脑电双频指数用于监测颅脑手术病人镇静深度的可行性:与非颅脑手术的比较
张海静 菅敏钰 张利勇 景龙年 彭宇明 韩如泉
(首都医科大学附属北京天坛医院麻醉科,北京 100050)
· 临床研究 ·
脑电双频指数用于监测颅脑手术病人镇静深度的可行性:与非颅脑手术的比较
张海静 菅敏钰 张利勇 景龙年 彭宇明 韩如泉*
(首都医科大学附属北京天坛医院麻醉科,北京 100050)
目的 比较脑电双频指数(bispectral index,BIS)用于颅脑和非颅脑手术病人监测麻醉深度的差异,探讨BIS监测颅脑手术病人镇静深度的可行性。方法 择期全身麻醉下行幕上入路颅内肿瘤切除术病人25例,美国麻醉医师协会(American Society of Anesthesiologists,ASA)Ⅰ-Ⅲ级,椎管内肿瘤切除术病人25例作为对照。入室后按标准电极贴敷方法连接右侧额部BIS监测。采取相同血浆浓度丙泊酚靶控输注,记录诱导前、切皮、去骨瓣、剪硬膜、切瘤、止血、睁眼时BIS值,比较两组BIS值差异是否存在统计学意义。结果 两组病人人口学指标差异无统计学意义。相同血浆浓度下,血压、心率差异无统计学意义,颅内肿瘤组和椎管肿瘤组BIS值结果:诱导前(93.0±4.2vs92.8±4.1)、切皮后(39.3±7.3vs38.6±6.7)、去骨瓣(39.0±7.2vs39.1±6.1)、剪硬膜后(37.4±7.1vs39.7±7.4)、切瘤(38.8±8.2vs39.9±5.5)、止血(39.9±11.0vs41.5±5.2)、睁眼后(81.2±5.8vs80.8±4.6),两组差异均无统计学意义(P<0.05),相同丙泊酚血浆浓度下,颅脑和非颅脑手术病人BIS监测镇静深度结果差异无统计学意义。结论 BIS监测可以有效地应用于全身麻醉下颅内肿瘤病人手术中镇静深度监测。
脑电双频指数;神经外科麻醉;脑电图
脑电双频指数(bispectral index,BIS)已经成为判断全身麻醉下麻醉镇静深度的金标准。BIS来源于原始脑电,经过功率谱分析、双谱分析、近暴发抑制及抑制分析去寻求脑电在麻醉镇静中的特征,最终产生BIS[1]。目前,丙泊酚诱导下颅内肿瘤对BIS的影响存在争议[2-3],另外,在创伤性脑损伤,脑电会发生变化[4-5]。因而笔者假设颅脑手术在去骨瓣、剪硬膜后以及切除肿瘤中,颅内压、脑血流变化以及脑实质发生塌陷移位,此时BIS监测仪位于前额的脑电电极获取的原始脑电已发生变化,进而脑电参数发生变化,最终影响BIS。通过比较同等麻醉药物浓度下颅脑和非颅脑肿瘤切除术中BIS值的差异,探讨BIS用于颅内肿瘤病人监测镇静深度的准确性。
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
研究选择择期全身麻醉下行幕上入路颅内肿瘤切除术病人25例,按年龄、性别、体质量指数、美国麻醉医师协会(American Society of Anesthesiologists,ASA)分级匹配选择行椎管内肿瘤切除术病人25例,年龄18~60岁,ASAⅠ~Ⅲ级。排除既往中枢神经系统疾病、抑郁、癫痫、脑血管疾病、颅脑手术史者;排除心、肝、肾功能障碍及术中功能监测不能应用肌肉松弛药者。本研究获首都医科大学附属北京天坛医院伦理委员会批准。
1.2 麻醉方法
病人入室后,常规记录无创血压、心电图、血氧饱和度、呼气末二氧化碳浓度、体温、四个成串刺激(train of four,TOF)肌松监测。麻醉诱导前用乙醇擦拭皮肤,待乙醇挥发后,将BIS监测仪电极片(BIS-TM Quatro Sensors, Aspect Medical Systems USA 186-0106)置于病人右侧前额部。舒芬太尼0.3~0.5 μg/kg、靶控输注丙泊酚,血浆药物浓度初始4 μg/mL(marsh模型),顺阿曲库铵0.2 mg/kg,气管插管后机械通气, 麻醉维持丙泊酚血浆药物浓度3 μg/mL, 顺阿曲库铵0.06 mg·kg-1·h-1, 瑞芬太尼0.15~0.2 μg·kg-1·min-1, 维持血流动力学稳定,维持PETC0235~45 mmHg(1 mmHg=0.133 kPa)、T4/T1<25%(TOF),术前及切除肿瘤中行动脉血气分析。BIS监测仪维持电极阻抗 <5 000 Ω,Bislog时间窗为1 min(包括MAX、MIN、MEAN、SQI、EMG),阵发性肌电活动增高归为假数据,相应的BIS值不纳入数据分析。
