具有周期系数包含脉冲效应的比率依赖捕食-被捕食模型的周期解
孙钰淑,王凯华
(海南师范大学 数学与统计学院,海南 海口 571158)
具有周期系数包含脉冲效应的比率依赖捕食-被捕食模型的周期解
孙钰淑,王凯华*
(海南师范大学 数学与统计学院,海南 海口 571158)
文章主要研究包含脉冲效应且系数为周期函数的比率依赖捕食与被捕食模型的周期解存在性问题.通过Mawhin延拓定理和分析工具,证明了该模型周期解的存在性,得到了周期解存在的充分条件.经过数值模拟,进一步验证了所得周期解判定条件的有效性.
脉冲效应;周期系数;比率依赖;周期解
文献[1]对带捕食者收获的包含比率依赖Holling II型功能反应的捕食与被捕食模型做了详细的动力学分析,其模型如下:

模型(1)中的系数都是固定的常数,这在某些特定的情况下是合适的.但在现实世界中,自然环境和生物各类特性的变化具有周期性.例如一年四季气候更替使生物的出生率、死亡率、环境允许量、捕食率等产生周期变化.因此,为了更精准的反映客观世界中捕食与被捕食者种群数量随时间的演化规律,我们把模型(1)中固定的常数参数改为周期为ω的函数,从而使原模型有更广的适用范围.与此同时,考虑到农牧业生产中并非每时每刻进行种群的收获(或投放),更多情况是每隔一段时间集中收获(或投放)一次,原模型中收获项出现在微分方程中,这与描写生物特性的实际情况不符,需要用脉冲微分方程更好地刻画实际情况[4-6].因此,本文对模型(1)进行改进,提出如下包含脉冲的周期系数微分方程模型:
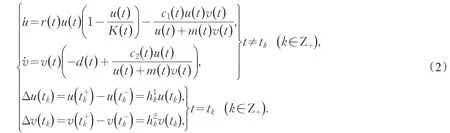
在下文的讨论中,我们假设系统(2)满足:
(A1)r(t),c1(t),d(t),c2(t),K(t),m(t)均为连续的非负ω周期函数.
(A2)1+>0,且存在一个正整数q,使得tk+q=tk+ω,
1 基本概念和引理
设J⊂R,记PC(J,RN)是函数ϕ∶J→RN构成的空间,其中ϕ在t∈J,t≠tk处连续,t=tk∈J为ϕ的第一类间断点且在该点处ϕ左连续.记

为讨论系统(2)周期解的存在性,需要介绍Gaines和Mawhin引入的一些概念[8-9].设X与Y是赋范线性空间,L∶DomL⊂X→Y是一线性映射.若dim KerL=codimImL<∞,且ImL是Y的闭子空间,则称L为指标为零的Fredholm算子.此时存在连续投影算子P∶X→X,Q∶Y→Y使得ImP=KerL且这样是可逆的,其逆记为KP.设N∶X→Y为连续映射,Ω是X的一个有界开子集,并且有界,是紧的,那么N叫做在上L紧.由于ImQ与KerL同构,故有同构映射J∶ImQ→KerL.
为了证明周期解的存在性,我们需要下面的Mawhin延拓定理.
引理2[8-9]设L∶DomL⊂X→Y是一个指标为零的Fredholm算子,在上L紧,如果:
(1)若λ∈(0 ,1),x∈∂Ω,则有Lx≠λNx,
(2)若x∈∂Ω⋂KerL,则有QNx≠0,
则Lx=Nx在内至少有一个解.
2 正周期解的存在性
根据前面的准备工作,本节给出主要结果及其证明.


