黄河下游溶解态营养盐季节变化及入海通量研究*
谷文艳, 陈洪涛, 姚庆祯, 张晓琳
(中国海洋大学化学化工学院,山东 青岛 266100)
黄河下游溶解态营养盐季节变化及入海通量研究*
谷文艳, 陈洪涛**, 姚庆祯, 张晓琳
(中国海洋大学化学化工学院,山东 青岛 266100)
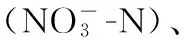
黄河;营养盐;浓度;月际变化;通量
河流输送是河口及近海营养盐的主要来源,其在营养要素的生物地球化学循环中发挥着至关重要的作用。营养盐输送量主要取决于河流向河口输送的水沙通量以及与此两载体相关联的氮、磷和硅的含量[1],而河流中营养盐的来源与它们的季节变化以及水情要素有关[2]。营养盐通过地表径流向海洋的输入有利于维持海洋初级生产力,但营养盐过剩则会产生富营养化现象,导致浮游植物异常繁殖,因此关注主要无机营养盐氮、磷和硅的输送通量变化对渤海生态环境所造成的影响具有重要意义。
黄河以其泥沙多,河道善淤、善决、善徙而著称于世,巨量泥沙和营养物质随河流输入渤海,对渤海的营养状况产生直接的影响。近几十年来,受人类活动影响,黄河流域的营养盐含量呈上升趋势[3-6]。但是在自然因素与经济的发展以及不断增长的人口压力等社会因素的共同影响下,近年来黄河入海水沙通量锐减[7-9],严重影响了河口及近海生态环境[10-12]。近年来渤海的生态环境发生了巨大变化[13-19],赤潮频发、水质恶化、海洋生态系统失衡、渔业资源衰退等海洋生态问题日益严重。
