石家庄市冬季大气颗粒物中水溶性离子与重金属成分研究
张鉴达,周美玲,杨小雨,康全影,于国强
(1.河北师范大学资源与环境科学学院,河北石家庄 050024;2.河北省环境演变与生态建设重点实验室,河北石家庄 050024;3.河北省环境科学研究院,河北石家庄 050000)
石家庄市冬季大气颗粒物中水溶性离子与重金属成分研究
张鉴达1,2,周美玲1,2,杨小雨1,2,康全影3,于国强1,2
(1.河北师范大学资源与环境科学学院,河北石家庄 050024;2.河北省环境演变与生态建设重点实验室,河北石家庄 050024;3.河北省环境科学研究院,河北石家庄 050000)
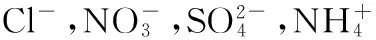
大气污染防治工程;石家庄市;大气颗粒物;重金属;离子
从以上研究可以看出,国内外对于大气颗粒物化学组分的研究主要集中在PM2.5中无机元素、重金属、水溶性无机离子以及有机物等的研究。但是关于石家庄市大气颗粒物中的水溶性离子和重金属含量的报道较少,本文针对石家庄市大气颗粒物PM10和PM2.5中水溶性离子和重金属含量以及相关性进行了分析研究,以期为石家庄市的空气污染防治提供依据。
1 采样和分析
1.1 样品采集
大气采样点设置在河北师范大学校园内(东经114 °10′,北纬37°59′),采样点周边无大型高层建筑遮挡,环境较洁净。大气采样器采用武汉天虹智能仪表厂提供的TH-150型中流量采样器,流量为100 L/min,采样器上放置PM10和PM2.5的切割器,采样滤膜为90 mm石英纤维滤膜(英国Whatman公司提供),采样前将滤膜放置于恒温恒湿环境中24 h,采样时间为2015-01-05到2015-01-18,每天采样时间不少于20 h。
1.2 样品处理与分析
将滤膜样品剪碎后放置于塑料试管中,加入10 mL去离子水后采用超声振荡60 min,取上清液经0.22 μm滤膜过滤器过滤后进入离子色谱进行分析。对样品的阳离子分析采用美国戴安公司提供的Dionex 600型离子色谱仪,CS12A 分离色谱柱和CSRS 抑制器,使用20 mmol/L的甲磺酸溶液作为淋洗液,流速为1 mL/min;阴离子分析采用ASRS抑制器(美国戴安公司提供),AS14分离柱,3.5 mmol/L的Na2CO3作为淋洗液。