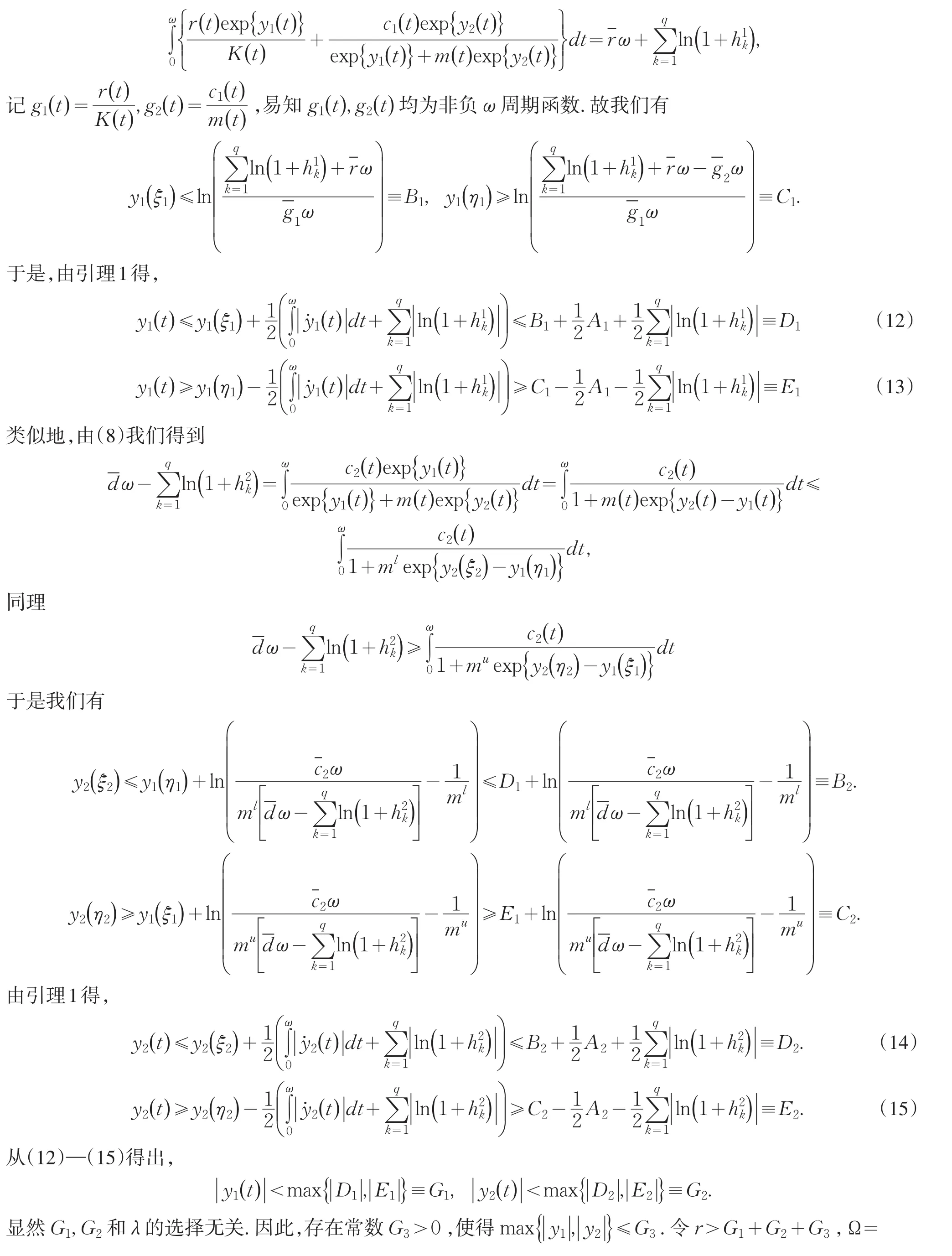
定理1 假设系统(2)满足条件(A1)、(A2)和以下两个条件{y∈X∶‖y‖<r},则Ω满足引理2的条件(1).当y=(y1,y2)T∈∂Ω⋂KerL=∂Ω⋂R2,y是R2中的常值向量,且‖y‖=r,易证QNx≠0.此外,直接计算可得deg(JQN|∂Ω⋂KerL)≠0.至此,Ω满足引理2的全部条件.因此,系统(3)至少存在一个ω周期解,即系统(2)至少存在一个正的ω周期解.证毕.
3 数值模拟
对系统(2),我们取tk=kT,r=1.5+0.5sint,c1=1.2+0.6cost,c2=2.2+0.5sint,m=1,d=0.9+(注:此处参数值在符合系统(2)的生物意义条件下,随机选择).
若T=π/2,定理1的全部条件都满足,则系统(2)有唯一的2π-周期解(一个周期含4次脉冲).我们取初始值为其随时间演化情况见图1—图3,其中脉冲效应的影响十分明显.
若T=2,则条件(A2)不满足,系统(2)的周期解被脉冲破坏.数值结果显示,此时系统(2)有类似文献[10-12]的更复杂的动力学现象,见图4.