已有不少学者对黄河下游及邻近海域营养盐及其分布情况进行过研究[20-25],对黄河下游历史数据的研究发现,数十年来黄河营养盐含量显著升高[26-28],这可能会对河口及渤海海洋环境和生态系统稳定产生重要的影响[18,26]。本研究系统分析了2010年4月—2011年3月期间黄河下游利津站溶解态营养盐及入海通量的变化情况,有助于全面了解人类活动影响下黄河营养盐变化及对渤海生态系统的影响,并为相关研究开展提供营养盐基础数据,丰富已有的关于黄河下游营养盐分布及形成机制的认识,为流域和河口环境问题的解决提供科学依据。
1 采样及分析方法
1.1 采样站位
2010年4月—2011年3月期间,每月20日前后在黄河利津大桥下游约20km的浮桥上平均取5个点采集样品,将5个采样点观测数据的平均值作为每次观测的结果。采样地点位于黄河下游的利津水文站附近,距河口104km,以下无重大工业和生活污水排入。
1.2 样品处理及测定方法

2 结果与讨论
2.1 黄河下游营养盐的季节变化
2010年4月—2011年3月黄河利津站流量的变化范围为62—1 850 m3/s。从图1可以看出,黄河下游径流主要集中在7~10月,占全年水量的72.8%,其他月份入海水量较少。
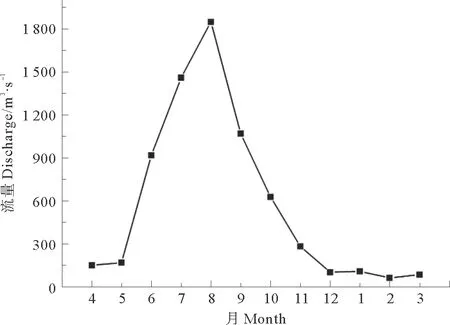
图1 2010年4月—2011年3月黄河利津流量变化
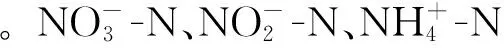
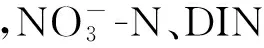

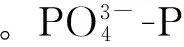
湖北华贵为提高产品生产率和质量投入了大量资金,研发设计了多项拥有专利的生产机械与技术,实现了生产自动化、机械化、标准化。从选品到生产,严格把控分级切割、清洗、冷却、包装杀菌等每一个步骤,保证每一环节的专业化、标准化生产。湖北华贵的产品质量监管严格,2016年通过了HACCP质量体系认证。除此之外,湖北华贵扩大产品市场供应多样性和提高品牌附加值的意识强烈,不断向绿色产品方向拓展。
