天水市马铃薯单产变化趋势分析
赵国良,梁更生,温宏昌,王娟,赵春燕,卜虎虎

摘要:利用1978 — 2014 年的馬铃薯单产数据资料,对天水市37 a来马铃薯单产变化趋势进行了分析。结果表明,天水市1978 — 2014年马铃薯单产的变化可划分为4个阶段,马铃薯单产整体呈上升趋势,但年际波动较大。产量增加的年份略多于减少的年份。
关键词:马铃薯;单产;趋势分析;天水市
中图分类号:S532 文献标志码:A 文章编号:1001-1463(2017)11-0041-03
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1001-1463.2017.11.013
Benefit Analysis of Potato Intercropping with Soybean
in Northwest Irrigation Areas
YANG Guo 1, CHEN Guangrong 2, 3, WANG LiMing 2, 3, YANG Ruping 2, 3, DONG Bo 2, 3, ZHANG Guohong 2, 3, Li Chende 4 , YANG Guifang 5
(1. Jingyuan Farming and Animal Husnbandry Bureau, Jingyuan Gansu 730600, China; 2. Institute of Dryland Agriculture, Gansu Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Lanzhou Gansu 730070, China; 3. Key Laboratory of Northwest Drought Crop Cultivation of Chinese Ministry of Agriculture, Lanzhou Gansu 730070, China; 4. Gansu Institute of Agriculture Technology, Lanzhou Gansu 730020, China; 5. Gansu Central Keya green agriculture Technology Ltd, Lanzhou Gansu 730070, China)
Abstract:Field experiments are conducted in Northwest irrigation districts along Yellow river from 2013 to 2016. The concept related to yield equivalent and value of output equivalent is proposed, using various quantitative standards such as land equivalent ratio, yield equivalent, and value of output equivalent, the efficiency and the economic benefit. The physiological effect and micro ecological benefit on photosynthetic properties, soil microorganism populations, crop quality and weed control in intercropping systems are studied systematically. Early potato and soybean intercropping could significantly improve illumination effective utilization, ≥10 ℃ temperature effective utilization, rainfall effective utilization during green period and ground cover effective utilization. Intercropping significantly improved the land use efficiency, the unit area yield and the unit area value are 1.53 and 1.49 times of sole cropping. Intercropping also significantly improved soil microbial structure and crop quality, and therefore alleviated the obstacles of continuous cropping. Early potato and soybean intercropping is an effective cultivation method with great ecological and economic benefits. In addition to Labor, soil, heat and water resource intensively utilizing temporally and spatially, Early potato and soybean intercropping could increase the crop yield per unit area greatly, which could be extended at large scale.
Key words:Potato/ Soybean;Northwest Irrigation areas;Continuous croppingbostacle;Quality;Yield effect;Ecological benefit