1.3 观察指标
由监测仪拷贝BIS数据,取诱导前(T1)、切皮(T2)、去骨瓣(T3)、剪硬膜(T4)、切瘤(T5)、止血(T6)、睁眼(T7)7个时间点5 min的BIS值的均值作为各时间点的BIS数值。各个时间点的循环数据由监护仪拷贝。
1.4 统计学方法
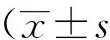
2 结果
2.1 两组病人一般资料比较
颅内肿瘤切除术组和推管内肿瘤切除术组病人性别组成、年龄、体质量、身高差异均无统计学意义,详见表1。
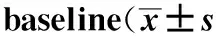
表1 两组病人基本特征Tab.1 Characteristics of the patients at )
2.2 两组病人术中血压、心率变化情况比较
相同血浆浓度下,2组病人相同时间点平均动脉压(mean arterial pressure, MAP)、心率(heart rate, HR)差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),详见表2。
2.3 颅内肿瘤和非颅内肿瘤病人BIS比较
两组病人各个时间点的BIS值差异无统计学意义,详见表3。
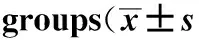
表2 两组病人术中血压心率变化情况Tab.2 Comparative changes in intraoperative hemodynamic values between two )
△1 mmHg=0.133 kPa; T1:before induction of anesthesia; T2:after incision; T3:craniotomy; T4:dura opening; T5:during tumor resection; T6:hemostasis; T7:spontaneous eye opening; MAP:mean arterial pressure; HR:heart rate.
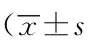
表3 颅内肿瘤和非颅内肿瘤病人BIS比较Tab.3 Comparison of BIS between two groups ,n=25)
BIS:bispectral index; T1:before induction of anesthesia; T2:after incision; T3:craniotomy; T4:dura opening; T5:during tumor resection; T6:hemostasis; T7:spontaneous eye opening.
3 讨论
BIS在1996年被美国食品和药物管理局(Food and Drug Administration, FDA)批准作为唯一用于检测麻醉效果的手段,广泛应用于意识状态评价,成为判断全身麻醉下麻醉镇静深度的金标准。BIS来自于原始脑电图(electroencephalogram, EEG)信号,滤除干扰(心电、起搏器脉冲、眼动等),监测时域信号漂移情况,检测突发抑制时域参数(“QUAZI”“BSR”),经过功率谱分析、双谱分析、接近突发抑制及抑制分析去寻求脑电在麻醉镇静中的特征,最终产生BIS[1]。
BIS与许多麻醉药物浓度良好相关。Ibrahim等[6]比较了BIS监测丙泊酚、七氟烷和咪达唑仑镇静深度,认为BIS与丙泊酚相关性最好。大脑皮质与基底神经节之间,是由运动神经回路和联合回路连接的,而将尾部与联合区域的输入与基底神经节的输出连接起来的联合回路在大脑皮质前额叶区域表现的尤为突出[7],因而将电极置于额部,BIS值相对平稳,不易受到干扰。但在开颅术中随着骨瓣去除、剪硬膜后颅内压、脑血流随之变化以及肿瘤切除术中脑实质的塌陷,原始脑电可能发生变化或者远离脑实质的BIS电极截取的脑电信号已发生改变,最终都可能使BIS值与镇静深度一致性产生差异,即颅脑术中BIS监测的准确性存疑。本研究结果显示相同丙泊酚血浆浓度,清醒时、麻醉手术中以及苏醒后各时间点,颅脑和非颅脑手术病人术中BIS值差异无统计学意义,脑电双频指数可应用于颅脑手术病人,有效的判断镇静深度。Sahinovic等[3]在丙泊酚诱导下比较额叶肿瘤和非颅脑肿瘤病人BIS值,在意识消失和恢复时,两者BIS值无差异,与本研究结果一致。