黄河流域水体中溶解态磷的主要来源包括农业施肥、城市污水及大气干湿沉降等[20]。2010年4月—2011年3月黄河下游磷酸盐的浓度在7~10月存在相对的高值,这可能是因为丰水期黄河高含量的悬浮物中携带的磷发生解吸作用[36-37]导致的。
黄河流域中磷酸盐浓度与中国的其他河流及全球未受污染的河流相近,这归因于磷酸盐在大量悬浮颗粒物上的吸附[32-34]。


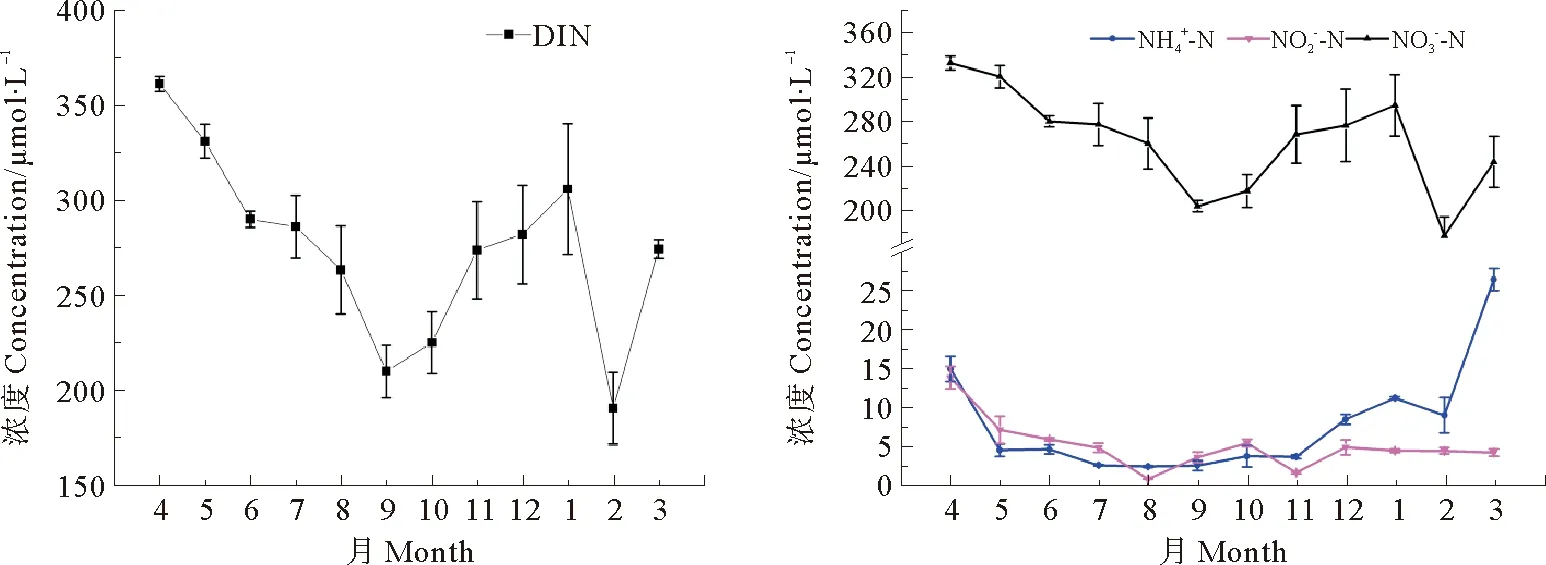
图2 2010年4月—2011年3月黄河下游各形态氮浓度月际变化
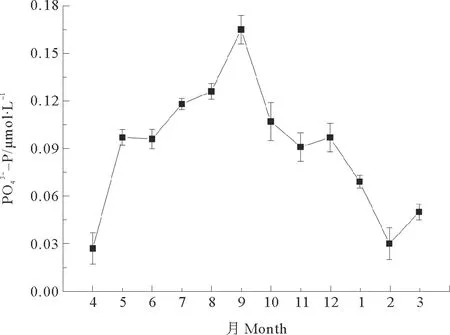
图3 2010年4月—2011年3月黄河下游磷酸盐浓度月际变化
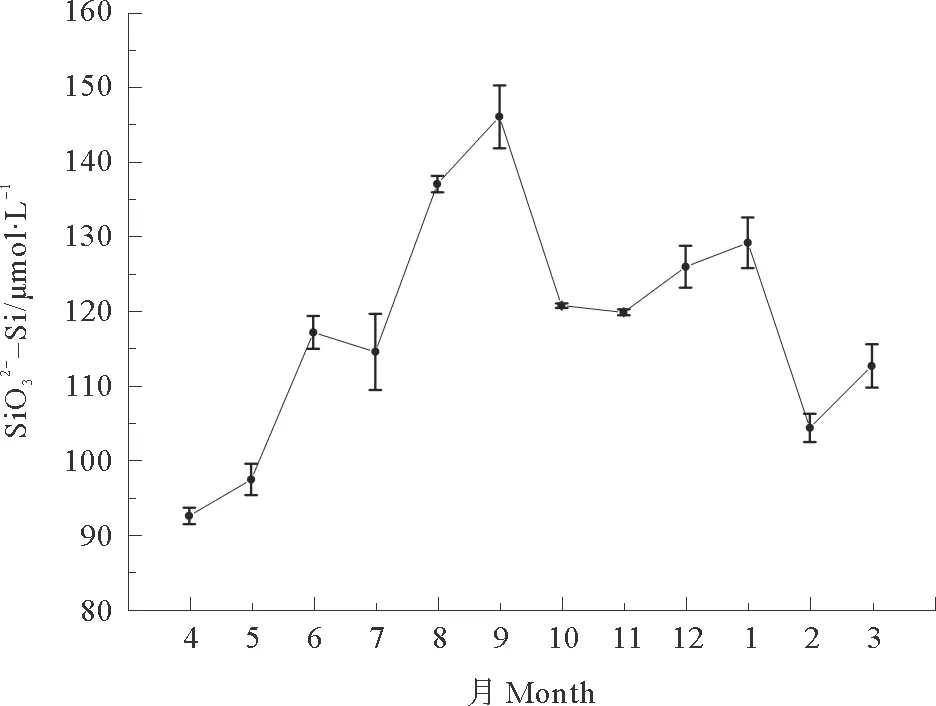
图4 2010年4月—2011年3月黄河下游硅酸盐浓度月际变化
与位于寒冷干燥的北方的其他河流(如大辽河、淮河)相比,黄河流域的硅酸盐含量较高,而与长江、珠江的含量水平相近,这主要是由于较强的化学风化作用所致[32]。
2.2 黄河下游水体中营养盐含量与径流量的关系
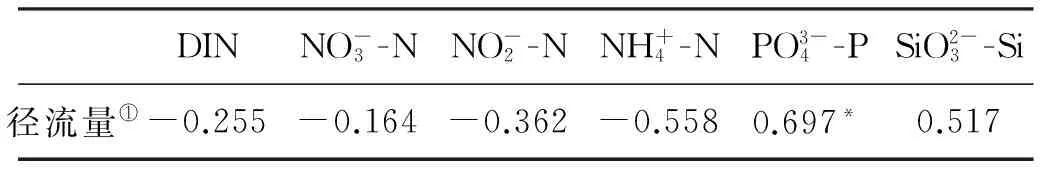
表1 2010年4月—2011年3月黄河下游营养盐含量与径流量的相关性
注:*表示在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关;样本数为12。*said it had significant correlation at the 0.05 level (double side);Sample of 12.
