):e000828
[43] Venojarvi M,Wasenius N,Manderoos S,et al.Nordic walking decreased circulating chemerin and leptin concentrations in middle-aged men with impaired glucose regulation[J].Ann Med,2013,45(2):162-170
[44] Neuparth M J,Proenca J B,Santos-Silva A,et al.The positive effect of moderate walking exercise on chemerin levels in portuguese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus[J].J Investig Med,2014,62(2):350-353
Effects of Chemerin on Aerobic Exercise-induced Improvements of Blood Lipid and Aortic Sclerosis in Atherosclerosis Rats
LIN Xiaojing, LU Lin,WANG Xiaohui
To investigate the effects of chemerin on aerobic exercise-induced improvements of blood lipid and aortic sclerosis in atherosclerosis(AS)rats.Methods:Thirty male SD rats were randomly divided into AS model group(n=20)and control group (Con,n=10),the former rats were fed with 8-week high fat diet after an intra-peritoneal injection of vitamin D3(600 thousand IU/kg body weight)to establish AS model rats while the latter fed with normal diet after an injection of the same amount of normal saline.The AS model rats were further randomly divided into 2 groups:AS group and exercise AS(EAS)group,8 rats in each group.The EAS rats participated in moderate intensity aerobic exercise on a treadmill with an increasing load for 4 weeks,6 days per week.The severity of AS were evaluated according to the plaques appeared in gross aortas stained with oil red O as well as the pathological changes of aortic paraffin section stained with HE.Blood lipid(serum levels of triglyceride(TG),total cholesterol (TC),low -density lipoprotein(LDL),and high density lipoprotein (HDL)) were detected using full automatic biochemical analyzer.Fasting glucose were determined by Roche glucometer.Serum levels of chemerin were measured by ELISA.The mRNA and protein expression of chemerin in livers were detected by real time PCR and Western blot,respectively.Results: 1)Successful establishment of AS model rats:compared with control,significant increases of serum levels of TC,TG and LDL as well as decrease of serum HDL were showed in the AS rats;and the atherosclerotic plaque appeared in the gross aortas and the proliferation and arrangement disorders of smooth muscle cells in aorta membrane were found in the AS rats.2)Compared with AS group,significant improvements of blood lipid(lower of TC,TG and LDL),as well as decreases of relative weight of perirenal adipose and AS severity(alleviations of gross and pathological disorders of aortas)were found in EAS rats.3)The serum chemerin as well as the mRNA and protein levels of chemerin in livers were significant higher in the AS rats than that of Con.4) The levels of chemerin in serum and livers were significant down-regulated in EAS rats compared with AS rats.Conclusions:1) The serum chemerin as well as the mRNA and protein levels of chemerin in livers were increased in AS rats.2)Aerobic exercise induced improvements of blood lipid and severity of AS in aortas,which may be associated with the decreases of chemerin in serum and livers.
inflammatory factor;chemerin;rat;atherosclerosis; aerobic exercise;blood lipid
G804.2
A
1000-5498(2017)04-0049-08
2016-12-16;
2017-02-27
国家自然科学基金资助项目(31271274)
林小晶(1990-),女,福建宁德人,上海体育学院硕士研究生;Tel.:(021)51253520,E-mail:flyjjing@ 163.com
王晓慧(1972-),女,江苏淮安人,上海体育学院教授,博士生导师;Tel.:(021)51253520,E-mail: wangpan96@126.com
DOI10.16099/j.sus.2017.04.009