术中肌松药、阿片类药等相关药物的应用可能是影响结果的因素。Greif等[8]应用TOF研究不同肌松水平与BIS值的关系,结果显示BIS值不受肌松水平或肌电活动的影响。 肌松药对BIS值的影响与镇静深度有关,在无伤害性刺激时,肌电活动对BIS影响主要发生在清醒期和较浅的镇静状态时,随着镇静深度的增加其影响逐渐减弱[9-10]。当病人处于深度镇静时,肌肉的紧张度已降低,对维持大脑兴奋状态的作用很小,同时头面部肌肉的自主活动也减弱,此时使用肌松药对肌电活动的影响有限,BIS则不再出现明显变化[11]。本研究术中麻醉稳定期(切皮至缝硬膜前)肌肉松弛药物对BIS无明显影响,而缝硬膜时停止使用肌松药,手术结束所需时间不同,两组病人苏醒期肌松药物的代谢程度可能不同,即睁眼时颅内肿瘤组和非颅内肿瘤组肌电活动性可能不同。
相关研究[12-13]表明阿片类药物对术中BIS值无影响。在丙泊酚持续静脉靶控输注时,阿片类受体激动剂能减少伤害性刺激引起的BIS值增加[14-15]。阿片类药物在镇痛浓度时,仅有极小的镇静或遗忘作用,大脑皮质没有或者仅微小的脑电改变,即阿片类药物抑制伤害性刺激条件下,对BIS无明显影响。
颅脑手术和椎管内肿瘤切除术,两者的手术时间、药物使用总剂量、刺激强度以及手术仪器的应用等存在差异,可能影响研究结果。
总之,相同丙泊酚血浆浓度下,颅脑和非颅脑手术病人镇静深度(BIS值)无差异,即BIS监测可以有效地应用于颅内肿瘤病人丙泊酚镇静深度监测。
[1] 乐建威,莫国民,林敏. 麻醉镇静深度的脑电双谱指数监护技术[J].中国医疗器械杂志,2005,29(5): 321-324.
[2] Ferreira D A, Nunes C S, Lobo F, et al. Brain tumors may alter the relationship between bispectral index values and propofol concentrations during induction of anesthesia[J]. J Clin Anesth, 2008, 20(2): 116-121.
[3] Sahinovic M M, Beese U, Heeremans E H, et al. Bispectral index values and propofol concentrations at loss and return of consciousness in patients with frontal brain tumours and control patients[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2014, 112(1): 110-117.
[4] Schmitt S, Dichter M A. Electrophysiologic recordings in traumatic brain injury[J]. Handb Clin Neurol, 2015, 127: 319-339.
[5] Hartings J A, Wilson J A, Hinzman J M, et al. Spreading depression in continuous electroencephalography of brain trauma[J]. Ann Neurol, 2014, 76(5): 681-694.
[6] Ibrahim A E, Taraday J K, Kharasch E D. Bispectral index monitoring during sedation with sevoflurane, midazolam, and propofol[J]. Anesthesiology, 2001,95(5): 1151-1159.
[7] 张连毅,郑崇勋. 基于α波自相关特性的麻醉深度监测[J]. 航天医学与医学工程, 2007, 20(4): 289-293.
[8] Greif R, Greenwald S, Schweitzer E, et al. Muscle relaxation does not alter hypnotic level during propofol anesthesia[J]. Anesth Analg, 2002, 94(3): 604-608. table of contents.