① Water discharge
2.3 黄河下游营养盐的入海通量
表2列出了2010年4月~2011年3月期间黄河下游水体中各形态营养盐的入海通量,其计算公式如下[43]:
Qi=Ci˙qi,
(1)
Q=∑Qi(i=4,5,6,......12,1,2,3)。
(2)
其中:Qi为营养盐入海月通量(t/m);Ci为营养盐含量(μg/L);qi为黄河下游月径流量(109m3);Q为营养盐入海年通量(t/a)。
从表2中可以看出,黄河下游营养盐的入海通量随季节有明显变化,最高值均在2010年7、8月,最低值均出现在2011年2月。

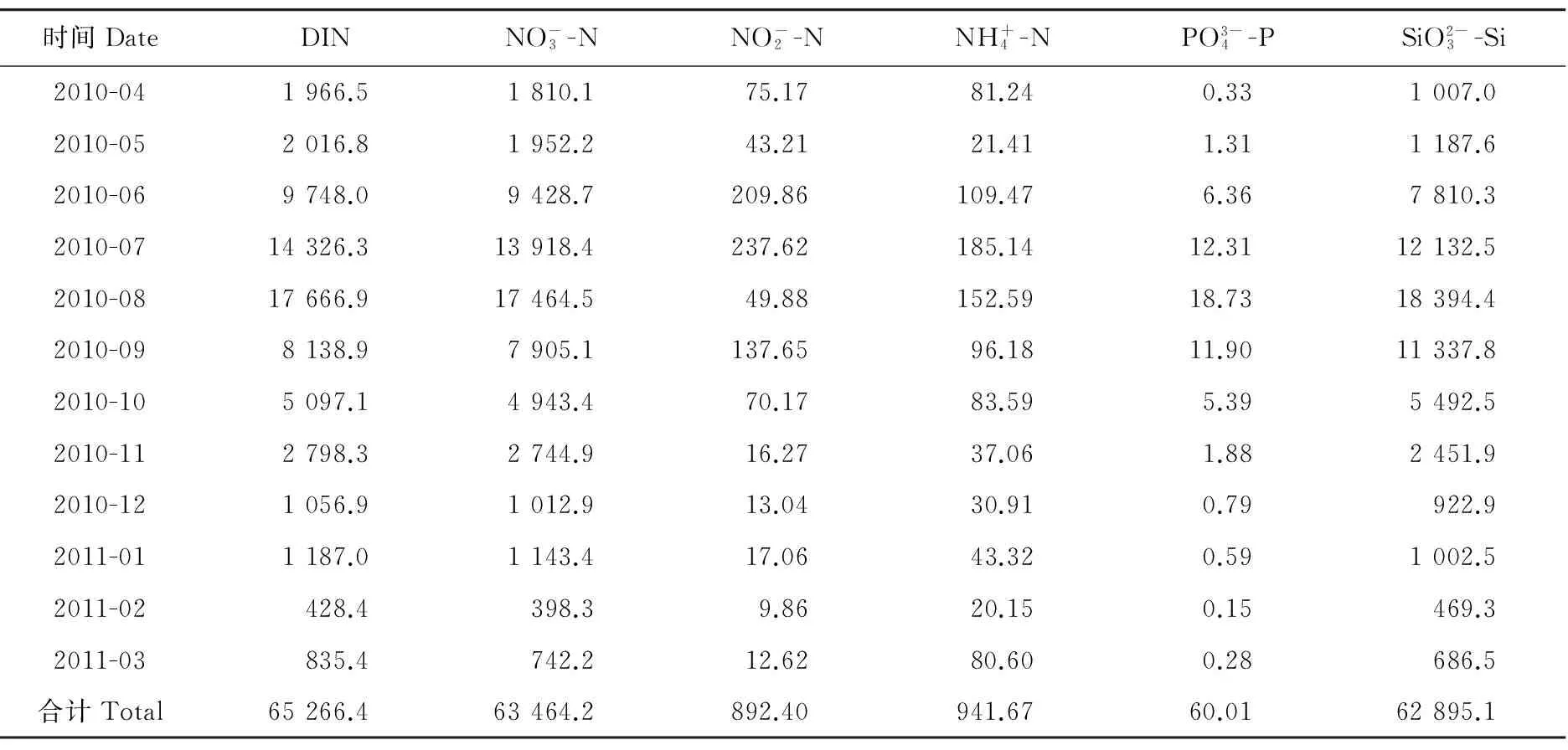
表2 2010年4月~2011年3月黄河下游各形态营养盐通量
注:表中溶解无机氮通量均以N计,磷酸盐均以P计,硅酸盐以Si计。Flux of Dissolved inorganic nitrogen are calculated in N, phosphate in P, silicate in Si in the table.