图1 T=π/2时系统(2)的u(t)演化图Fig.1 Time evolution ofu(t)in system(2)withT=π/2
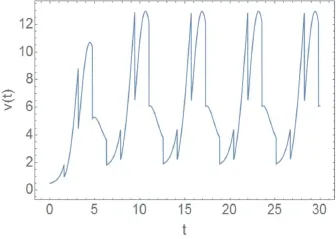
图2 T=π/2时系统(2)的v(t)演化图Fig.2 Time evolution ofv(t)in system(2)withT=π/2

图3 T=π/2时系统(2)的2π周期解的轨线图Fig.3 Trajectory of 2π-periodic solutions in system(2)withT=π/2

图4 T=2时系统(2)的奇怪吸引子轨线图Fig.4 Trajectory of strange attractor in system(2)withT=2
4 结论
本文改进了包含比率依赖Holling II型功能反应和捕食者收获的捕食-被捕食模型,模型中的系数为周期函数且对捕食与被捕食者进行脉冲收获(或投放),使模型更符合收获(或投放)捕食与被捕食者的实际情况.通过Mawhin延拓定理和分析工具,证明了该模型周期解的存在性,给出了周期解存在的充分条件,当一定条件被满足时,从理论上证明了该系统在进行定期收获(或投放)的时候,可以达到某种生态平衡.通过数值模拟,验证了所得周期解判定条件的正确性.通过数值模拟还进一步发现,原系统在不符合周期判定条件时,可呈现出更复杂的动力学行为.
[1]Heggerud C M,Lan K Q.Local stability analysis of ratio-dependent predator-prey models with predator harvesting rates[J].Ap⁃plied Mathematics&Computation,2015,270(1):349-357.
[2]Hsu S B,Hwang T W,Kuang Y.Global analysis of the Michaelis-Menten-type ratio-dependent predator-prey system[J].Jour⁃nal of Mathematical Biology,2001,42(6):489-506.
[3]Yang K,Beretta E.Global qualitative analysis of a ratio-dependent predator-prey system[J].Journal of Mathematical Biology,1998,36(4):389-406.
[4]Wang Q,Ding M M,Wang Z J,et al.Existence and attractivity of a periodic solution for an N-species Gilpin-Ayala impulsive competition system[J].Nonlinear Analysis:Real World Applications,2010,11(4):2675-2685.
[5]Bainov D D,Simeonov P S.Impulsive differential equations:periodic solutions and applications[M].New York:Longman Scien⁃tific&Technical,1993.
[6]He M,Chen F,Li Z.Permanence and global attractivity of an impulsive delay Logistic model[J].Applied Mathematics Letters,2016,62:92-100.
[7]Wang Q,Dai B,Chen Y.Multiple periodic solutions of an impulsive predator–prey model with Holling-type IV functional re⁃sponse[J].Mathematical&Computer Modelling,2009,49(9-10):1829-1836.
[8]Gaines R E,Mawhin J L.Coincidence degree,and nonlinear differential equations[M].Berlin:Springer-Verlag,1977.
[9]Liu X.Impulsive periodic oscillation for a predator-prey model with Hassell-Varley-Holling functional response[J].Applied Mathematical Modelling,2014,38(4):1482-1494..
[10]Zhang J,Gui Z.Periodic solutions of nonautonomous cellular neural networks with impulses and delays[J].Nonlinear Analysis Real World Applications,2009,10(3):1891-1903.
[11]Zhang J,Gui Z.Existence and stability of periodic solutions of high-order Hopfield neural networks with impulses and delays[ J].Journal of Computational&Applied Mathematics,2009,224(2):602-613.
[12]Wang K H,Gui Z J.The existence and simulations of periodic solution of predator-prey models with impulsive perturbations and Holling type III functional responses[C].Advances in Intelligent Systems Research,2015,122:159-162.
责任编辑:吴兴华
Periodic Solution of Ratio-Dependent Predator-Prey Model with Periodic Coefficients and Impulsive Effects
SUN Yushu,WANG Kaihua*
(School of Mathematics and Statistics,Hainan Normal University,Haikou571158,China)
The main purpose of this paper is to explore the existence of the periodic solution of ratio-dependent predatorprey models with periodic coefficients and impulsive harvest(feed).The existence of the periodic solution is proved by us⁃ing Mawhin's continuation theorem and analysis techniques,and the sufficient existence-conditions are also obtained.Fur⁃thermore,the numerical simulations confirm our analytic results.
impulsive effect;periodic coefficient;ratio-dependent;periodic solution
O 29
A
1674-4942(2017)01-0007-07
2016-12-08
海南省自然科学基金(20151003)
*通讯作者:王凯华,副教授,E-mail:kaihuawang@qq.com
10.12051/j.issn.1674-4942.2017.01.002