滤膜样品的重金属分析(Cr,Cu,Zn,Cd,Pb,Ni)采用ICP-MS(Agilent 7500a,美国安捷伦科技有限公司提供)测定。用HNO3-HClO4方法进行消解,将滤膜样品剪碎后放置于烧杯中,加入20 mL的HNO3和2 mL的HClO4(均由美国Sigma公司提供),在加热板上消化分解,将溶液蒸发完以后冷却,加纯净水过滤后定容至25 mL待测。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 重金属与水溶性离子的质量浓度
2015-01-05到2015-01-18石家庄市大气PM10和PM2.5中6种重金属元素和8种水溶性离子的平均质量浓度水平见表1。
表1 石家庄市大气颗粒物中重金属和水溶性离子的质量浓度
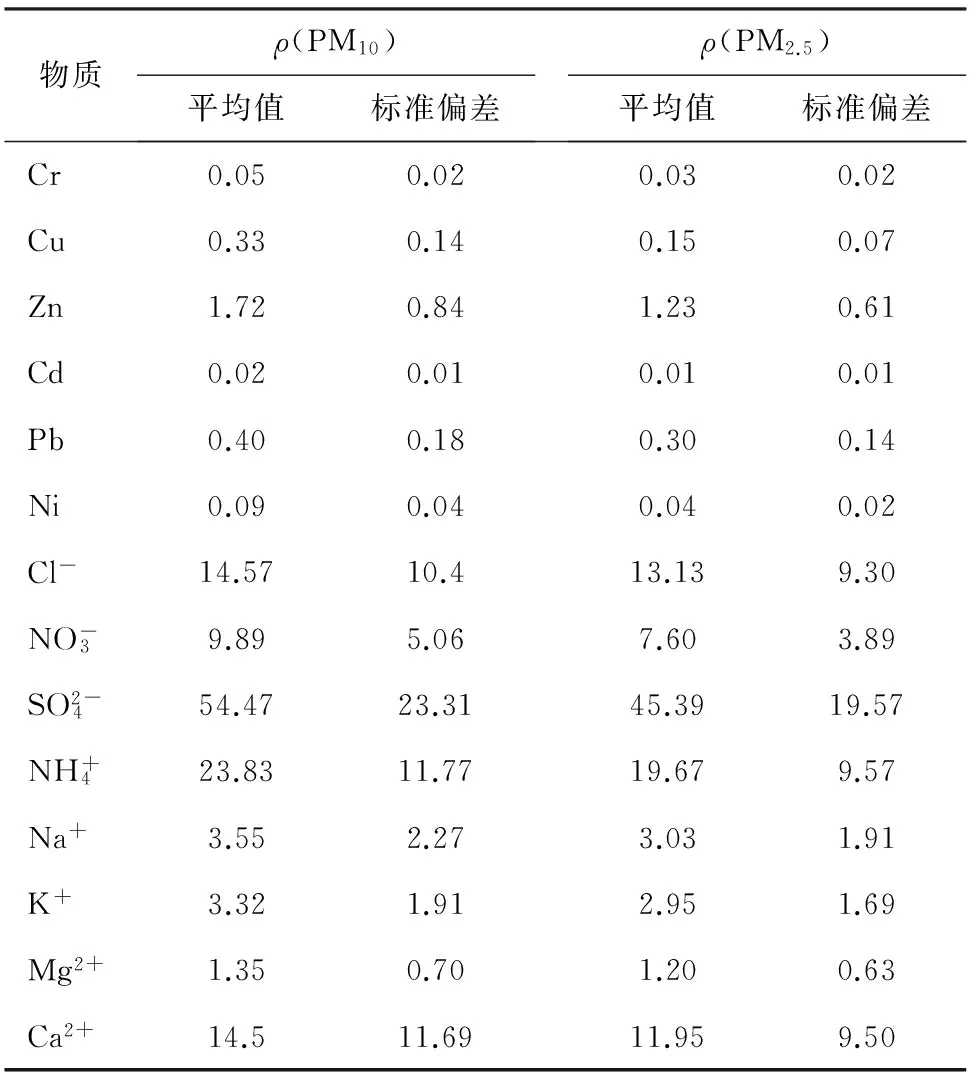
Tab.1 Water soluble inorganic ions and heavy metal in different diametric atmospheric particles in Shijia- zhuang City μg/m3
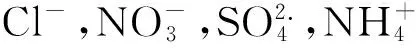
2.2 水溶性离子的相关性分析
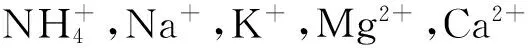

表2 PM10中水溶性离子相关性分析
注:**表示P<0.01时极显著相关。

表3 PM2.5中水溶性离子相关性分析
注:**表示P<0.01时极显著相关。
2.3 重金属的相关性分析
PM10和PM2.5样品中重金属含量的相关性分析结果见表4和表5。大气颗粒物中重金属相关性分析是确定大气颗粒物中重金属来源的依据之一,如:重金属中汽车尾气排放和冶金行业的特征元素是Pb和Cu,石油燃烧表征元素是Ni,Cd和Cr可认为是煤燃烧的特征元素,Zn是焚烧垃圾和轮胎磨损的特征元素。由表4和表5可以看出,PM10和PM2.5样品中重金属的相关性基本一致,Cr和Ni的相关性较好,表明其可能来源于同一污染源,Cu,Zn和Ni之间的显著性相关说明这3个元素有可能同源,原因很可能是交通运输需要消耗大量的燃油且伴随轮胎的磨损,会同时释放出Cu,Zn,Ni等元素。
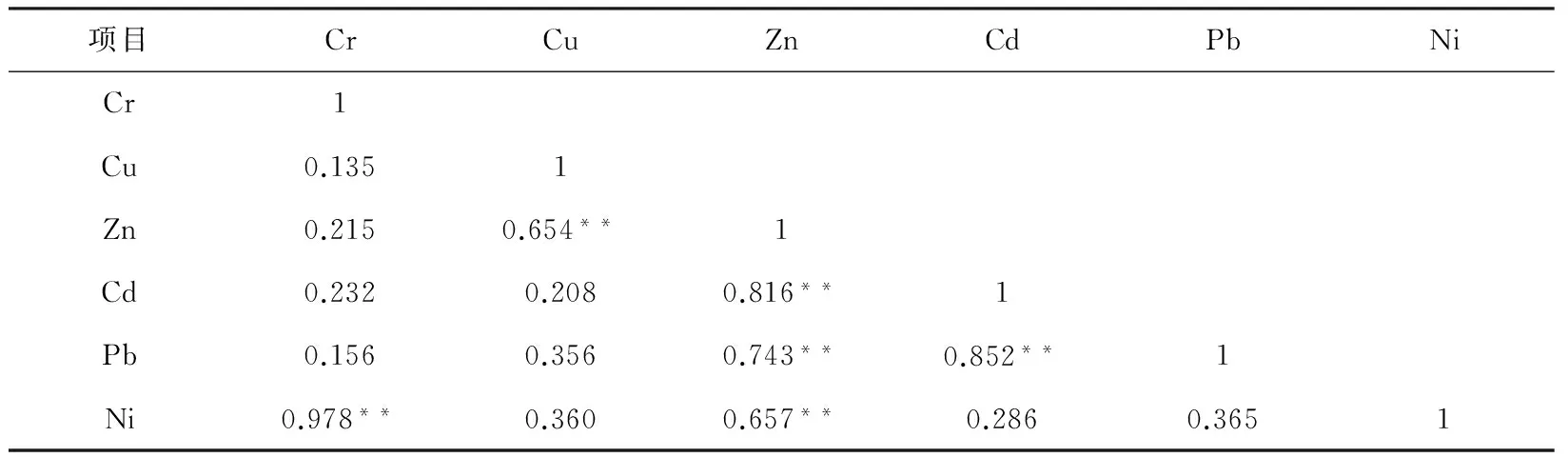