表3是2010年4月—2011年3月期间黄河下游营养盐入海通量与径流量的相关关系。从表中可以看出,各营养盐入海通量与径流量间均存在显著的正相关关系,说明影响黄河下游营养盐入海通量的主要因素是流量而非营养盐浓度。这种河流输送营养盐通量主要取决于径流量的现象在九龙江河口和长江口也有报道[45-46]。

表3 2010年4月~2011年3月黄河下游营养盐月入海通量与径流量的相关性
注:**表示在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关,*表示在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关;样本数为12。said it had significant correlation at the 0.01 level (double side),*said it had significant correlation at the 0.05 level (double side);Sample of 12.
① Water discharge
3 结论
(1)溶解无机氮的季节变化明显,表现为枯水期含量较高,丰水期含量较低;磷酸盐的变化与其相反;硅酸盐一年中最大浓度出现在9月,为受降水影响而流量较大的月份。
(2)磷酸盐浓度与径流量显著正相关,硅酸盐浓度与流量存在一定的正相关关系;而溶解无机氮与径流不存在相关关系。

(4)丰水期黄河向渤海输送的溶解无机氮、磷酸盐及硅酸盐是全年输送通量的主要贡献者,营养盐通量的主要控制因素是径流量。
[1] Tappin A D. An examination of the fluxes of nitrogen and phosphorus in temperate and tropical estuaries: current estimates and uncertainties[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2002,5(5): 885-901.
[2] 段水旺, 章申.中国主要河流控制站氮、磷含量变化规律初探[J].地理科学, 1999, 19(5): 411-416. Duan Shuiwang, Zhang Shen.The Variations of nitrogen and phosphorus concentrations in the monitoring stations of the three major rivers in China[J].Scientia Geographic Sinica, 1999, 19(5): 411-416.
[3] Zhang J.Chemical trend of national rivers in China: Huanghe and Changjiang[J].AMBIO, 1995, 24: 274-278.
[4] Xia Xinghui, Zhou Jingsong, Yang Zhifeng.Nitrogen contamination in the Yellow River Basin of China[J]. Environ Qual, 2002, 31: 917-925.
[5] Chen Jingsheng, He Dawei, Zhang Na, et al.Characteristics of and human influence on nitrogen contamination in Yellow River system.China[J].Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 2004, 93: 125-138.
[6] Li Z H, Wang H M, Han G D, et al.Review on the flow-break in the lower reaches of Yellow River[J].Ecology and Environment, 2007, 16(2): 686-690.
[7] Saito Y, Yang Z S, Hori K.The Huanghe(Yellow River) and Changjiang(Yangtze River) deltas: a review on their characteristics, evolution and sediment discharge during the Holocene [J].Geomarphology, 2001, 41: 219-231.
[8] Wang H, Yang Z, Saito Y, et al.Stepwise decreases of the Huanghe(Yellow River)sediment load(1950-2005): impacts of climate change and human activities[J].Glob Planet Change, 2007, 57: 331-354.
[9] 樊辉, 刘艳霞, 黄海军.1950-2007年黄河入海水沙通量变化趋势及突变特征[J]. 泥沙研究, 2009, 5: 9-16. Fan Hui, Liu Yanxia, Huang Haijun.Long-term trend and change point analysis on runoff and sediment fluxes into the sea from the Yellow River during the period of1950-2007[J].Journal of Sediment Research, 2009, 5: 9-16.
[10] Fan H, Huang H.Response of coastal marine eco-environment to river fluxes into the sea: a case study of the Huanghe(Yellow) River mouth and adjacent waters[J].Mar Environ Res, 2008, 65: 378-387.