[9] Schuller P J, Newell S, Strickland P A, et al. Response of bispectral index to neuromuscular block in awake volunteers[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2015, 115 Suppl 1: i95-i103.
[10]Yue H, Han J, Liu L, et al. Effect of rocuronium on the bispectral index under anesthesia and tracheal intubation[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2016, 12(6): 3785-3789.
[11]沈亮言,谢言虎,方才.肌松药对脑电双频指数监测麻醉深度的影响[J]. 国际麻醉学与复苏杂志, 2010, 31(4): 372-374.
[12]Nakayama M, Ichinose H,Yamamoto S, et al. The effect of fentanyl on hemodynamic and bispectral index changes during anesthesia induction with propofol[J]. J Clin Anesth, 2002,14(2): 146-149.
[13]Yufune S, Takamatsu I, Masui K, et al. Effect of remifentanil on plasma propofol concentration and bispectral index during propofol anaesthesia[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2011,106(2): 208-214.
[14]Brocas E, Dupont H, Paugam-Burtz C, et al. Bispectral index variations during tracheal suction in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients: effect of an alfentanil bolus[J]. Intensive Care Med, 2002, 28(2): 211-213.
[15]Yoo K Y, Jeong C W, Park B Y, et al. Effects of remifentanil on cardiovascular and bispectral index responses to endotracheal intubation in severe pre-eclamptic patients undergoing caesarean delivery under general anaesthesia[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2009, 102(6): 812-819.
编辑 陈瑞芳
The feasibility of bispectral index for monitoring the depth of anesthesia in patients undergoing craniotomy: comparison of non-intracranial tumor surgery
Zhang Haijing, Jian Minyu,Zhang Liyong, Jing Longnian, Peng Yuming, Han Ruquan*
(DepartmentofAnesthesiology,BeijingTiantanHospital,CapitalMedicalUniversity,Beijing100050,China)
Objective To compare the difference of bispectral index (BIS) between intracranial tumor and non-intracranial tumor patients under general anesthesia with the same target-controlled infusion (TCI) propofol and to investigate the feasibility of BIS to monitor the sedation level of intracranial tumor patients under general anesthesia.Methods Twenty-five patients scheduled for elective intracranial tumor resection by under general anesthesia were enrolled in the study, ASA I-Ⅲ. And 25 subjects with spinal tumors were included as controls. We placed BIS sensor on the frontal area. The patients were anesthetized with the same TCI propofol and BIS values were collected before the induction of anesthesia, after incision, craniectomy, dura opening,during tumor resection,hemostasis,spontaneous eye opening. We compared the difference of BIS between intracranial tumor and non-intracranial tumor group. Results At the same Cp,BIS values were not statistically different between intracranial tumor group and non-intracranial tumor group:before induction of anesthesia(93.0±4.2vs92.8±4.1);after incision(39.3±7.28vs38.6±6.7); craniotomy (39.0±7.2vs39.1±6.1); dura opening(37.4±7.1vs39.7±7.4); during tumor resection (38.8±8.2vs39.9±5.5); hemostasis(39.9±11.0vs41.5±5.2); spontaneous eye opening(81.2±5.8vs80.8±4.6). Conclusion The BIS values can accurately reflect the actual level of consciousness of intracranial tumor patients under general anesthesia with TCI propofol.
bispectral index;neurosurgical anesthesia; electroencephalography
北京市医院管理局“扬帆计划”重点医学方向(ZYLX201708), 首都卫生发展科研专项重点攻关项目(2016-1-20410)。This study was supported by Clinical Medicine Development of Special Funding Support from Beijing Municipal Administration of Hospitals(ZYLX201708), Capital Development Research Found Project(2016-1-20410).
时间:2017-06-09 17∶25 网络出版地址:http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3662.r.20170609.1725.004.html
10.3969/j.issn.1006-7795.2017.03.024]
R614
2017-01-24)
*Corresponding author, E-mail:ruquan.han@gmail.com