表4 PM10中各重金属元素间的相关性分析
注:**表示P<0.01时极显著相关。
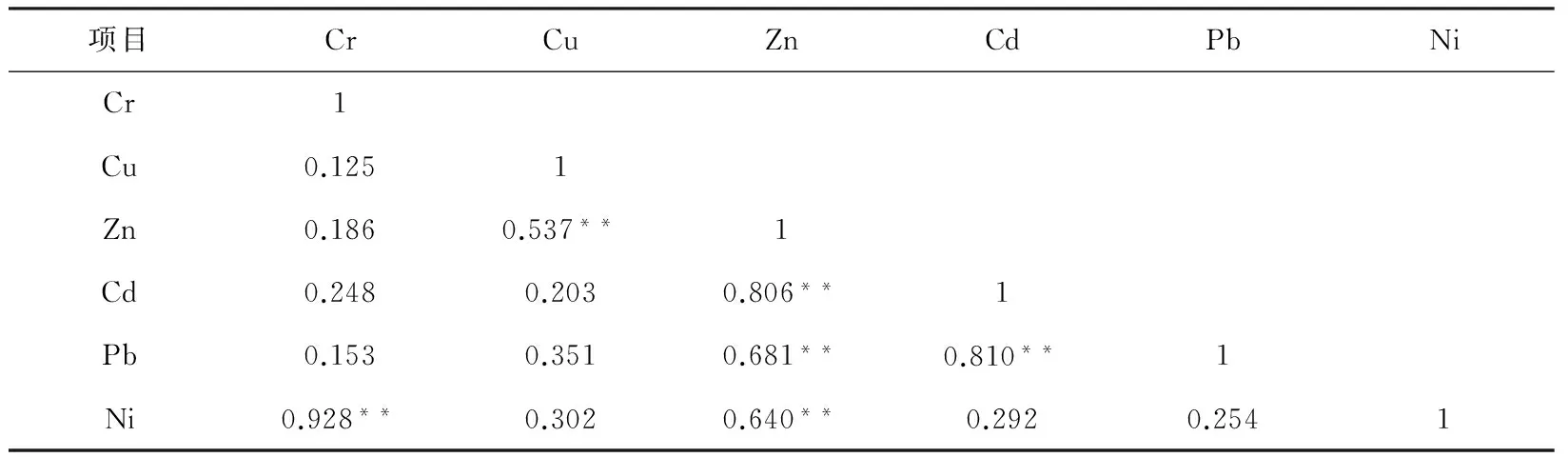
表5 PM2.5中各重金属元素间的相关性分析
注:**表示P<0.01时极显著相关。
3 结 论
本文通过对石家庄市冬季大气颗粒物中PM10和PM2.5中水溶性离子和重金属进行采样分析,得到如下结论。
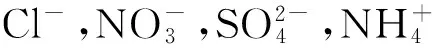

3)PM10和PM2.5样品中重金属的相关性基本一致,Cr和Ni的相关性较好,表明可能来源于同一污染源,Cu,Zn和Ni之间的显著性相关说明这3个元素有可能同源。
/References:
[1] 张夏琨,王春玲,王宝鉴.气象条件对石家庄市空气质量的影响[J].干旱气象,2011,29(1):42-47. ZHANG Xiakun, WANG Chunling, WANG Baojian. Influence of meteorological condition on air quality over Shijiazhuang of Hebei Province [J].Journal of Arid Meteoro-logy, 2011,29(1):42-47.
[2] 孙霞,银燕,孙玉稳,等.石家庄地区春季晴、霾天气溶胶观测研究[J].中国环境科学,2011,31(5):705-713. SUN Xia, YIN Yan, SUN Yuwen, et al. An observational study of aerosol particles over Shijiazhuang area in clean and hazy days during spring [J]. China Environmental Science, 2011,31(5):705-713.
[3] 胡引翠,孙凯军,王国舟,等.石家庄市环境治理措施对大气质量的影响[J].安徽农业科学,2011,39(1):402-404. HU Yincui, SUN Kaijun, WANG Guozhou, et al. Impact of urban environmental measures on atmospheric quality in Shijiazhuang City[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences, 2011,39(1):402-404.
[4] 魏巍,王丽涛,潘雪梅,等.河北城市霾污染来源的模拟研究[J].环境科学与技术,2013,36(2):116-119. WEI Wei, WANG Litao, PAN Xuemei, et al. Simulation study of haze pollution sources in cities of Hebei Province[J].Environmental Science & Technology,2013,36(2):116-119.
[5] 徐曼,张璇,张晓彤.石家庄冬季典型重污染过程分析[J].河北工业科技,2015,32(4):364-370. XU Man, ZHANG Xuan, ZHANG Xiaotong. Analysis of typical heavy pollution episode in winter in Shijiazhuang City[J]. Hebei Journal of Industrial Science and Technology, 2015,32(4):364-370.
[6] LONG R W, EATOUGH N L, MANGELSON N F, et al. The measurement of PM2.5, including semi-volatile components, in the EMPACT program: Results from the Salt Lake City study[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2003, 37(31): 4407-4417.
[7] RINEHART L R, FUJITA E M, CHOW J C, et al. Spatial distribution of PM2.5associated organic compounds in central California[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2006,40(2): 290-303.