[11] Liu Sumei, Li Lingwei, Zhang Guiling, et al.Impact of human activities on nutrient transports in the Huanghe(Yellow River) estuary[J].Journal of Hydrology, 2012(430/431): 103-110.
[12] 赵鹏, 江文胜, 毛新燕, 等.2000-2005年莱州湾盐度的变化及其主要影响因素[J].海洋与湖沼, 2010, 41(1): 12-23. Zhao Peng, Jiang Wensheng, Mao Xinyan, et al.Salinity change and influencing factor in the Laizhou Bay from 2000 to 2005[J].Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2010, 41(1): 12-23.
[13] Zhang J, Yu Z G, Raabe T, et al.Dynamics of inorganic nutrient species in the Bohai Sea waters[J].Journal of Marine System, 2004, 44: 189-212.
[14] Liu Sumei, Zhang Jing, Chen Hongtao, et al.Benthic nutrient recycling in shallow coastal waters of the Bohai Sea[J].Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2004, 22(4): 365-372.
[15] Wang Xiulin, Cui Zhengguo, Guo Quan, et al.Distribution of nutrients and eutrophication assessment in the Bohai Sea of China[J].Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology, 2009,27(1): 177-183.
[16] Liu Sumei, Li Lingwei, Zhang Zhinan.Inventory of nutrients in the Bohai[J].Continental Shelf Research, 2011, 31: 1790-1797.
[17] Liu S M, Zhang J, Gao H W, et al.Historic changes in flux of materials and nutrient budgets in the Bohai[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2008, 27: 1-17.
[18] Ning X, Lin C, Su J, et al.Long-term environmental change and the responses of the ecosystems in the Bohai Sea during 1960-1996[J].Deep-Sea Research Ⅱ, 2010, 57: 1079-1091.
[19] 孙军, 刘东艳, 杨世民, 等.渤海中部和渤海海峡及邻近海域浮游植物群落结构的初步研究[J].海洋与湖沼, 2002, 33(5): 461-471. Sun Jun, Liu Dongyan, Yang Shimin, et al.The preliminary study on phytoplankton community structure in the central Bohai Sea and the Bohai Strait and its adjacemt area[J].Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2002, 33(5): 461-471.
[20] 陈沛沛. 黄河下游与长江流域营养盐变化规律的研究[D].青岛:中国海洋大学, 2012. Chen Peipei.Study on the Nutrients in the Lower Yellow River and Changjiang Drainage Basin[D].Qingdao:Ocean University of China, 2012.
[21] 巩瑶. 黄河下游利津站营养盐输送规律及影响因素研究[D].青岛:中国海洋大学, 2012. Gong Yao. Influencing Factor of Nutrient Transport in the Lower Reach of Yellow River[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2012.
[22] 孟伟, 于涛, 郑丙辉, 等.黄河流域氮磷营养盐动态特征及主要影响因素[J]. 环境科学学报, 2007, 12: 2046-2051. Meng W, Yu T, Zheng B H, et al. Variation and influence factors of nitrogen and phosphorus transportation by the Yellow River[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2007, 27(12): 2046-2051.
[23] 王婷. 2002~2004 年及调水调沙期间黄河下游营养盐的变化特征[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2007. Wang T. The Variations of Nutrients in the Lower Main Channel of the Yellow River from 2002 to 2004 and Water-sediment Regulation[D].Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2007.
[24] 姚庆祯, 于志刚, 王婷, 等. 调水调沙对黄河下游营养盐变化规律的影响[J]. 环境科学, 2009, 12: 3534-3540. YAO Qing-zhen, YU Zhi-gang, WANG Ting, et al.Effect of the first water-sediment regulation on the variations of dissolved inorganic nutrients' concentrations and fluxes in the lower main channel of theYellow River[J]. Environmental Science, 2009, 12: 3534-3540.