甘肃省马铃薯种植面积达67万hm2,鲜薯产量达238万t(折粮),面积居全国第3,产量居全国第2[1 ],这得益于甘肃省委省政府把马铃薯产业作为全省农业和农村经济发展的战略性主导产业来扶持,促进了马铃薯产业的健康稳定发展。天水市马铃薯产业发展也很快,种植面积已达6.72万hm2,鲜薯产量达24.85万t(折粮) [2 ],马铃薯产业已成为农民脱贫致富的支柱产业。但天水市是典型的雨养农业区,马铃薯生产没有完全摆脱靠天吃饭的局 面[3 - 4 ]。我们选取了天水市1978 — 2014年的相关数据,研究了37 a来天水市马铃薯单产的变化,分析马铃薯单产变化的阶段性、趋势性特征,以期在天水市粮食面积每年减少879.73 hm2的情况下[5 ],通过提高马铃薯单产来保证粮食增产。
1 资料与方法
1.1 资料来源
选取1978 — 2014年甘肃省天水市马铃薯播种面积、单产等数据资料。数据资料来自《天水经济年鉴》 [2 ]。
1.2 研究方法
采用Microsoft Excel 2003 软件就马铃薯37 a播种面积、产量的变化进行数据统计分析,说明其变化趋势及特征。计算时通常折粮以淀粉产量计算 (淀粉产量=鲜薯产量×20% )。
2 结果与分析
2.1 天水市马铃薯播种面积变化分析
由图1可以看出,1978年以来,天水市的马铃薯播种面积总体呈增加趋势,年均增加774.32 hm2,由1978年的3.83万hm2增加到2014年的6.72万hm2。马铃薯播种面积的变化总体可分三个阶段分析,第一阶段是1978 — 1988年,缓慢增加阶段;第二阶段是1988 — 2002年,种植面积不稳定,呈锯齿形变化,其中2000年达到最大值;第三阶段是2002 — 2014年,呈稳定增加的态势。
2.2 天水市马铃薯单产的时序变化分析
2.2.1 总体分析 37 a来天水市的马铃薯单产总体呈上升的趋势,由1978年的1 743.0 kg/hm2增长到2014年的3 697.5 kg/hm2,增长了1.12倍。但由于天水市处于雨养农业区,马铃薯单产的年际波动较大。
2.2.2 阶段性分析 根据图1所示,将1978—2014年分为4个阶段進行分析。
第一阶段是1978 — 1992年的徘徊阶段。此阶段天水市马铃薯单产处于徘徊时期,呈锯齿形,增长与减少几乎交替进行,15 a间,减产年份8 a,增产年份7 a,可谓“七上八下”,单产由1978年的1 743.0 kg/hm2增加到1992年的2 193.0 kg/hm2,15 a间平均增长率只有3.46%。此期为改革初期,地力薄弱,新品种、新技术应用少,增长缓慢。
第二阶段是1992 — 1997年的严重减产阶段。在该时期,天水市的马铃薯单产几乎持续减少,期间只有1996年表现增长,其余年份均为减产,并且减产幅度较大,年均减产13.21%,单产从1992年的2 193.0 kg/hm2减少到1997年的684.0 kg/hm2。减产的主要原因是气候因素的影响,特别是1994 — 1997年,连续4 a年降水量不到400 mm,平均仅有365.6 mm。据姚小英等[3 ]研究,天水市秦州区在1981 — 2005年的25 a间,春旱就有16次,其中重旱7次。春旱对天水市马铃薯生产的影响较大。
第三阶段是1997 — 2008年的快速增长阶段。马铃薯单产从1997年的684.0 kg/hm2增加到2008年的3 696.0 kg/hm2,是37 a单产增长最快的阶段,年增长率达20.13%。此阶段国家的各种惠农政策较多,农民的种粮积极性有所提高,同时优良品种庄薯3号、陇薯3号、天薯11号、陇薯7号等的推广、脱毒种薯普及率提高及高产栽培技术的配套应用,均推动了天水市马铃薯单产水平的显著提高。
第四阶段是2008 — 2014年的稳定阶段。2007年,天水市马铃薯单产首次突破了3 000 kg/hm2,此后数年单产一直稳定在3 600 kg/hm2左右, 2008 — 2014年,年均增长率只有0.21%,作为粮菜兼用型高产作物,可以说单产几乎没有增长。
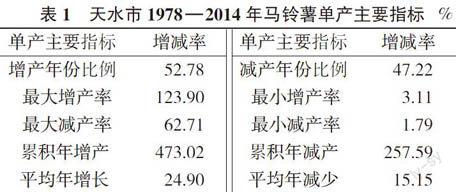
2.2.3 趋势分析 由表1可以看出,1978年以后,天水市马铃薯单产增产和减产的年份相近,增产年份略多于减产年份,单产增产的年份占52.78%,最大增幅为123.9%;增产年份平均年增长24.9%,减产年份平均年减少15.15%。
3 小结与讨论
统计结果表明,1978年以来,天水市马铃薯播种面积虽有波动,但总体呈增加趋势,年均增加774.32 hm2。
1978 — 2014年天水市马铃薯单产发展经历了徘徊、减产、增长、稳定4个阶段。总体上天水市马铃薯单产水平较低,增长和减少年份相近,产量低而不稳,虽然1997年以来单产增幅较大,但与世界平均水平特别是发达国家的水平相差很大,提升空间也很大。虽然1978 — 2014年天水市马铃薯单产整体呈上升趋势,但年际波动较大。因此,需要在品种、栽培技术等方面多下功夫,在单产上寻求新突破。建议科研和推广机构要不断引育、示范、推广马铃薯新品种、新技术,克服不利气象因素的影响。政府应大力扶持发展马铃薯专业合作社,提高当地马铃薯产业规模化生产、集约化经营水平[4 ],着力提高马铃薯产量和质量,促进马铃薯产业快速发展。
参考文献:
[1] 中国甘肃网. 我省马铃薯产量居全国第二 [EB/OL].[2016-01-07](2017-03-06)http://gansu.gscn.com.cn/system/2016/01/07/011230723.shtml.
[2] 天水年鉴编委会. 天水经济年鉴[M]. 天水:天水市统计局,2015.
[3] 姚小英,朱拥军,把多辉. 天水市45 a气候变化特征对林果生长的影响[J]. 干旱地区农业研究,2008,26 (2):240-245.
[4] 张英莺,张俊莲,邢 国,等. 甘肃省马铃薯产业发展调查[J]. 甘肃农业科技,2013(4):38-40.
[5] 高 强,郭 恒,赵国良,等. 作物种植结构变化及影响粮食产量的因素分析[J]. 中国农业资源与区划,2012,33(4):36-41.
(本文责编:杨 杰)