[8] ARX H V, GOTSCHI T, ACKERMANN-LIEBRICH U,et al. PM2.5and NO2assessment in 21 European study centres of ECRHS Ⅱ: Annual means and seasonal differences[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2004, 38(13): 1943-1953.
[9] DZUBAY T G, STWVENS R K, LEWIS C W, et al. Visibi-lity and aerosol composition in Houston[J]. Environment Science and Technology, 1982,16(8): 514-524.
[10]BARTHELMIE R J, PRYOR S C. Implications of ammonia emissions for fine aerosol formation and visibility impairment case study from the lower Fraser Valley, British Columbia[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 1998,32(3):345-352.
[11]于凤莲,刘东贤,胡英.有关气溶胶细粒子对城市能见度影响的研究[J].气象科技,2002,30(6):379-383. YU Fenglian, LIU Dongxian, HU Ying. The study of aerosol fine particle impact on urban visibility[J].Meteorological Science and Technology, 2002,30(6):379-383.
[12]SISLER J F, MALM W C. Characteristics of winter and summer aerosol mass and light extinction on the Colorado Plateau[J]. Journal of the Air Waste Management Association, 1997,47(3):317-330.
[13]CHU S H, PAISIE J W. An evaluation of current PM2.5conditions in the US[J]. Atmospheric Environment, 2006,40(2): 206-211.
[14]SEINFELD J H, PANDIS S N. Atmospheric Chemistry and Physics-From Air Pollution to Climate Change[M]. 2nd ed. New York: John Wiley & Sons Inc, 2006.
[15]路娜,周静博,李志国,等.中国雾霾成因及治理对策[J].河北工业科技,2015,32(4):371-376. LU Na, ZHOU Jingbo, LI Zhiguo, et al. Causes and solutions of haze in China[J]. Hebei Journal of Industrial Science and Technology,2015,32(4):371-376.
[16]MIGUEL E D, LLAMAS J F, CHACONE E, et al. Sources and pathways of trace elements in urban environments: A multi-elemental qualitative approach[J]. The Science of the Total Environment, 1999, 235(1):355-357
[17]古金霞,董海燕,吴丽萍,等.天津市PM2.5中无机元素污染特征及来源分析[J].公路交通科技(应用技术版),2010(10):495-500.
[18]杨复沫,贺克斌,马永亮,等.北京市大气PM2.5中矿物成分的污染特征[J].环境科学,2004,25(5):26-30. YANG Fumo, HE Kebin, MA Yongliang, et al. Characteristics of mineral component in ambient PM2.5in Beijing[J].Environmental Science, 2004,25(5):26-30.
[19]温新欣.济南市环境空气细颗粒物(PM10和PM2.5)污染特征研究[D].济南:山东大学,2009. WEN Xinxin. Study on the Pollution Characteristics of Airborne Fine Particulate Matter (PM10and PM2.5) in Jinan [D].Jinan: Shandong University, 2009.
[20]LIN J J.Characterization of water-soluble ion species in urban ambient particles[J]. Environmental International, 2002,28(1/2):55-61.
[21]王静,高晓梅,寿幼平,等. 济南春季大气PM2.5水溶性组分的半连续在线观测[J]. 中国环境科学,2010,30(1):18-24. WANG Jing, GAO Xiaomei, SHOU Youping, et al. Semi-continuous analysis on the water-soluble inorganic ions of PM2.5in spring in Jinan City[J].China Environmental Science, 2010,30(1):18-24.
[22]薛立杰,苏领彦,吴少伟,等.北京市大气PM2.5中四种水溶性阴离子的水平变化比较[J].生态环境学报,2011,20(8):1315-1319. XUE Lijie, SU Lingyan, WU Shaowei, et al. Comparison of levels of four water-soluble ionic species in ambient PM2.5in Beijing[J].Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2011,20(8):1315-1319.