[25] 张晓晓, 姚庆祯, 陈洪涛, 等. 黄河下游营养盐浓度季节变化及其入海通量研究[J].中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 40(7): 82-88. Zhang X X, Yao Q Z, Chen H T, et al. Seasonal variation and fluxes of nutrients in the lower reaches of the Yellow River[J].Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2010, 40(7): 82-88.
[26] 于志刚, 米铁柱, 谢宝东, 等.二十年来渤海生态环境参数的演化和相互关系[J]. 海洋环境科学, 2002, 19(1): 15-19. Yu Z G, Mi T Z, Xie B D, et al. Changes of the environmental parameters and their relationship in recent twenty years in the Bohai Sea[J]. Marine Environmental Science, 2002, 19(1): 15-19.
[27] 陈静生. 河流水质原理及中国河流水质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2006: 151-167. Chen J S. The Principle of River Water Quality and River Water Quality in China[M]. Beijing:Beijing Science Press, 2006: 151-167.
[28] Yu T, Meng W, Ongley E, et al. Long-term variations and causal factors in nitrogen and phosphorus transport in the Yellow River, China[J].Stuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2010, 86(3): 345-351.
[29] 何大为, 丁廷华, 赵振华. 河水中无机氮化合物转化规律的研究[J]. 环境科学, 1979(3): 28-32. He D W, Ding T H, Zhao Z H.Research on the laws of the transformation of inorganic nitrogen compound in the river[J]. Environmental Sciences, 1979(3): 28-32.
[30] 叶常明, 谢永明, 穆环珍, 等.沱江氮污染物转化规律及污染容量[J].环境科学学报, 1986, 6(1): 37-42. Ye Changming, Xie Yongming, Mu Huanzhen, et al.Nitrogenous pollutants transformation and assimulation capacity of water from Tuojiang River[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 1986, 6(1): 37-42.
[31] 王珊龄, 张更生, 蒋建国, 等.苏州地区地表水中三态氮迁移、转化的研究. 环境中氮污染与氮循环文集[C].北京: 中国科学院环境科学情报网, 1983:141-150. Wang Shanling, Zhang Gengsheng, Jiang Jianguo, et al.The study of the migration and transformation of the three nitrogen in the surface water on the Suzhou area[C]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Sciences, Environmental Science Intelligence Network, 1983: 141-150.
[32] Liu S M, Hong G H, Zhang J, et al. Nutrient budgets for large Chinese estuaries[J]. Biogeosciences, 2009, 6, 2245-2263.
[33] Smith S V, Swaney D P, Talaue-McManus L, et al. Humans, hydrology, and the distribution of inorganic nutrient loading to the ocean[J]. Bioscience, 2003, 53, 235-245.
[34] Liu S M, Li L W, Zhang G L, et al. Impacts of human activities on nutrient transports in the Huanghe (Yellow River) Estuary[J]. J Hydrol, 2012, 430-431, 103-110.
[35] Xia X H, Yang Z F, Huang G H, et al. Nitrification in natural waters with high suspended-solid content-a study for the Yellow River[J]. Chemosphere, 2004, 57: 1017-1029.
[36] 石晓勇, 史致丽, 于恒, 等.黄河口磷酸盐缓冲机制的探讨[J].海洋与湖沼, 1999, 30(2): 193-198. Shi Xiaoyong, Shi Zhili, Yu Heng, et al.Phosphate buffer mechanisms in the Huanghe River estuary[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 1999, 30(2): 193-198.
[37] Patrick W H, Khalid R A.Phosphate release and sorption by soils and sediments: Effects of acerbic and anaerobic conditions[J].Science, 1974, 186: 53-55.
[38] 李晶莹, 张经.中国主要流域盆地风化剥蚀率的控制因素[J].地理科学, 2003, 4: 434-440. Li Jingying, Zhang Jing.Natural controls of fluvial denudation rates in major drainage basins of China[J].Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2003, 4: 434-440.
[39] Qu C H, Chen C Z, Yang J R, et al.Geochemisry of dissolved and particulate elements in the major rivers of China (the Huanghe, Changjiang and Zhujiang rivers)[J],Estuaries, 1993,16, 475-487.
[40] Mallin M A,Paerl H W,Rudek J. Seasonal phytoplankton composition,productivity and biomass in the Neuse River estuary,North Carolina[J]. Estuarine,Coastal and Shelf Science,1991,32(6): 609-623.
[41] Jarvie H P, Whitton B A, Neal C. Nitrogen and phosphorus in east coast British river: Speciation sources and biological significance[J].Sci Total Environ, 1998, 210/211: 79-109.
[42] 冯兆忠, 王效科, 冯宗炜, 等.河套灌区秋浇对不同类型农田土壤氮素淋失的影响[J]. 生态学报, 2003, 10: 2027-2032. Feng Zhaozhong, Wang Xiaoke, Feng Zongwei, et al.Influence of autumn irrigation on soil N leaching loss of different farmlands in Hetao irrigation district, China [J].Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2003, 10: 2027-2032.
[43] PARCOM.Principles of the comprehensive study on riverine inputs[C]. Lisbon: Annex 9, Tenth Meeting of the Paris Commission, 1988: 15-17.
[44] 陈沛沛, 刘素美, 张桂玲, 等.黄河下游营养盐浓度、入海通量月变化及“人造洪峰”的影响[J]. 海洋学报(中文版), 2013(2): 59-71. Chen Peipei, Liu Sumei, Zhang Guiling, et al.Monthly variation of nutrient concentrations and fluxes in the lower Huanghe Riverz: under the influence of artifical floods[J].Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2013(2): 59-71.
[45] Shen Z L. Preliminary study on the Changjiang River mainstream nutrients fluxes (in Chinese)[J]. Oceanol Limnol Sin, 1997, 28: 522-528.
[46] Yan Xiuli, Zhai Weidong, Hong Huasheng, et al.Distribution, fluxes and decadal changes of nutrients in the Jiulong River Estuary, Southwest Taiwan Strait[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2012, 18: 2307-2318.
责任编辑 徐 环
Seasonal Variation and Fluxes of Dissolved Nutrients in the Lower Reaches of the Huanghe
GU Wen-Yan, CHEN Hong-Tao, YAO Qing-Zhen, ZHANG Xiao-Lin
(College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266100, China)
The monthly variations and fluxes of dissolved inorganic nutrients were studied, based on continuously observation data in the lower main channel of the Huanghe (Lijin station) during the period from April,2010 to March,2011.The results showed that concentrations ranged from 190.4 to 361.3 for dissolved inorganic nitrogen(DIN),177.1 to 332.5 μmlo/L for nitrate,0.74 to 13.81 μmol/L for nitrite, 2.27 to 26.44 μmol/L for ammonia nitroge,with averages of 277.5,269.3,4.90 and 5.26 μmol/L,respectively.Concentrations of phosphateand silicateranged from 0.027 to 0.138 μmlo/Land from 92.5 to 146.0 μmol/L,with averages of 0.094 and 118.1 μmol/L respectively. The concentrations of DIN were lower in the flood season than those in the dry season,whilewas opposite.was the predominant species of DIN and fluxes ofwere the main contributors of DIN transport fluxes from the river into the Bohai. The concentrations ofhad positive linear correlation with fresh water discharge. Nutrient fluxes in the flood season were the main contributors to the annual loads and nutrient transport patterns highly depended on freshwater discharge.
Huanghe; nutrients; concentration; monthly variation; flux
国家自然科学基金项目(41276070)资助 Supported by Natural Science Foundation of China(41276070)
2015-08-20;
2015-12-11
谷文艳(1989-),女,硕士生。E-mail:avagwy@163.com
** 通讯作者: E-mail:chenht@mail.ouc.edu.cn
P734.4+4
A
1672-5174(2017)03-074-07
10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20150293
谷文艳, 陈洪涛, 姚庆祯, 等. 黄河下游溶解态营养盐季节变化及入海通量研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 47(3): 74-79.
GU Wen-Yan, CHEN Hong-Tao, YAO Qing-Zhen, et al. Seasonal variation and fluxes of dissolved nutrients in the lower reaches of the Huanghe[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2017, 47(3): 74-79.