[23]古金霞,吴丽萍,霍光耀,等.天津市PM2.5中水溶性无机离子污染特征及来源分析[J].中国环境监测,2013,29(3):30-34. GU Jinxia, WU Liping, HUO Guangyao, et al. Pollution character and source of water-soluble inorganic ions in PM2.5over Tianjin[J]. Environmental Monitoring in China, 2013,29(3):30-34.
[24]OSADA K, KIDO M, NISHITA C, et al. Changes in ionic constituents of free tropospheric aerosol particles obtained at Mt. Norikura (2 700 m a.s.l.), central Japan, during the Shurin period in 2000[J].Atmospheric Environment, 2002, 36(35):5469-5477.
[25]李粟,苗海斌,康富华. 石家庄市春季PM10和PM2.5浓度及其水溶性离子组分特征分析[J].河北工业科技,2015, 32(1):90-94. LI Su, MIAO Haibin, KANG Fuhua. Analysis of mass concentration and water soluble ionic components characteristics of PM10and PM2.5in spring in Shijiazhuang City[J]. Hebei Journal of Industrial Science and Technology, 2015,32(1):90-94.
Study on water soluble ions and heavy metals in atmospheric particulates in winter in Shijiazhuang City
ZHANG Jianda1,2, ZHOU Meiling1,2, YANG Xiaoyu1,2, KANG Quanying3, YU Guoqiang1,2
(1.College of Resources and Environmental Science, Hebei Normal University, Shijiazhuang, Hebei 050024, China; 2. Hebei Key Laboratory of Environmental Change and Ecological Construction, Shijiazhuang, Hebei 050024, China; 3. Hebei Academy of Environmental Sciences, Shijiazhuang, Hebei 050000,China)
In order to study the composition of atmospheric particulates in Shijiazhuang, PM10and PM2.5samples are collected in Shijiazhuang in January, 2015. Ion chromatography and ICP-MS are used to determine the contents of 8 kinds of water soluble ions and 6 kinds of heavy metal elements. The results show that the concentrations of Cr, Cu, Zn, Cd, Pb, Ni in PM10are in the range of 0.02~1.72 μg/m3. The average concentration of water-soluble inorganic ions is 125.5 μg/m3, and Cl-, NO-3, SO2-4and NH+4are the main components, whose ion mass fraction are 11.6%, 7.8%, 43.4% and 19.0%, a total of 81.8%. The concentration range of 6 kinds of heavy metals in PM2.5is 0.01~1.23 μg/m3, and the average concentration of water-soluble inorganic ions is 104.9 μg/m3. Cl-, NO3, SO2-4and NH+4are the main components, whose ion mass fraction are 12.5%, 7.2%, 43.3% and 18.7%, a total of 81.7%. NH+4has good correlation with SO2-4in PM10and PM2.5, and NH+4may exist mainly as sulfate. The correlation of heavy metals in PM10and PM2.5samples is basically the same. The correlation between Cr and Ni is good and may be derived from the same source, and the significant correlation between Cu, Zn and Ni indicates that these three elements are likely to be homologous.
air pollution prevention and control engineering; Shijiazhuang City; atmospheric particulate matter; heavy metals; ions
1008-1534(2017)03-0202-06
2017-04-13;
2017-04-27;责任编辑:王海云
国家自然科学基金(41401562);河北省高等学校青年拔尖人才计划项目(BJ2014041);中国博士后基金(2014M561197);河北省自然科学基金(E2013205067);河北师范大学校内科研基金(L2013Z04)
张鉴达(1981—),男,河北东光人,副教授,博士,主要从事区域环境污染分析评价方面的研究。
E-mail:zjdrf@163.com
X513
A
10.7535/hbgykj.2017yx03009
张鉴达,周美玲,杨小雨,等.石家庄市冬季大气颗粒物中水溶性离子与重金属成分研究[J].河北工业科技,2017,34(3):202-207. ZHANG Jianda, ZHOU Meiling, YANG Xiaoyu,et al.Study on water soluble ions and heavy metals in atmospheric particulates in winter in Shijiazhuang City[J].Hebei Journal of Industrial Science and Technology,2017,34(3):202-207.

